Tumors
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
melanomas/nevus
uveal lymphoma
metastatic carcinoma
diffuse choroidal hemangioma
choroidal osteoma
what are the choroidal tumors?
retinoblastoma
retinal astrocytoma
retinal capillary hemangioma
retinal cavernous hemangioma
what are the tumors of the retina?
melanocytoma of the optic disc
combined hamartoma of the RPE & retina
what are the tumors of the RPE?
malignant melanoma
choroid > ciliary body > iris
most common primary intraocular tumors in adults
risk factors:
caucasian/fair-skinned individuals
dysplastic nevus syndrome
melanocytosis
nevus
commonly presents 5th-6th decade
melanomas
1% of cases secondary to inherited BAP1 mutation (nuclear protein)
sx:
usually begins asymptomatic
blurry vision, VF loss, flashes/floaters
circumscribed (nodular) or diffuse (rarer form)
appearance:
pigmentation: gray-green or brown, amelanotic
elevated >2mm
oval, dome-shape or mushroom/collar button if break in bruch’s
overlying lipofuscin (orange pigment)
presence of overlying RPE changes (atrophy, drusen, PED w/ subretinal fluid)
choroidal folds, hemorrhage, exudate, CNVM, secondary glaucoma, cataract, uveitis
poor prognosis w/ increasing age
referral to retinal subspecialist ASAP
PCP/oncologist referral
tx:
observe small tumors
radioactive plaques for small-medium tumors
transpupillary thermotherapy
photodynamic therapy
enucleation
testing:
ultrasound
IVFA
liver enzymes
systemic testing to r/o metastasis
observe small tumors
radioactive plaques
transpupillary thermotherapy
photodynamic therapy
enucleation
what are the options for management of malignant melanomas?
no difference in mortality rates after 12yr for medium sized tumors treated with brachytherapy or enucleation
in cases w/ distant metastases, tx of the intraocular melanoma become palliative & systemic chemo is primary tx
what did COMS find about melanoma management?
no difference
COMS showed there was _________ in gender for the prognosis of a malignant melanoma
16
___% 5y mortality rate for small malignant melanomas (<2-3mm)
32
____% 5y mortality rate for medium malignant melanomas (3-8mm)
53
____% 5y mortality rate for large malignant melanomas (>8mm)
15-GEP testing
done w/ fine needle aspiration
able to differentiate high risk from low risk of metastasis
may aid in how intense pts are monitored/treated
mottled fluorescence in arteriovenous phase, progressive staining, prolonged dye retention, double circulation
what does a choroidal melanoma show on IVFA?
low-medium reflectivity, excavation of underlying uveal tissue, shadowing of subjacent soft tissues, internal vascularity, acoustic hollowing
what do intraocular melanomas show on B-scan?
acoustic hollowing
characteristic finding on B-scan of an intraocular melanoma; acoustic quiet zone at the base of the tumor
liver (lung, bone, skin, CNS)
what is the most common metastatic site for a choroidal melanoma?
30-50
______% of pts w/ malignant melanoma will die w/in 10y of diagnosis
larger, older
____ sized malignant melanomas in ____ patients have the greatest risk of mortality
VA of affected eye
VA of other eye
size of tumor
age
general health of pt
ocular structures involved
presence of metastasis
what are the factors to consider when treating malignant melanoma?
30
ocular melanocytosis is ___x more common in pts w/ uveal melanoma
increased
there is an _____ incidence of uveal melanoma in white patients w/ ocular or oculodermal melanocytosis
choroidal nevus
found in 10% of pop, present at birth
maximum growth occurs pre-puberty
usually asymptomatic
appearance:
flat or minimally elevated
oval, circular, slate gray-pigmented or nonpigmented
drusen develop over time
usually less than 2mm thick
may develop RPE atrophy, hyperplasia
CNVM risk
thickness
fluid
symptoms
orange pigment
margin of tumor less than 2DD from disc
ultrasonographic hollowness
halo absence
drusen absence
what are the risks for malignant transformation of a nevus?
3%
if the melanoma suspect has 0 risk factors, there is a ____ chance for growth at 5y (most likely choroidal nevi)
38
if the melanoma suspect has 1 risk factor, there is a ____ chance for growth at 5y
50+
if the melanoma suspect has 2+ risk factors, there is a ____ chance for growth at 5y
observation
RTC x3-4mo to determine stability
if stable, RTC 2x/yr to document any change
what is the management for a low risk melanoma suspect?
monitor more closely every 3-6mo
what is the management for a high risk melanoma suspect?
uveal lymphoma
typically affect immune compromised individuals
more commonly non-Hodgkin’s B-cell type
may be T-cell or Hodgkin’s
typically a metastatic form of a systemic lymphoma
unilateral > bilateral
highly variable presentation:
circumscribed or diffuse
flat or elevated
amelanotic
yellow-white infiltration
can be multifocal (resembling birdshot or MFC)
may have associated conjunctival & orbital involvement
testing:
ultrasound
OCT
biopsy
uveal thickening, characteristic ovoid echolucent mass
what does a uveal lymphoma show on ultrasound?
characteristic rippled seasick pattern
what does a uveal lymphoma show on OCT?
systemic evaluation
systemic tx
local radiation
rarely, if no systemic involvement: observation
what is the management for uveal lymphoma?
choroidal hemangioma
unilateral, benign vascular tumor
no sexual or racial predilection
not a cancer
does not metastasize
appearance:
can be well circumscribed or diffuse
unilateral VA loss in adulthood (or incidental finding)
tumors compromised of blood vessels
smoothly elevated, dome-shaped (NOT mushroom shaped)
oval/circular shape
most common location is posterior pole
most 3-9mm in diameter
can cause CME, exudative RD, & secondary glaucoma
testing:
photograph to document location & size
B-scan: sharp borders, acoustic solidity
FA: not pathognomonic
tx:
usually none unless subretinal fluid threatens macular region
laser photocoagulation if VA threatened due to serous RD
choroidal osteoma
slow growing intrachoroidal bone-like tumor
rare, benign
unilateral > bilateral
found in healthy, young females
typically near optic nerve or posterior poles
sx depend on location but often asymptomatic
ocular manifestations:
yellow-white to red-orange in apperance
oval or round
edges are scalloped-pseudopod-like projections
can cause macula detachments or neo
tx/prognosis:
depends on lesion location
growth suggests malignant, must r/o
metastatic carcinoma of choroid
more common than primary malignancies
seed of cancer that started in a cancer elsewhere & spread to eye via blood flow
features:
cream, yellow, light brown
flat or slightly elevated mottled pigment clumping on surface
extensive exudative RD
maybe multifocal or bilateral
testing:
B scan: diffuse choroidal thickening
tx:
no enucleation unless painful
chemo
external beam radiation
breast
what is the most frequent primary site for metastatic carcinoma of the choroid for females?
lungs
what is the most frequent primary site for metastatic carcinoma of the choroid for males?
choroid
what is the most common site for metastasis?
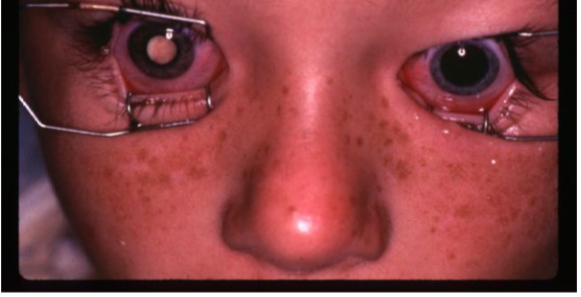
retinoblastoma
cancer affecting retinal photoreceptors
most common primary intraocular malignant tumor of childhood
predisposed to secondary non-ocular malignancies
unilateral > bilateral (except in inherited cases)
average age of dx: 18mo (90% under 5y)
5-10% of pts have +FHx (AD)
ocular manifestations:
leukocoria
strabismus
dome-shaped lesion
whitish pink nodular mass
can cause RRD
secondary glaucoma & pseudouveitis
iris neo
testing:
B-scan
CT
MRI
genetic testing & counseling
tx/prognosis:
early detection is critical
enucleation is last resort
remove worse eye if bilateral
remove long piece of optic nerve too
radiation
photocoagulation or cryotherapy
systemic chemo (**tx of choice)
external beam radiation
photocoagulation or cryotherapy (for small tumors behind retina & confined to sensory retina, contraindicated if vitreous seeding)
systemic chemotherapy
enucleation is last resort
what are the tx strategies for retinoblastoma?
systemic chemo
what is the tx of choice for retinoblastoma?
15%
what is the overall mortality rate for retinoblastoma?
scleral or optic nerve involvement
tumor size & location
cellular differentiation
age of pt
laterality (bilateral is worse)
what characteristics of a retinoblastoma influence mortality rate?
high reflectivity
what does a retinoblastoma show on B-scan?
endophytic
retinoblastoma type
white, pearly-pink, creamy nodular mass that breaks through the ILM into vitreous
vitreous seeding
fine blood vessels on surface
secondary calcification leads to sharp demarcations (cottage cheese)
multiple tumors possible
exophytic
retinoblastoma type
yellowish subretinal mass lesion often underlying a serous RD
total RD risk
tumor is difficult to view
endophytic
exophytic
diffusely spreading lesion simulating posterior uveitis
what are the types of retinoblastoma?
retinal capillary hemangiomas
75% not associated w/ systemic disease
may be multiple & bilateral in 50% of pts
tx:
may initially just observe
laser or cryo to preserve vision
retinal cavernous hemangioma
rare, congenital unilateral asymptomatic vascular lesion
clumps of thin-walled saccular aneurysms filled w/ dark blood
cluster of grapes
tx:
usually not needed
melanocytoma of optic disc
rare, benign, unilateral melanotic lesion
usually affects darkly skinned individuals
usually incidental finding
appearance:
jet black, feathery edges, inferior location
stable or slow growing
tx:
none
FAF will show hypofluorescence for melanoma
how do you differentiate a melanoma or nevus of optic disc?
combined hamartoma of RPE & retina
rare, unilateral hamartoma
involves RPE, neurosensory retina, retinal vessels, & adjacent vitreous
males > females
appearance:
juxtapapillary more common than peripheral
strabismus
slightly elevated
variable amount of intraretinal gliosis
ERM
dilated capillaries & retinal blood vessels
solitary idiopathic choroiditis
unknown etiology
occurs at any age
no predilection for age or sex
appearance:
yellow-ish white lesion
usually good VA except if lesion in juxtapapillary or foveal area
normal IOP & AC
pt usually lacks any medical, systemic, or ocular hx
dx of exclusion
active & inactive phase
choroidal melanoma
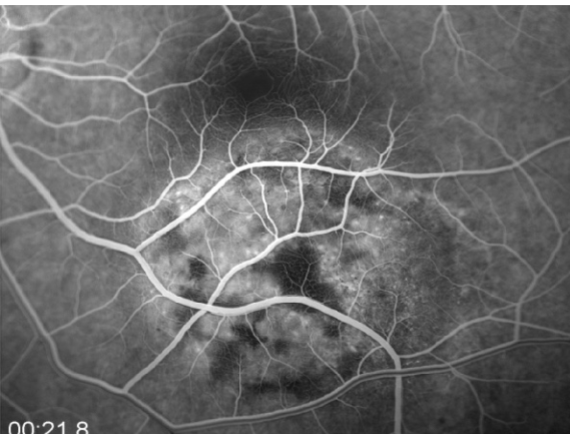
melanoma
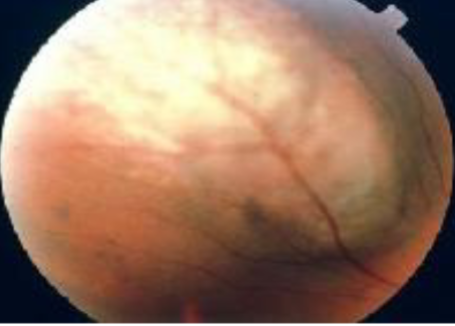
melanoma
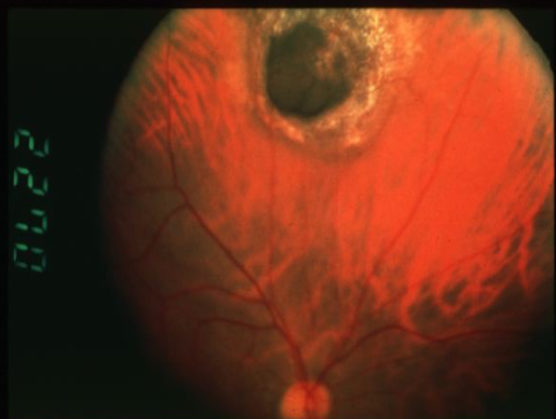
melanoma
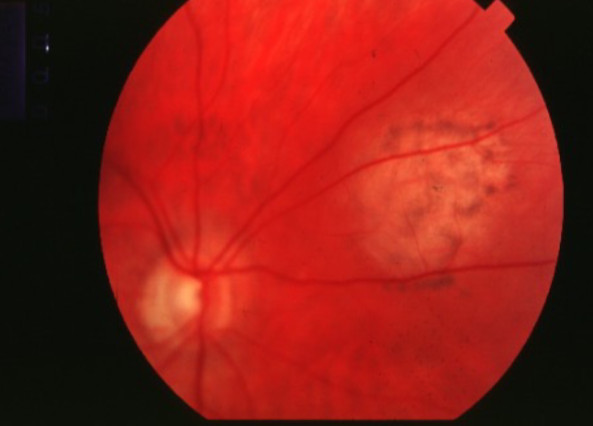
melanoma
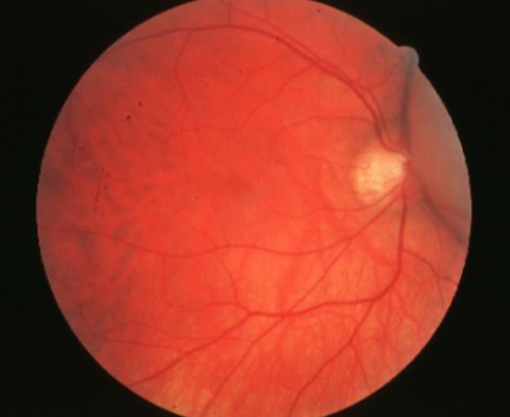
melanoma
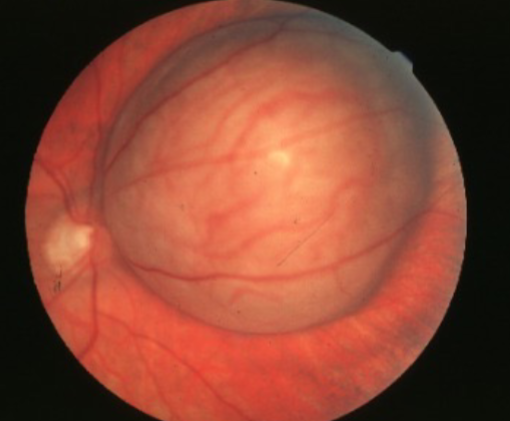
melanoma
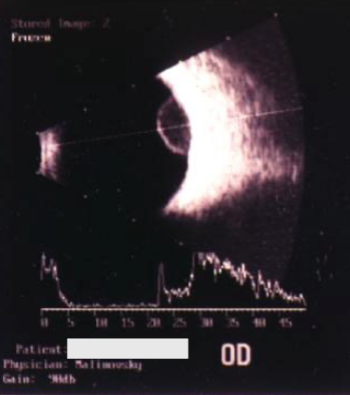
melanoma
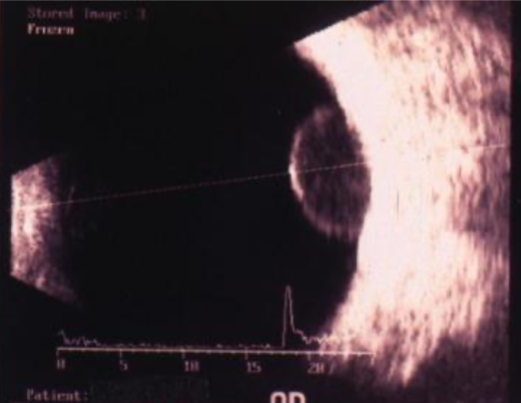
melanoma
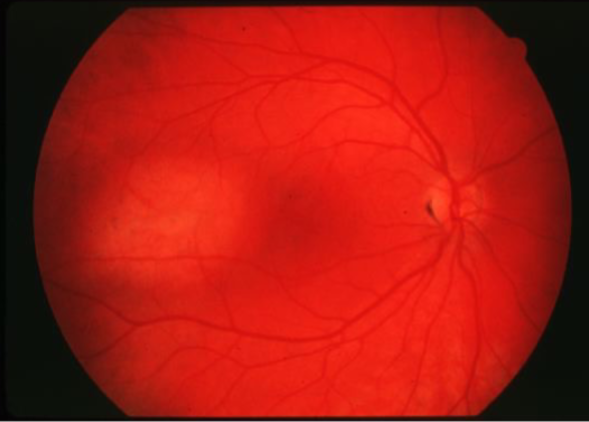
melanoma
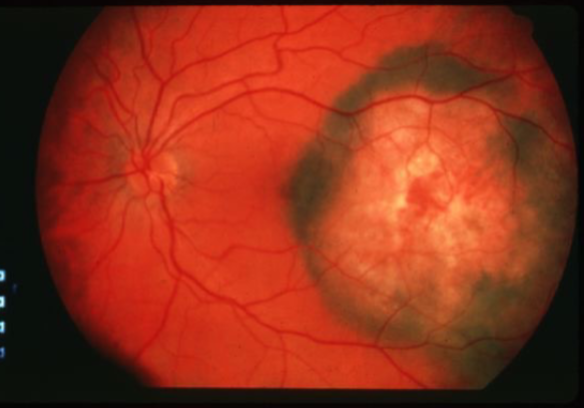
melanoma

melanoma
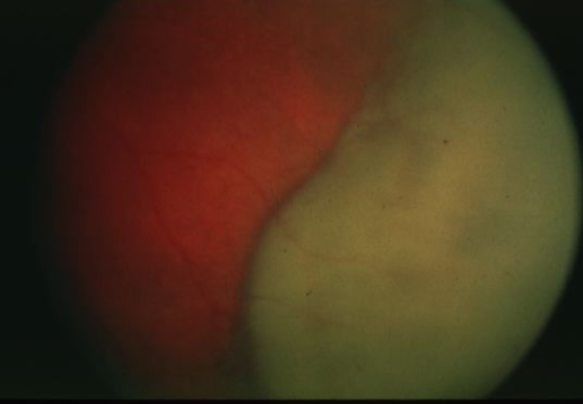
melanoma
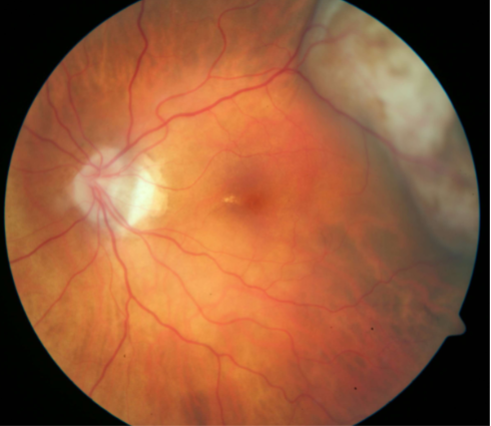
melanoma
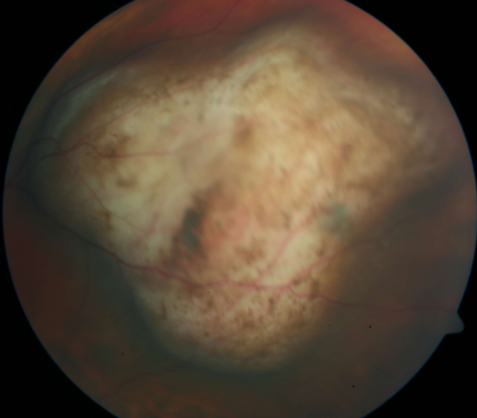
melanoma
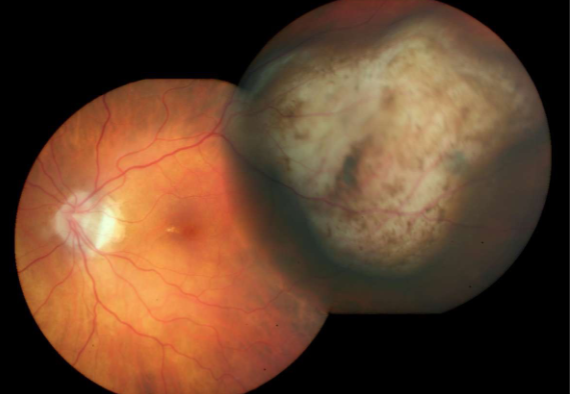
melanoma
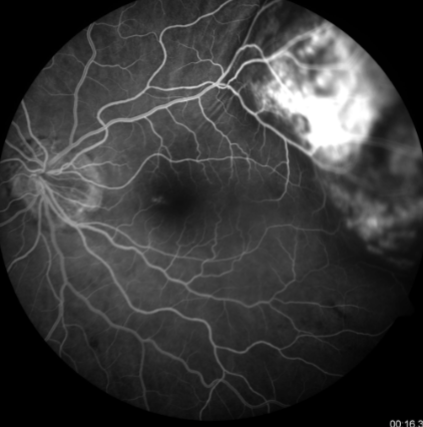
melanoma
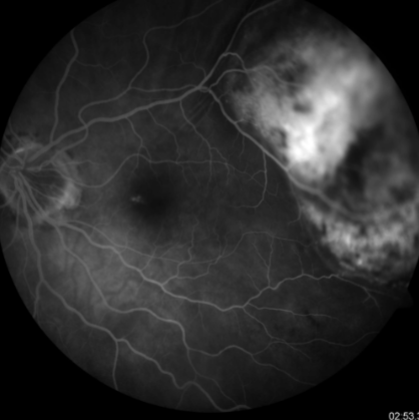
melanocytosis/uveal melanoma
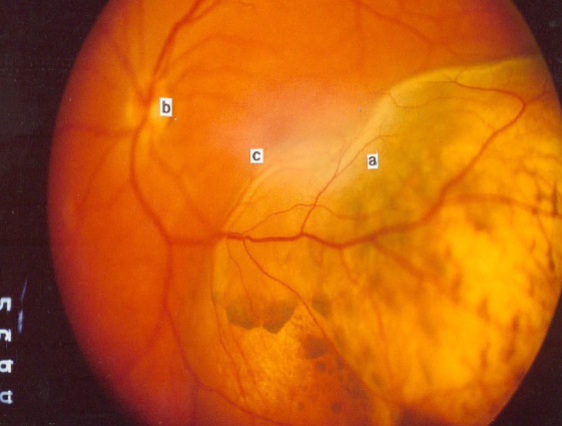
melanocytosis/uveal melanoma
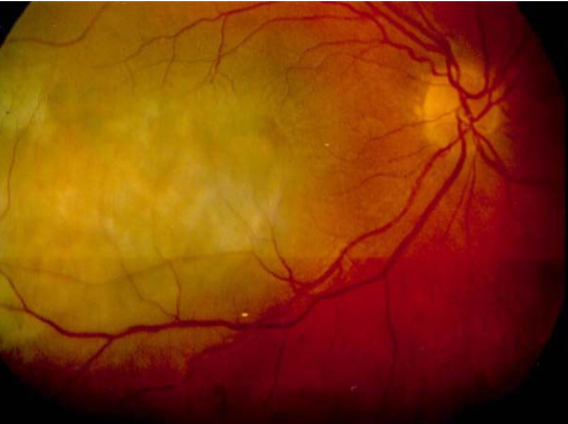
low
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
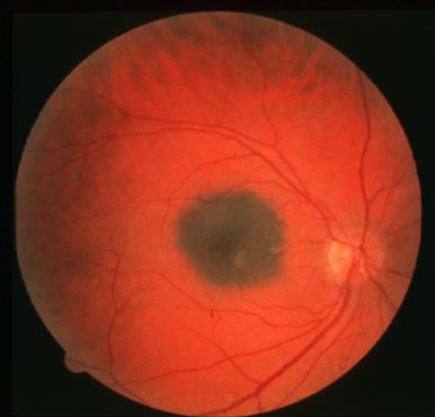
low
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
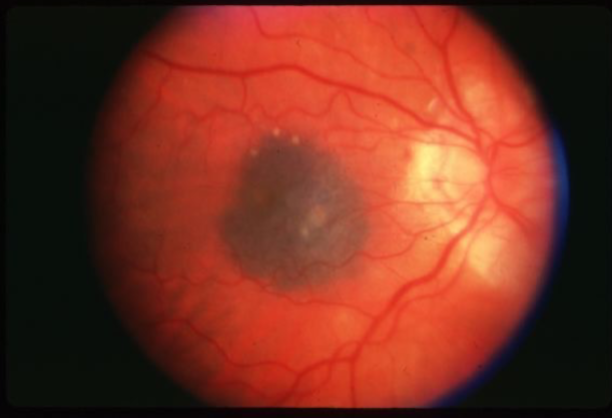
low
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
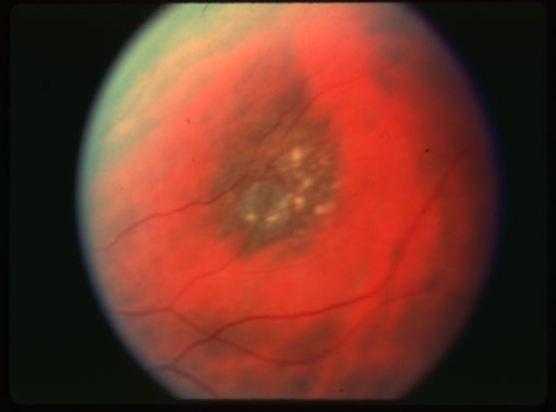
increased
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
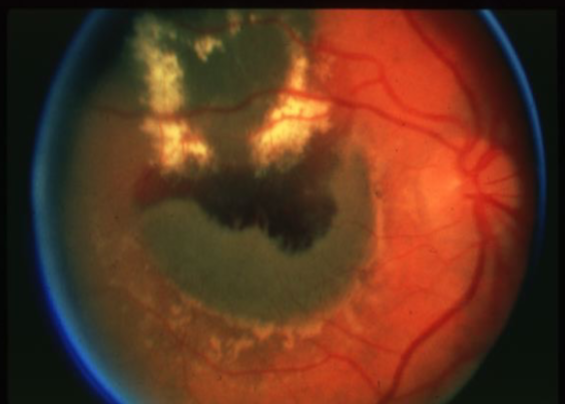
high
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
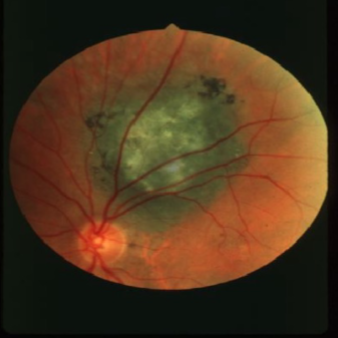
low
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
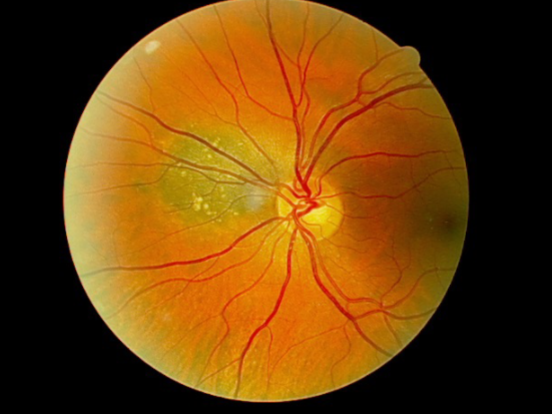
increased
what is the concern for this being melanoma?
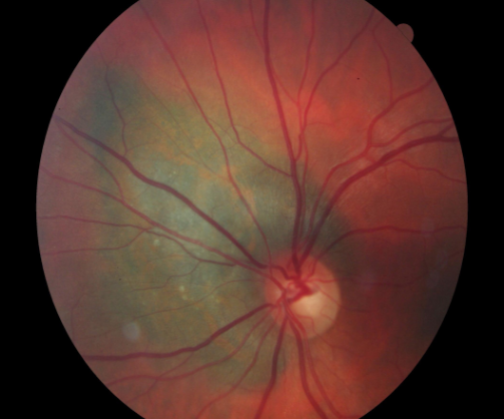
uveal lymphoma
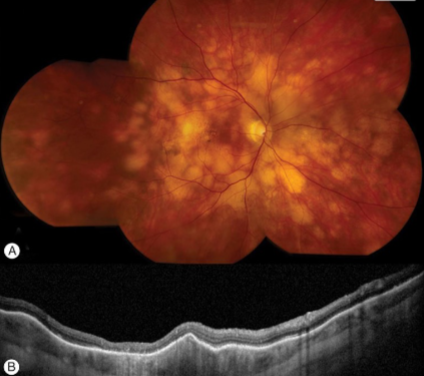
solitary choroidal hemangioma
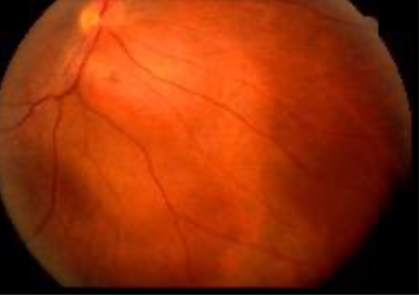
choroidal hemangioma
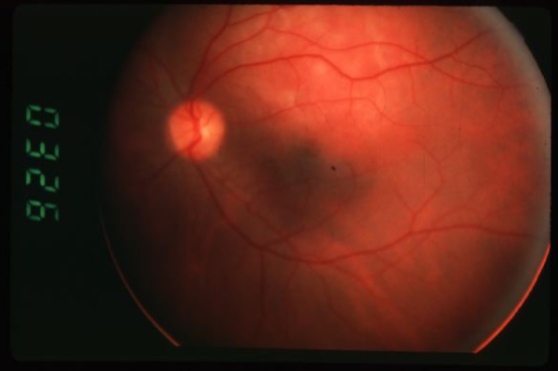
choroidal hemangioma
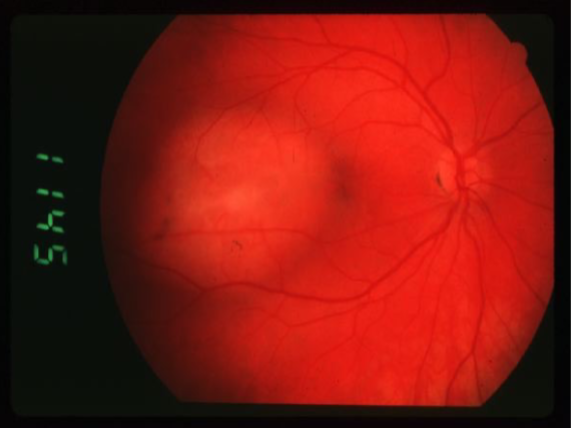
choroidal hemangioma
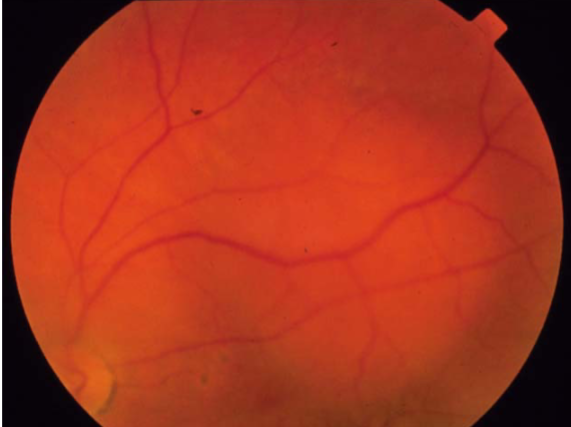
choroidal hemangioma
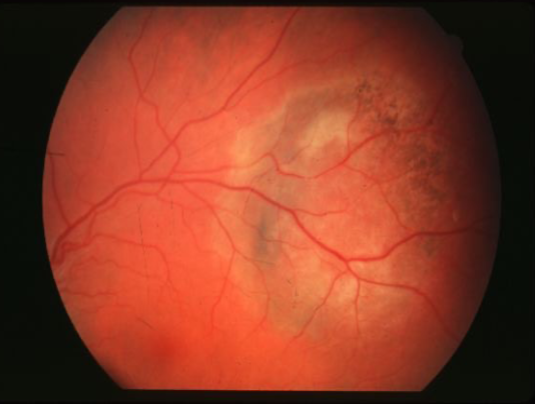
choroidal hemangioma
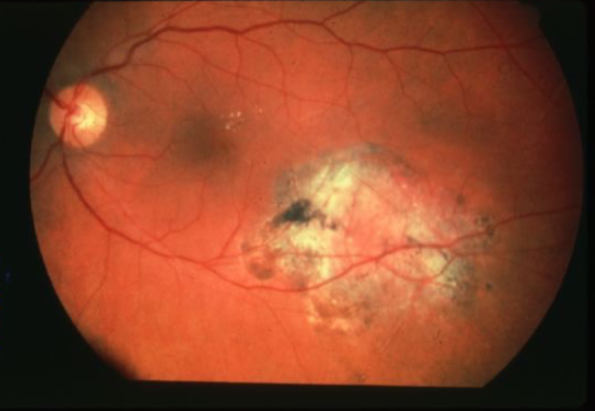
choroidal osteoma
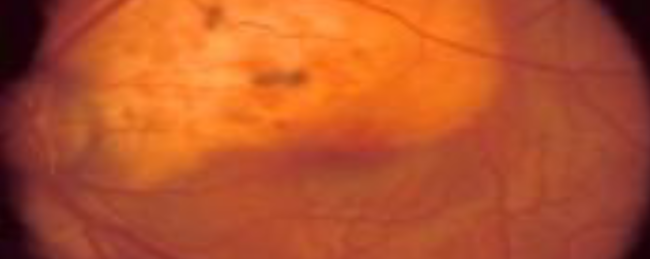
choroidal osteoma
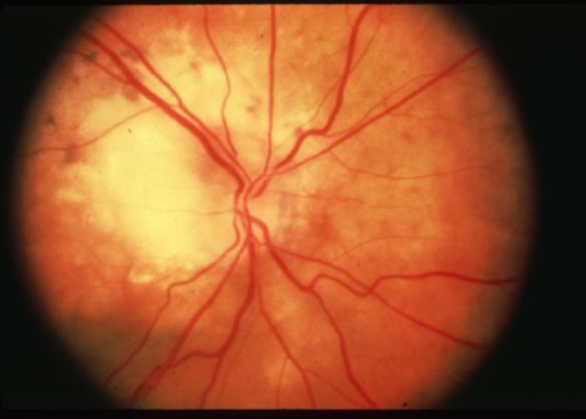
metastatic carcinoma
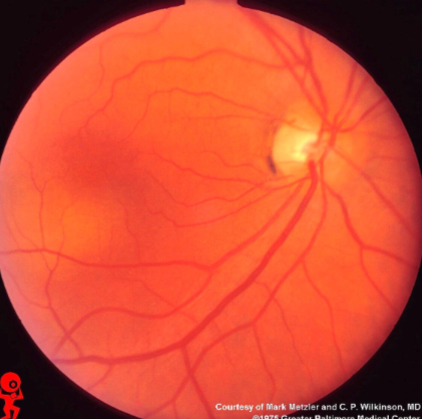
metastatic carcinoma
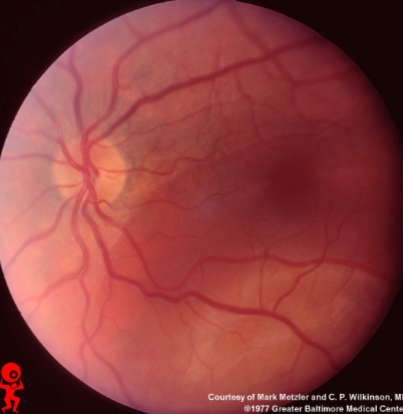
metastatic carcinoma
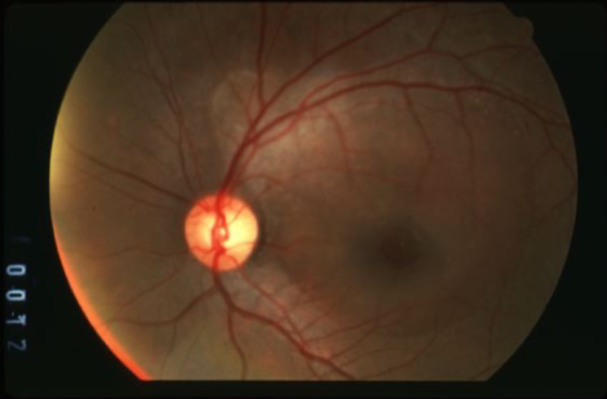
metastatic carcinoma
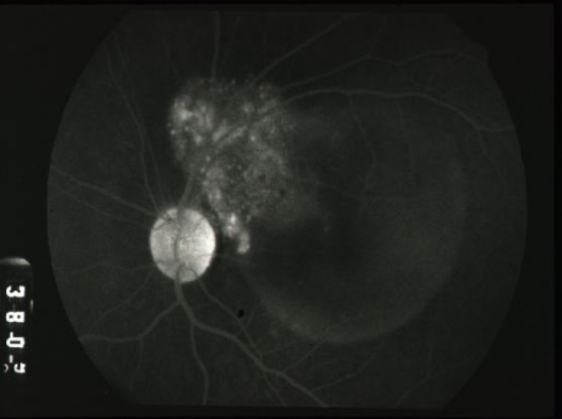
metastatic carcinoma
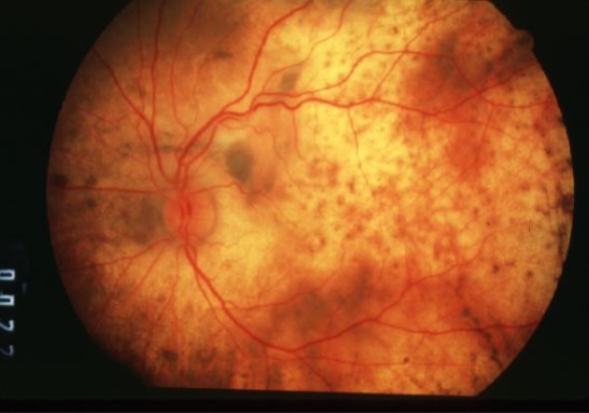
metastatic carcinoma
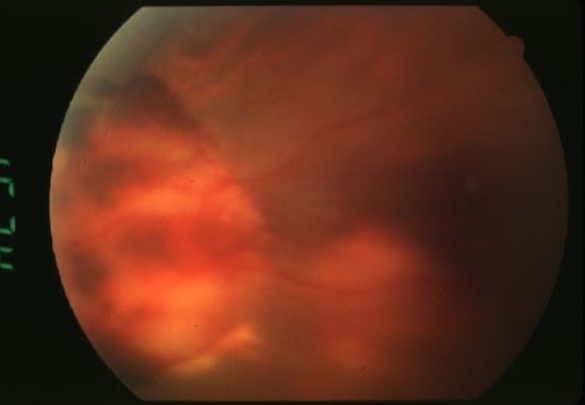
metastatic carcinoma
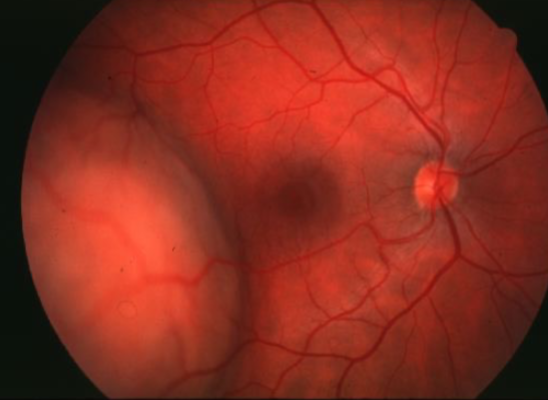
metastatic carcinoma
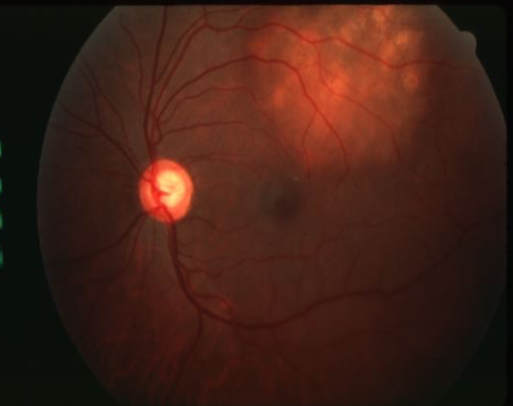
metastatic carcinoma
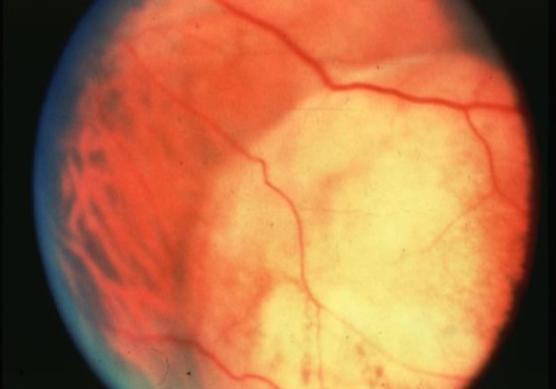
retinoblastoma
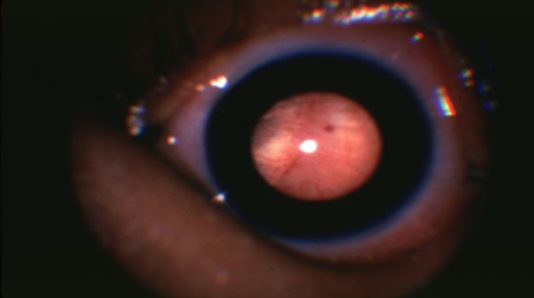
retinoblastoma
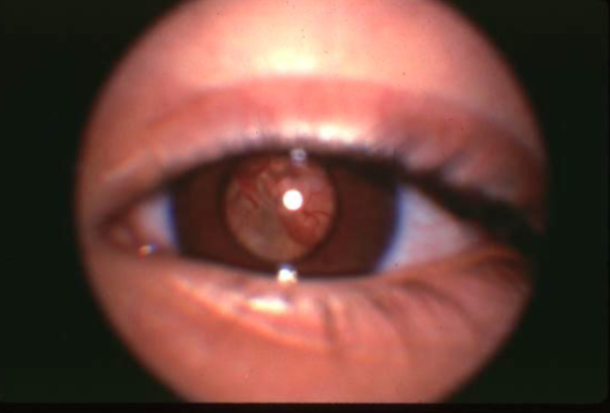
retinoblastoma