PHR 926 fungi map Block4
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what are the 2 types of molds?
1) septate hyphae
2) Aseptate hyphae
what is an example of a septate hyphae mold?
-Aspergillus
what is an example of a Aseptate hyphae molde?
-zygomycetes (aggressive)
what are the three common types of zygomycetes?
1) mucor
2) Rhizopus
3) others
what are the important fungal structures of mold?
1) hyphae
2) conidia
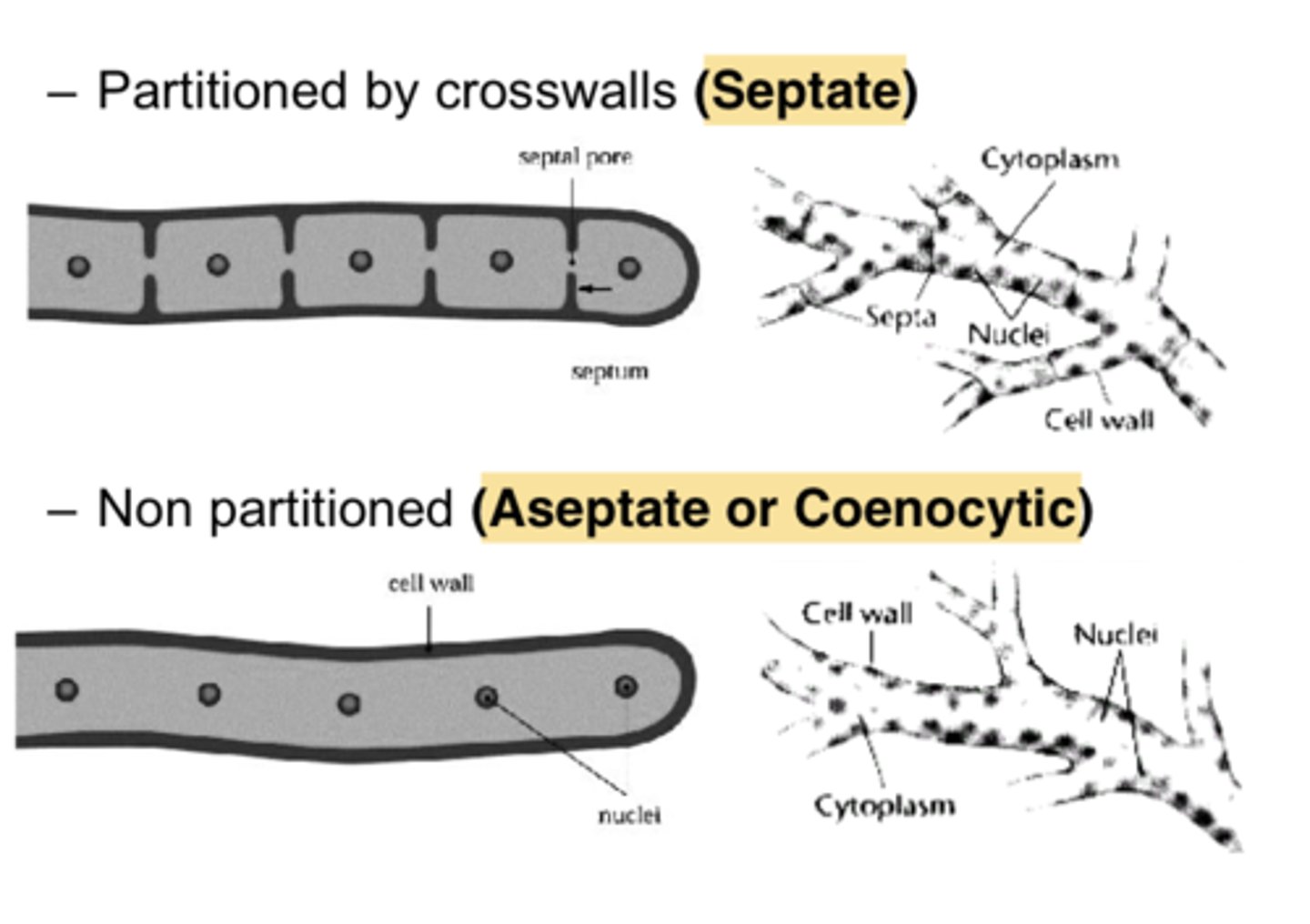
what does hyphae look like?
-long filament structures that are either septate (have branches) or aseptate (no branches)
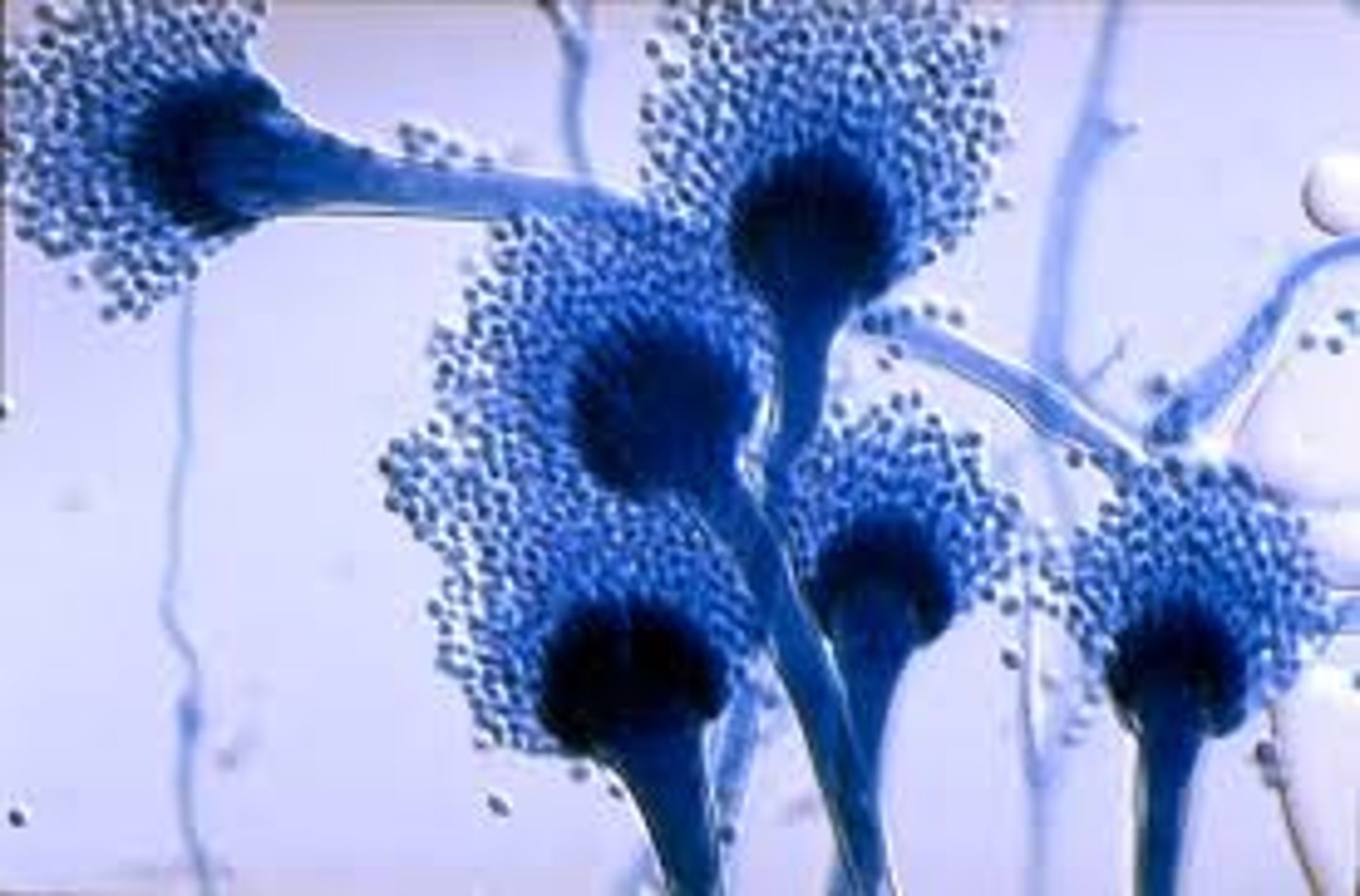
what does conidia look like?
-asexual, non-motile spores produced by fungi, particularly in the group Hyphomycetes
what is dimorphic fungi?
-has 2 shapes
-presents itself based on location
-generally endemic to certain areas
what are the 3 common dimorphic fungi?
1) coccidoides
2) Histoplasma
3) Blastomyces
what kind of dimorphic fungi will you find in kentucky?
1) Histoplasma
2) Blastomyces
what are the 2 types of yeast?
1) candida spp.
2) cryptococcus neoformans
what are the 4 common different types of candida spp?
1) C. albicans
2) C. glabrata
3) C. parapsilosis
4) C. tropicalis
what are common fungal habitats?
1) decaying organic matter
2) fecal matter
3) soil
4) skin and GI tract (mostly candida)
what are common characteristics of ALL fungi?
1) eukaryotic
2) nonmotile
3) aerobic
4) saprophytic
what antifungal drug is a DNA synthesis inhibitor?
-flucytosine
which drugs are polyenes?
1) amphotericin B
2) nystatin
what is the MOA of polyenes?
-bind to ergosterol to form pores in cell membrane
what are notable ADRs of amphotericin B (original formulation)?
-toxicities can be severe (but are improved with lipid product version)
-kidney injury (nephrotoxicity)
-infusion related reactions
true or false?
amphotericin B only comes in an IV form?
true
what are the 3 IV formulations for amphotericin B?
1) conventional amphotericin B
2) amphotericin B lipid complex
3) liposomal amphotericin B
what is the MOA of echinocandins?
-target cell wall
-inhibit glucan synthesis
-all are IV only
what are the echinocandins?
1) micafungin
2) anidulafungin
3) caspofungin
what is the MOA of AZOLs?
-are cell membrane active
-inhibit ergosterol synthesis
what drugs are AZOLs?
-anything ending in AZOL
1) fluconazole
2) itraconazole
3)voriconazole
4) Posaconazole
5) isavuconazole
describe fluconazole
-IV and oral formulations
-moderate drug interactions
-both renal and hepatic elimination (CYP3A4)
what spectrum of fungi does fluconazole cover?
1) cryptococcus
2) candida spp. (does not cover C. glabrata)
what are the possible toxicities of fluconazole?
-pretty safe drug
-occasional liver injury
describe itraconazole
-oral only
-can cause liver injury
-solution better absorbed than capsule
-a lot of DDI
what spectrum of fungi does itraconazole treat?
1) cryptococcus
2) candida spp
3) aspergillus
4) dimorphic
describe voriconazole
- IV and oral
- a LOT of DDI
-fully metabolized by liver (3 different CYP enzymes)
-IV formulations have a nonaqueous diluent which is renally eliminated
-non-linear elimination
what are the possible toxicities for voriconazole?
-liver injury
-melanoma (long-term use)
-visual disturbances (will go away once you stop voriconazole)
what is the spectrum of fungi that voriconazole covers?
1) cryptococcus
2) candida spp.
3) aspergillus (first line therapy of choice for this fungi)
4) Dimorphic
describe Posaconazole
-IV and oral formulations
-can cause liver injury
-fully metabolized
what is the spectrum of fungi that Posaconazole covers?
1) cryptococcus
2) candida spp.
3) aspergillus
4) dimorphic
5) zygomycetes
describe isavuconazole
- IV and oral formulations
- can cause liver injury
- fully metabolized
what is the spectrum of fungi that isavuconazole covers?
1) cryptococcus
2) candida spp
3) aspergillus
4) dimorphic
5) zygomycetes
- note how same spectrum of coverage as Posaconazole
what are 3 things that we are actively doing that is increasing fungi infections?
1) transplants
2) antimicrobial treatment
3) other immune suppressing drugs
what similarity between humans and fungi causes delay in new treatment options and some toxicity with antifungals?
-ergosterol (in fungi) is structurally similar to cholesterol (in humans)
true or false?
fungi are not here (generally) to infect humans
true
true or false?
when we take away immune defense, fungi can cause disease
true
where are cocidoides generally found?
in desert and south west
what is the most common (and possibly most relevant) candida yeast?
-C. albicans (susceptible to drug treatment)
what is the most worrisome and resistant candida yeast to treat?
C. glabrata
which two types of candida yeast are uncommon?
1) c. parpsilosis
2) C. tropitcalis
true or false?
cryptococcus neoforms can occur in uncontrolled HIV and some cancer patients. the ability to control and prevent HIV has decreased the rate of this yeast
true
true or false?
dimorphic is NOT a true mold
true
true or false?
Polyenes look for already synthesized ergosterol and clump them together in a circle with a hole in the middle which them forms pores in cell membrane
true
true or false?
a second line drug for aspergilus is caspofungin
true
true or false
because we are not too great at treating fungal infections you will see some places start with 2 drugs at the start at treatment
true
what drugs can treat cryptococcus?
1) fluconazole
2) itraconazole
3) voriconazole
4) posaconazole
5) isavuconazole
6) amphotericin
what drugs can treat candida albicans?
1) fluconazole
2) itraconazole
3) voriconazole
4) posaconazole
5) isavuconazole
6) amphotericin
7) caspofungin
8) micafungin
9) anidulafungin
what drugs can treat candida parapsilosis?
1) fluconazole
2) itraconazole
3) voriconazole
4) posaconazole
5) isavuconazole
6) amphotericin
7) caspofungin
8) micafungin
9) anidulafungin
what drugs can treat candida glabrata?
1) voriconazole (some resistance)
2) pasoconazole (some resistance)
3)isavuconazole
4) amphotericin
5)caspofungin
6) micafungin
7) anidulafungin
what drugs can treat C. tropicalis?
1) fluconazole
2) itraconazole
3) voriconazole
4) posaconazole
5) isavuconazole
6) amphotericin
7) caspofungin
8) micafungin
9) anidulafungin
what medications can treat aspergillus?
1) itraconazole
2) voriconazole
3) posaconazole
4) isavuconazole
5) amphotericin
6) caspofungin
7) micafungin
8) anidulafungin
what drugs can treat zygomycetes?
1) posaconazole
2) isavuconazole
3) amphotericin