B4 flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is photosynthesis?
The process by which plants synthesise glucose using light energy from the sun.Light energy is converted into chemical energy
Where does photosynthesis take place?
Within chloroplast in leaf palisade cells.They contain chlorophyll,a pigment which absorbs light energy
State the word and symbol equation for photosynthesis
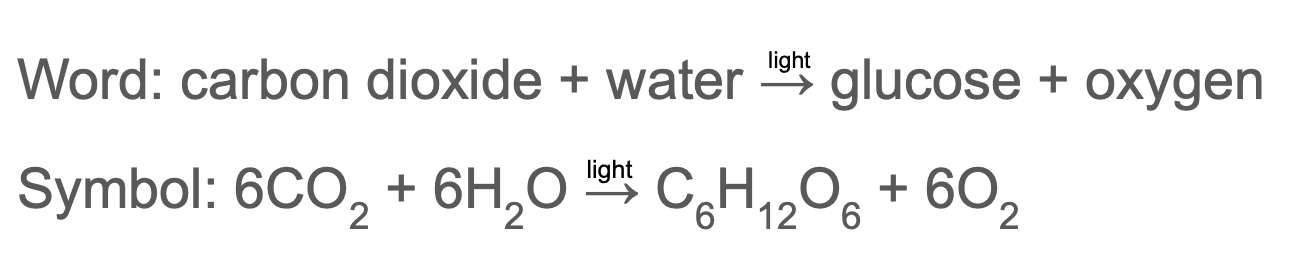
Is photosynthesis an endothermic reaction or exothermic reaction and why?
Endothermic-energy is transfered from the environment to chloroplast by light
How can you show that a plant gives off oxygen during photosynthesis?
Using a water plant,collect gas bubbles produced during photosynthesis.The gas will relight a glowing splint as it contains oxygen
Give 4 leaf adaptations which maximise the rate of photosynthesis
.Thin leaves-short diffusion path
.Air spaces-allow CO2 and 02 to leave
.Guard cells-control opening of stomata for gaseous exchange and prevent water loss
.Broad leaves-maximises surface area
What are the four main factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
.Temperature
.Light intensity
Carbon dixide conentration
.Amount of chlorophyll
How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis as the kinetic energy of particles is increased.The rate decreases past a certain temperature as enzymes become denatured
How does light intensity affect the rate of photosythesis?
Increasing the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis until another factor becomes limiting
How does carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Increasing the carbon dioxide concentration increases the rate of photosynthesis(until another factor becomes limiting)as co2 is required to make glucose
How does the amount of chlorophyll affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Decreasing the amount of chlorophyll(eg. due to lack of magnesium)decreases the rater of photosynthesis as chlorophyll is required to absorb light energy
What is a limiting factor?
An environment factor which can restrict the rate of photosynthesis eg.light intensity
Explain how you can calculate the rate of photosynthesis by measuring oxygen production
.Set up bubble potometer apparatus (pondweed in a sealed tube of water,attached to a capillary tube and a gas syringe)
.Oxygen gas produced causes the bubble in the capillary tube to move.The distance moved by the bubble is used to calculate the volume of oxygen production
How can farmers use their knowledge oflimiting factors to increase their profits?
They can control temperature,light intensity and CO2 concentration to achive the fastest possible rate of photosynthesis,leading to a greater yield.
State the law which describes the relationship between the distance of a light source from a plant and light intensity
Inverse square law- light intensity 1/distance 2
State 5 uses of the glucose produced during photosynthesis
.Respiration
.Starch for storage
.Cellulose for strength
.Amino acid and protein synthesis (combined with nitrates)
.Lipids for energy storage in seeds
What is aerobic respiration?
Anbexothermic reaction in which glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy which can be used by cells
What are the symbol equation for aerobic resiration?
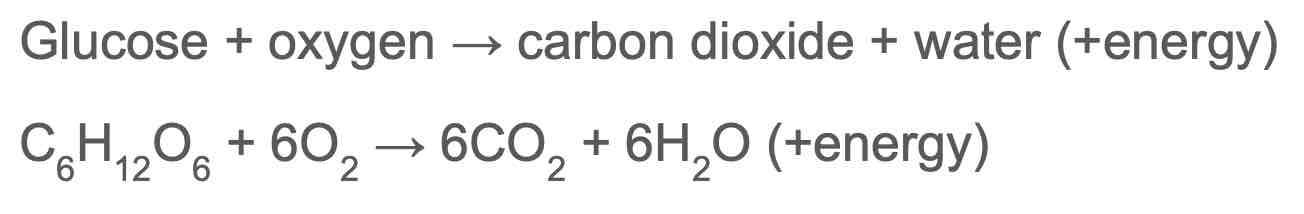
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
In the mitochondria
Why do organisms require the energy released by respiration?
.Synthesis of larger molecules
.Muscle contraction
.Maintenance of body temperature
.Active teansport
What is anaerobic repiration?
An exothermic reaction in which glucose is brocken down to release enery in the absence of glucose
What is the equation for anaerbobic repiration?
Glucose- lactic acid (+energy)
Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient that aerobic respiration?
Glucose is not completely broken down,so less energy is transferred
Why can anaerobic repsiration lead to muscle fatigue?
lactic acid 9product of anaerobic respiration) builds up in muscles,preventing efficient contraction
What is oxygen debt?
The amount of xoygen needed to convert lactic acid back into glucose after anaerobic espiration
What is fermentation?
A type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in yeast cells
What is the equation for fermentation?
Glucose-ethanol+carbon dioxide (+energy)
Why is fermentation important?
It is used in the production of bread and alcolic drinks
What are differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
.Aerobic requires oxygen;anaerobic does not
.Aerobic produces CO2 and water ;anaerobic produces lactic acid or ehtanol +co2
.Aerobic transfers a greater amount of energy
How do muscles store glucose?
As glycogen
What chnages take place when muscular aactivity increases in the body?
.Heart rate increases and areteries dilate-increases flow of oxygenated blood to muscles
.Breathing rate increases and breathing is deeper-increases the rate of gaseous exchange
.Stored glycogen is converted back into glucose
How is lactic acid transported away from the muscles?
Blood flow through the muscles transports lactic acid to the liver,where it is oxidised back to glucose
What is metabolism?
The sum of all the reactions that take place in a cell or an organism
How do cells use the energy transferred by respiration?
To continuously carry out enzyme-controlled processes which lead to the synthesis of new molecules
Give 3 examples of metaboplic reactions
.Glucose and nitrate ions into amino acids
.Photosynthesis
.Respiration