Electric Power Generation, Transmission and Distribution
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
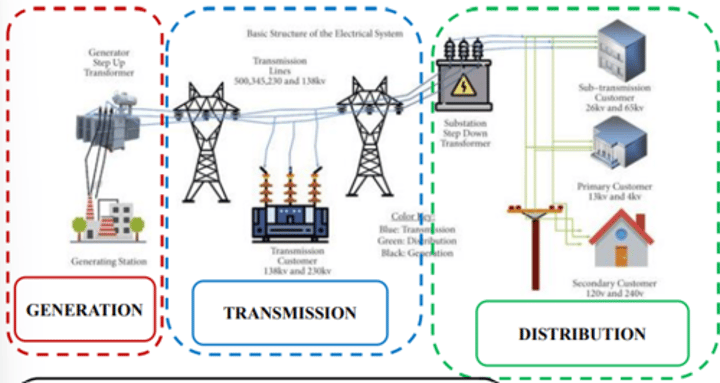
Three components of a electric power grid (Power System)
Generation, Transmission, and Distribution
4 key points of Generation ?
1) Takes place in power plants by driving alternators with turbines
2) primary energy sources are converted into ME power by alternators, which is converted into three-phase electric power.
3) done using an AC generator(s) or alternators.

Generation: What is the voltage range of electric power generators, and what is South Africa's typical voltage range ?
15 to 25KV and 22KV
Via what device are generator stations connected to the grid.
Generator Step Up Transformers
How is energy generated ?
2)
1) Driving the alternator with engine or turbines (called prime movers).
2) the rotor in a alternator is rotated by prime movers and electricity is generated in all three sets of stator conductors
Describe Alternators ?
1) 3 sets of conductors or wires on its non moving part (stator) and a rotating magnet (rotor)
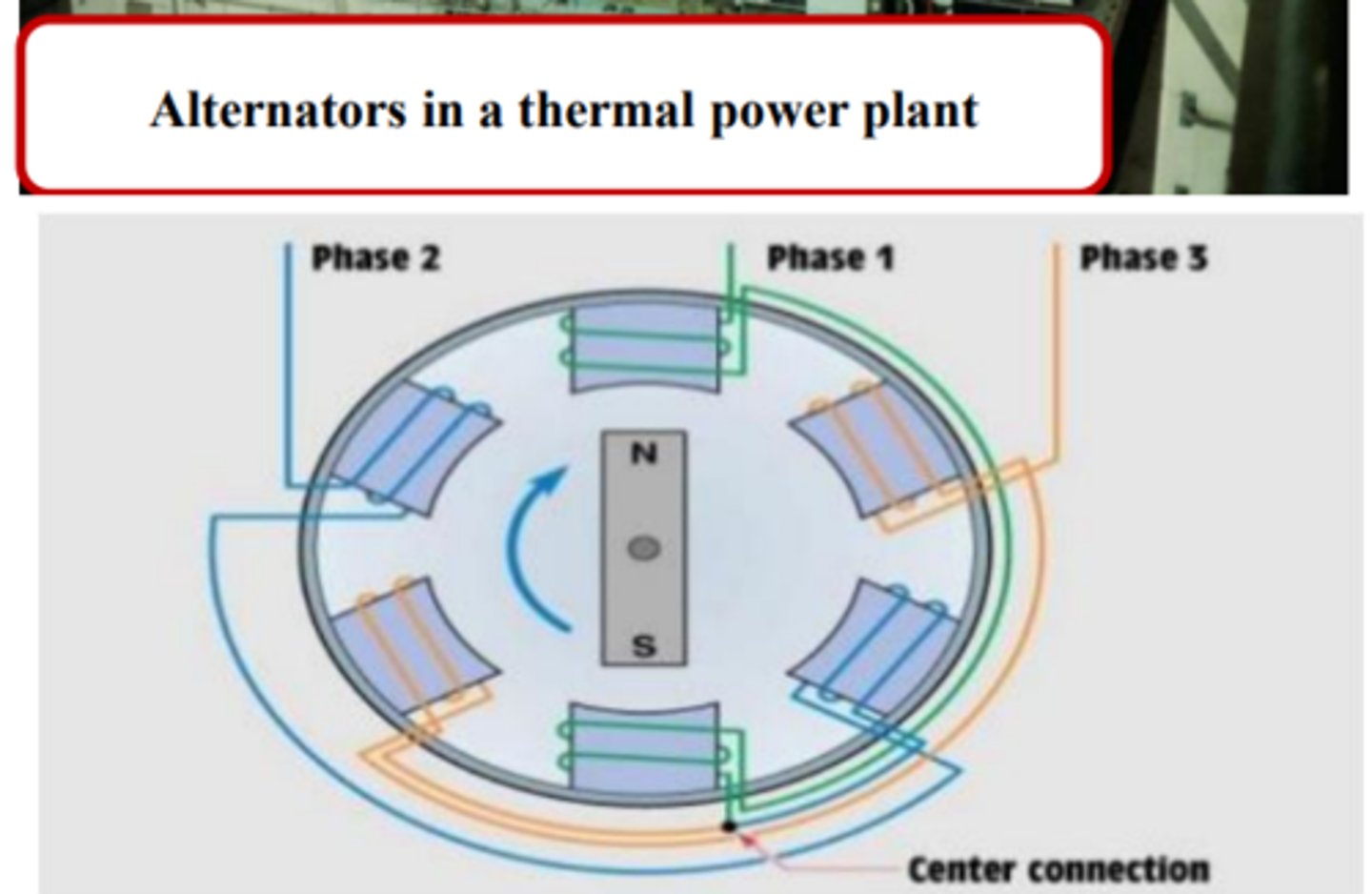
What are a set of conductors in a alternator called and 2) what are their individually named ?
1)phase conductor
2) Red/Yellow and Blue
1)Describe how an alternator generates electricity ?
give three points.
1)generates a balanced 3 phase sinusoidal alternating voltage.
2)exactly similiar waveforms
3) mutually apart by a time phase of 120 degrees
What are the 3 types of conventional power plants ?
Hydroelectric power plant ,Coal-fired power pant and Nuclear power plant
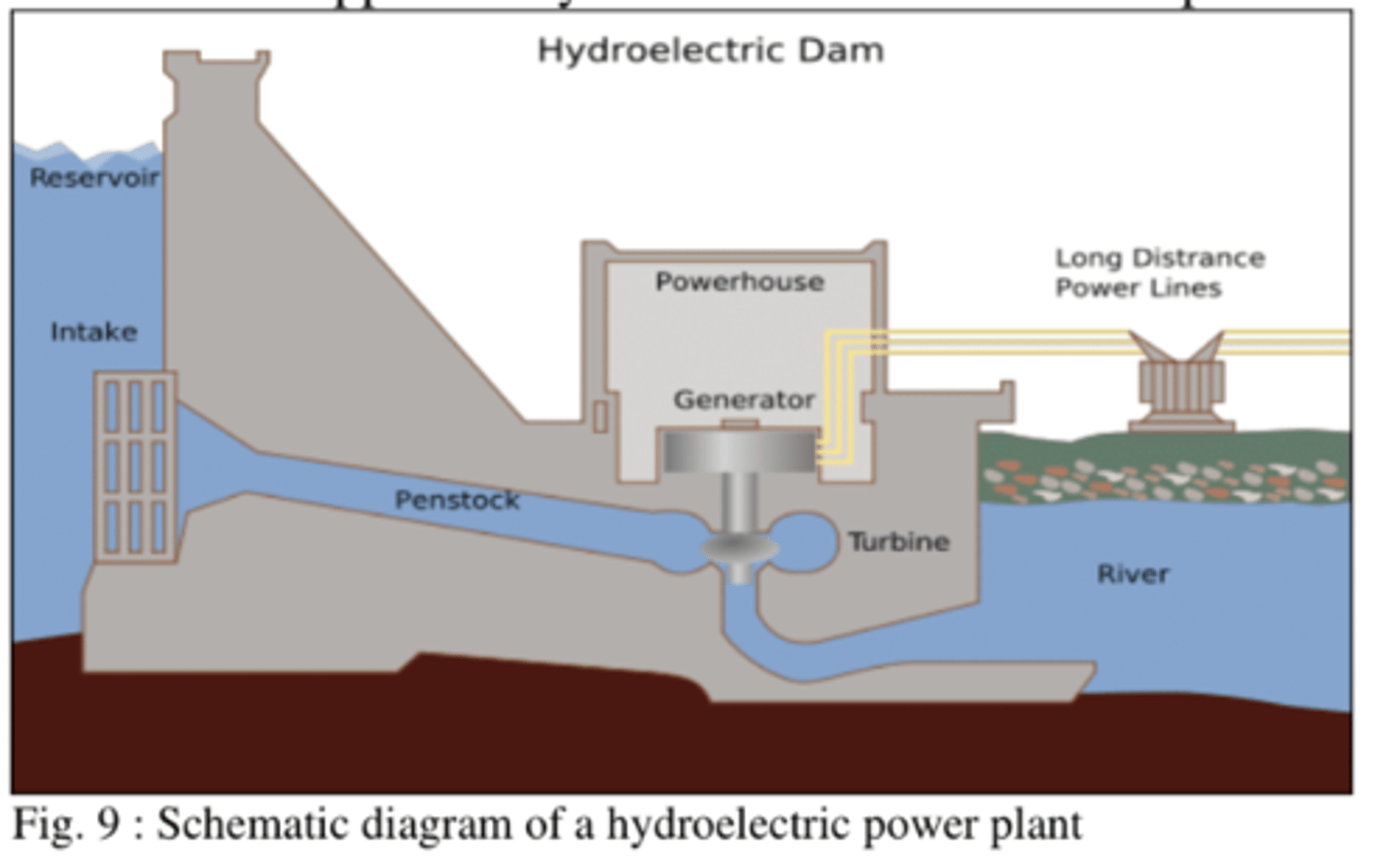
Explain how a Hydroelectric power plant generates electricity?
4 points.
1) potential energy of water at high levels is used to a turbine which is connected to a generator.
2) power determined by water volume and height of source
3) height difference (head)
4) water delivered through a pipe (penstock)
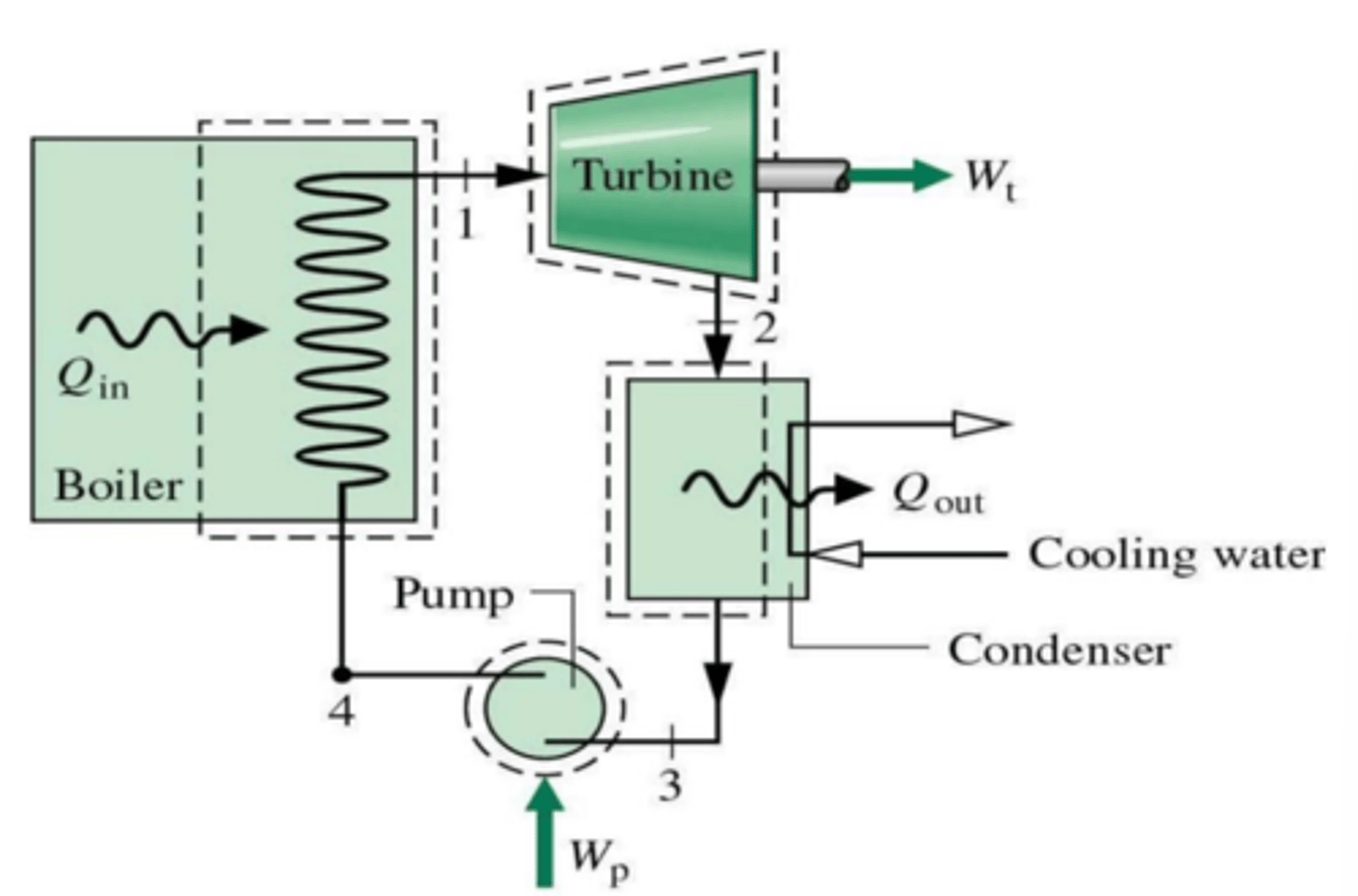
Explain how a Coal-fired power plant generates electricity?
5 points.
1) thermal power station (fossil fuel power station).
2) generates electricity by burning coal.
3) coal is burnt in a boiler to generate energy.
4) steam produced turns turbines (coupled to an alternator). HE converted to ME which is converted to EE in the alternator.
5) steam is condensed in the condenser back into water, then pumped back to the boiler.
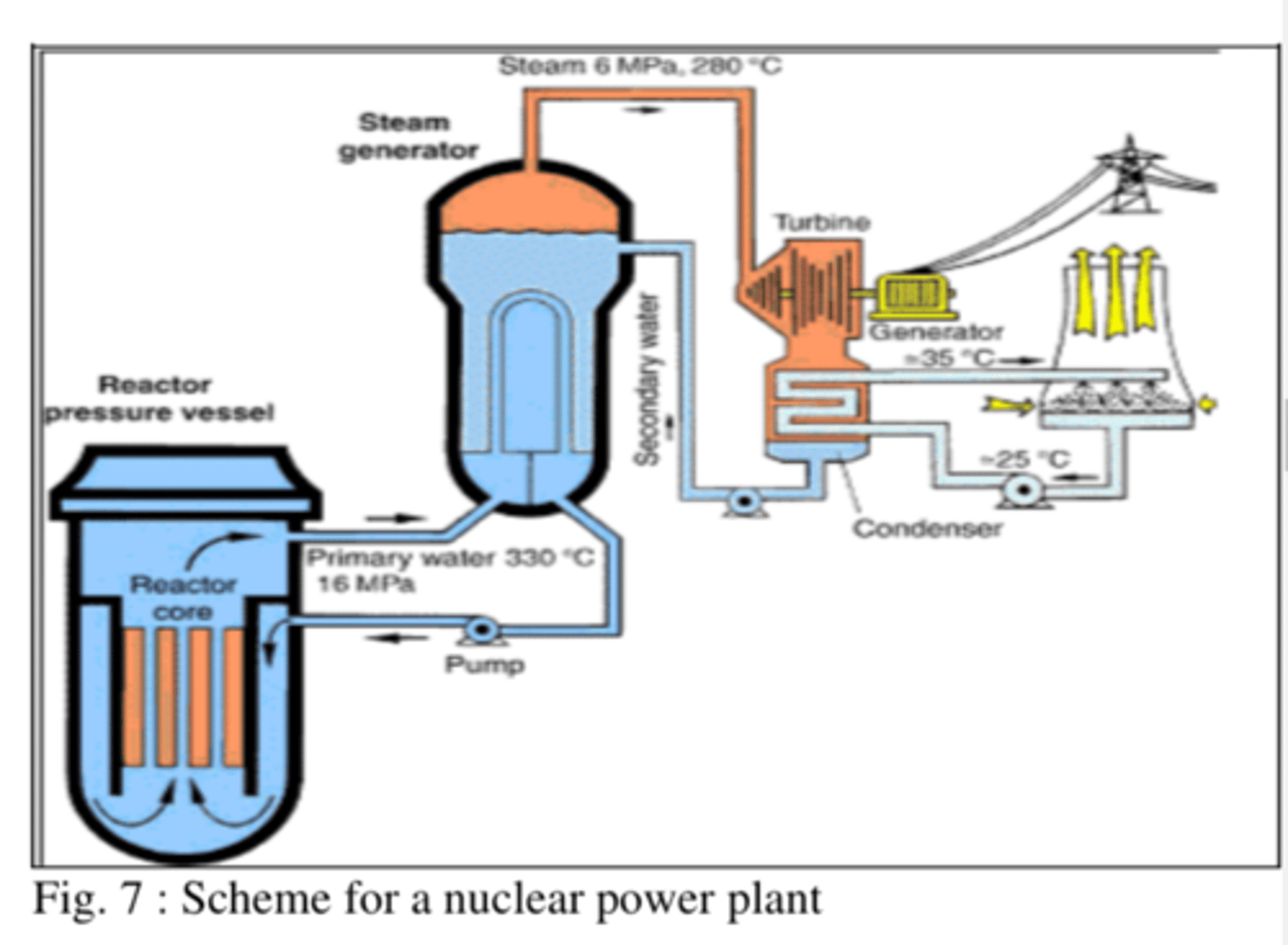
Explain how a Nuclear power plant generates electricity?
4 points.
1) produces energy using a nuclear fission process (splitting of uranium atoms)
2) Creates heat energy that is used to boil water and turn turbines.
2) The fuel is uranium
3) low carbon energy source
How does a coal fired power plant look
List the four air pollutants from coal and their characteristics.
1)Sulphur oxides (SOx) - oxidation of SO2 with NO2 creates H2SO4 (acid rain)
2)Nitrogen oxides(NOx) - NO2 emmitd through high temp combustion and is a toxic and brown gas with a sharp odour
3)Carbon oxides(CO) - CO is a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas. CO2 is a colorless, odorless, non toxic greenhouse gas .4)Particulate matter (PM) - fine particles of solid or liquid in the atmosphere. Linked to heart disease lung cancer.
5 Gases that contribute to greenhouse effect
water vapour (H20), methane (CH4), Carbon dioxide CO2, nitrous oxide(N2O), and ozone (O3)
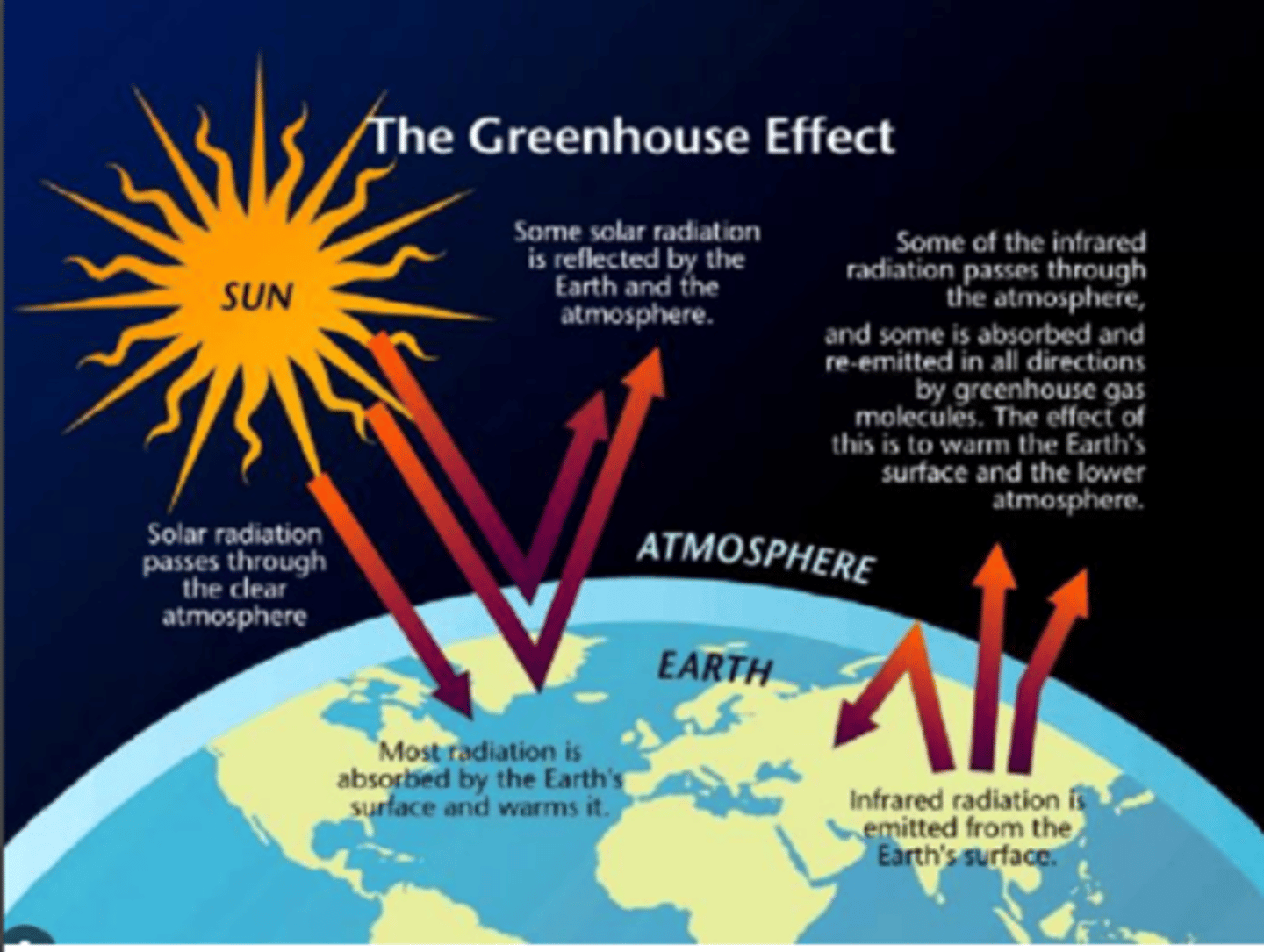
5 causes of greenhouse gases
1) Burning natural gas ,coal and oil
2)Farming practices and land-usage changes (increases CH4 and NO)
3) Factories
4)Deforestation (less absorbtion of CO2)
5)Population growth
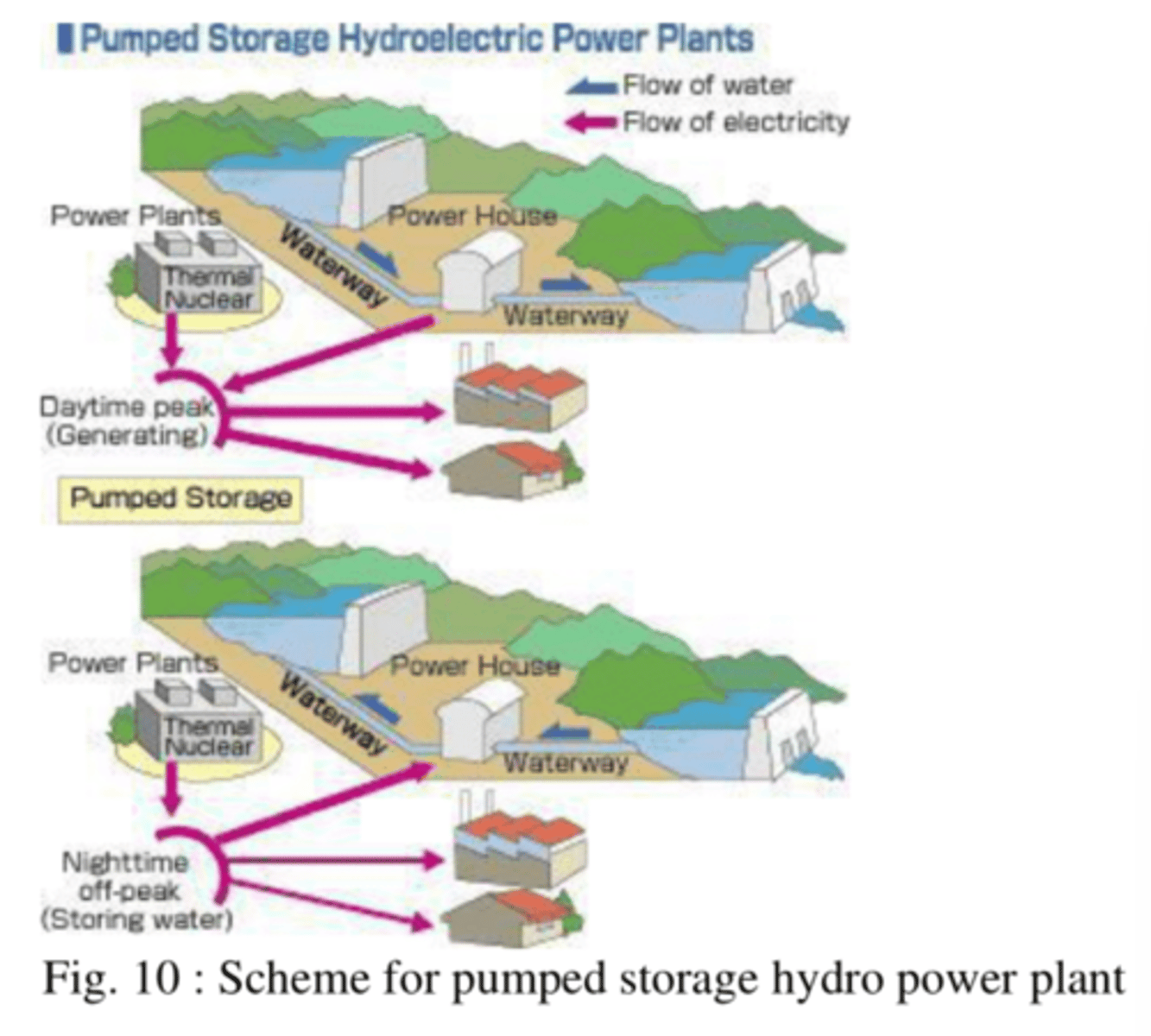
Pumped Storage Power Plants
Modes of operation and explanation
Generating mode - water flows from the upper reservoir to the lower reservoir and electricity energy is generated .
Pumping mode - water is pumped from lower reservoir to upper reservoir.
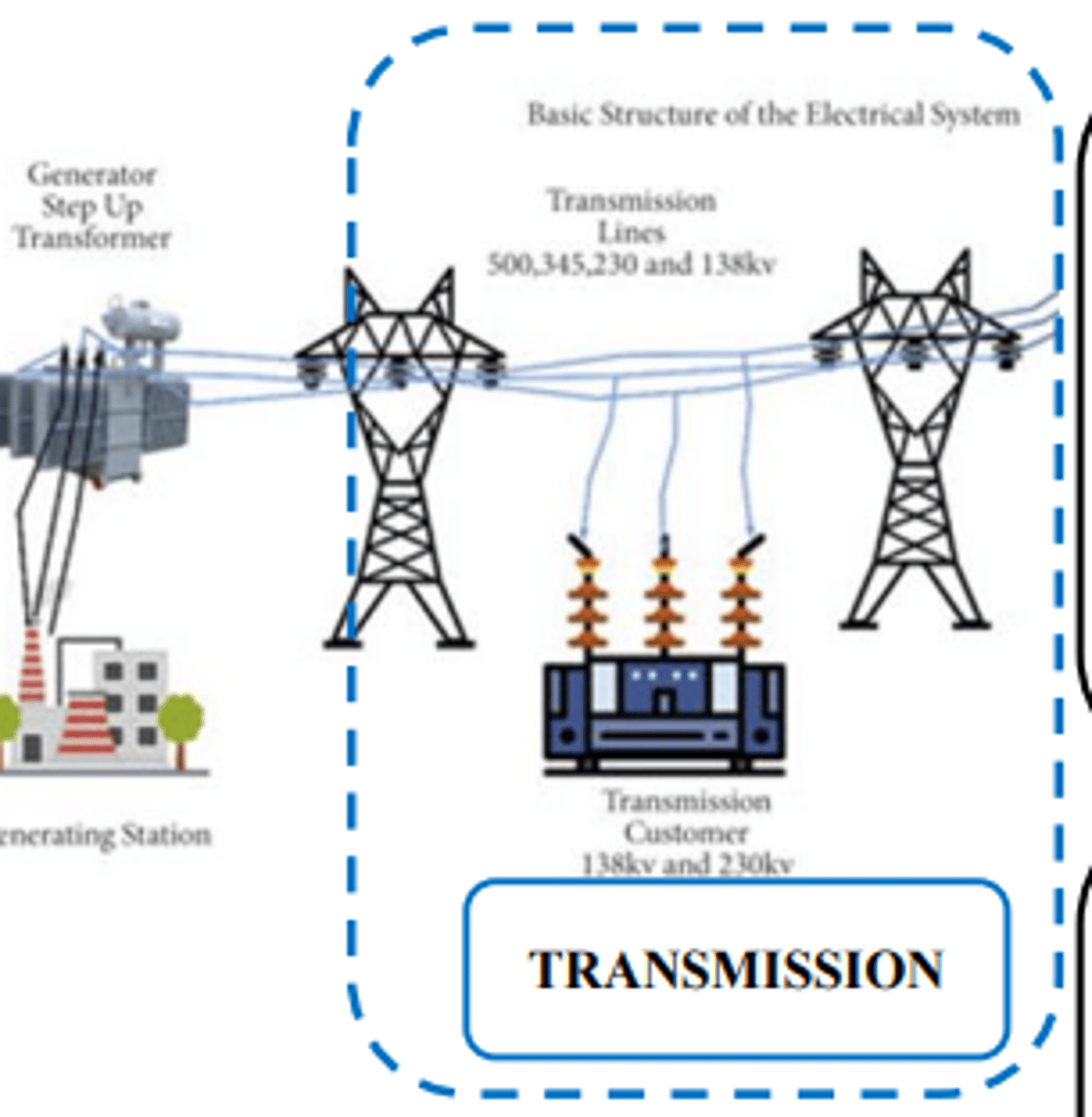
Transmission:
1) What is a power transmission system called
To what voltage is generated voltage step up via Generator step up transformers in south Africa and why.
1) grid
2) 765KV and for efficiency.
Larger V means we can have a smaller I for the same value of P. You need smaller wires and loose less energy lost to resistance in the form of heat .
what devices/systems converts AC to DC, DC to AC, and allows for transmission over long distance/connecting of AC systems.
1)Rectifier
2)Inverter
3)High Voltage Direct Systems.
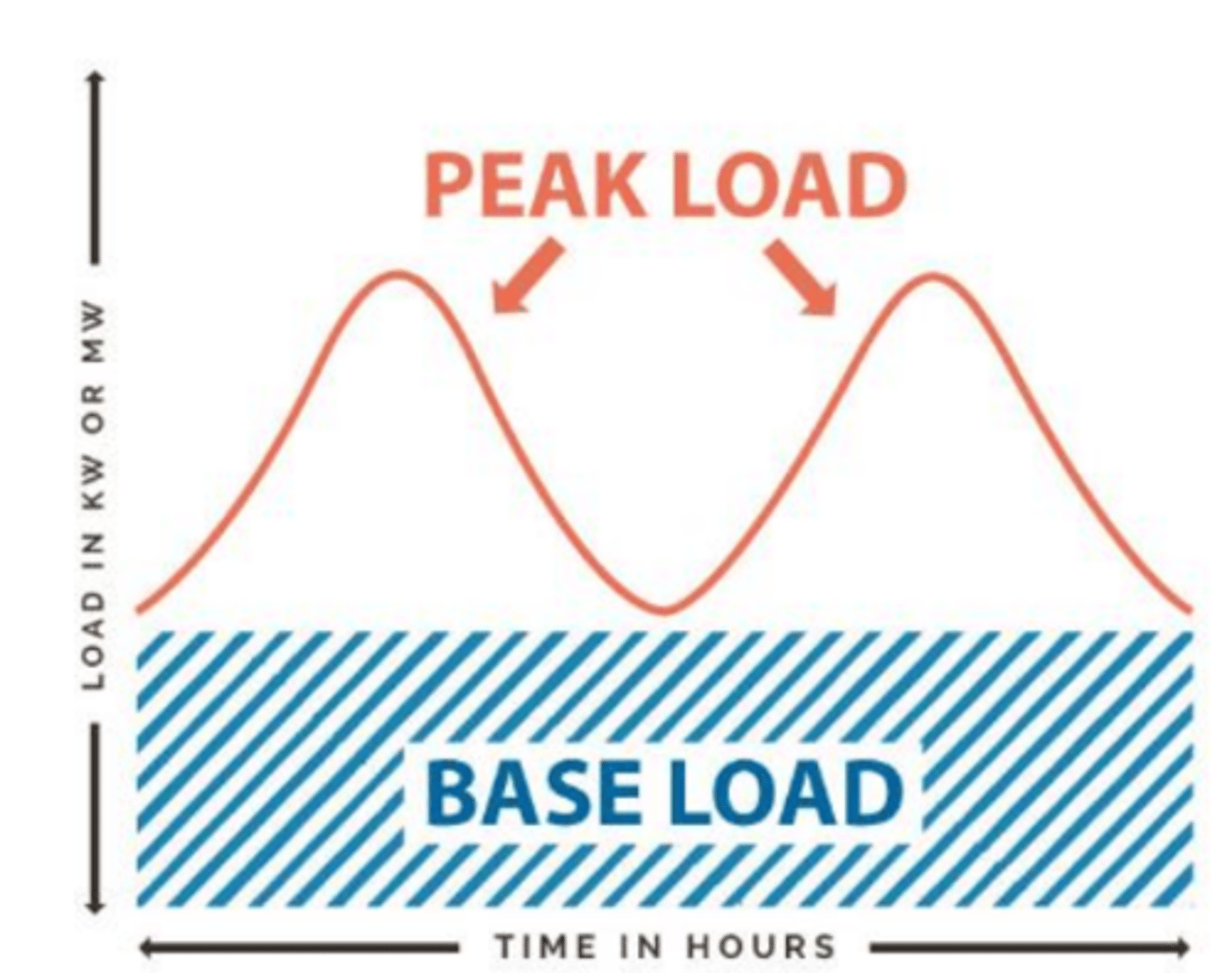
What is peak load.
peak load is the additional load that a power plant needs to supply over a constant base load
Distribution :
Features of a distribution network
list 5.
1) Medium voltage power lines
2)distribution substations
3) pole mounted transformers (where voltage is stepped down)
4) low voltage distribution wiring
electricity meters.
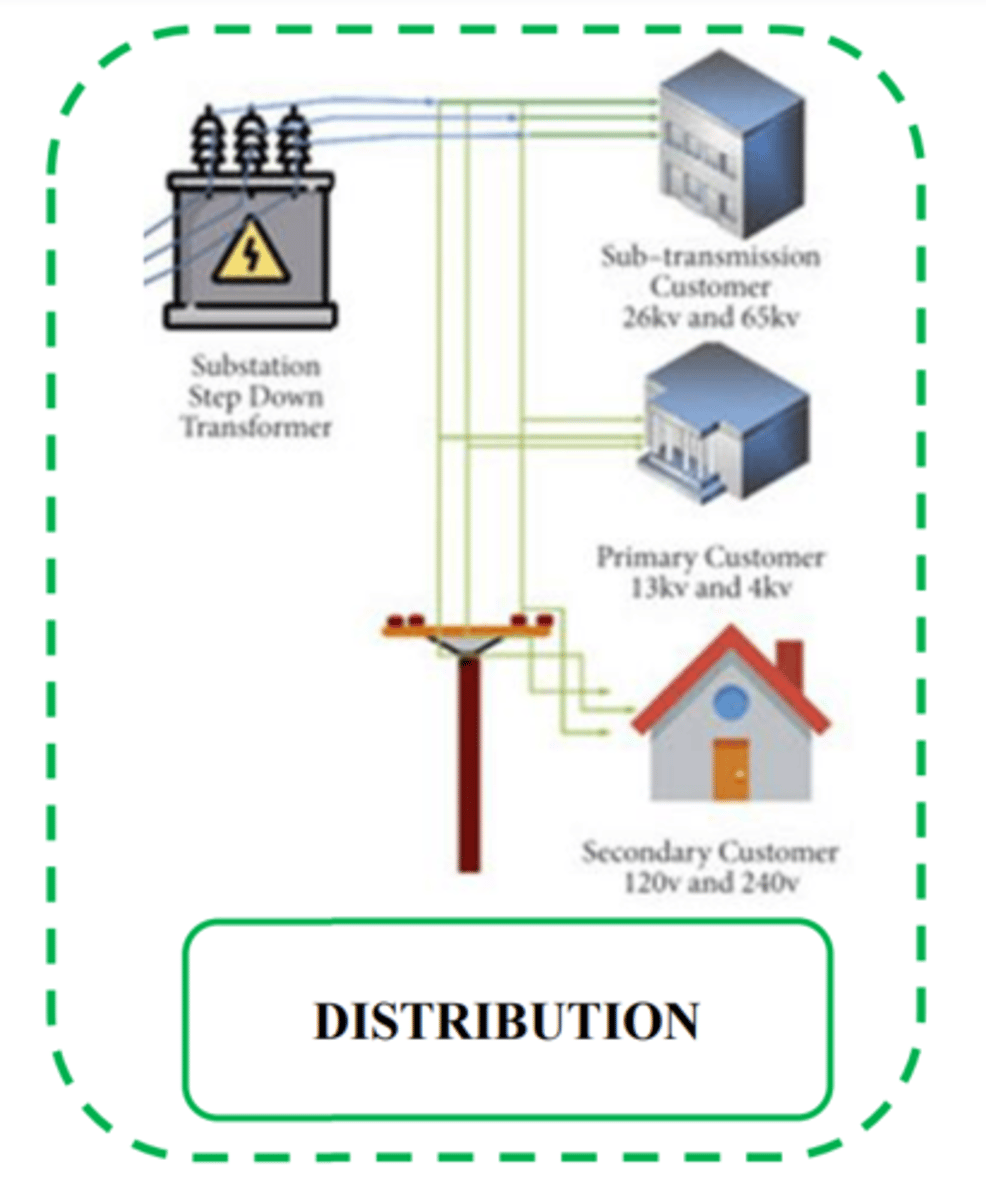
Define transmission
bulk transmission of electricity to the consumers
In what ways is electricity transmitted and what is its benefits. Also compare Cu and Al conductors.
3 points.
1) Overhead transmission lines (typical)
2) Underground cables (for densely populated areas/higher cost and maintenance )
3) Compared to Al, Cu is costlier and and is a better conductor.