Pharm week 9-antibacterials
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
All antimicrobial drugs affect 1 or more of the ____ MOA
5
Antimicrobial drugs most
Achieve the minimum effective concentration (MEC)
Sensitive bacteria are
able to be killed by antibiotics
Resistant bacteria are
not able to be killed
Types of antibiotic resistance
Inherent (natural) & Acquired (After exposure)
The 3 causes of antibiotic resistance
1.Miuse/overdose
2. Incomplete treatment
3. HIAs (Health-associated infections)
Major resistant pathogens
MRSA, VREF/VRSA
3 Preventions for antibiotic resistance
1. Pt education
2. Correct use
3. C & S (culture and sensitivity) testing
Antibacterial general AR
Mild allergic reaction, severe allergy, superinfection, and organ toxicity.
Signs of mild allergic reaction to Antibacterials
rash, pruritus, and hives
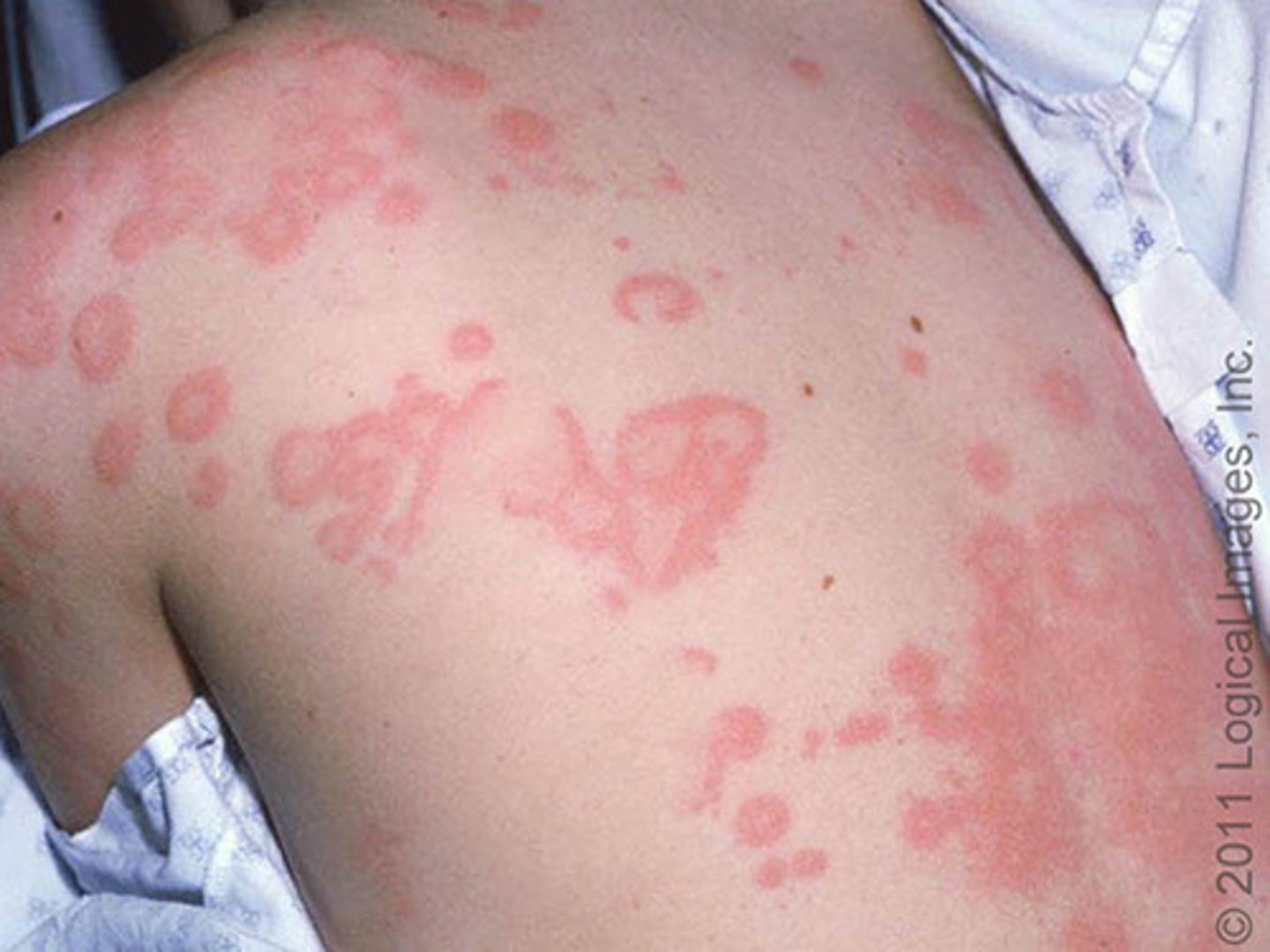
Signs of severe allergy to Antibacterials
Anaphylactic shock: bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, cardiac arrest, SOB)
Time frame of occurrence of severe allergy signs
within 20 minutes
Treatments for severe allergy to Antibacterials
Antihistamine, Epinephrine, and bronchodilator
Suprainfection defn. from antibacterial reactions
Normal flora killed in the mouth, skin, resp. tract, vagina, and intestines
Suprainfection occurs when antibacterials are used more than
1 week
Common SE of antibacterials
GI DISTURBANCES (N/V/D)
Cephalosporins are
similar to penicillins and interfere with alcohol, cepha-
Macrolides are
+ & - antibiotics, not IM, for pt allergic to PCN.
What is the last resort drug used for severe infections
Glycopeptides- Vancomycin
What drug can cause extravasation with IV
Glycopeptides- Vancomycin
For what drug do we monitor peak and trough levels
Aminoglycosides- Gentamicin
Peak levels of Aminoglycosides- Gentamicin
45-60 minutes after admin, 5-8 mcg/mL
Trough levels of Aminoglycosides- Gentamicin
minutes before next dose, <1-2 mcg/mL
IV must be administered over 60-90 min for ____
Levofloxacin and Vancomycin
Drug that, if taken with NSAIDs, increases the risk of seizures, theophylline (bronchodilator) effects, caffeine, and hyperglycemia.
Levofloxacin
Treatment for this bacterial infection requires the use of at least two medications
tuberculosis
How long is the initial phase for TB treatment
2 months (elimination of the active form, so it is not infectious).
Daily therapy for TB (RIPE)
Combination of 2-3 drugs:
R (rifampin)*
I (isoniazid) INH*
P (pyrazimide)
E (ethambutol)
How long is the continuous phase for TB treatment
4-7 months
Treatment for resistance to isoniazid and rifampin
three drugs for 1-2 yrs
____Infection is a risk factor for developing TB, but still treated with RIPE
HIV
For peds with latent TB
Preventive treatment should be initiated, INH or INH + rifampin