Hardy-Weinberg Principle
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Gene pool
combination of all genes (including alleles) present in a reproducing population or species
large gene pool has extensive genomic diversity and is better able to withstand environmental challenges
can be any population - frogs in a pond, trees in a forest, or people in a town
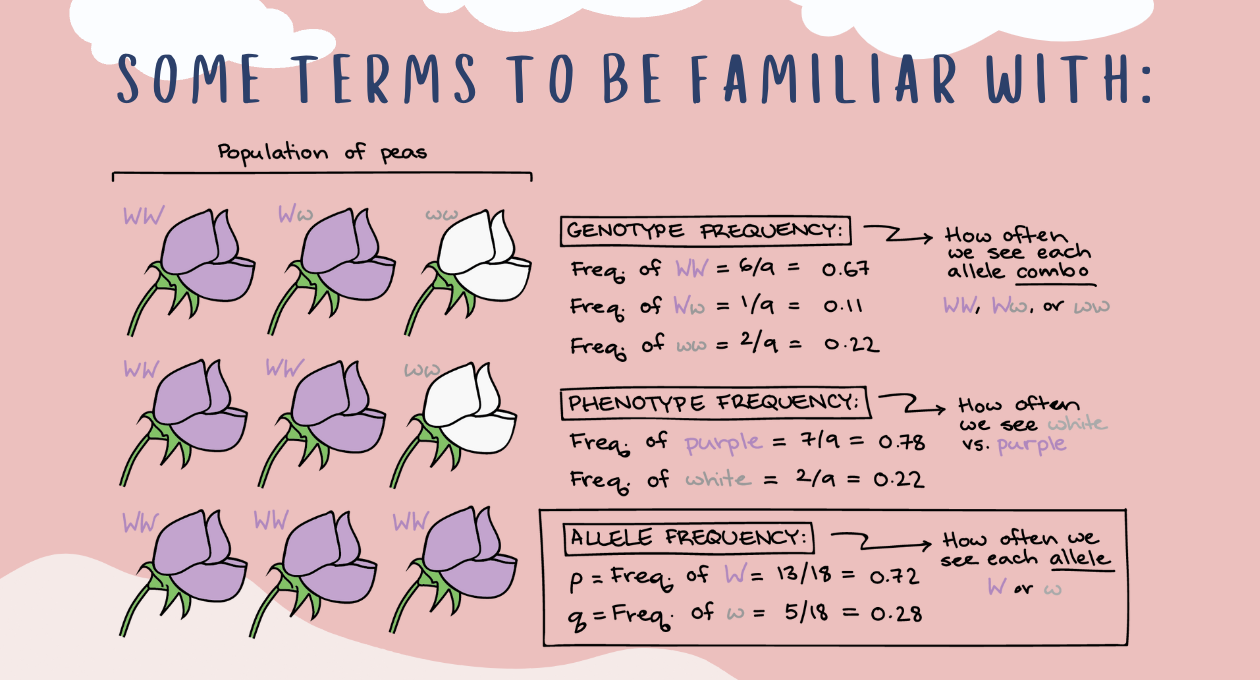
gene or allele frequency
relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a particular locus in a population
fraction of all chromosomes in the population that carry allele over total population or sample size
EX: in population of pea plants purple (W) and white (w) alleles can be found
hardy-weinberg equilibrium
population in which allele frequencies do not change over time = genetic equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium HWE) / stable non-evolving state.
Factors that disrupt genetic equilibrium
in a large random-mating population, genotype + allele frequencies remain constant in the absence of any evolutionary influences from one to another generation
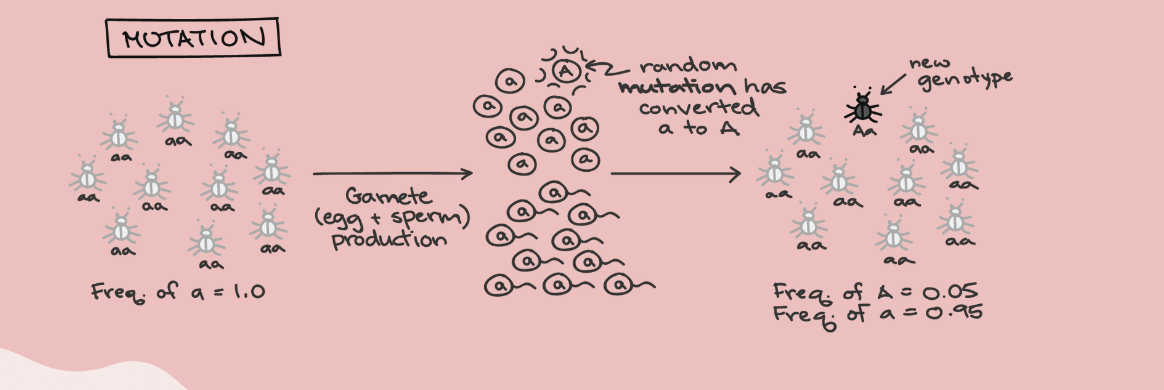
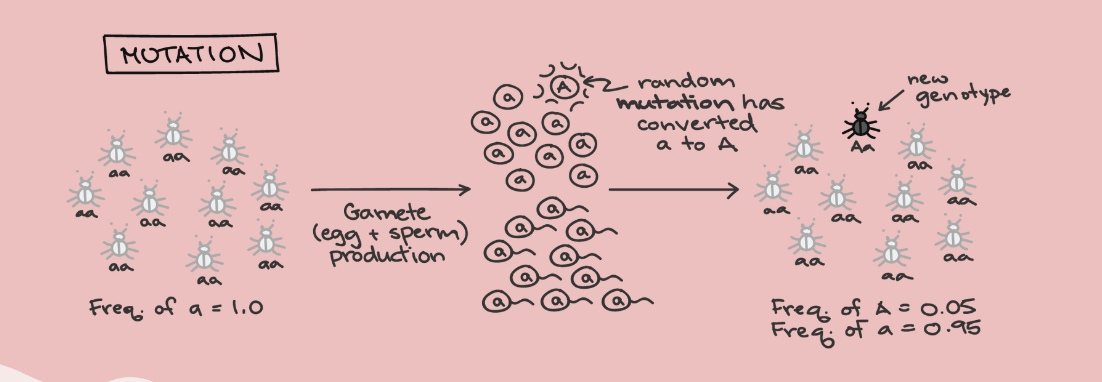
mutations
natural selection
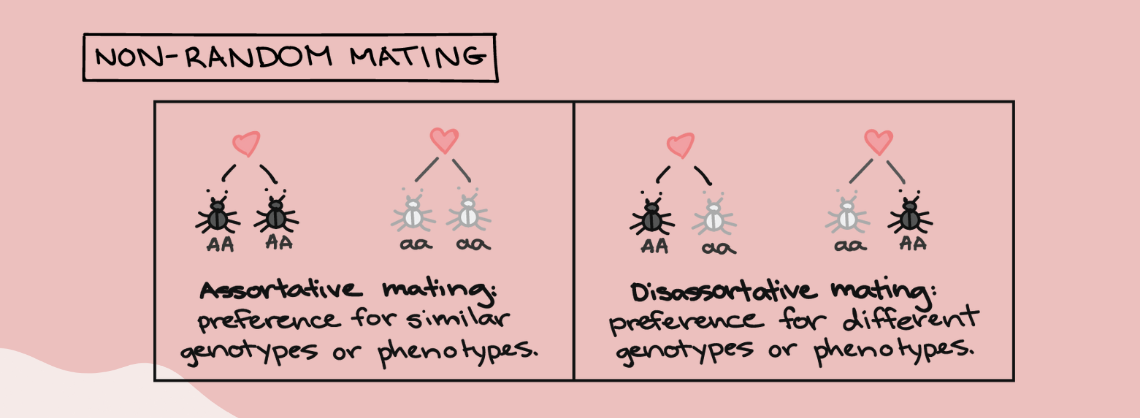
nonrandom mating
genetic drift
gene flow
mutations
disrupt equilibrium of allele frequencies by introducing new alleles into a population
permanent changes in the gene sequence of DNA
alter genes + alleles leading to genetic variation in a population

natural selection & nonrandom mating
result in gene frequencies
occurs because certain alleles help or harm reproductive success of organisms that carry them
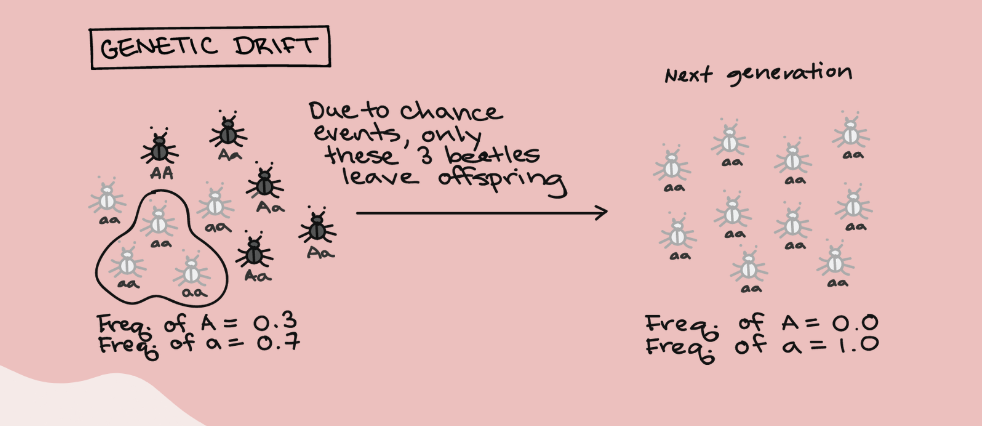
Genetic drift
occurs when allele frequencies grow higher or lower by chance and typically takes place in small populations
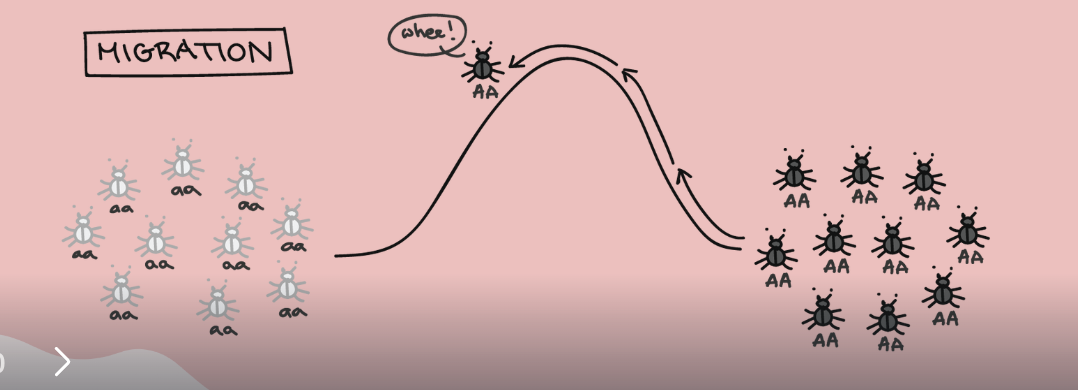
Gene flow
occurs when breeding between two populations transfers new alleles into a population
FORMULAS
Allele Frequency
p + q = 1
p: dominant allele frequency (A)
q: recessive allele frequency (a)
Genotype Frequency
p²+2pq+q²=1
p²: Homozygous dominant (AA)
2pq: Heterozygous dominant (Aa)
q²: Homozygous recessive (aa)