Geology 111 (Chapter 16)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is a river?
They carry sediment to our oceans to build up beaches and streams.
They allow travel and industry has often been located along rivers to easily move materials down or upstream.
Recreation
Can be used to produce energy
Biological habitats
They erode rock, carve landscape and form landforms
What is a drainage basin?
Each stream drains a naturally defined are
factors affect how a drainage basin will react to a storm event
Streams have a main channel fed by smaller subsidiary channels called tributaries. Each tributary drains part of the larger drainage basin but a tributary can have higher flows than the main stream. The combination of tributaries and the main stream forms a drainage network. The response of a stream to precipitation is influenced by the number and size of tributaries.
How can the geology of the material beneath the river influence the drainage pattern?
The patterns that the river systems care across the land surface are strongly influenced by the geology. Channels form preferentially in weaker material and so reflect differences in rock type and the geometry of folds faults, joints, and other structural features.
What are the different patterns mentioned?
Dendritic Drainage patter, Radial Drainage pattern, and Structurally Controlled pattern
Do all rivers reach the sea?
Yes
What does the continental divide represent
A continental divide is a boundary that separates a continent's river systems. Each river system feeds into a distinct ocean, bay, or sea. ... Each river system feeds into a distinct ocean basin, bay, or sea. Continental dividesare broad, continent-wide example of drainage divides, sometimes just called divides.May 11, 2016
What is the sediment load and what factors determine how much material is carried by the stream?
The amount of sediment c arrived by the stream including material chemically dissolved in solution is the sediment load.
How is fine grained sediment carried
Carried suspended in the moving water even in relative slow current this material is the suspended load.
How are cobbles and boulders moved?
Generally moved by rolling and sliding a process called traction but they only move during times of high flow. the largest of these class can be briefly picked up but only by extremely high flows.
How do sand grains move?
Rolled along the bottom or be picked up and carried down-current by bouncing along the stream bed the process of saltation.
How does a stream/river erode materials?
Occurs along the base and sides of the channel and can fragment and remove sediment within the channel. The silt, sand, and larger clasts carried by the water enhance its ability to erode.
How does the gradient change from the mountains to the coast
if the stream had the same width from the mountains to the coast, then the only control would be the slope. The higher the slope or gradient the faster the velocity of the water.
How does velocity determine what size of material can be moved in rivers and streams? What is a stream's capacity?
Velocity changes as you move across the stream. The fastest velocity will be in the middle of the stream just below the water where there is no air contact to cause drag and far away from the sides where drag can occur. The slowest velocities will be along the sides of the stream where the water is slowed down by coming in contact with the sides of the stream. Velocity controls the flow of the stream, how much erosion the stream can cause and how much sediment the steam can carry.
Velocity is controlled by gradient, size shape and roughness of the stream, and discharge.
What is the difference in an ephemeral stream versus a perennial stream?
Flow in a headwater may be year-round, seasonal, or rain-dependent. Year-round streams(perennial) typically have water flowing in them year-round. ... Rain-dependent streams(ephemeral) flow only after precipitation. Runoff from rainfall is the primary source of water for these streams.
What is base level?
the theoretical lowest limit that a stream can erode.
What is the ultimate base level?
The lowest a stream can go, usually sea level.
How can temporary base levels be created?
being dammed up by rocks in a natural area or by man behind a dam.
What are the different types of bends or curves that you see in a river?
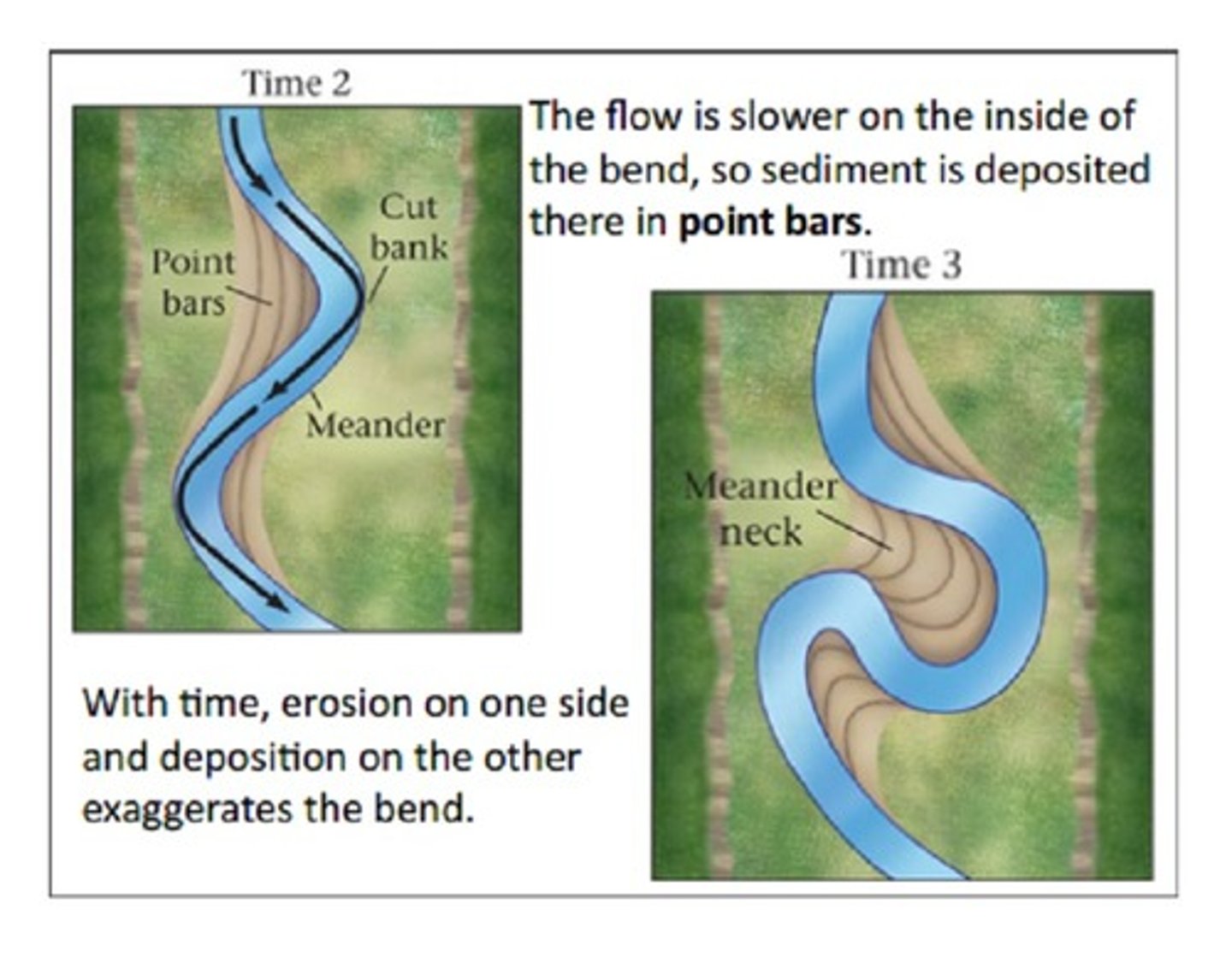
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves, bends, loops, turns, or windings in the channel of a river, stream, or other watercourse. It is produced by a streamor river swinging from side to side as it flows across its floodplain or shifts its channel within a valley.
In a meander is the velocity higher on the inside or outside of the meander?
Higher velocity portions of a stream tend to be driven to the outside of a meander (1). On the outside of the meander, the surface of the water has a tendency to be slightly higher, or super-elevated, because it has gained momentum and acceleration.
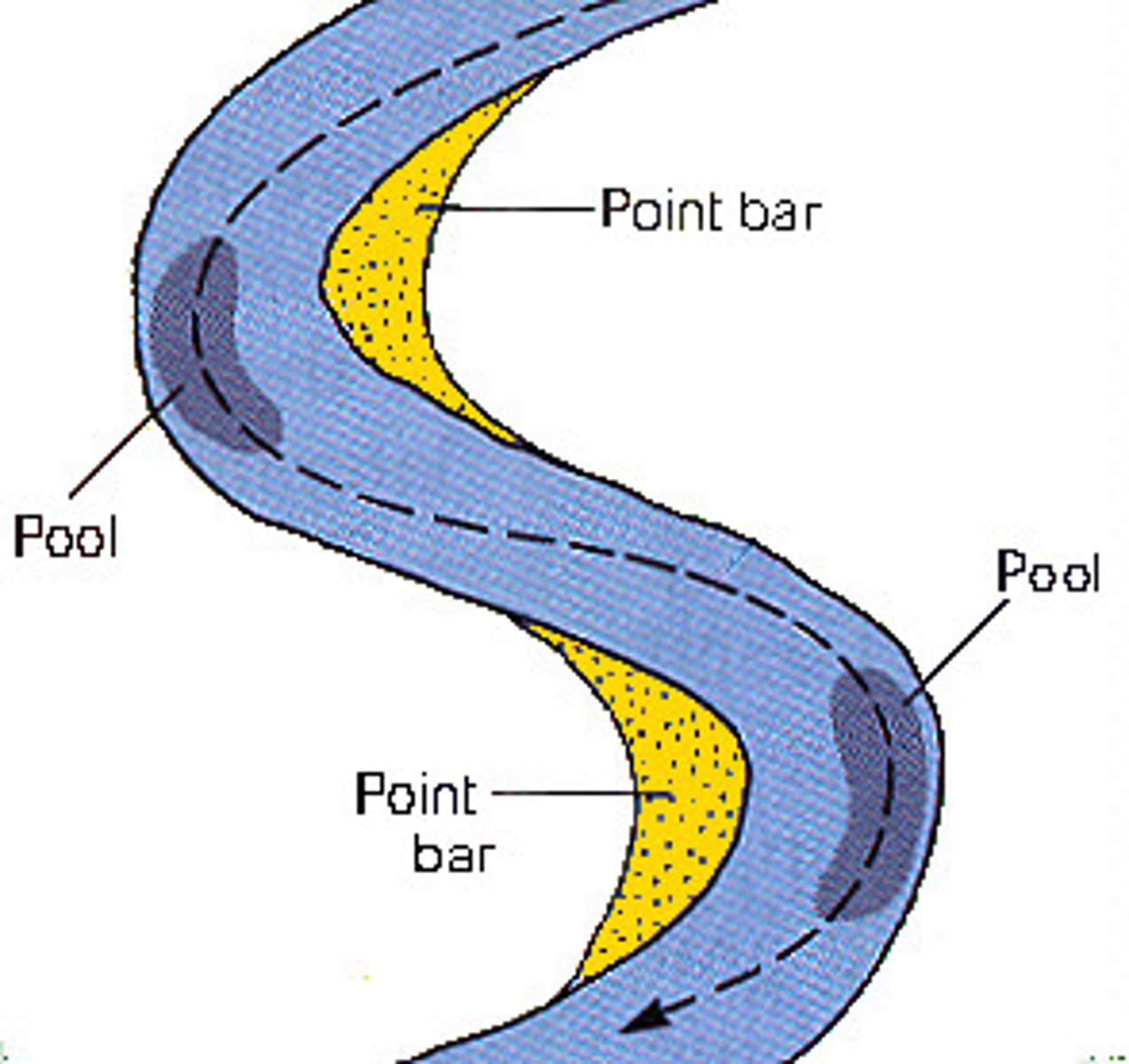
What causes the cutbank to form on the outside of the meander and the point bar to form on the inside?
Low ridges formed by sandy sediments rapidly deposited by flood waters. ... Erosion on the outside of a meander forms a cutbank, and deposition on the inside of a meander formsa point bar. This erosion-deposition relationship causes the meander to move across the floodplain.
Be able to recognize the point bar and cutbank on a map of the meander.
cutbank
How does a cutoff meander form?
A meander cutoff, the natural form of a cutting or cut in a river occurs when a pronounced meander (hook) in a river is breached by a flow that connects the two closest parts of the hook to form a new channel, a full loop. ... Cutoffs are a natural part of the evolution of a meandering river.
What is a floodplain?
an area of low-lying ground adjacent to a river, formed mainly of river sediments and subject to flooding.
What is an oxbow lake and how does it form
As a meanders get larger and larger they eventually break through creating a straighter river channel. Oxbow lakes are pinched off part of the meander.
Under what conditions do braided rivers form?
formations are common where water flow is slow and there is a build up of sediment in the river. This can cause changes in the direction of the river and create new channels.
stream with high gradient enters a flat area and velocity dramatically decreases.
glacier region with lots of sediment
heavy downpours moving sediments into stream
Where are the headwaters of streams
smallest parts of river and streamnetworks, but make up the majority of river miles in the United States. They are the part of rivers furthest from the river's endpoint or confluence with another stream.
What shape of valleys do streams form?
The commonly V-shaped
How do dams affect base level
The dam created a new local base level for the stream.
stream terraces
old floodplain deposits left high as streams downcut through their own floodplains
Levees
Barriers composed of sediments made on either side of a river due to flooding.
How are deltas formed?
When a river hits a larger body of water it loses it energy and drops the sediment forming a delta.
Where is the largest delta in the U.S.?
Mississippi Delta
What is runoff?
Runoff is water that falls on a watershed that does not soak into the ground to become groundwater.
After learning about rocks are there some rocks that the streams may erode more quickly than others?
soft rock erode more quickly than hard rocks
How are entrenched meanders formed?
a river or stream that flows in a narrow trench or valley cut into a plain or relatively level upland. Because of lateral erosion streams flowing over gentle slopes over a time develops meandering (snake like pattern) course.
What is a flood?
an overflowing of a large amount of water beyond its normal confines, especially over what is normally dry land.
How do we measure floods
Floods are measured by stream gauges that are installed in bodies of water located near populated areas. They are installed and operated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), collecting all data before sending it to the National Weather Service (NWS).