lec 12 synapse elimination and critical periods
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Not all cells that are born in the nervous system survive and not all synapses that are initially formed during development are _________
maintained
Some synapses are maintained while others are eliminated- this is related directly through the activity of these synapses through sensory or motor experiences "___ __ __ ____ __"
use it or lose it
in what ways do axonal projections become refined from development to adulthood
axons can become refined through three refinement properties which are
Topography, convergence, and postsynaptic compartment
refinement of topography- individual axons spread out further in early development in their topographical zone therefore some of these branches are ________ in refinement
eliminated
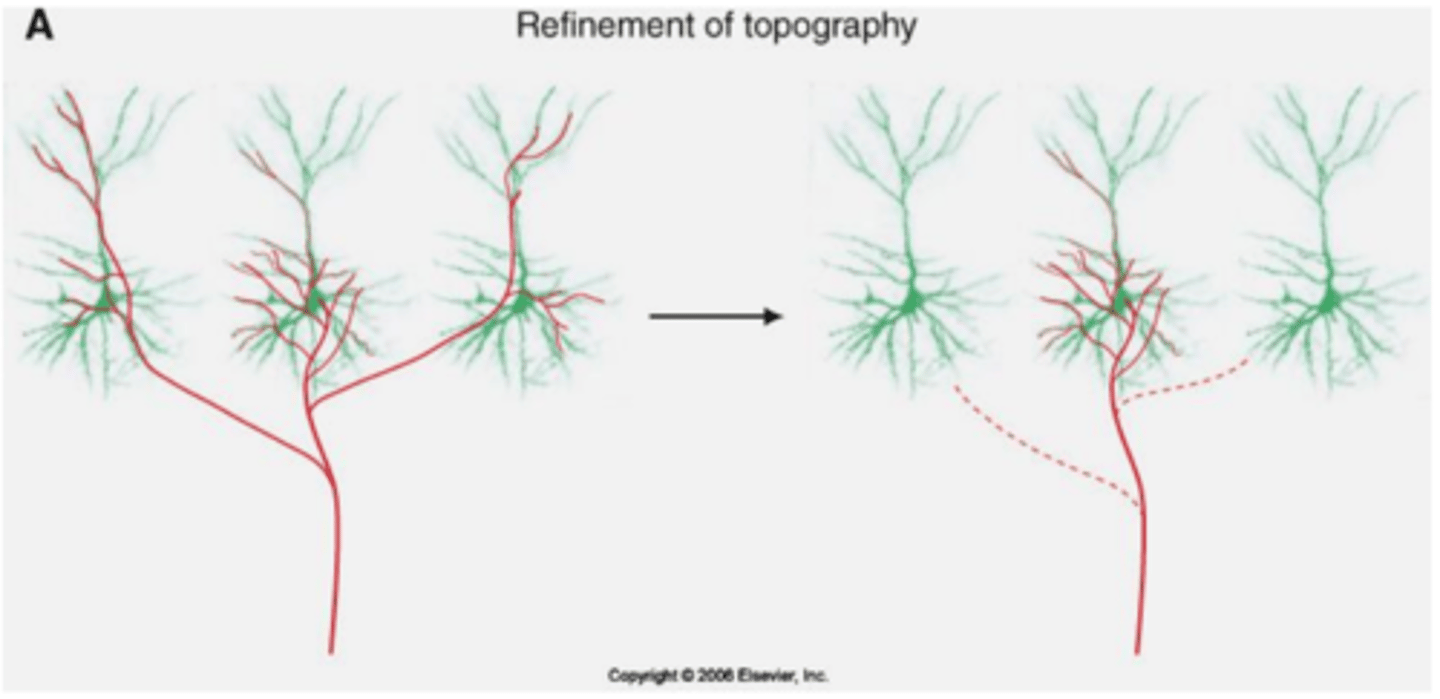
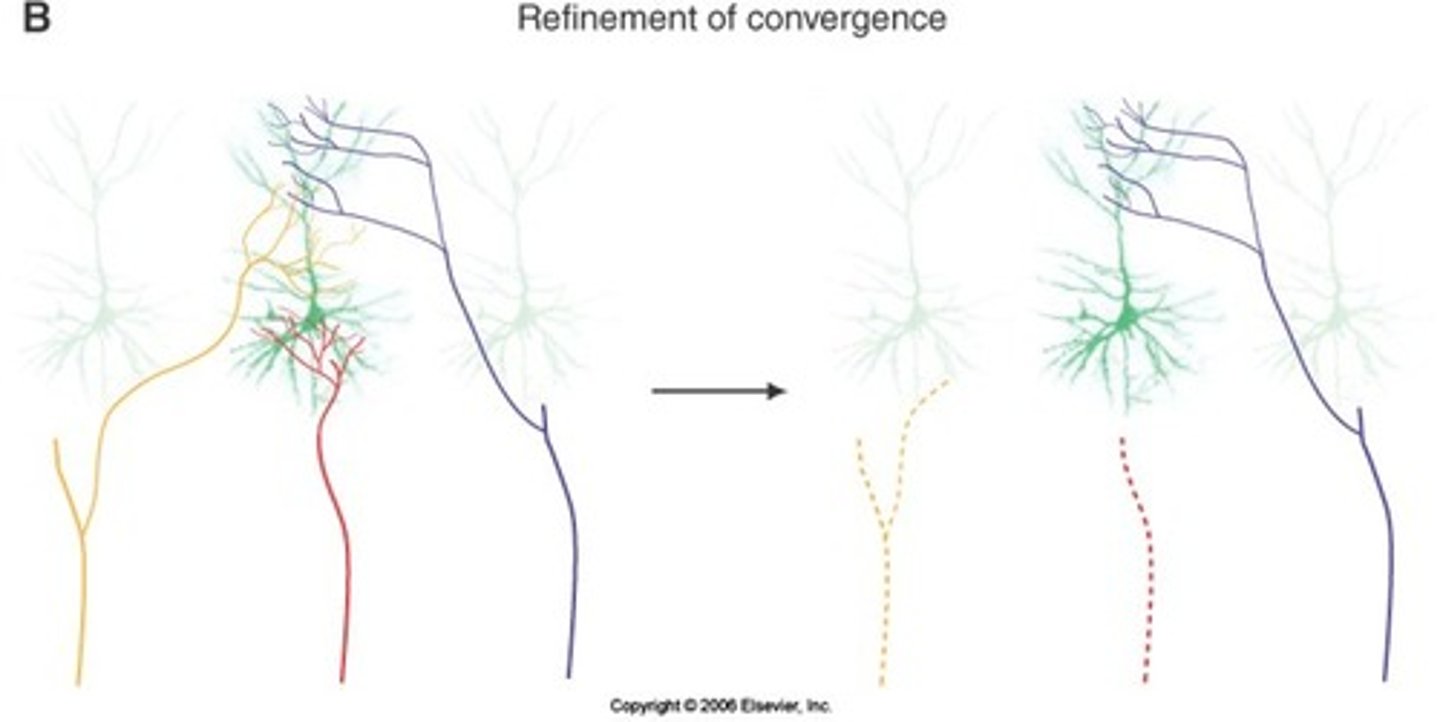
refinement of convergence- a single neuron will receive more presynaptic inputs during development than will remain in adulthood
less presynaptic inputs in adulthood
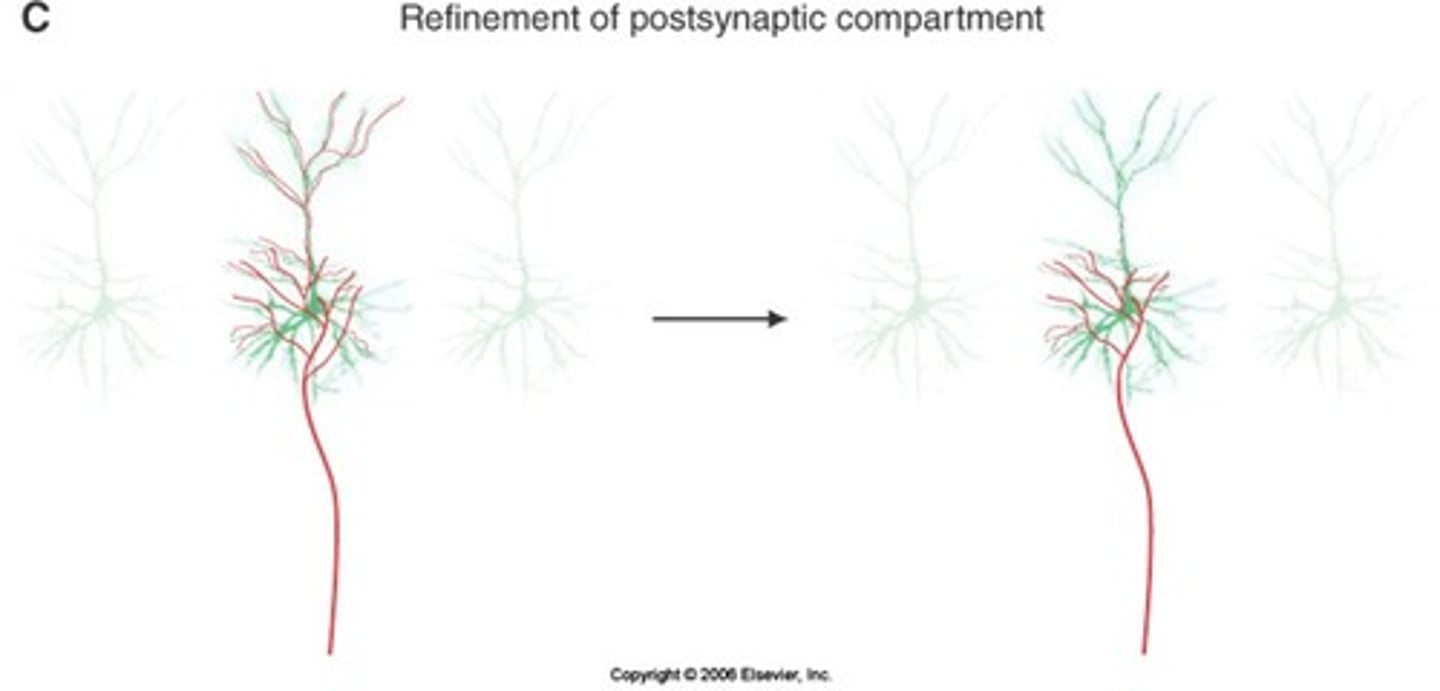
Refinement of postsynaptic compartment
there is refinement of synaptic connections on specific regions of the neuron
a neuron that comes in and blankets the postsynaptic cell, needs to prune back so that it is only in one particular part of the cell
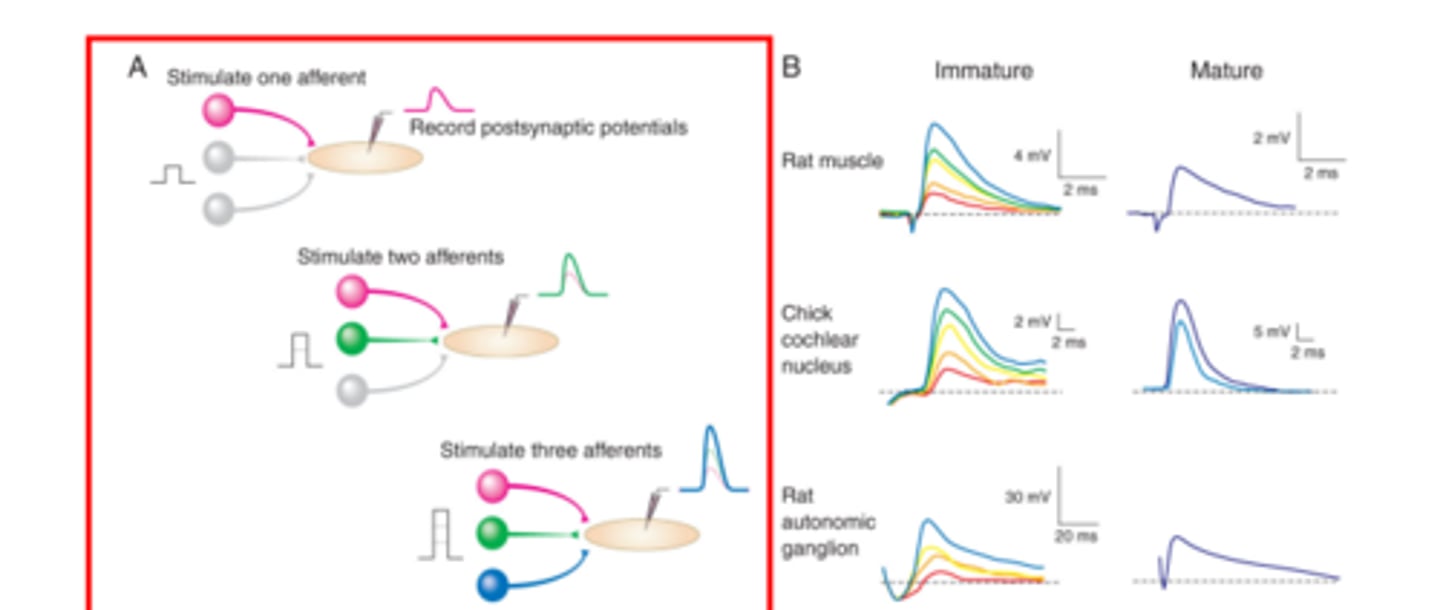
How can convergence be quantified?
by measuring the postsynaptic potential (PSP) amplitude or examining structural changes
if a target cell has afferent input from three different neurons. Stimulating one afferent neuron evokes PSP of a given amplitude But stimulating 2 or 3 afferent neurons result in PSP doing what to the amplitudes?
increasing
convergence on adult cells ________ over time which indicates what?
decreases because some synaptic inputs are eliminated over time
synapse elimination is widespread and occurs in most cases but may occur to what degree & region?
different degree in different brain regions or cell types
what's the issue with counting PSP amplitude?
some systems receive hundreds or thousands of presynaptic contact
Synapse elimination can be studied indirectly by examining the degree of
axon arborization over time
The elimination of axon projection is a common phenomenon in many different regions of the nervous system. Seemly bizarre transient projections arise an example is that in rats the visual cortex sends projection to the spinal cord in the first postnatal week.
These projections were _________ by the second week
eliminated
collateral neurons
An axon typically develops side branches called axon collaterals, so that one neuron can send information to several others. These collaterals, just like the roots of a tree, split into smaller extensions called terminal branches. Each of these has a synaptic terminal on the tip.
Consider the development of the visual system. How do projections become refined over time?
arborizations are refined by RCG from one eye form transient collaterals into inappropriate layers of LGN which are then lost leading to arborization to be located in correct layer/
refinement of innervation happens when there is multiple axon terminals for control of the NMJ and one axon eventually wins out while others retract
a mature NMJ single muscle fiber is innervated by how many motor axon terminals?
one
What are ocular dominance columns?
Ocular dominance columns are specialized structures within the visual cortex that organize neural responses based on input from each eye. They are essential for processing binocular visual information and are subject to modification of sensory experiences during development
What inappropriate projection are transiently established?
During innervation of the LGN in embryonic development, RGC from one eye form transient collaterals into the inappropriate larger of the LGN. Later these collaterals are lost and all arborization are located in the correct layer
describe the experiments that were performed to asses the refinement of projections in the visual system over time
Wiesel & Hubel manipulated the visual input to one or both eyes of cats during early development.
-light evoked activity was prevented by suturing one of the cat's eyelids close during birth to induce monocular deprivation
-after the eyelid was open, majority of cortical neurons in all layers no longer responded to stimulation of the eye
- Different experiment shut both eyes and results showed that most cortical neurons remained responsive to stimuli from both eyes but total number of light-responsive cortical neurons were decreased
-The conclusion to both experiments was that the total amount of evoked activity does not necessarily determine the strength of a visual pathway but the difference in activity determines strength of the projection known as the competition hypothesis
explain how visual deprivation or strabismus during development can influence ocular dominance in adulthood
strabismus the visual cortex showed that majority of neurons responded to stimulation of one eye or the other but not both meaning that neurons were mostly monocular.
In conclusion synapses from each eye must be active at same instant to keep strong functional contacts with same neurons
what is strabismus?
the misalignment of the eyes so that the visual stimuli activate different positions on both retinas
The neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is polyneuronally innervated at birth but all but one axon are eliminated over the first _______ postnatal weeks (#?)
two
____ _____________ and other colleagues provided strong evidence that this competition of nerve terminals for control of individual muscle fibers is activity-dependent
Wes Thompson
describe the experiments that first demonstrated activity-dependent synapse elimination at the NMJ
Thompson blocked nerve transmission with tetrodotoxin (TTX) at the NMJ in a rate during normal period of synapse elimination
-several muscle fibers remained polyneruonally innervated, suggesting that competition occurs via activity pattern
-electronic stimulation of muscle fiber was shown to speed up at synapse elimination
-This suggest postsynaptic electrical activity influences the competition of individual motor axon
further experiments demonstrated that a synapse can only influence its neighbors if they are located within a
short physical distance
to demonstrate that synapses can only influence neighbors in short distances two motor axons were positioned on the same muscle fiber and intracellular recordings were made from muscle to monitor polyneuronal innervation
If synapses from the two axons were established close together, synaptic elimination occurs within
a few weeks
If synapses are farther than 1-2mm, synaptic elimination would
fail to occur
How can sensory coding in the brain be altered experimentally?
in early development mice were treated to high frequency clicks which widened their tuning curve in development and synchronously activated a population of cochlear neurons
the coding properties of a neuron refer to the response of a neuron to
specific ranges of stimuli
an example of sensory coding properties is neurons in the visual cortex respond to
vertical vs horizontal movement
What is a critical period?
limited periods in development during which neural systems are particularly plastic
the first solid evidence of critical periods was observed in
visually impaired cats
A critical period is most important in what stages of develpoment?
early stages
Take an a sensory pathay like visual for example. If a young mice at early stage of development is deprived of vision in one eye then what happens to their ocular dominance?
(in mouse eyes theres a bias in ocular dominance called ipsilateral eye)
it shifts toward the other eye
If an adult mice at late stage of development is deprived of vision in one eye, what happens to their oculuar dominance and why?
no change because they are past the critical period
what kind of signaling can be lost for there to be ocular dominance shift in late development?
GABA/GAD65
What mechanisms underlie critical periods?
critical period can be brought forward by enhancing GABA and promoting rapid maturation of interneurons through BDNF expression