the nervous system!
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Nervous system
Made of the structures that control the actions and reactions of the body in response to stimuli from the environment
CNS stands for:
central nervous system
PNS stands for:
Peripheral nervous system
what does the cns consist of?
the brain and the spinal cord
what does the pns consist of?
sensory and motor neurons
Brain
The body’s central command organ that constantly receives impulses from all over the body
Spinal cord
A structure that allows the brain to communicate with the rest of the body
Function of the PNS
Connects the CNS to the rest of the body
Parts of the PNS
Sensory and motor
Involuntary actions
Processes that the brain controls that happen automatically (e.g. heart beating)
Voluntary actions
Processes that you can control yourself (e.g. moving arms and legs)
Main areas of the brain
Cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain where you think and problem-solve, and where memories are stored. Controls voluntary movements and senses
Cerebellum
Second largest part of the brain that processes information from your body, and allows the brain to keep track of your body’s position and coordinate movements
Brain stem
Connects the brain to your spinal cord. the medulla controls involuntary processes, such as blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, and breathing.
The spinal cord
Made of a bundle of nerves surrounded by protective bones called vertebrae
Nerves
A collection of nerve cell extensions bundled together with blood vessels and connective tissue, they’re also everywhere in the body
What does the spinal cord do?
special cells carry sensory information to the spinal cord, which carries these impulses to the brain. the brain interprets these impulses as a sensation and sends information back to the spinal cord.
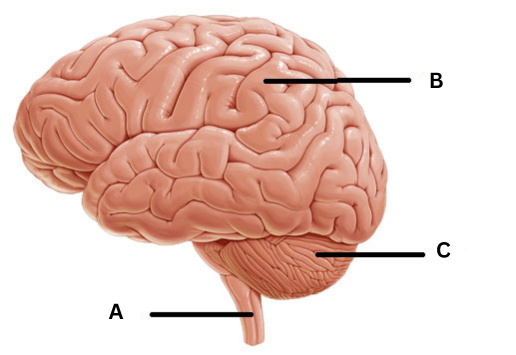
A: Brain stem, B: Cerebrum, C: Cerebellum
What are the parts of a neuron?
A large region called the cell body, a long extension called the axon, short branches called dendrites, and an axon terminal.
Dendrite
A short, branched extension of the cell body. A neuron has one, two, or multiple.
Axon
Extensions of the neuron which carry away impulses from the cell body. A neuron only has one, and they can be short or long.
Axon terminal
Where a signal is changed from an electrical signal to a chemical signal
Neurotransmitter
Chemical signal that is released into the gap between the neuron and other cells
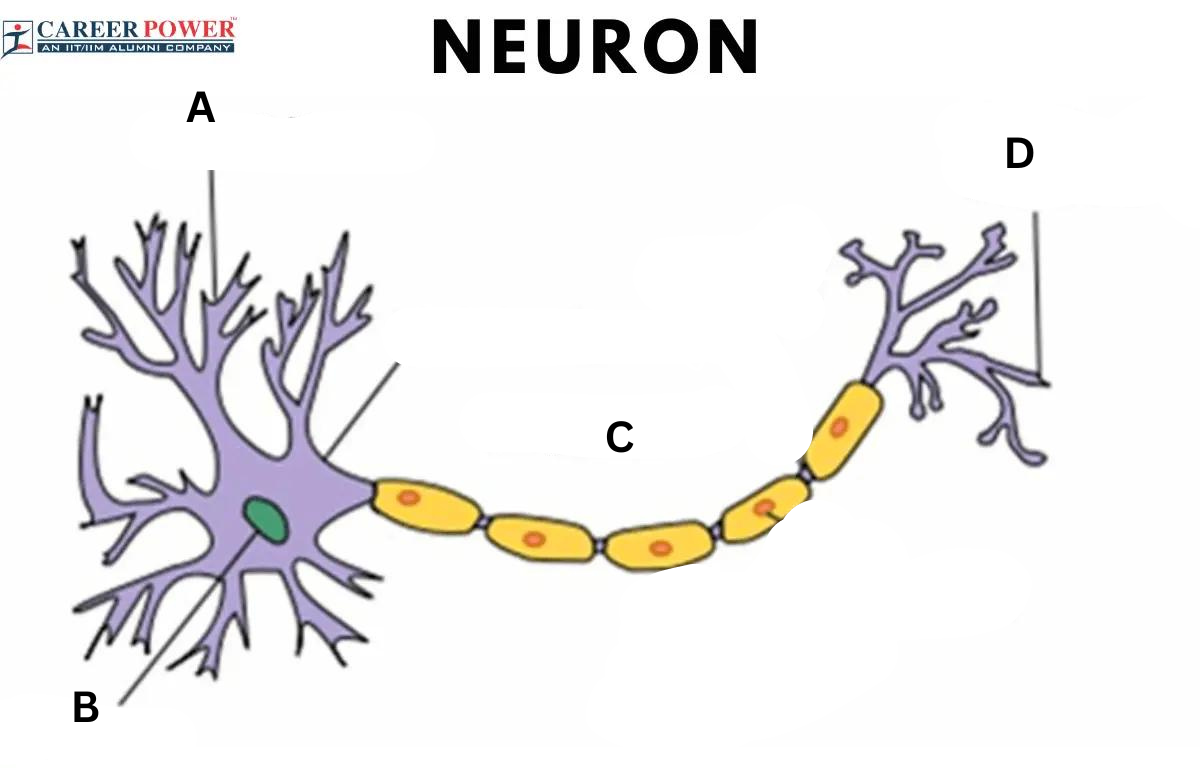
A: Dendrite, B: cell body, C: axon, D: axon terminal
Neuron
A cell that moves messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy
Impulses
Electrical messages moved by neurons
Glial cells
Cells that protect and support neurons
Function of sensory neurons
Gather information from in or around your body, and move the information to the brain.
Function of motor neurons
Move impulses from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body
Sensory organs
Eyes, mouth, ears, skin, and nose.
Cornea
A clear membrane that covers the front of the eye
Pupil
An opening in the eye where light in an object passes
Lens
An oval-shaped piece of clear, curved material in the eye
Retina
A layer of light-sensitive photoreceptor cells that change light into electrical impulses
Eardrum
A thin membrane separating the outer ear from the middle ear
Cochlea
A fluid-filled organ of the outer where vibrations make waves in the fluid.
The five basic tastes
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and savory..
Olfactory cells
Sensory receptors in the nose that react to chemicals in the air