Chemotherapy Exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Angiogenesis Inhibitor - Rationale
tumors require new blood vessels (angiogenesis) to provide oxygen and nutrients for supporting growth beyond certain sizes
blocking angiogenesis may block tumor growth
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a key role in tumor-induced angiogenesis
Bevacizumab (Avastin)
First-in-class VEGF inhibitor
Bevacizumab (Avastin) - Target
VEGF
monoclonal antibody against VEGF
VEGF is a ligand to VEGF receptor (VEGFR)
Bevacizumab (Avastin) - Mechanism
binds to VEGF (ligand)
prevents the ligands from binding to VEGFR
Blocks the activation of VEGFR
Bevacizumab (Avastin) - Clinical use
in combination with chemotherapy for multiple cancers
lung, colon, renal, ovarian, brain cancers
Modest effects
Ex: a median survival benefit of 4-5 months for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (in combination with chemotherapy)
Potential reasons for modest effects
hypoxic environment stimulates a compensatory VEGF production (feedback mechanism)
compromised blood supply causes a hypoxic (low-oxygen) environment
Hypoxic environment simulates the production of VEGF and other growth factors
Differential sensitivity of tumor blood vessels
Compromised vasculature reduces the efficiency of drug delivery to tumors
Bevacizumab (Avastin) - Side effects
hypertension, bleeding, impaired wound healing
VEGFR signaling affects nitric oxide synthesis (regulates blood pressure) and normal blood vessel survival and integrity
Bevacizumab (Avastin) - Resistance
increased level of VEGF
Upregulation of other pro-angiogenic factors (ex: FGF) and receptor signaling
potential combating strategies: combining with other receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Apoptosis inducer - Rationale
Some cancer cells are particularly reliant on elevated levels of anti-apoptotic proteins to survive
over-expression of anti-apoptotic proteins (ex: Bcl-2)
Alterations in cellular responses that increase reliance on anti-apoptotic proteins
inhibiting anti-apoptotic proteins could restore and promote programmed cell death in cancer cells
Venetoclax (Venclexta)
First-in-class BCL-2 inhibitor
Venetoclax (Venclexta) - Target
BCL-2
Bcl-2 is an anti-apoptotic protein
Bcl-2 sequesters pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax and Bak), preventing them from forming dimers and inducing apoptosis
High levels of Bcl-2 confer resistance to apoptosis
Venetoclax (Venclexta) - Mechanism
small molecular competitive inhibitor of Bcl-2
BH3-mimetic
BH3 is a protein domain that mediates the dimerization between anti- and pro-apoptotic proteins
Releases pro-apoptotic proteins (ex: Bax and Bak) from Bcl-2
Allows pro-apoptotic proteins to dimerize and induce apoptosis
Venetoclax (Venclexta) - Clinical Use
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
CLL patients have a high level of Bcl-2
AML (acute myeloid leukemia) in combination with chemotherapy
Bcl-2 is linked to chemotherapy resistance in AML
Venetoclax (Venclexta) - Side Effects
tumor lysis syndrome (TLS)
caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells
can lead to acute electrolyte and metabolic imbalances
potential kidney failure (requires gradual dosing and close monitoring)
Patients with impaired kidney function are more susceptible
Low white blood cell count (Neutropenia)
due to inhibiting Bcl-2 in neutrophil precursors
neutrophile precursors are very sensitive to Bcl-2 level
increased risk of infection
PARP inhibitor - rationale
poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARPs) are involved in detecting and signaling cellular responses to single-strand DNA break (SSB)
Cancer cells with other DNA repair defects are more reliant on PARP1 to maintain DNA integrity and cell viability
Olaparib (Lynparza) - Target
PARP1
Poly ADP-ribose polymerase 1
PARP1 facilitates DNA repair (base excision repair, BER)
Olaparib (Lynparza) - Mechanism
small molecular inhibitor of PARP1
Failure of BER causes an accumulation of SSB (single-strand break) and traps PARP1 on DNA
Promotes DSB (double-strand break) during DNA replication
Lethal to cancer cells with defects in DSB repair (ex: BRCA1/2 mutations) - unrepaired DSB is lethal to cells
Synthetic Lethality
condition 1: PARP1 inhibition (PARP1 “defects”) - promotes DSB
Condition 2: DSB repair defects - due to existing mutations (BRACA1/2)
results → Accumulation of too many DBS that become lethal to cells
Olaparib (Lynparza) - Clinical Use
ovarian and breast cancers with BRCA mutations
BRCA genes facilitate DSB repair
Olaparib (Lynparza) - Side effect
Myelosuppression (suppression of bone marrow where blood cells are produced)
hematopoietic progenitors (blood cell precursors) in bone marrow are more sensitive to DSB
Low white blood cell counts (increased risk of infection)
Low red blood cell counts (anemia)
patients with underlying bone marrow defects are more susceptible
Olaparib (Lynparza) - Resistance
PARP1 mutations that diminish inhibitor binding
Restoration of other defective DNA repair mechanisms
reversion mutations on BRCA (additional mutations in BRCA that restore function)
Amplification of wide-type or hypomorphic (partial loss of normal gene function) BRCA
Becoming less reliant on PARP1 for DNA repair
Development of Targeted Therapy
identification of specific molecular targets and vulnerabilities in the cancer cells
Development of effective therapeutic agents against the candidate targets
biomarkers for selecting patient populations
toxicity limits treatment doses and duration
diverse therapeutic resistant mechanisms
Enabling the acquisition of various cancer hallmarks
avoiding immune destruction
tumor-promoting inflammation
Tumor-Promoting Inflammation
Inflammation is a normal biological response to injury or infection
Chronic and deregulated inflammation can promote cancer
Inflammation is a normal biological response to injury or infection
Defenses against infections and promotes repair
Mediated by:
immune cells
Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes (T-cells, B-cells, Natural Killer cells)
Chemicals released by immune cells, stromal cells, and/or cancer cells
cytokines, chemokines, interleukins
regulate immune responses (ex: recruit immune cells, activate immune cells)
Chronic and deregulated inflammation can promote cancer
Cytokines, chemokines, interleukins can support various cancer hallmarks
Simplified Hematopoietic Lineage
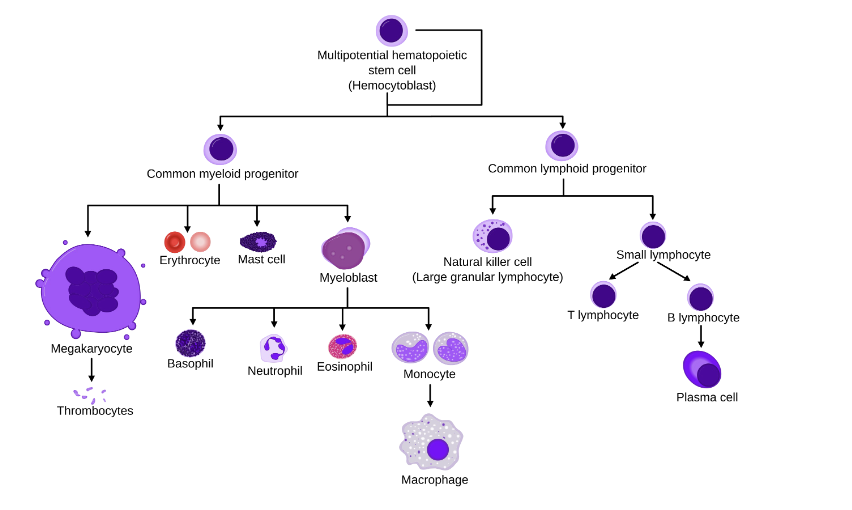
Inflammatory microenvironment - Cancer promoting effects
Mediated by chemokines, cytokines, and interleukins
Angiogenesis
Proliferation
Metastasis
Therapy resistance (promote survival)
Inflammatory Microenvironment - Immune cell types
tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)
secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines
promote growth and angiogenesis
Nutrophils
release reactive oxygen species and proteases
Promotes invasion and metastasis
Avoiding immune destruction
Immune cells can recognize and destroy/control cancer cells
How do immune cells recognize cancer cells?
mutant antigens: somatic mutant proteins can be processed and presented as neoantigens
“Missing-self”: insufficient levels of MHC-I (major histocompatibility complex class I) trigger the “missing-self” signal
Bound Antibody: Cancer cells bound by antibodies can be recognized
How do cancer cells evade immune surveillance
suppress antigen presentation
Suppress immune cell activation
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment
Cancer immunotherapy
harness the immune system capability to recognize and target cancer
Major immune cell types that directly target cancer cells
cytotoxic (CD8+) T lymphocytes (T cells)
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Cytotoxic (CD8+) T lymphocytes (T cells)
adaptive immune system
recognize neoantigens on cancer cells through T cell receptor (TCR)
Directly kill cancer cells
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
innate immune system
recognize cancer cells through “missing-self” signal and bound antibodies
directly kill cancer cells
Cancer immunotherapy
Immunomodulator
Immune checkpoint modulator
Adoptive Immunotherapy
Emerging areas in Immunotherapy
Example of an Immunomodulator
Aldesleukin
Examples of a Immune Checkpoint Modulator
Ililimumab
Pembrolizumab
Examples of Adoptive Immunotherapy
Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-cel)
Aldesleukin (Proleukin)
Recombinant human interleukin 2 (IL2) analog
modified human IL2
Aldesleukin (Proleukin) - Mechanism
IL-2 is an interleukin that stimulates the growth and differentiation of T cells
Stimulates the immune system
Aldesleukin (Proleukin) - Clinical use
metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Aldesleukin (Proleukin) - Side Effects
Allergic reactions
rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing
Immune check point modulators
a therapeutic strategy based on modulating the immune checkpoint to promote immune responses against cancer cells
Immune checkpoint
limits the strength and duration of immune responses
prevents immune system hyperactivation
exploited by cancer cells to suppress immune cell activation
T-cell Response to Cancer Cells
T cells are major mediators of the immune response against cancer cells
T-cell activation:
antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (ex: dendritic cells) capture tumor antigens. → presentation
APCs present antigens to and activate naive T cells in the lymphatic tissues → Priming
Cytotoxic T cells recognize antigens on cancer calls and exert cytotoxic effects → Effector
T-cell Activation
activation of Naive T cells promotes maturation (Priming)
activation of mature cytotoxic T cells triggers clonal expansion and cytotoxic effect (Effector)
Mediated by stimulatory and inhibitor signals
stimulatory receptor signals
T cell receptors (TCR): how T cells recognize antigens
CD28
Inhibitory receptor signals (Immune checkpoints)
CTLA-4
PD-1
Activation promotes survival, clonal expansion, differentiation/maturation (naive T cells), and cytotoxic function (cytotoxic T cells)
Immune Checkpoint Signals - Negatively Regulate Immune Responses
CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4)
PD-1 (Programmed Cell Death Protein 1)
CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4)
Transmembrane glycoproteins are primarily on naive T cells
Binding to ligand on antigen presenting cells (APC) negatively regulates naive T cell activation
Compete with CD28 (a stimulatory receptor) for the same ligands (B7)
PD-1 (Programmed cell Death Protein 1)
Transmembrane glycoproteins are primarily found on mature T cells
Binding to ligands negatively regulates T cell activation
The ligand PD-1 or PD-L2 is expressed on some tumor cells, antigen-presenting cells (APC), and other immune cells (ex: tumor-associated macrophages)
Negatively regulate T-cell activation
checkpoint signal
CTLA-4
PD-1
T-cell Activation Phase
Priming
Effector
Tissue Location
Lymphoid Tissue
Tumor Microenvironment
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Block the immune checkpoint signals
Promote T cell activation
Ipilimumab
A monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4
Ipilimumab - Mechanism
blocks the CTLA-4 inhibitory signal
binds to CTLA-4 and blocks the binding of B7 (ligand)
Indirectly promotes the CD28 stimulatory signal
Available B7 can bind to CD28
Promote naive T-cell activation at the priming phase in lymphoid tissues
Pembrolizumab
A monocolonal antibody against PD-1
Pembrolizumab - Mechanism
Blocks the inhibitory PD-1 signaling
binds to PD-1 and prevents the binding of PD-L1 or PD-L2 (ligands)
PD-L1 and PD-L2 are expressed on some cancer cells and other cells in the tumor microenvironment
Promotes T-cell activation primarily at the effector phase in the tumor microenvironment (TME)
Pembrolizumab - Clinical Use
unresectable and metastatic melanoma (Iplilimumab and Pembrolizumab)
Other advanced stage cancers (Pembrolizumab)
Micro satellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) cancers (High mutation loads)
Pembrolizumab - Side Effects
Autoimmune-like symptoms
Damages in normal tissues and organs
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Other Immune checkpoints as potential therapeutic targets
LAG-3 (Lymphocyte activation Gene-3)
TIM-3 (T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain caontaining-3)
TIGIT (T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain)
VISTA (V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation)
BTLA (B and T lymphocyte Attenuator)
Adoptive Immunotherapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell (CAR-T cells)
Tisagenlecleucel
Tisagenlecleucel
Engineer T cells from patients to recognize and attack B-cell malignancies in the same patient
Some B cell malignancies have increased levels of CD19
Tisagenlecleucel - Procedures
Isolate T cells from patients
Genetically engineer the T cells to express a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) that recognizes CD19
Expand and enrich these engineered T-cell population
Infuse into the same patients (autologous)
Tisa-cel - clinical use
relapsed B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
Tisa-cel - Side effects
Cytokine-release syndrome (CRS)
massive release of cytokines due to T cell activation
Rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, and trouble breathing
Risk of developing T-cell malignancies
Limitations of CAR-T Cell Therapy
T-cell exhaustion
Heterogenous tumor populations
Challenges in solid tumors
complex personalized procedures
Severe cytokine-released syndrome (CRS)
Advances in Chimeric Antigen Receptor Design
Co-stimulatory signaling domains in newer generations of CAR
Improve T cells expansion and survival
New CAR designs
Bispecific CAR
bind multiple antigens
Diminish antigen escape
Tunable and regulate CAR
Kill switch in the event of severe toxicity
Reversible switch to prevent T cell exhaustion
T Cell Receptor (TCR)-like CAR
CAR: Surface protein, MHC-independent
TCR (native T cells): Processed intracellular proteins, MHC-dependent
Emerging areas in Immunotherapy
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
Lifileucel
Immune cell engager
Blinatumomab
Natura killer (NK) Cells
Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes
Lifileucel
Lifileucel - Procedure
isolate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) from a patient’s tumor
Expand the TIL populations in facilities
Infuse back to the same patient (autologous)
No cell engineering (distinct from CAR-T)
First cellular therapy to be approved for a solid tumor (Melanoma)
Blinatumomab
Bispecific T-cell engager
Blinatumomab - Mechanism
Bispecific antibody engaging T cells to cancer cells
CD19-directed CD3 T-cell engager
CD3 on T cells
CD19 on malignant B cells
Blinatumomab - clinical use
CD19-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Blinatumomab - side effects
Cytokine Release Syndrone (CRS)
natural Killer (NK) cells
Recognize cancer cells by:
“missing-self” signals
imbalance between stimulatory and inhibitory signals
insufficient levels of MHC-I on cancer cells leads to lowered inhibitory signals and activation of NK cells
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Bound antibodies on cancer cells are recognized by NK cells through a surface receptor CD16
Harnessing NK Cells to Target Cancers - Immune cell engagers
Bispecific antibody (NK cell engagers)
CD19 on NK cells
Antigens on cancer cells
CAR-NK
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
similar concepts to CAR-T but distinct design
Harnessing NK Cells to Target Cancers - Advantages
allogenic
do not require cells from the same patient
able to utilize NK cells from donors
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is less common
NK cells have a lower cytokine response than T cells
Harnessing NK Cells to Target Cancers - Limitations
Shorter lifespan (1-2 weeks)
CAR-T can last for months to years
Tumor infiltration and suppressive tumor environment (similar to CAR-T)
Personalized (precision) Medicine
a way health care providers can offer and plan specific care for their patients, based on genes, proteins, and other substances in a person’s body
With regards to cancer, precision medicine most often means looking at how changes in certain genes or proteins in a person’s cancer cells might affect their care, such as their treatment options
Personalized (precision) medicine - ultimate goal
to shift healthcare from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more individualized, precise, and effective method of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, improving patient outcomes and reducing adverse effects
Diagnostic techniques in personalized medicine
Major techniques in cancer diagnosis
DNA/RNA sequencing
Proteomics
Immuno-profiling
Imaging
DNA sequencing in cancer detection - Tumor profiling
Involves tumor biopsy for either targeted or whole genome sequencing
categorize mutations enriched in specific cancer types and potentially primary tumor sites vs. metastatic sites
Pharmacogenomics in cancer therapy
Pharmacogenomics is important to understand an individual’s genes affect how they respond to specific medications, which may vary cancer treatment outcomes
Development of patient-derived models for preclinical studies
Patient-derived cancer methods
Patient tumor biopsy can be used to generate ex vivo cancer models
cell lines - 2D in vitro culture
Tumor organoids - 3D in vitro culture
Tumor xenografts - typically in an immunocompromised mouse
used for genome sequencing to biomarker analyses
Patient-specific cells to determine new drug or drug combination for treatment options
Minimal invasive method for cancer detection and therapeutic monitoring - liquid biopsy
Typically, blood samples
minimally invasive
can determine appropriate treatment
monitor cancer development
track response to treatment
assess rick for cancer progression/resistance
Imaging techniques in cancer detection - Antibody-radioisotope labeling
used to detect biomarker-positive cancer sites
What is the main goal of clinical trials?
Determine the safety and efficacy of the investigational new drug (IND)
Phase 1 - Clinical Trial
Safety
is the investigational medication/treatment safe?
are there side effects
how does it affect or move through the body
is it safe to use at the same time as other medications
Who is in it
small group of healthy people, generally less than 100
Phase 2 - Clinical Trial
Efficacy
Is the investigational medication/treatment effective in treating the targeted condition?
Does the treatment relieve, reverse or stop the progression of the condition?
How safe is it?
What is the most effective dosage?
Who’s in it?
generally 100-300 people with the exact condition being studied
Phase 3 - Clinical Trial
Confirmation
How does the investigational medication/treatment compare to the standard treatment for the condition?
more effective, less effective, the same?
Longer-term adverse effects?
How does it affect quality of life, or survival?
How might it be used along with existing treatments?
Who’s in it?
Often 300-3,000 people with the exact condition being studied
Phase 4 - Clinical Trial (post-FDA approval)
Follow Up
After the investigational medication/treatment is approved, how does it work for other patients with the condition?
More safety/efficacy information is gathered
are there long-term benefits?
are there long-term risks?
Who’s in it?
often several thousand people who have been prescribed the investigational medication
Basket Trials
prospective clinical trials that test one or more targeted interventions across multiple types of diseases
Umbrella Trials
Prospective clinical trials that test multiple targeted interventions for a single disease based on predictive biomarkers or other predictive patient risk factors