PROTEIN DENATURATION
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
PROTEIN DENATURATION
Protein denaturation is the partial or complete disorganization of a protein’s characteristic three-dimensional shape
Result of disruption of its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structural interactions.
does not affect the primary structure of a protein
biochemical activity
Because the biochemical function of a protein depends on its three-dimensional shape, the result of denaturation is loss of ..
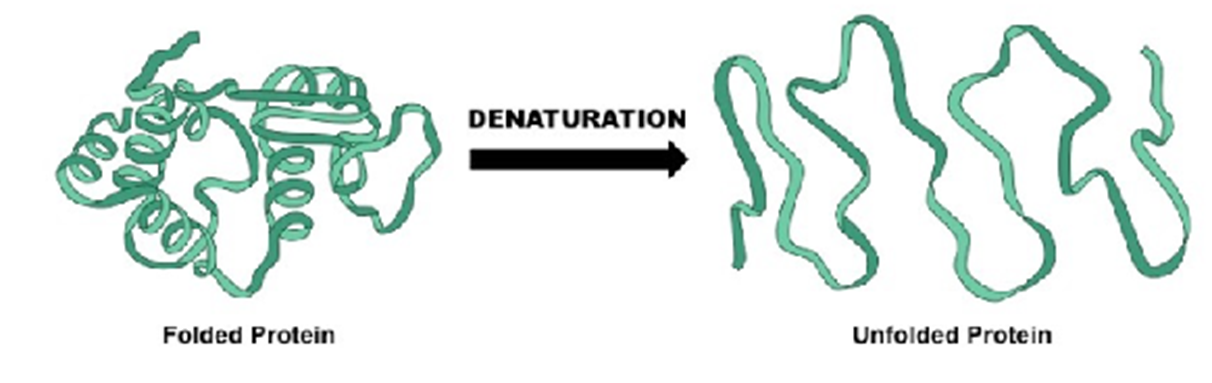
Some proteins lose all of their three-dimensional structural characteristics upon denaturation, most proteins maintain some 3D structure
Renaturation
limited denaturation changes conditions can be reversed, in which the protein is “refolded,”
IRREVERSIBLE
For extensive denaturation changes, the process is usually ….
Loss of water solubility
is a frequent physical consequence of protein denaturation.
Coagulation or precipitation
precipitation out of biochemical solution of denatured protein
Protein denaturation
involves loss of the protein’s three-dimensional structure. Complete loss of such structure produces an “unstructured” protein strand.
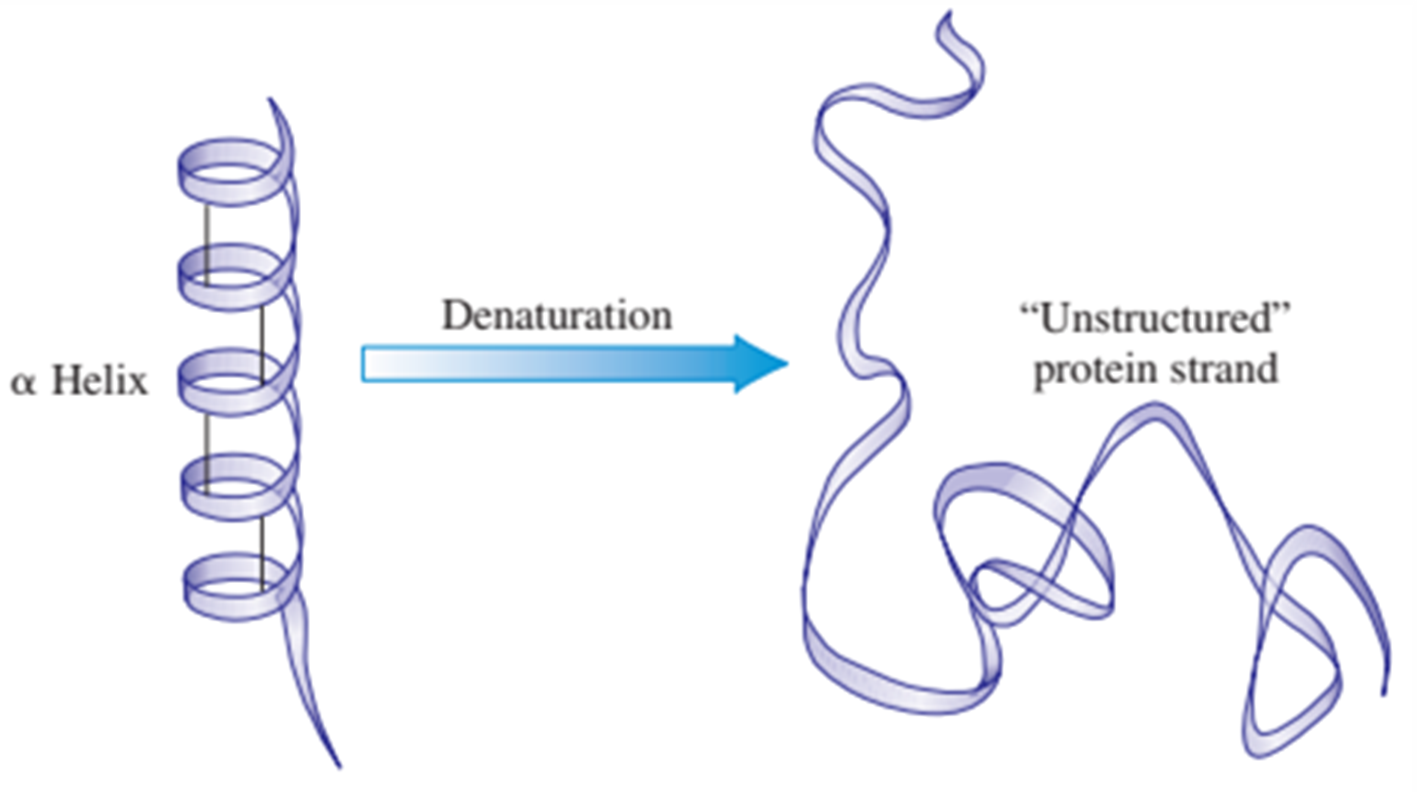
HEAT
disrupts hydrogen bonds by making molecules vibrate too violently; produces coagulation, as in the frying of an egg
violent whipping or shaking (mech.agitation),microwave and UV, vibration
causes molecules in globular shapes to extend to longer lengths, which then entangle (e.g., beating egg white until thickens)
H-Bond
organic solvents (e.g., ethanol, 2-propanol, acetone)
interferes with R-group interactions because these solvents also can form hydrogen bonds; quickly denatures proteins in bacteria, killing them (e.g., the disinfectant action of 70% ethanol)
strong acids and bases
disrupts hydrogen bonds and salt bridges; prolonged action leads to actual hydrolysis of peptide bonds
salts of heavy metals (Hg2+ Ag+, Pb2+)
metal ions combine with -SH groups and form poisonous salts
Effect of Heat
disrupt hydrogen bonds and non-polar hydrophobic interactions
increases the kinetic energy and causes the molecules to vibrate so rapidly and violently that the bonds are disrupted
proteins in eggs denature and coagulate during cooking. foods are cooked to denature the proteins to make it easier for enzymes to digest them
heating
Medical supplies and instruments are sterilized by … to denature proteins in bacteria and thus destroy the bacteria
High levels of thermal energy
energy may disrupt the hydrogen bonds that hold the protein together
As these bonds are broken, the protein will begin to unfold and lose its capacity to function as intended
body temperature (37 degree centigrade)
Temperatures at which proteins denature may vary, but most human proteins function optimally at ….
Effect of Alcohol

amide groups in the secondary protein structure
Hydrogen bonding occurs between ——
Hydrogen bonding between "side chains" occurs in tertiary protein structure in a variety of amino acid combinations

Alcohol
denatures proteins by disrupting the side chain intramolecular hydrogen bonding
70% alcohol
is able to penetrate the bacterial cell wall and denature the proteins and enzymes inside of the cell.
95% alcohol solution
merely coagulates the protein on the outside of the cell wall and prevents any alcohol from entering the cell.
Ions
form strong bonds with the carboxylate anions of the acidic amino acids or -SH groups of cysteine, disrupting ionic and disulfide linkages
Disulfide Bonds
Heavy Metal Salts Disrupt ???
Heavy metals
also disrupt disulfide bonds because of their high affinity and attraction for sulfur and which lead to the denaturation of proteins
can disrupt bonds in the protein, causing it to lose its structure.
mercury and lead
Salts of heavy metals such as … may be used to denature can interact with a protein's functional side chain groups to form complexes.
Protonation
of the amino acid residues changes whether or not they participate in hydrogen bonding, so a change in the pH can denature a protein.