COMPTIA A+ Core 2
1/639
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
640 Terms
policy
a set of configuration settings applied to users or computers
(1 word)
Group Policy Object (GPO)
Collections of policy settings are stored in a [blank] and can be used to apply registry settings, run scripts, apply templates, set up software, make configuration settings, etc. (word word word (acronym))
Not configured
GPO setting that indicates the GPO has no value for that setting and does not change the current setting. (2 words)
Enabled
indicates the GPO identifies a value to enforce. (1 word)
domain
A [blank] is an administratively defined collection of network resources that share a common directory database and common security policies. The [blank] is the basic administrative unit of an Active Directory structure.
- Database information is replicated (shared or copied) within a [blank].
- Security settings are not shared between [blank].
- Each [blank] maintains its own set of relationships with other [blank]s.
- [blank] are identified using Domain Name System (DNS) names. The common name is the [blank] name itself (for example, CorpNet). The distinguished name includes the common [blank] name along with the top-level DNS [blank] name (for example, CorpNet.xyz).
- Depending on the network structure and requirements, the entire network might be represented by a single [blank] with millions of objects. It is also possible that the network might require multiple [blank]s.
(1 word)
domain controller
A Windows server that holds a copy of the Active Directory database.
- is a member of only one domain.
A domain can contain multiple [blank]s. Each [blank] holds a copy of the Active Directory database.
- Can make changes to the Active Directory database.
- Replication is the process of copying changes made to the Active Directory database between all [blank]s in the domain.
(2 words)
replication
the process of copying changes made to the Active Directory database between all domain controllers in the domain.
(1 word)
Organizational Unit (OU)
Like a folder that subdivides and organizes network resources within a domain.
- Is a container object.
- Can contain other [blanks]s or any type of leaf object (such as users, computers, and printers).
- Can logically organize network resources.
- Simplifies security administration.
(2 words (acronym))
Built-in containers
Like OUs, generic [blank]s are used to organize Active Directory objects.
[blank] objects differ from other containers in that they:
- Are created by default.
- Cannot be created, moved, renamed, or deleted.
- Have very few editable properties.
(word-word word)
object
Within Active Directory, each resource is identified as an [blank]. Common [blank]s include:
- Users
- Groups
- Computers
You should know the following about [blank]s:
- Each [blank] contains attributes that include information about the [blank] itself such as a user's name, phone number, and email address. This information is used for locating and securing resources.
- Active Directory uses DNS for locating and naming [blank]s.
- Container [blank]s hold other [blank]s. These can be either other containers or leaf [blank]s. (1 word)
attributes
Each object contains [blank]s that include information about the object itself such as a user's name, phone number, and email address. This information is used for locating and securing resources. (1 word)
group policy
allows the administrator to simultaneously apply multiple settings to multiple objects within the Active Directory domain simultaneously (2 words)
Computer Configuration
GPO setting category. Type of policy (also called machine policies) are enforced for the entire computer and are applied when the computer boots.
[blank] policies include:
- Software that should be installed on a specific computer.
- Scripts that should run at startup or shutdown.
- Password restrictions that must be met for all user accounts.
- Network communication security settings.
- Registry settings that apply to the computer (the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE subtree).
[blank] policies are applied as the computer boots and are enforced before any user logs on
(word word)
User Configuration
GPO setting category. Type of policy that is enforced for specific users.
[blank] policy settings include:
- Software that should be installed for a specific user.
- Scripts that should run at logon or logoff.
- Internet Explorer user settings (such as favorites and security settings).
- Registry settings that apply to the current user (the HKEY_CURRENT_USER subtree).
[blank] policies are applied as the user logs on and often customize Windows-based user preferences.
Account Policy
This policy type is in effect only when configured in a GPO linked to a domain. Used to control the following:
- Password settings
- Account lockout settings
- Kerberos settings
([word] policy)
local policy/audit policy
Used to configure auditing for events such as logging on, account management, or privilege use.
(Local policy/word policy)
Local Policies/User Rights Assignment
Computer configuration policies include a special category of policies called [blank]. [Blank] identify system maintenance tasks and the users or groups who can perform those tasks. Examples include:
- Access this computer from the network (the ability to access resources on the computer through a network connection).
- Load and unload device drivers.
- Allow log on locally (the ability to log on to the computer console).
- Allow log on through Terminal Services (the ability to log on using a Remote Desktop connection).
- Back up files and directories (does not include restoring files and directories).
- Shut down the system.
- Remove a computer from a docking station.
(Local Policies/word word word)
Local Policies/Security Options
Allows you to apply or disable rights for all users the Group Policy applies to. Examples of this policy type include:
- Computer shutdown when the Security event log reaches capacity.
- Unsigned driver installation.
- Ctrl+Alt+Del is required for log on.
(Local Policies/word word)
Registry
This policy type is used to:
- Configure specific registry keys and values.
- Specify if a user can change registry values, view subkeys, or modify key permissions.
(word)
File System
This policy type is used to configure file and folder permissions that apply to multiple computers. For example, you can limit access to specific files that appear on all client computers.
(word word)
Software Restriction Policies
This policy type is used to define the software permitted to run on any computer in the domain. You can apply these policies to specific users or all users.
You can use these policies to:
- Identify allowed or blocked software.
- Allow users to run only the files you specify on multi-user computers.
- Determine who can add trusted publishers.
(word word Policies)
Administrative Templates
Registry-based settings that you can configure within a GPO to control the computer and overall user experience. They include the ability to do such things as:
- Use Windows features such as BitLocker, Offline Files, and Parental Controls.
- Customize the Start menu, taskbar, or desktop environment.
Control notifications.
- Restrict access to Control Panel features.
- Configure Internet Explorer features and options
(word word)
Search Menu
Win + s opens what menu
(word Menu)
Run command
Win + r opens what command?
(word command)
Settings app
Win + i opens what app?
(word app)
File Explorer
Win + e opens what app?
(word word)
gpedit.msc
This command opens the Local Group Policy Editor.
gpupdate
This command forces a computer to ask the domain controller for new or updated group policy objectives. These updates usually occur automatically, but on occasion, you may need to force the updates to a computer.
gpresult
This command displays a listing of the group policy objects that have been applied to the computer and the user.
kernel
The core of the operating system.
It is loaded into memory when the system boots.
It controls security, manages the file system, and provides a platform for applications to run.
The user rarely interacts directly with this component.
(word)
driver
is a type of computer program that enables the operating system to interact with hardware devices. (word)
interface
This tool allows the user to interact with the kernel and the utilities. There are two main types of [blank]s, command line and GUI. (word)
utilities
Features or programs included with an operating system that perform system-related tasks.
Common Windows [blank]s include the Settings, Disk Management, and Computer Management.
Common Linux [blank]s are cd, cp, grep, and Is. (word)
application
A subclass computer program designed for end users.
Examples are databases, spreadsheets, and word processing programs.
[Blank]s frequently come in suites. (word)
128GB, 2TB, 6TB, 6TB
Random access memory (RAM) limitations: Having adequate RAM for each device is very important; having the right edition of Windows to support it is important as well. Each edition of Windows has its own RAM support limitations. Please answer with the #GB or #TB of the following Windows editions:
(Home Edition, Pro Edition, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise)
Pro, Pro for workstations, Enterprise
Bitlocker is available on which windows editions? (version, version, version)
Group Policy Editor
a graphical snap-in for Windows settings stored in the registry. It:
- Provides a simplified GUI for changing settings in the registry.
- Contains more than 3,000 Windows settings to choose from.
- Allows you to centrally configure and enforce settings on all computers in an Active Directory network.
- Uses the domain controller to implement the settings in an Active Directory network.
- Can also be used on a small scale for enforcement of restrictions or to run specific scripts at specified times.
(word word word)
Workgroup
This account type is for small networks on a local network. How they work:
- All computers are peers to each other. There isn't a central administrator.
- Each device has its own storage.
- The user manages the device.
- A user must have an account on the device to log on to it.
- Allows users to share files, printers, and local network resources.
- Usually consist of twenty or fewer computers.
(word)
Windows Update, Installation Assistant, ISO Installation Media, SCCM task sequence
What are the four most common in-place upgrade installation options for Windows Machines? (Windows U****, I******** A******, I I********* M**, S* t* s******)
SSCM task sequence
This is a good in-place Windows upgrade option if you are currently manually deploying operating systems and managing software updates through the Configuration Manager.
(word word word)
ISO Installation Media
This Windows upgrade method performs the in-place upgrade from an ISO file containing the Windows 11 installation files. You download the ISO file from the Microsoft site. The advantage of using this method is that the upgrade performs more quickly from the downloaded file. This is very advantageous if you are upgrading several computers, since you need to download the software only once. It also gives you the ability to upgrade a system that does not have access to the internet or the connection to the internet is very slow.
(word word word)
SetupDiag Diagnostic Tool
If an in-place upgrade fails, you can use this tool to determine the cause of the failure. You can run the tool on the computer that failed the upgrade, or in an offline mode on another computer using logs exported from the computer that failed to upgrade. (word word Tool)
10 Home
Windows version intended for home use.
Offers the most basic features.
Includes safety features:
- Device encryption
- Firewall and network protections
- Windows Defender antivirus
- Windows Hello authentication
- Secure Boot
- Internet protection
- Parental controls
Includes fundamental features:
- Battery saver mode
- Mobile function for connecting to mobile devices
- Microsoft Edge browser
- Voice for hands-free functions
- Digital pen and touch
(# word)
Pro
Windows version intended for business professionals.
Offers all Home edition features plus:
- BitLocker device encryption
- Windows Information Protection (WIP)
- Mobile device management
- Windows update for business
- Microsoft Store for Business
- Support for Active Directory and Azure Active Directory
- Group Policy
- Assigned Access
- Dynamic provisioning
- Enterprise State Roaming with Azure
- Hyper-V
(word)
Pro for workstations
Windows version:
- Intended for business professionals whose work requires high-end hardware for intense computing, with fast data processing and large storage capacity. Examples include: CAD engineers, graphic designers, medical scientists, and media producers.
- Offers all Pro edition features, plus:
-> Resilient file system (ReFS)
* Fault-tolerant storage
* Auto-correcting
* Cloud-based
-> Persistent memory
* Non-volatile memory modules (NVDIMM-N)
* Fast reading and writing of files
* Data saved in memory, even when powered down
-> SMB Direct
-> Capacity to use Intel Xeon or AMD Opteron
-> Capacity of up to 4 CPUs
-> Capacity of up to 6 TB of memory
(word word word)
10 Enterprise
Windows Edition:
- Intended for large organizations that have IT professionals managing the systems.
- Requires a volume licensing agreement.
- Offers all the features of the Pro edition plus the following features:
-> Credential Guard
-> Application Guard
-> Application Control
-> Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
-> Device Guard
-> Direct Access
-> User Experience Control
-> Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V)
-> Microsoft User Environment Virtualization (UE-V)
(# word)
11 Home
Windows edition:
- Intended for home use.
- Offers Windows' most basic features.
- Includes fundamental features such as:
-> Snap layouts
-> Desktops—for grouping and easily changing desktop groups
-> Microsoft Teams—for communicating with others through chats and video conferencing
-> Widgets—accessible from taskbar and customizable
-> Enhanced gaming features
-> Microsoft Edge
-> Microsoft Store
-> Touch, Pen, and Voice features
Includes security features such as:
- Device encryption
- Find my device
- Firewall and network protection
- Internet protection
- Secure Boot
- Windows Security
- Windows Hello
- Parental controls
(# word)
11 Enterprise
Windows Edition:
- Offers options within the [blank] editions including:
-> Windows [blank] E3
* Intended for mid-size to large organizations.
* Includes all Windows 11 Pro features plus:
> OS deployment and update control options
> Device and application management features
> Serverless print management and Universal Print
> Added security protections
-> Windows [blank] E5:
* Intended for organizations that want to use cloud-delivered endpoint security.
* Includes all [blank] E3 features plus Microsoft
Defender for Endpoint
-> Windows [blank] E3 in Microsoft 365 F3:
* Intended for mid-size to large organizations with frontline workers.
* Includes all [blank] E3 features.
(# word)
Windows Registry Keys
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, HKEY_CURRENT_USER, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, HKEY_USERS, HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG, and HKEY_DYN_DATA are the six main types of what? (3 words)
partition
a logical division of a storage device (e.g. a hard disk drive or solid-state drive). Before a drive can be [blank]ed, it must first be initialized. During this process, a [blank] style is selected, such as Master Boot Record (MBR) or GUID [blank] Table (GPT). A single storage device can contain one or more [blank]s.
A [blank] can be initially created without being formatted, but in most cases it is formatted to allow an operating system to be installed or to store data. When a [blank] is formatted, it is given a drive letter to help a user distinguish which [blank] is being used, such as C:\ or D:\. A [blank] cannot span to a separate physical storage device.
(word)
volume
a single accessible storage area within a file system. A [blank] can encompass a single partition or span multiple partitions depending on how it is configured and the operating system you are using. [Blank]s are identified by drive letters.
To access storage space within a partition, the partition has to be formatted with a file system by creating a [blank].
(word)
directory
(also called a folder) is a container in a volume that holds files or other [blank]s. You use it to logically sort and organize data to keep related files grouped together. Most operating systems use a hierarchical filing structure.
(word)
file
a one-dimensional stream of bits treated as a logical unit.
The most basic component that a file system uses to organize raw bits of data on the storage device itself.
The complete [blank] name is made up of the directory path plus the file name.
An extension can also be added to the [blank] name to identify the [blank] type and the program used to create, view, and modify the [blank].
(word)
Compact Disk File System (CDFS)
A virtual file system used with Linux
(word word word word (acronym))
Network File System (NFS)
A distributed file system that allows client computers to access files over a computer network.
(word word word (acronym))
Ext4
The default Linux file system (and its predecessor ext3, which is still in use).
(acronym)
formatting
the process of preparing a partition to use a specific file system (word)
FAT32
This file system has the following properties:
- Partition size: 2 terabytes
- Volume size: 2 terabytes
- File name length: Long File Names (255 characters, spaces)
- File size: 4 gigabytes
- Number of files allowed: 268,435,437
*Although a [blank] partition can be up to 2 terabytes, the Windows Disk Management tool can create only a 32 GB [blank] partition. To create larger [blank] partitions, you must use the Command Prompt, PowerShell, or a third-party tool.
(acronym)
NTFS
This file system has the following properties:
- Partition size: 256 terabytes
- Volume size: 256 terabytes
- File name length: Unicode (255 characters, excluding the / character)
- File size: 16 terabytes
- Number of files allowed: 4,294,967,295
- Windows recommended file system
(acronym)
exFAT
(sometimes called FAT64) file system is a special file system that is designed to support large flash drives. Using NTFS on flash drives is usually not a good idea due to its high overhead and risk of corruption if the device is not stopped properly prior to removal.
However, many flash drives exceed the 32 GB limit discussed above. Microsoft introduced native [blank] support in Windows 7 to allow large removable flash storage devices to continue to use a FAT-type file system.
(acronym)
Create partition, create volume, format disks
What are the three steps of hard disk preparation?
Account Policies, Computer Configuration Policies, Registry Policies, Software Restriction Policies, Administrative Templates
What are the five main types of GPO Settings/policy areas? (A***** Policies, C***** C********** Policies, R***** Policies, S***** R******** Policies, A********** T********)
assigned access
What is the Windows implementation of Kiosk Mode known as? (word word)
Ctrl+Shift+Esc
What is the one step key sequence to open task manager (does not require any additional clicks)
(key+key+key)
Ctrl+Alt+Delete, Windows Key+X
What are the two 2-step key sequences to open task manager (requires an additional click after the key sequence)
(key+key+key, key+key)
Processes
This task manager tab is used to view the status of all current applications running on the computer. Use this tab to terminate unresponsive applications. For each [blank] running you can view the resources used by the [blank], such as CPU, Memory, and disk.
(word)
Performance
This task manager tab is used to view system-wide processor, memory, disk, and network statistics. This is a more detailed view of what is also shown in the Processes tab. (word)
App History
This task manager tab is used to collects statistics of how long an app or program has been running on your computer for the past month. (2 words)
Startup
This task manager tab is used to enable or disable applications that start automatically when the system is powered on. (word)
Users
This task manager tab is used to monitor users currently logged on to the system. A selected user can be disconnected. (word)
Details
This task manager tab is used to view the status of all current processes running on the computer, and the CPU and memory resources they use. Use this tab to modify the priority of a process or terminate unwanted processes. As opposed to the Processes tab which groups processes into categories, this tab provides a granular, technical view or all running processes, where each process is shown individually. It contains advanced columns such as:
- PID (Process ID)
- Status
- User name
- CPU time
- I/O reads/writes
- Memory details (working set, commit size, etc.) (word)
Services
This task manager tab is used to view a list of services running on the computer. You can use this tab to start and stop a particular service. (word)
false
True or false: There is a one step key sequence to open Control Panel (word)
System and Security
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
- Security and Maintenance - used to review recent error messages and options for resolving issues.
- Windows Defender Firewall - used to check firewall status and allow apps through the Windows Firewall.
- System - allows you to view RAM and processor speed, remote access, remote assistance, or to see the computer name.
- Power Options - used to change battery settings, change what the power buttons do, or change when the computer sleeps.
- File History - used to save backup copies of your files and to restore your files.
- Backup and Restore (Windows 7) - used to back up and restore with the legacy Windows 7 backup utility and to restore files using the legacy Windows 7 backup utility.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption - used to manage BitLocker settings and protect your files and folders from unauthorized access.
- Storage Spaces - used to save files to two or more drives to help protect you from drive failure.
- Work Folders - used to make your work files available on all devices you use, even when offline.
- Administrative Tools - used to clean up hard disk space, run defragmenter, optimize drives, format disks, view event logs, and schedule tasks.
(word word word)
Network and Internet
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
- Network and Sharing Center - used to view network status, connect to a network, and to view network computers and devices.
- Internet Options contains the following tabs:
-> General - modifies your browser home page, startup window, tabs, history, and appearance.
-> Security - determines your security zone and security level.
-> Privacy - manages website privacy and enables and disables pop-ups and InPrivate Browsing.
-> Content - views certificate, AutoComplete, and Feeds and Web Slices settings.
-> Connections - sets up an internet connection.
-> Programs - manages your default browser, add-ons, and other internet programs and file associations.
-> Advanced - sets and resets advanced browser settings.
(word word word)
Hardware and Sound
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
Used to view and configure the current system sound settings, installed audio devices, sound cards, printer settings, and other hardware settings.
(word word word)
Programs
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
Used to uninstall programs, turn Windows features on or off, view installed updates, run programs from previous versions of Windows, get additional programs, and change default settings for media and devices. (word)
User Accounts
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
Used to view and modify user accounts, give users access to the computer, change account types, manage web credentials, and manage windows credentials. (word word)
Appearance and Personalization
This Control Panel category contains the following settings:
Used to configure navigation properties, modify the behavior of input and display devices to accommodate users with special needs, specify single or double click options, show or hide hidden files, and add or remove fonts on the computer.
(word word word)
Clock, Language, and Region
This Control Panel category contains settings to configure various items such as language preference, default currency symbols, and date and time notation. (word, word, and word)
Ease of Access
This Control Panel category is used to optimize visual display, modify sound and visual cues, change mouse and keyboard settings, and set up speech recognition or a microphone. (word word word)
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
This is a framework that provides a common user interface for performing system administration tasks. Management of a set of related features is done by adding snap-ins to the console. The [blank] provides the shell for running these snap-ins, while the snap-ins provide the details for performing specific management tasks. Microsoft provides snap-ins for managing:
- Local Users and Groups
- Device Manager
- Disk Management
- Print Management
- Component Services
- Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
(word word word [acronym])
![<p>This is a framework that provides a common user interface for performing system administration tasks. Management of a set of related features is done by adding snap-ins to the console. The [blank] provides the shell for running these snap-ins, while the snap-ins provide the details for performing specific management tasks. Microsoft provides snap-ins for managing:</p><p>- Local Users and Groups</p><p>- Device Manager</p><p>- Disk Management</p><p>- Print Management</p><p>- Component Services</p><p>- Windows Firewall with Advanced Security</p><p>(word word word [acronym])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8323e5e1-5a49-4c37-a88a-0af3e9c3e544.jpg)
Computer Management
This is a saved MMC console that includes common snap-ins used to manage your computer.
The [blank] console is a preset management tool that contains the most common snap-ins, including:
- Task Scheduler
- Event Viewer
- Shared Folders
- Local Users and Groups
- Performance
- Device Manager
- Disk Management
(word word)
System Information (Msinfo32.exe)
This System Information tool is used to view hardware and configuration information for the computer. While much of this information is available through other tools, [blank] provides a single location for viewing information such as:
- Operating system version.
- Computer manufacturer, processor type, available memory.
- Installed devices and drivers used.
- Running tasks.
- Applications that run at system startup.
- Services loaded on the system.
You can view or export configuration settings in [blank]. You can't modify them.
(word word (acronym.exe))
![<p>This System Information tool is used to view hardware and configuration information for the computer. While much of this information is available through other tools, [blank] provides a single location for viewing information such as:</p><p>- Operating system version.</p><p>- Computer manufacturer, processor type, available memory.</p><p>- Installed devices and drivers used.</p><p>- Running tasks.</p><p>- Applications that run at system startup.</p><p>- Services loaded on the system.</p><p>You can view or export configuration settings in [blank]. You can't modify them.</p><p>(word word (acronym.exe))</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ab9d6786-88fa-47bc-84e7-15857318fd5c.jpg)
Event Viewer
This System Information tool is used to view logs about programs, system events, and security. Each entry is listed as a warning, error, or information event. Events display in the following logs:
- The Application log contains all application-related events such as application installations, un-installations, and application errors.
- The System log contains all system-related events such as system modifications, malfunctions, and errors.
- The Security log contains all security-related events such as security modifications and user login events.
Applications or services can add logs.
(word word)
Performance Monitor
This System Information tool displays statistics about the operation of the computer.
- A counter identifies a specific statistic, such as % Processor Time or % Disk Free Space.
- You can add or remove counters to customize the statistics you see.
- Real-time data is displayed in a graph.
- [Blank] by itself does not save any data. To save statistics, use a data collector set.
(word word)
![<p>This System Information tool displays statistics about the operation of the computer.</p><p>- A counter identifies a specific statistic, such as % Processor Time or % Disk Free Space.</p><p>- You can add or remove counters to customize the statistics you see.</p><p>- Real-time data is displayed in a graph.</p><p>- [Blank] by itself does not save any data. To save statistics, use a data collector set.</p><p>(word word)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/701df984-1109-4482-bf7d-b5605ea966ca.jpg)
Reliability Monitor
This System Information tool maintains historical data that describe the operating system's stability.
- Overall system stability is given a stability index that ranges from 1 to 10 (10 is the most stable). Application, hardware, Windows, and other failures affect the stability rating.
- [Blank] shows a historical chart that identifies when software installs/uninstalls and failures occur. You can click a day to view the changes affecting system stability on that day.
(word word)
Windows Memory Diagnostic (mdsched.exe)
This System Information tool tests the Random Access Memory (RAM) on your computer for errors. This utility is included with Windows 7 through Windows 11. (word word word (acronym.exe))
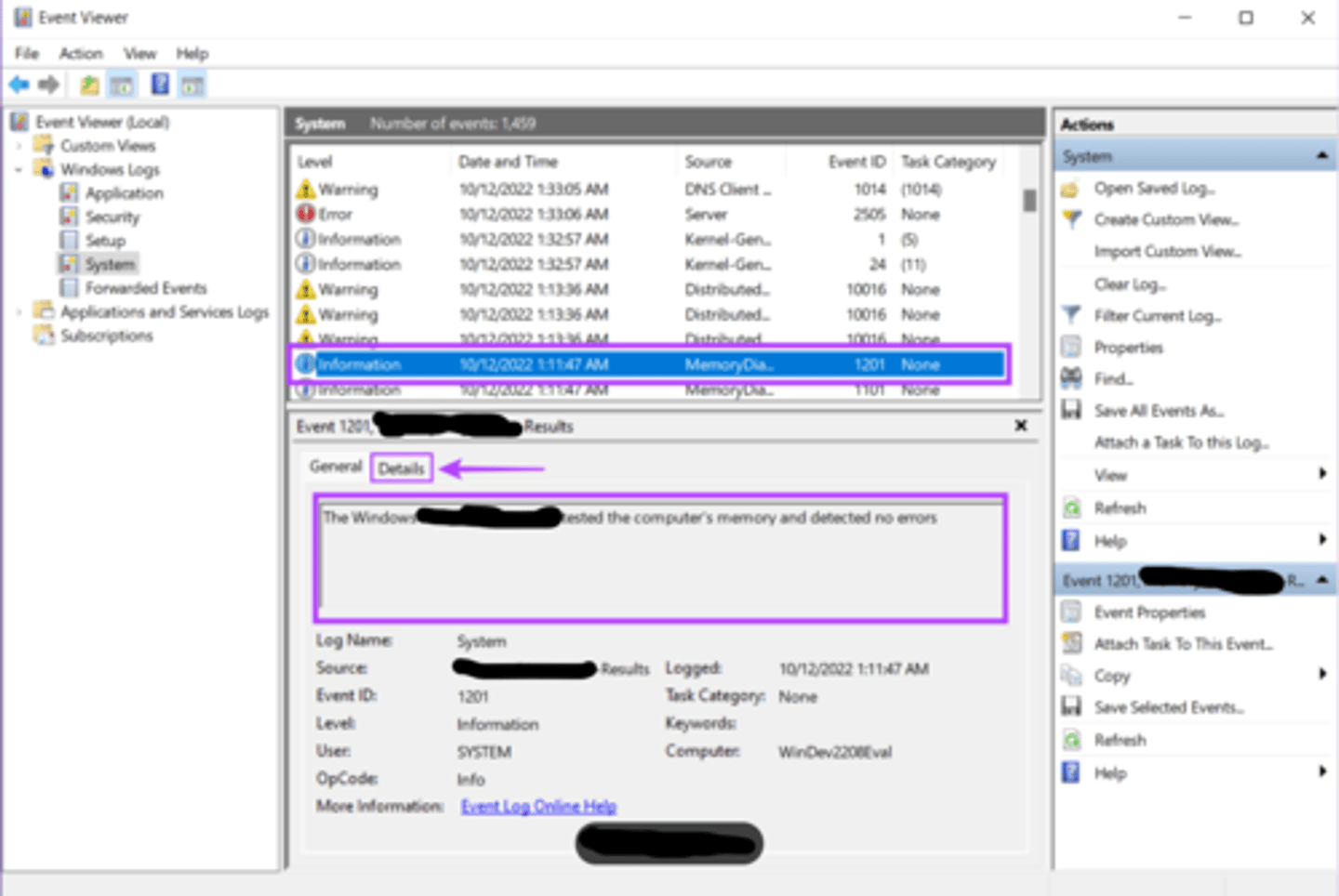
System Information Tools
These are tools to view details about computer hardware and software settings in Microsoft Windows (word word word)
System Configuration Tools
Windows allows users to configure options using tools such as Microsoft Registry Editor (Regedit.exe), DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag), Command Prompt, Services, Microsoft Terminal Services Client (mstsc), etc. These types of tools are referred to as (word word word)
System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe)
This utility is used to configure the system to enable optimal troubleshooting and diagnosis of technical issues. It controls the initial startup, the boot files, and services loaded along with other tasks.
(word word word (acronym.exe))
General
This tab of the System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe) displays by default when you open the System Configuration Utility. The three options under the [blank] tab are:
- Normal Startup loads all device drivers and services when Windows starts up.
- Diagnostic Startup loads only the basic devices and services. It is similar to starting Windows in safe mode.
- Selective Startup allows the user to choose what starts with Windows. (word)
Boot
This tab of the System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe) shows the operating system installed on the computer. This tab contains some of the following options:
- Boot Options allow the user to select options such as Safe boot along with additional options.
- Timeout specifies the number of seconds Windows displays the Boot menu before loading the operating system. The default is 30 seconds. (word)
Services
This tab of the System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe) displays all the services configured to start when the operating system boots. Uncheck services that you do not want Windows to start. (word)
Startup
This tab of the System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe) displays a shortcut to the Startup tab in Task Manager. (word)
Tools
This tab of the System Configuration Utility (msconfig.exe) displays utilities and tools that you can launch directly from the System Configuration Utility. (word)
Microsoft Registry Editor (Regedit.exe)
This System Configuration Tool modifies entries in the Windows registry. The registry is a database that holds hardware, software, and user configuration settings.
- Whenever you change preferences, software, hardware, and user-settings, the registry stores and reflects those settings.
- The preferred method of modifying the registry is to use applications or management tools that write to the registry. For example, many Control Panel applets make changes to registry settings.
- You must directly edit the registry to make some advanced settings.
(word word word (acronym.exe))
DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DxDiag)
This System Configuration Tool shows information related to DirectX operation. DirectX is a set of programming interfaces for multimedia (video and audio). [Blank] displays information such as:
- Operating system version.
- Processor and memory information.
- DirectX version.
- Settings and drivers used by display devices.
- Audio drivers.
- Input devices (mouse, keyboard, USB)
(word word word (acronym))
Services
This System Configuration Tool is a program that processes requests from other applications or users. This tool can start automatically and stay constantly running in the background, waiting for service requests. Use the snap-in to view and manage running services. The service startup behavior determines how the service is started.
- When set to Automatic, Windows automatically starts the service when the system boots.
- When set to Manual, you must manually start the service.
- When Disabled, the service will not run. (word)
Microsoft Terminal Services Client (mstsc)
This System Configuration Tool is a remote management service. [acronym].exe is the executable file that opens the [blank]. The [blank], which is Remote Desktop Services (RDS), is a component of Microsoft Windows that allows users to take control of remote computers over a network connection. The three Windows components that use RDS are:
- Windows Remote Assistance
- Remote Desktop Connection
- Fast User Switching
(word word word (acronym))