module 7 momentum and collisions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
momentum (p→) =
mv→
sum of force in terms of momentum
ΣF→ = dp→/dt
if sum of forces is zero
momentum is conserved, and vice versa
impulse (I→) =
Δp→ = F→avg * Δt
F→avg
1/Δt ∫t1 to t2 of F dt
elastic collision
total KE and momentum are conserved
inelastic collision
total KE changes while total momentum is conserved
perfectly inelastic collision
two colliding objects stick together after collision
vf of perfectly inelastic
m1v1 + m2v2 / m1 + m2 (v are vectors!)
elastic collision in 1d relation of velocities before and after
Δvi = -Δvf
v1f in 1d elastic
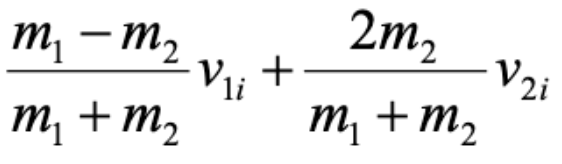
v2f in 1d elastic
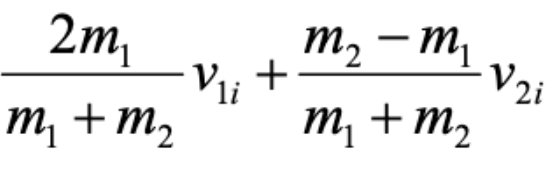
ballistic pendulum
v of projectile = (sum of masses/mass of projectile)√2gh, h is the height that the system rose
glancing elastic collision in 2D components
x: m1v1i = m1v1fcosθ + m2v2fcosφ
y: 0 = m1v1fsinθ - m2v2fsinφ
when m’s are equal in glancing collision (e.g. billiard balls)
v1i² = V1f² + V2f²
in billiard ball situation, dot product of final velocities is zero, meaning
they are orthogonal
left off on
center of mass and rockets
center of mass for a system of particles
summation of positions x masses / summation of masses
center of masses for extended object
1/M ∫ r→ dm
dm =
density dx dy dz
center of mass of a rod
L/2
center of mass of a right triangle
2/3 from the taller part
mass of a cone
1/3•density•height•area of base
center of mass of cone
3/4 • h
center of mass of a system of particles of combined mass M moves like
particle of mass M would move under influence of Fnet external
Macm =
summation of miai = summation Fi
rocket propulsion
vf - vi = veln(mi/mf)