Common Diseases of the Anorectum
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is known to
affect W>M,
can be associated with urinary incontinence, rectocele, cystocele, enterocele, CF in children
constipation
and is MC at >60yo?
rectal prolapse
What type of rectal prolapse is a circumferential, full-thickness protrusion of the rectal wall → anal orifice?
complete
What type of rectal prolapse involves only the mucosa?
partial
What type of nerve injury is usually associated with rectal prolapse and incontinence?
pudendal nerve
A pt presents with complaints of abd discomfort, incomplete BMs and straining, constipation, and has noticed a little bit of stool discharge.
Upon PE you note a "mass" that prolapses through the anus and pt states it is NOT painful — What is the likely dx?
rectal prolapse
When diagnosing a rectal prolapse there must be a distinction made between ______ prolapse and ______ prolapse such as a hemorrhoid.
full thickness /, isolated mucosal
When evaluating rectal prolapse, you must distinguish between rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids. How can you differentiate between them?
Rectal prolapses have concentric rings, hemorrhoids have radial/linear folds
What is expected to be seen for a rectal prolapse on a DRE?
↓rectal tone, open anus, fullness, folds, masses
What is the mainstay of therapy for rectal prolapse?
surgical correction
What type of procedure is done on a healthy pt with a rectal prolapse?
abd procedure (better results, but HIGHER risk)
What type of procedure is done on an older pt or more frail and sick with a rectal prolapse?
perineal procedure
What are some treatments for rectal prolapse?
hydration, 25-30g fiber, biofeedback therapy, pads and taping
MAINSTAY= surgery
What occurs due to the involuntary passage of fecal material for at least 1 month with a developmental age of at least 4 years, is associated with urinary incontinence in ~50% of patients, and is seen with a higher incidence in parous women?
fecal incontinence
What anal sphincter is made of SM and has continuation o the circular fibers of the rectal wall and is INVOLUNTARY?
internal
What anal sphincter is formed in continuation with the levator ani muscles and is under VOLUNTARY control and innervated by the pudendal nerve?
external
A pt presents with what started as minor flatus and an occasional liquid stool to now inability to hold and control solid stool. Upon DRE you note reduced tone and loss of the "anal wink" reflex. --- what is the likely dx?
fecal incontinence
Loss of “anal wink” reflex in fecal incontinence indicates a neurogenic dysfunction at what levels of the sacral spine?
Loss of “anal wink” reflex (S2-4 level control)
What are some possible diagnostic tools when suspecting fecal incontinence?
Anal manometry, pudendal nerve terminal motor latency (PNTML), endoanal ultrasound
What is the GS treatment for fecal incontinence?
Overlapping sphincteroplasty
What occurs bc of Distended veins due to Low-fiber, high-fat Western diet with constipation and straining?
hemorrhoidal disease
From a visual perspective, how can you differentiate between a rectal prolapse and hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids will have a more linear appearance
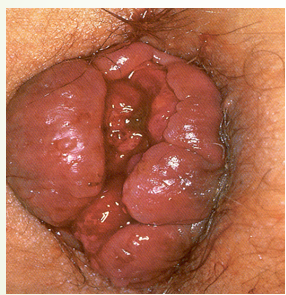
What etiology of hemorrhoids is more common, occurs below the dentate line and is PAINFUL when thrombosed?
external
What etiology of hemorrhoids occurs above the dentate line and BLEEDs?
internal
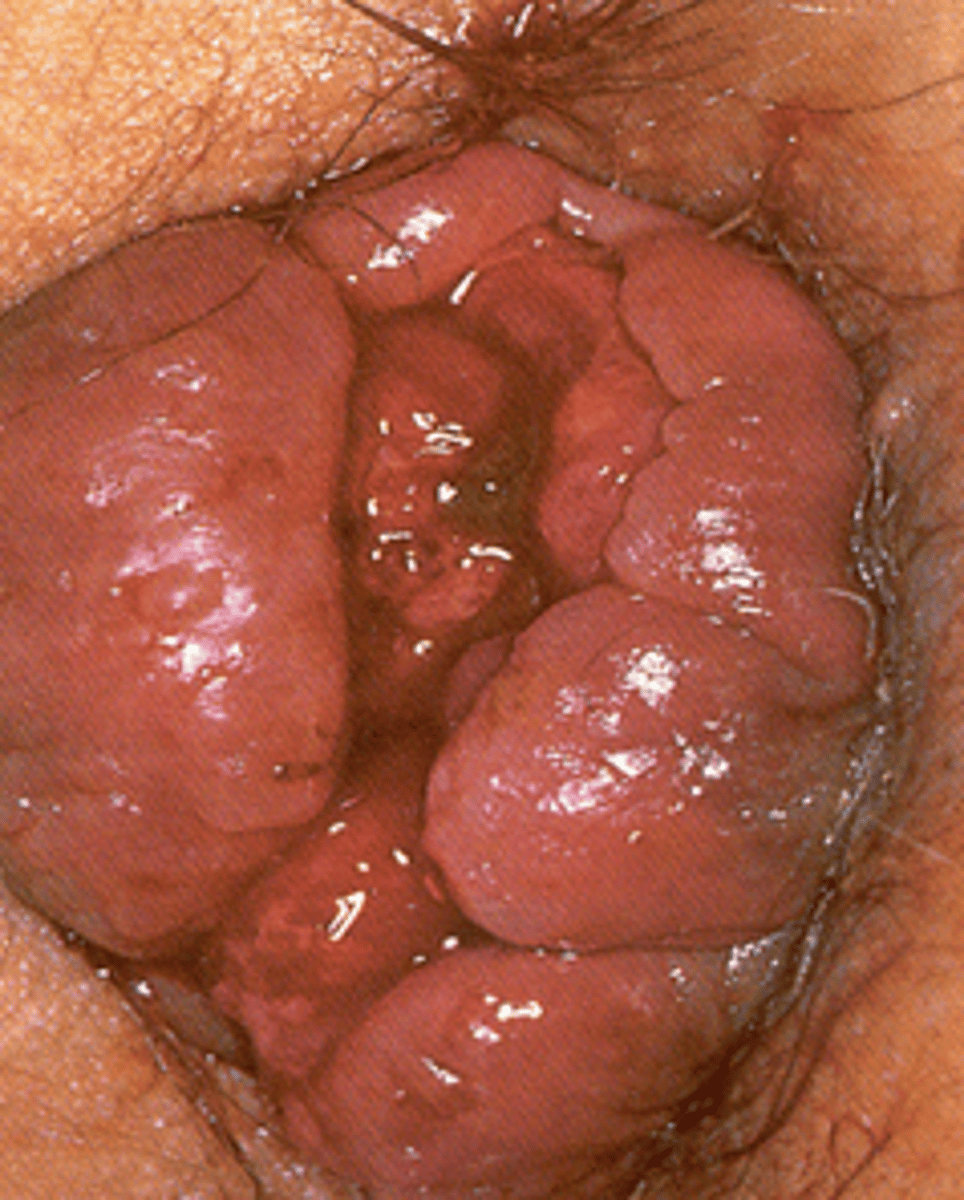
A pt presents with bleeding and protrusion. Upon PE you see the image attached. If the diagnosis is clinical --- what is the likely dx?
hemorrhoidal disease- internal
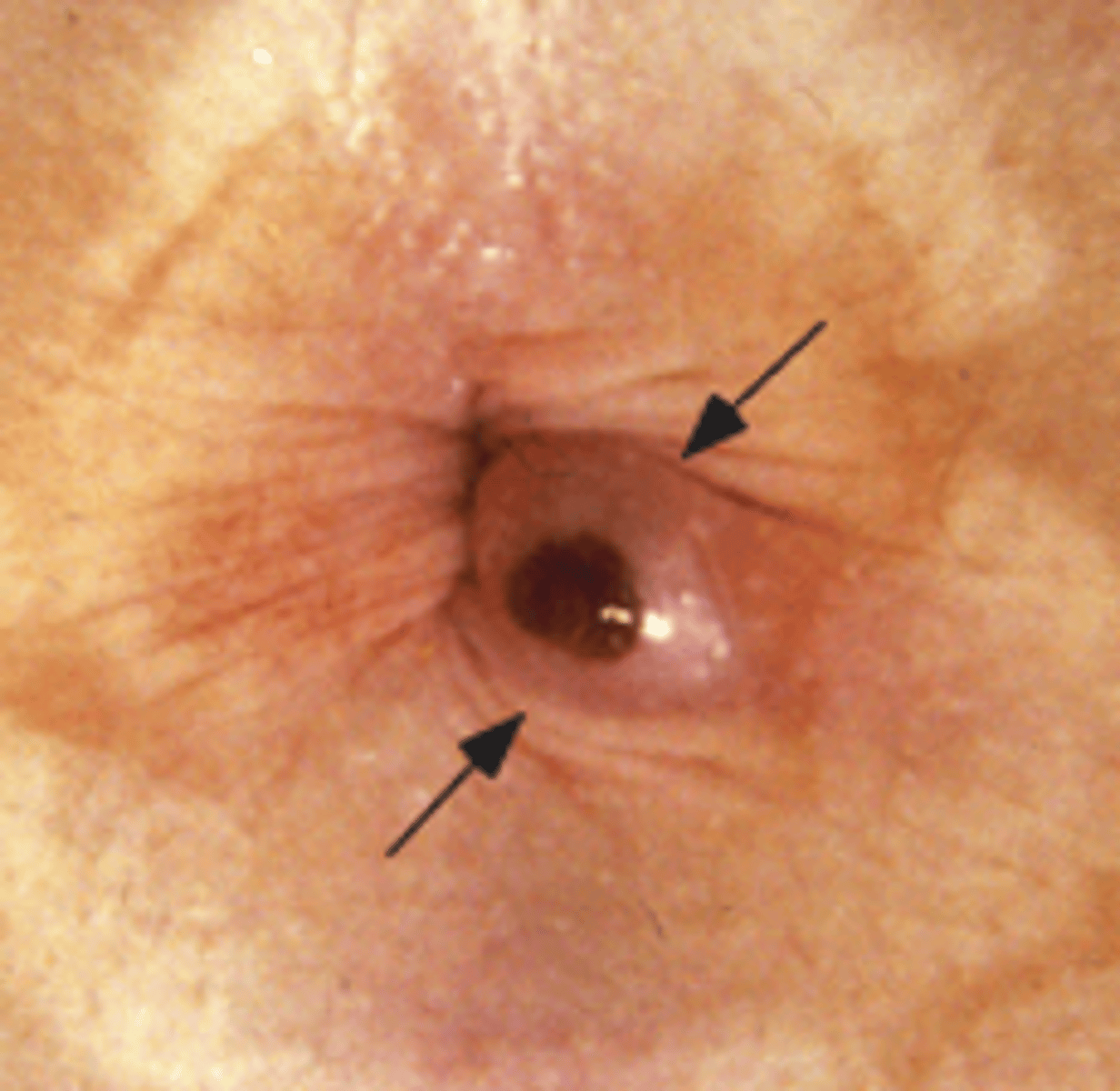
A pt presents with protrusion and severe pain → thrombosed. Upon PE you see the image attached. If the diagnosis is clinical --- what is the likely dx?
hemorrhoidal disease- external
How are painful thrombosed (external) hemorrhoids sometimes treated?
Lanced and clot is removed (I&D)
What is an abnormal fluid-containing cavity in the anorectal region resulting from infection involving the crypt glands surrounding the anal canal?
anorectal abscess
What is the MC anorectal abscess?
perianal
A MALE pt presents with perianal pain and throbbing, fever, difficulty voiding, and blood in stool. Upon PE you note erythema, swelling, and fluctuant area. On a DRE you also note fluctuance, induration, and pain.
-- What is the likely dx?
anorectal abscess
If an anorectal abscess is superficial (perianal) what is the diagnostic?
clinical
If an anorectal abscess is suspected to be a systemic infection what is the diagnostic?
leukocytosis
If an anorectal abscess is deep what is the diagnostic study used?
CT pelvis
What is the GS treatment for anorectal abscess?
I&D
simple perianal abscess maybe drained bedside
What are the possible ABX given to treat anorectal abscesses?
augmentin, or combo Cipro+Flagyl
If a patient with an anorectal abscess has continued drainage after 6-12 weeks of primary I&D of abscess, what should be considered?
FISTULA → should prompt eval for CD, LGV, rectal tuberculosis, or cancer
What occurs due to a continuation of the same processes as abscess and is a communication of an abscess cavity with an identifiable internal opening within the anal canal, and external opening in the perianal region?
anal fistula
In an anal fistula the ____ opening is most commonly located at the dentate line where the anal glands enter the anal canal.
internal
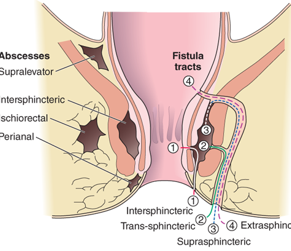
What is the MC anal fistula (which is classified by their relationship to the anal sphincter muscles)?
intersphincteric
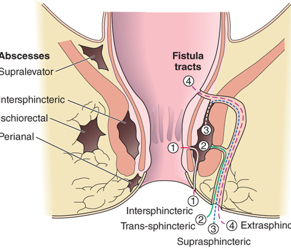
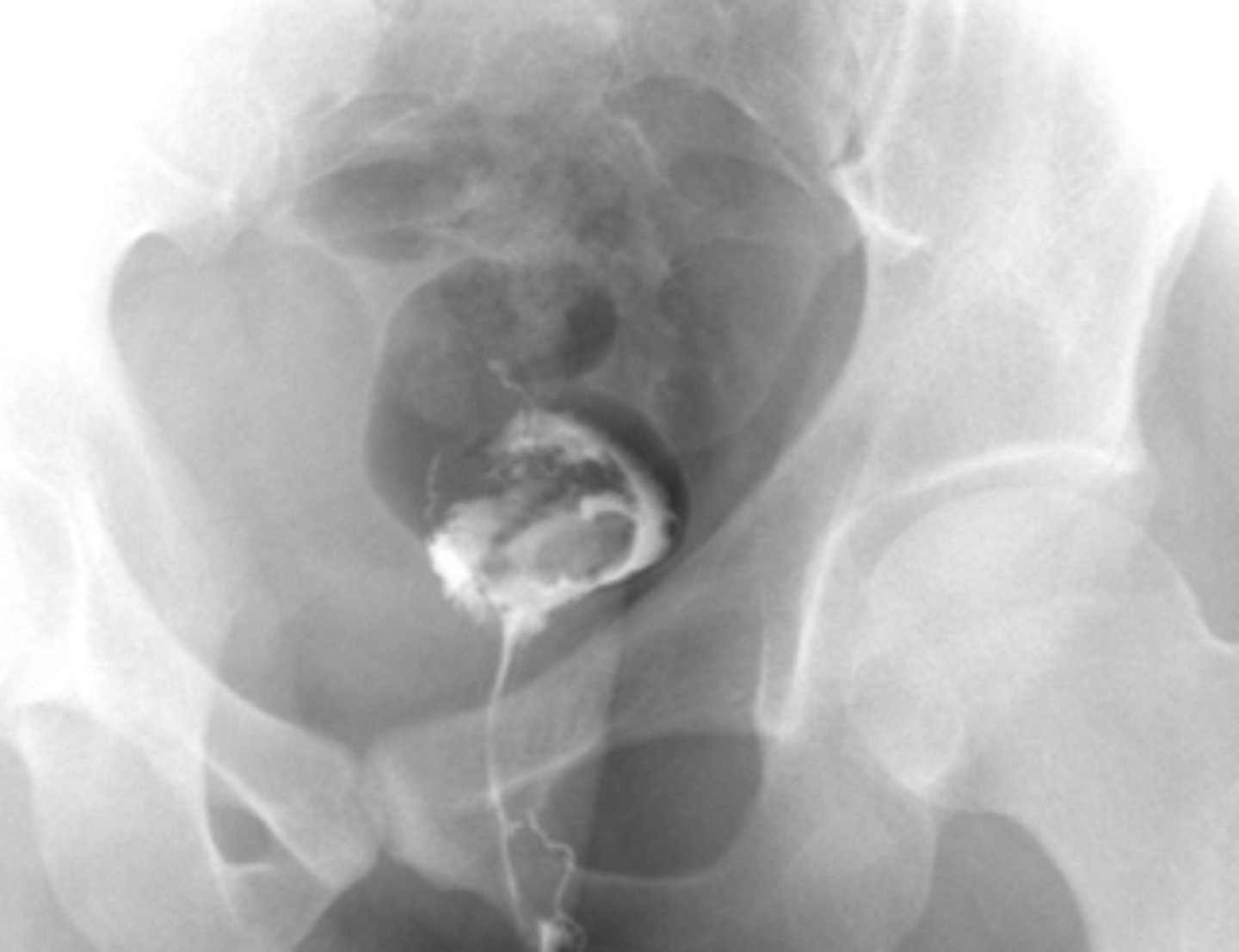
A pt presents with complaints of constant drainage from the perianal region. Upon PE you see an external opening with a dimple. The radiographic imaging is attached --- what is the likely dx?
anal fistula
What are some diagnostic tools for anal fistula?
EUA = exam under anesthesia (Anoscopy/proctoscopy will be performed)
- Alternative = MRI
- Fistulogram
What is the treatment for anal fistula
Surgery (primary or staged)!
Seton Placement- complex placed during EUA (closed loop- keep things open and allow for healing and drainage)
What are linear or rocket shaped ulcers <= 5mm and are the MCC of rectal bleeding in infancy?
anal fissuer
What area of the anal canal is commonly affected due to anal fissures?
posterior midline anal canal
fissures NOT found here should raise suspicion for TB, syphilis, Crohn’s, malignancy
A pt presents with severe tearing pain during a BM that lasted several hours after. She stated it was bright red (BRBPR). Upon PE you see cracks in the epithelium. -- what is the likely dx?
anal fissue
(BPBPR = bright red blood per rectum)
A young child presents with parents complaining of stool withholding and likely constipation. Upon PE you see cracks in the epithelium. -- what is the likely dx?
anal fissue
What is the general tx for anal fissure that has 45% success?
Stool softeners, increased dietary fibers, Sitz baths
- topical anesthetics
What are the treatment options for chronic fissures (those present >6 weeks with 50-80% success)?
Nitroglycerin 0.125-0.4%
Diltiazem 2%
All ointments AAA 1cm BID x 4-8 wks
Botulinum toxin 20 units internal sphincter