Chapter 3: Movement into and out of cells
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
diffusion
the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration (i.e. down a concentration gradient), as a result of their random movement
energy for diffusion comes from
the kinetic energy of random movement of molecules and ions
importance of diffusion of gases and solutes in living organisms
without it, molecules which are needed for life, for example glucose and oxygen for respiration, would not be able to get to the places they are needed, water is needed as a solvent
factors that influence diffusion
surface area
temperature
concentration gradient
distance
limiting factor diffusion; surface area
the bigger a cell, the smaller its surface area:volume ratio is, this slows down the rate at which substances can move across its surface. cells adapted for diffusion have larger surface areas, e.g. root hair cells
limiting factor diffusion; temperature
the higher the temperature, the faster molecules move, meaning there will be more collisions against the cell membrane
limiting factor diffusion; concentration gradient
the greater the difference in concentration on either side, the faster movements will occur, because on the higher concentration side, there’ll be more collisions.
limiting factor diffusion; distance
the smaller the distance the molecules have to travel,the faster transportation will happen.
osmosis
the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane
role of water as a solvent in organisms (osmosis)
digested food molecules in the alimentary canal need to be moved to cells, which can’t be done without water
toxic substances (e.g. urea) in excess of requirements (e.g. salt) can be dissolved, making them easier to excrete
dissolved substances can be easily transported around the organism e.g. xylem of plants or dissolved food molecules in the blood
how does water moves into and out of cells?
diffuses through partially permeable membranes by osmosis
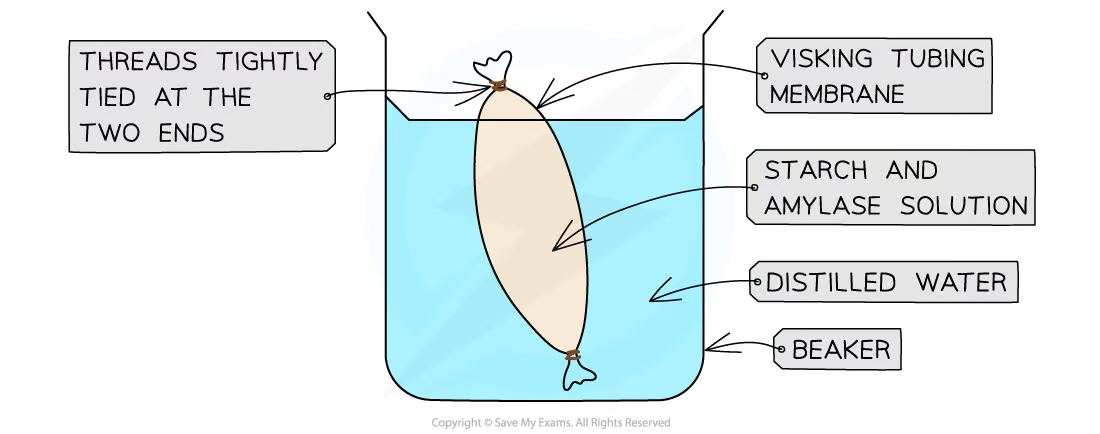
osmosis using materials such as dialysis tubing
dialysis tubing: non- living partially permeable membrane (aka visking tubing)
notice whether H2O levels go up or down, shows whether osmosis happened or not
the effects on plant tissues of immersing them in solutions of different concentrations
GAINS MASS: H2O moved into the cell via osmosis, solution is more dilute than tissue
LOSES MASS: H2O moved out of the the cell via osmosis, tissue is more dilute than solution
NO CHANGE: no net movement of H2O, concentration must be equal
plants are supported by (osmosis)
the pressure of water inside the cells pressing outwards on the cell wall
effects on plant cells of immersing them in solutions of different concentrations
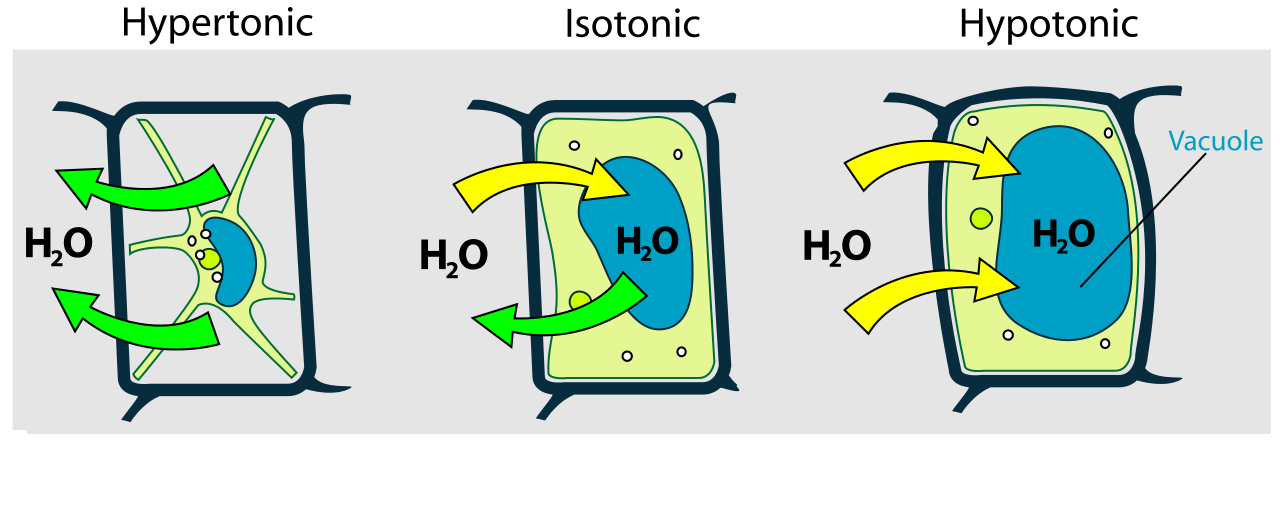
HYPOTONIC SOLUTION: cells have lower H2O potential than solution, net movement into cells of H2O into cell, cell may burst, no cell wall for turgor pressure
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION: cells have higher H2O potential than solution, net movement out of the cell, cell is shrivelled
ISOTONIC SOLUTION: H2O potential is equal, no net movement in or out of the cell
importance of water potential and osmosis in the uptake and loss of water by organisms
high H2O potential: H2O moves into the cell via osmosis, H2O molecules push the cell membrane against the cell wall, increasing turgor pressure, cell becomes turgid
low H2O potential: H2O molecules move out of the cell via osmosis, making the cell flaccid, cell may become plasmolysed, cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall
active transport
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (i.e. against a concentration gradient), using energy from respiration
importance of active transport
a process for movement of molecules or ions across membranes, including ion uptake by root hairs
who moves molecules or ions across what during active transport?
protein carriers, across a membrane