Population Dynamics and Demographics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are two methods of estimating population demographics?
Examples include census data collection and sampling techniques.
Sampling techniques; Plot-sampling, mark-recapture method.
Census data collection; measurement of- population size, population density.
What factors affect the number of individuals in a population?
Factors include birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
What is the equation for exponential growth?
What do the factors mean?
The equation is dN/dt = rN, where dN/dt is the change in population size, r is the intrinsic growth rate, and N is the population size.
Define biotic potential.
Biotic potential is the maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimal environmental conditions. For example, bunnies have high biotic potential, while elephants have low biotic potential.
Compare density-dependent limiting factors with density-independent limiting factors.
Density-dependent factors, such as disease and competition, increase in effect as population density increases, while density-independent factors, like natural disasters, affect populations regardless of density.
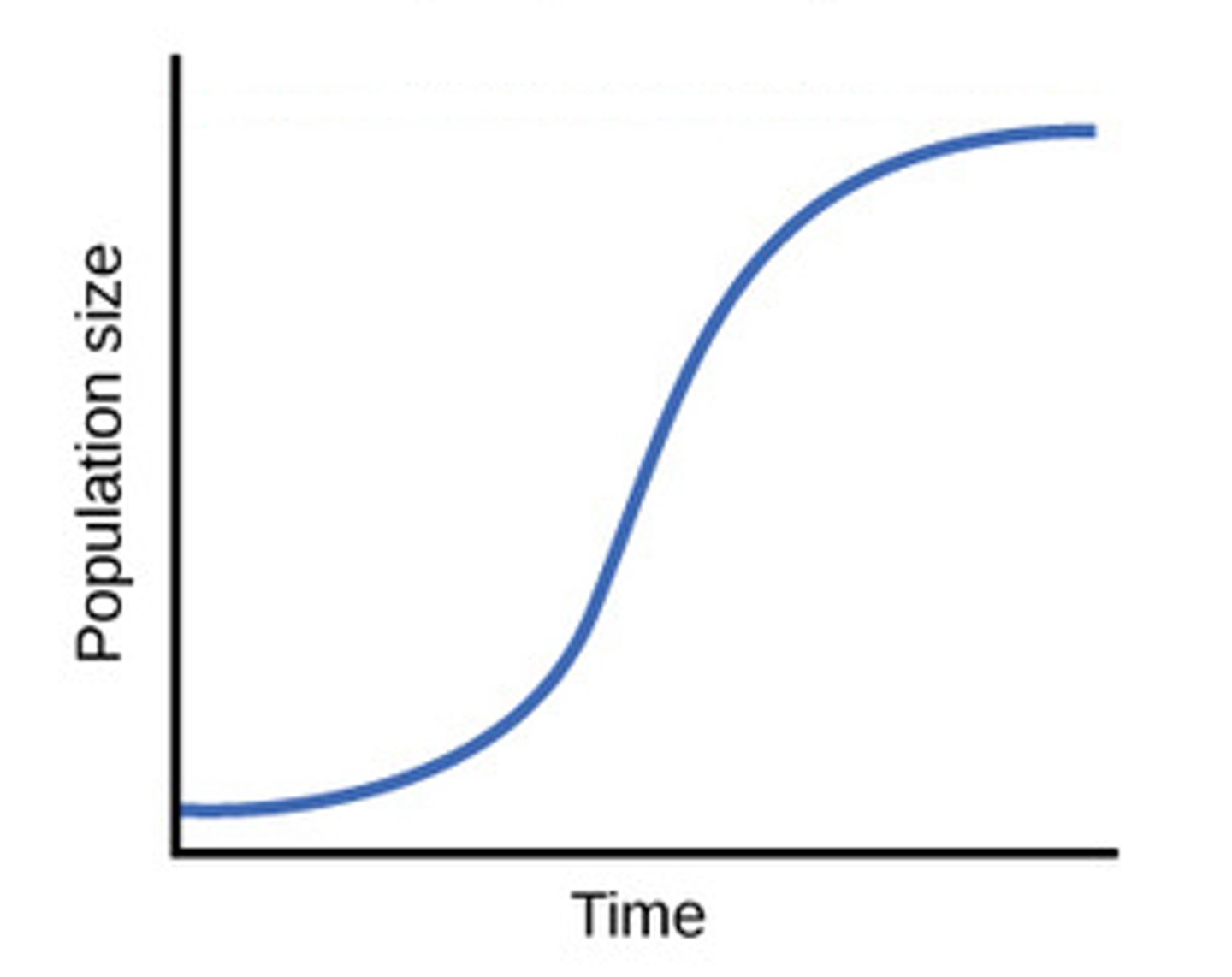
How do limiting factors result in logistic growth?
Limiting factors slow population growth as resources become scarce, leading to an S-shaped curve in population growth over time.
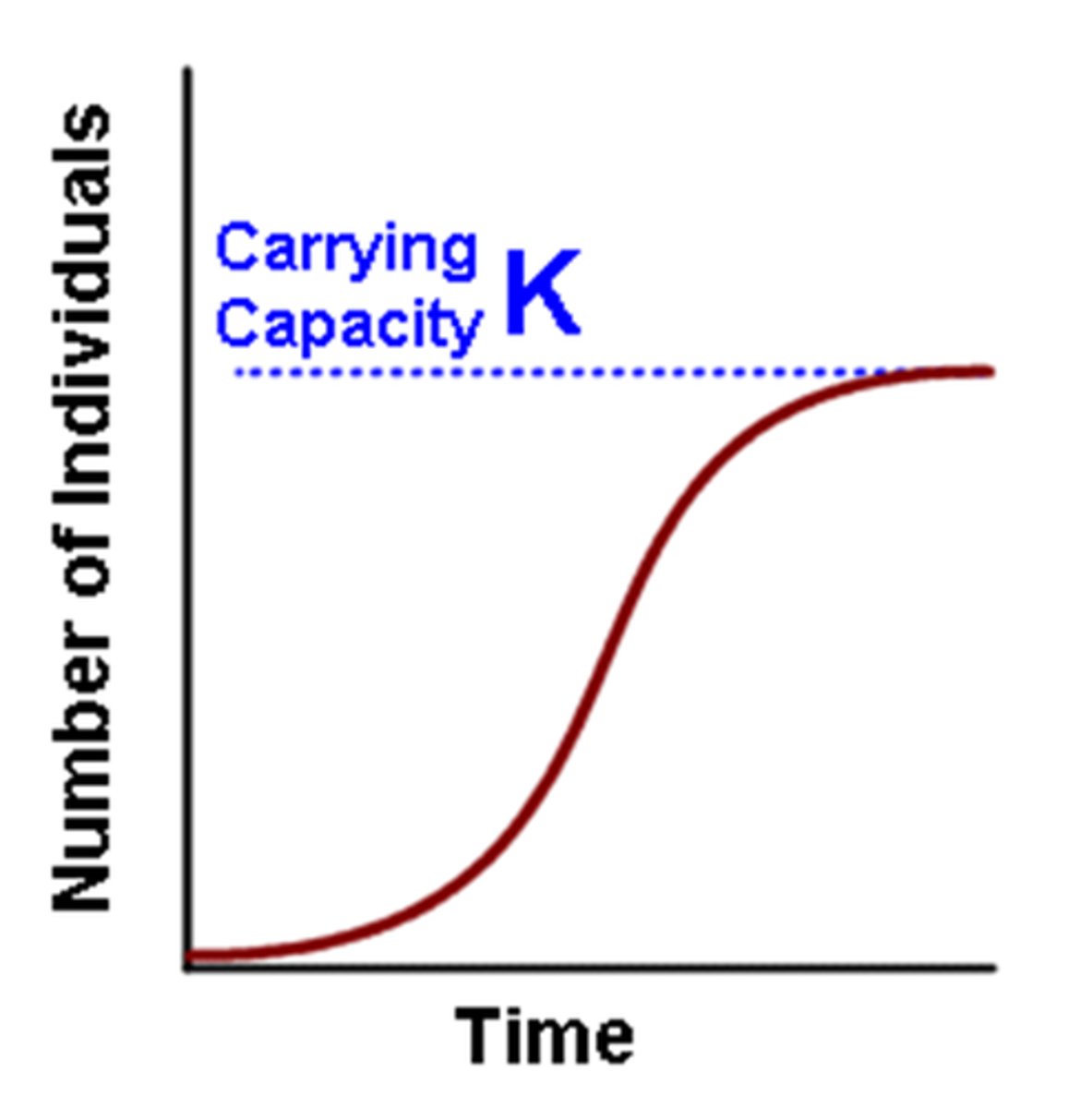
What are some factors that affect carrying capacity?
Factors include availability of resources, habitat space, and environmental conditions.
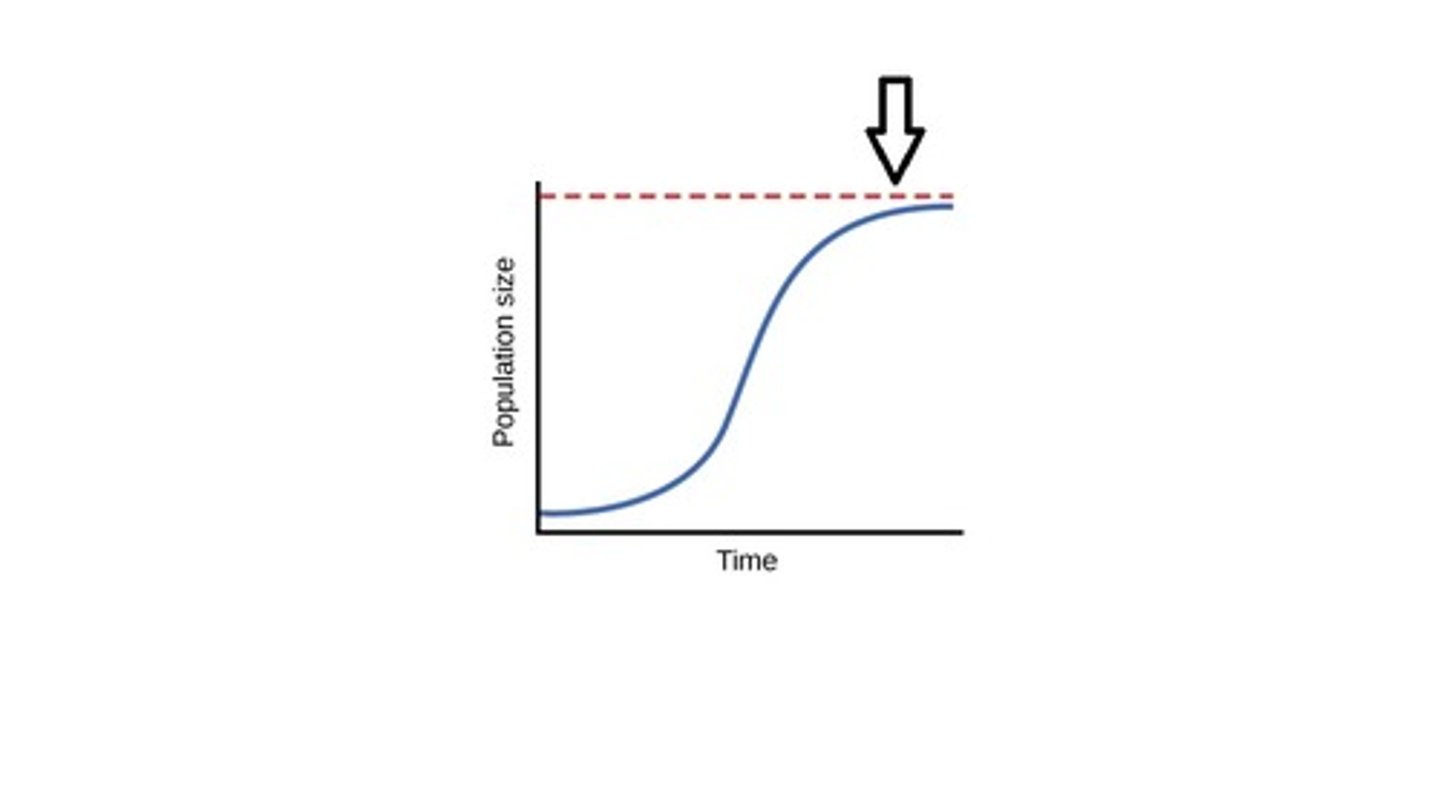
Why can carrying capacity change over time?
Carrying capacity can change due to alterations in resource availability, environmental changes, or human impact.
What are some examples of life history traits?
Examples include age at first reproduction, number of offspring, and parental care strategies.
What are opportunistic species?
Opportunistic species reproduce quickly in unstable environments.
What are equilibrial species?
Equilibrial species have slower reproduction rates and thrive in stable environments.
What type of selection is associated with opportunistic species?
R-Selection
What type of selection is associated with equilibrial species?
K-Selection
Describe the three types of survivorship curves.
Type I: high survival in early and middle life, low in old age (e.g., humans). Type II: constant mortality rate throughout life (e.g., birds). Type III: high mortality in early life, lower in adulthood (e.g., fish).
What factors allowed a rapid increase in the human population in the past 200 years?
Factors include advancements in medicine, agriculture, sanitation, and technology.
How does economic development influence population growth according to the demographic transition model?
Economic development typically leads to lower birth and death rates, resulting in slower population growth.
What is an ecological footprint?
An ecological footprint measures the environmental impact of an individual or population, indicating the amount of land and resources needed to sustain their lifestyle.
How does increasing development affect global resource use?
Increasing development raises resource consumption, leading to concerns about sustainability and environmental degradation.
How are opportunistic and equilibrial species different?
Opportunistic species reproduce quickly in unstable environments, while equilibrial species have slower reproduction rates and thrive in stable environments.