Chapters 1-25 OCR A-Level Chem: ⚗️
1/575
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
576 Terms
Bronsted-Lowry acid:
proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry base:
proton acceptor
what is a hydronium ion?
H3O+ → often just written as H+ instead
what does monobasic, dibasic, and tribasic acid mean?
the number of hydrogen ions in the acid that will be replaced per molecule
organic acids do not replace any hydrogen atoms from…
the carbon chain
acid + base → 🫵
salt + water 🫵
an alkali is…
a basic solution
a low value of [H+(aq)] is a … pH
high
a high value of [H+(aq)] is a … pH
low
relationship between pH and [H+(aq)]
pH = -log [H+(aq)]
reverse relationship between [H+(aq)] and pH
[H+(aq)] = 10-pH
because it is logarithmic, a change of 1 pH number is equal to
10 times different in [H+(aq)]
for a strong acid (that completely dissociates into ions), [H+(aq)] is equal to…
the concentration of the acid
general formula for the dissociation of weak acids:
HA(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + A-(aq)
what Ka?
the acid dissociation constant
how to calculate the acid dissociation constant?
[H+(aq)] [A-(aq)] / [HA(aq)]
![<p> [H<sup>+</sup><sub>(aq)</sub>] [A<sup>-</sup><sub>(aq)</sub>] / [HA<sub>(aq)</sub>] </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd1d385d-fb46-4bb8-b786-46370bf88c98.png)
units of the acid dissociation constant?
mol dm-3
the larger the value of Ka, the further the equilibrium is…
to the right
Ka can be converted into a logarithm (pKa) as to avoid negative indices. What is the relationship between them?
pKa = -logKa
reverse relationship between Ka and pKa
Ka = 10-pKa
for a weak acid, there is …. in a dissociation:
an equilibrium
When HA molecules dissociate, H+(aq) and A-(aq) ions are formed…
in equal quantities
what 2 approximations are made to simplify the Ka expression?
HA dissociates to product concentrations of H+ and A- that are equal
the equilibrium concentration of HA is smaller than the undissociated concentration
Ka expression:
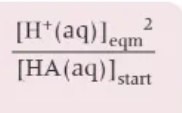
working out [H+(aq)] from the Ka expression:
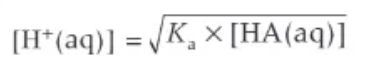
2 approximations in calculations involving weak acids:
dissociation of water is negligible
concentration of acid is much greater than the H+ concentration at equilibrium
water ionises very slightly, acting as an…
acid and base:
dissociation of water equation:
H2O (l) ⇌ H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
what is Kw?
the ionic product of water → [H+(aq)] x [OH-(aq)]
Ka x [H2O (l)] is a constant:
Kw
Kw at 25 degrees Celsius?
1.00 × 10-14 mol2 dm-6
for a dibasic acid/acid, multiply the concentration of OH or H by [what] in pH calculations
2
molecular formula of benzene:
C6H6
2 ways of showing benzene:
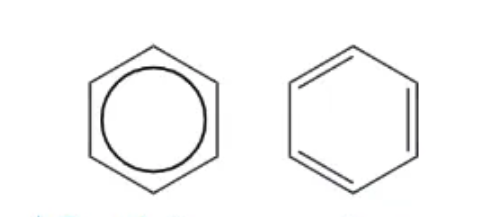
3 pieces of evidence that disprove Kekulé model of benzene:
lack of reactivity:
does not undergo electrophilic additions
does not decolourise bromine under normal conditions
therefore no C=C bonds
length of carbon-carbon bonds:
bond length found to be between the length of a single + a double bond
hydrogenation enthalpies:
expected to have an enthalpy change of hydrogenation that is 3x that of cyclohexane
enthalpy change of hydrogenation of cyclohexane, benzene, and predicted of benzene
cyclohexane = -120 kJ mol-1
benzene = -208 kJ mol -1
predicted of benzene = -360 kJ mol -1
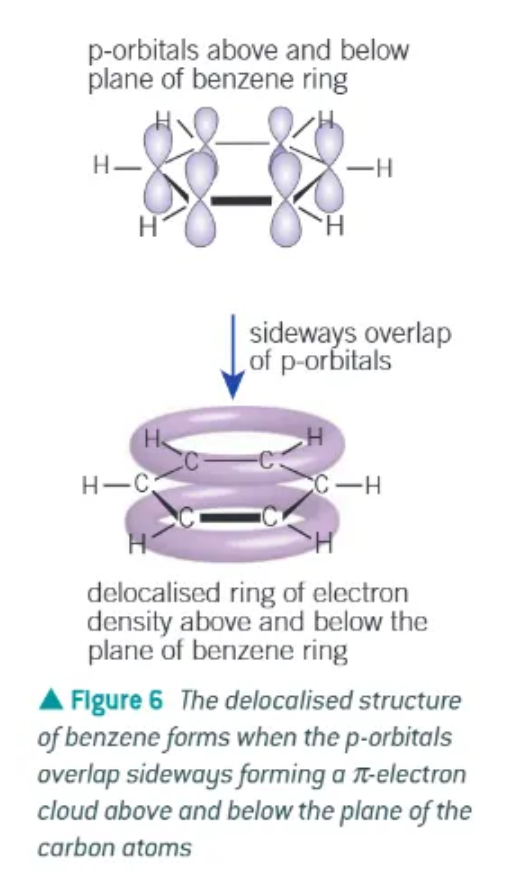
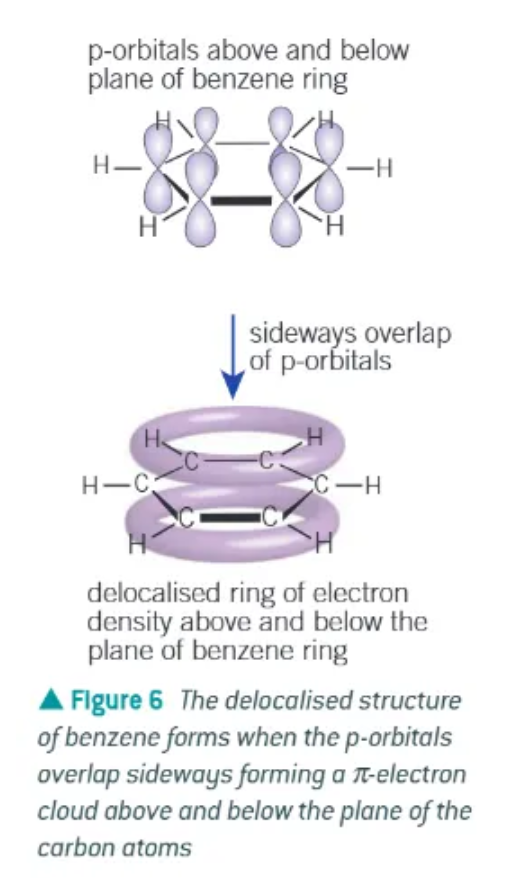
delocalised model of benzene:
planar
each carbon uses 3 of its available 4 electrons in bond to 2 other carbon atoms + 1 atom
each carbon has 1 electron in a p-orbital at right angles to the plane of the bonded carbon + h atoms
adjacent p-orbitals overlap sideways, in both directions above + below plane of carbons → forms a ring of electron density
overlapping of p-orbitals creates a system of pi bonds, spread over all 6 of the carbon atoms
the six electrons occupying the system of pi bonds is said to be delocalised
benzene nomenclature rules:
one substituent group = prefix + benzene
alkyl group + functional group, alkyl group with seven or more carbon atoms = phenyl + suffix
3 exceptions to benzene nomenclature:
benzoic acid
phenylamine
benzaldehyde
substituent groups are listed in…
alphabetical order
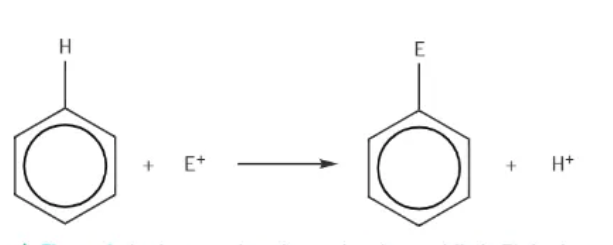
typical equation representing electrophilic substitution of benzene:
a hydrogen is substituted out of benzene:
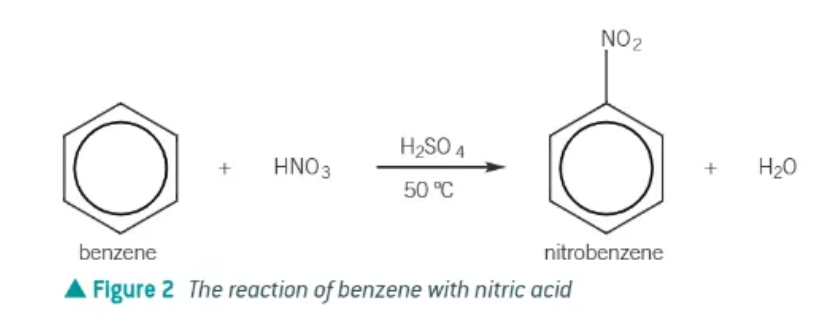
Nitration of benzene:
slow!!
H2SO4 catalyst
heated to 50 degrees to maintain a good rate of reaction → water bath
a hydrogen is replaced by a -NO2 group
benzene + HNO3 → nitrobenzene + H2O
nitration of benzene equation:
if the temperature of the nitration of benzene rises about 50 degrees C, what could/will happen?
further substitution leads to the production of dinitrobenzene
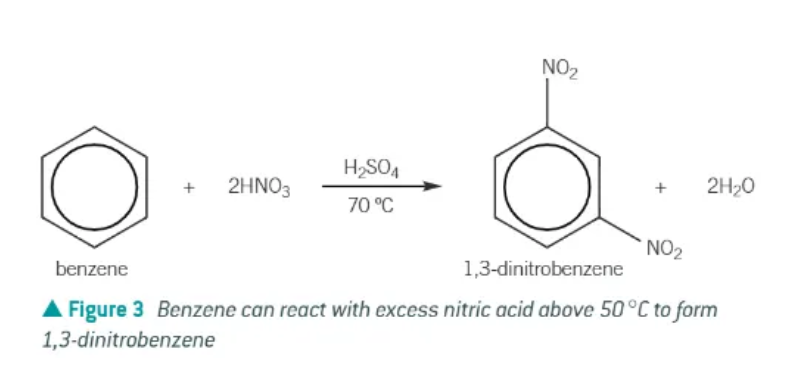
in the nitration of benzene, nitric acid is NOT the electrophile. What is?
the nitronium ion, NO2+ → produced in the reaction of concentrated nitirc acid with concentrated sulphuric acid
mechanism for the nitration of benzene:
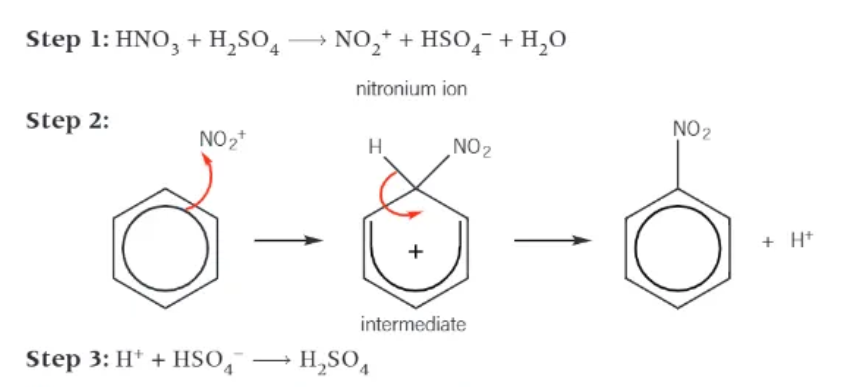
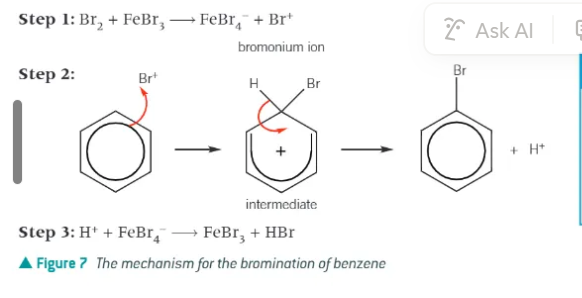
halogenation of benzene:
halogens do NOT react with benzene unless a catalyst called a halogen carrier is present.
common halogen carriers:
AlCl3, FeCl3, AlBr3, FeBr3
bromination of benzene:
electrophile = bromonium ion, Br+ - generated from the halogen carrier catalyst
bromonium ion accepts a pair of electrons from benzene to form a dative covalent bond
mechanism of the bromination of benzene:
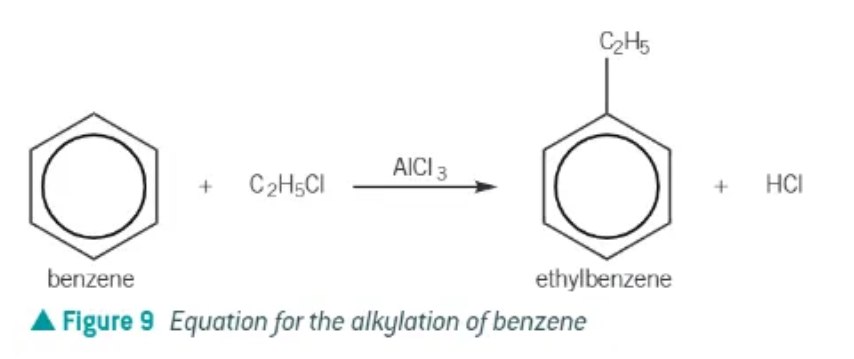
alkylation of benzene requirements:
benzene + haloalkane, in the presence of AlCl3
AlCl3 acts as a halogen catalyst, generating the electrophile
acylation reactions:
benzene + acyl chloride in the presence of an AlCl3 catalyst → forms an aromatic ketones
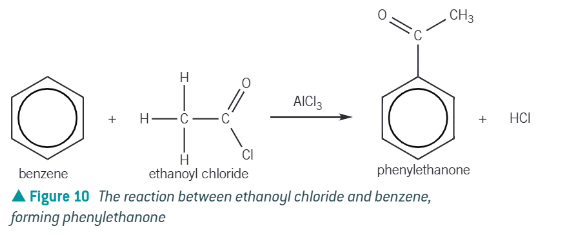
ethanoyl chloride + benzene →
phenylethanone + HCl
why are alkenes more reactive than arenes? (with bromine)
the pi bond in an alkene contains localised electrons, above and below the plan of the C=C double bond.
this is an area of high electron density.
localised electrons in the ⫪bond induce a dipole in the non-polar bromine molecule → δ+Br——Brδ-
mechanism for the electrophilic addition of Br2 with cyclohexene:
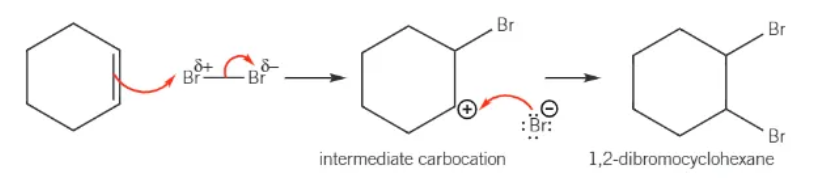
why does benzene only react with a halogen carrier present?
benzene has delocalised pi electrons spread above and below the plane of the carbon atoms in the ring structure
the electron density around any 2 carbon atoms in the benzene ring is less than that in a C=C double bond in an alkene
when a non-polar molecule approaches, there is insufficient pi electron density around any 2 carbon atoms to polarise the bromine molecule
alkenes react with bromine via…
benzene reacts with bromine via…
electrophilic addition
electrophilic substitution
what is a phenol?
an organic chemical containing a hydroxyl, -OH, functional group directed directly to an aromatic ring
difference between a phenol and an aromatic alcohol:
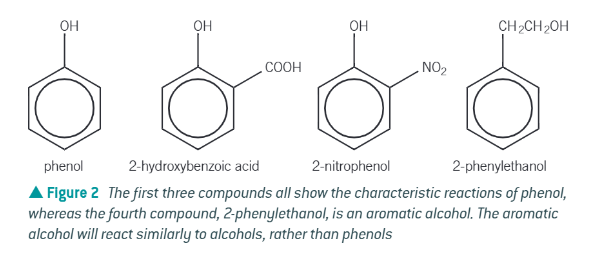
phenol is a … acid?
weak → presence of a non-polar benzene ring
when dissolved in water, phenol partially dissociates to form:
phenoxide ion and a proton
comparable acidity of phenols, alcohols, and carboxylic acids:
Carboxylic acid = most acidic
phenol
alcohol = least acidic
ethanol, phenol, and ethanoic acid reacting with sodium hydroxide + sodium carbonate:
ethanol = will NOT reach with either
phenol = react with sodium hydroxide (strong base)
ethanoic acid = will react with sodium hydroxide AND sodium carbonate (weak base)
reaction with sodium carbonate can be used to distinguish between a … and a …
phenol (will not react)
carboxylic acid (will react)
electrophilic substitution reaction of phenol + sodium hydroxide:
takes place under mild conditions
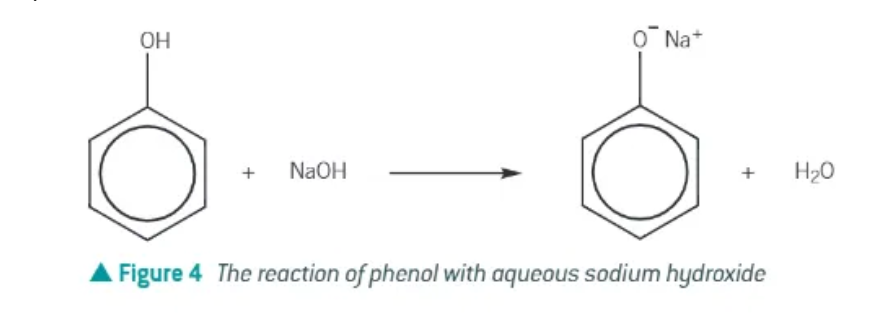
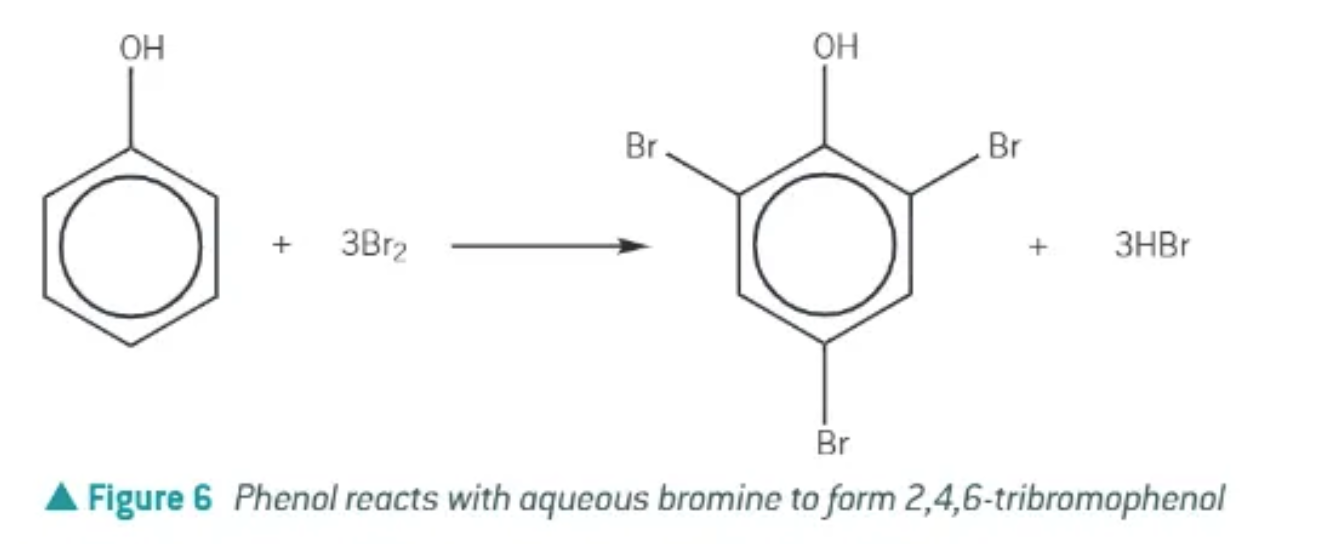
bromination of phenol:
phenol reacts with an aqueous solution of bromine to form 2,4,6-tribromophenol
decolourises the bromine water (orange to colourless)
a halogen carrier is not required!
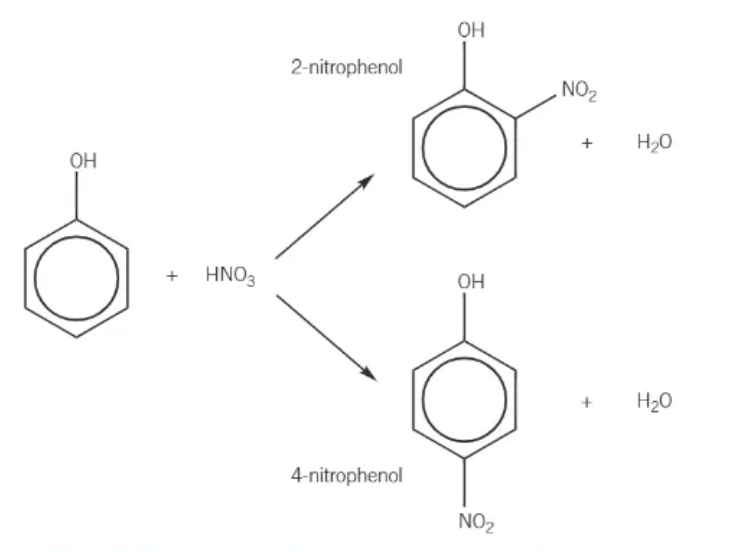
nitration of phenol:
reacts readily at room temperature
forms a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol
dilute nitric acid
addition of bromine water to phenol results in 2 observations:
bromine decolourises
white precipitate forms
why is phenol more reactive than benzene?
lone pair of electrons from the oxygen p-orbital of the -OH group being donated into the pi system of phenol
electron density of benzene ring increases
increased electron density attracts electrophiles more strongly than benzene
aromatic ring in phenol is therefore more susceptible to attack from electrophiles than in benzene
the electron density in the phenol ring is sufficient to …
polarise bromine molecules → no halogen carrier catalyst required
nitrobenzene reacts … with bromine, requiring:
slowly → halogen carrier catalyst and a high temperature
NH2 group [ what ] a benzene ring?
activates
what is an activating group?
helps the aromatic ring react more readily with electrophiles → e.g. NH2wh
what is a deactivating group?
makes the aromatic ring react less readily with electrophiles
-NH2 is said to be…
2- and 4- directing
-NO2 is said to be …
3- directing
directing effect:
a substituent group on benzene will have a directing effect on any second substituent group.
all 2- and 4- directing groups are…
activating groups
all 3- directing groups are …
deactivating groups
2- and 4- directing groups:
amine, NH2 or NHR
hydroxyl, -OH
ketone, -OR
-R or -C6H5
-halogen
a h k r h
rate of reaction definition:
the change in concentration of a reactant / product in a given time
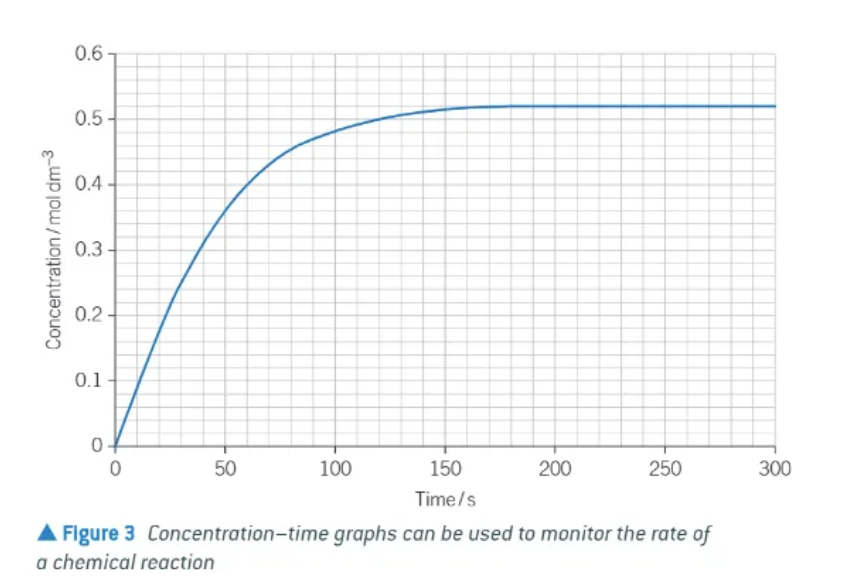
what shape does a typical concentration/time graph have?
curve:
steepest at start
becomes less steep
flattens off
4 factors that can change the rate of a reaction:
concentration (or pressure when reactants are gases)
temperature
use of a catalyst
surface area of solid contacts
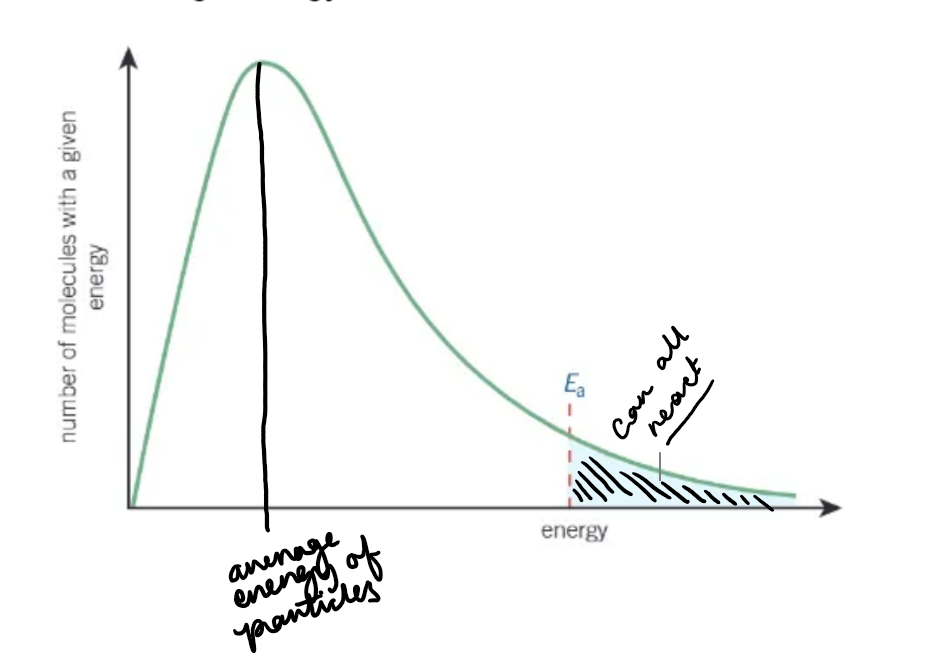
what does collision theory state?
2 particles must collide to react
why are some collisions effective, and some ineffective?
particles must collide with correct orientation.
particles must have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction
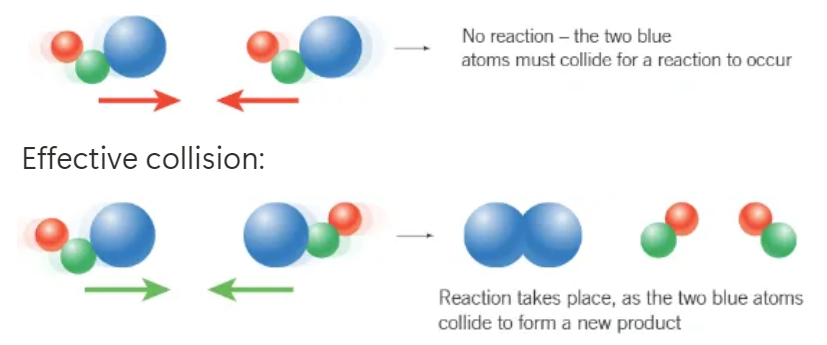
how does increasing concentration affect the rate of reaction?
rate of reaction generally increases
increases the number of particles in the same volume
particles are closer together + collide more frequently
therefore → more frequency + successful collisions (correct orientation + sufficient energy) → increased rate of reaction
how does increasing the pressure of a gas affect the rate of reaction?
gas = compressed in a smaller volume → pressure of gas is increased → rate of reaction increases
concentration of gas molecules increases as the same number of gas molecules occupy a smaller volume
gas molecules = closer together + collide more frequently → leads to more effective collision in the same time
2 methods for following the progress of a reaction:
monitor removal (decrease in conc.) of reactant
monitor formation (increase in conc.) of product
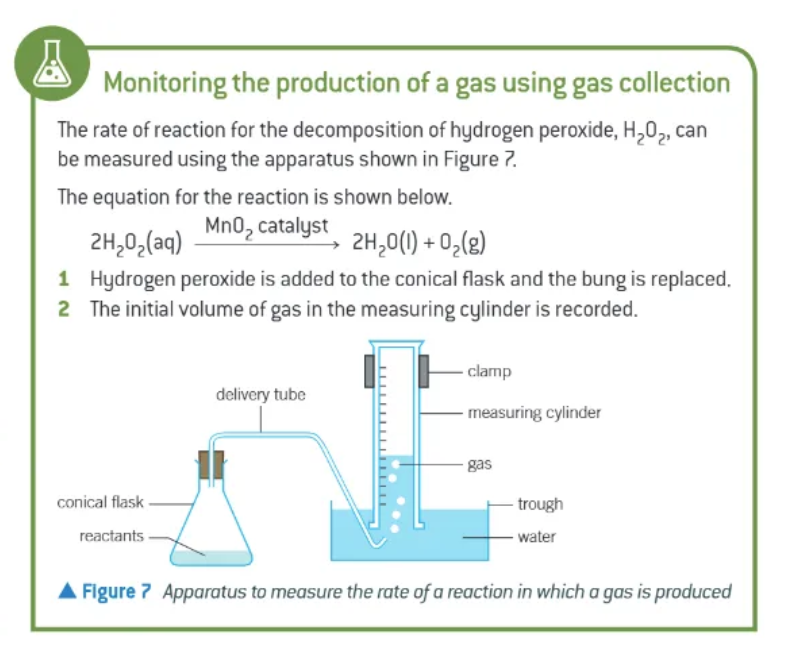
what 2 methods can be used for monitoring reactions that produce gas?
monitor volume of gas produced at regular time intervals → gas collection
monitor loss of mass of reactants using a balance → mass removal
draw the equipment for gas collection:
on a concentration-time graph, what represents the rate? 🫵
the gradient 🫵
on a (gas collection or mass lost) / time graph, what represents the rate?
the gradient
3 rules for catalysts:
catalyst not used up in the reaction
may form an intermediate / provide a surface on which the reaction can take place
catalyst is regenerated at the end of reaction
Exo + Endothermic reaction enthalpy profile diagrams (with catalyst!)
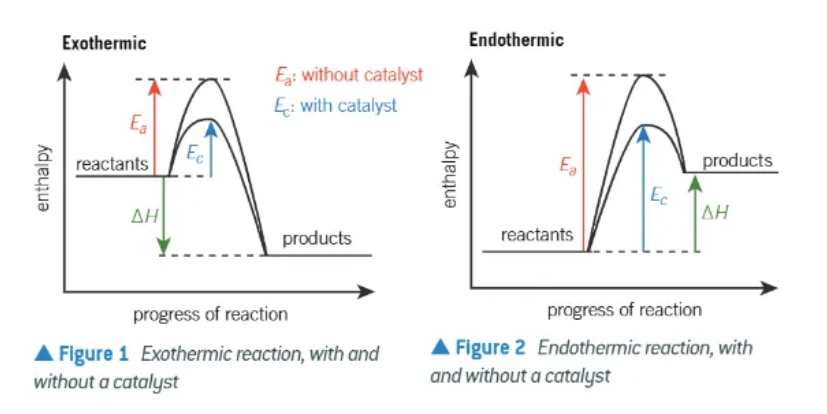
3 things to remember when drawing enthalpy profile diagrams?
reactants + products written out
∆H shown with an arrow pointing in correct direction
activation energy shown with upwards arrow
homogeneous catalysts:
same physical state as the reactants
forms an intermediate → breaks down to give catalyst + product
2 reactions that use homogeneous catalysis:
making esters (with sulphuric acid as a catalyst)
ozone depletion (Cl• catalyst)
heterogeneous catalyst:
different physical state from the reactants
usually solid → in contact with gaseous reactants/reactants in solution
reactant molecules are adsorbed (weakly bonded) → onto surface of catalyst → where the reaction takes place
product leaves surface of catalyst by desorption → at the end of the reaction
lower activation energy often means a lower…
temperature → this makes using catalysts more sustainable (less electricity etc.)
what does a Boltzmann distribution graph look like?