Classification of Tissues
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
2
New cards
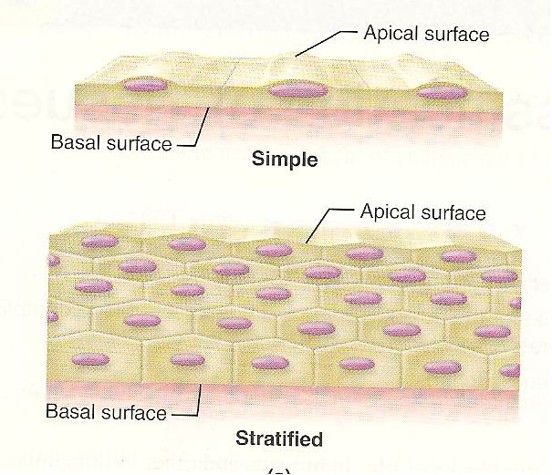
Simple and Stratified
Classification
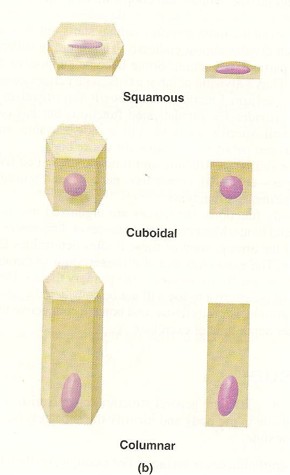
3
New cards
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar
Shapes
4
New cards
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar, Pseudostratified
Simple
5
New cards
Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar, Transitional
Stratified
6
New cards
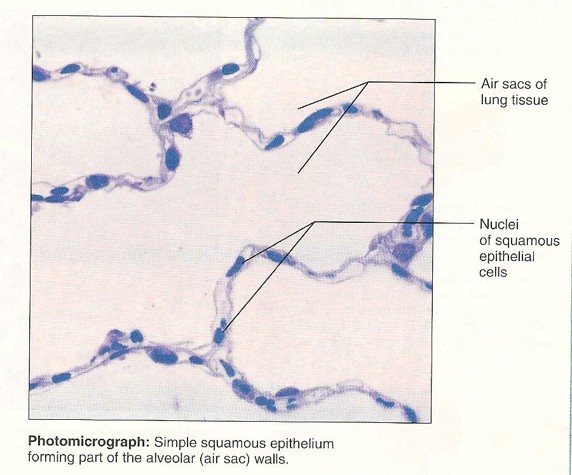
Simple Squamous
7
New cards
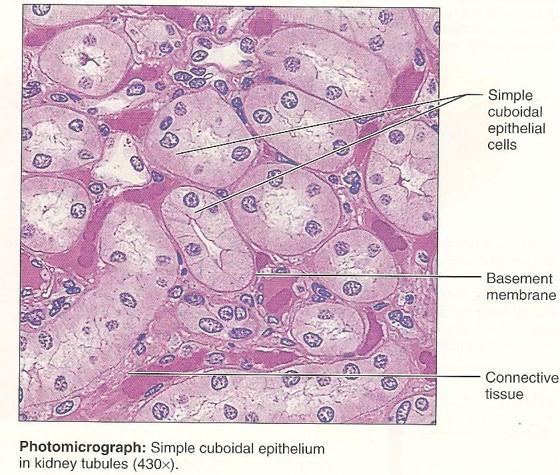
Simple Cuboidal
8
New cards
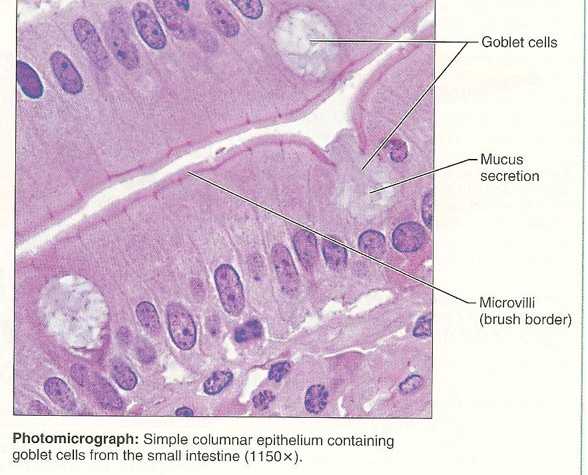
Simple Columnar
9
New cards
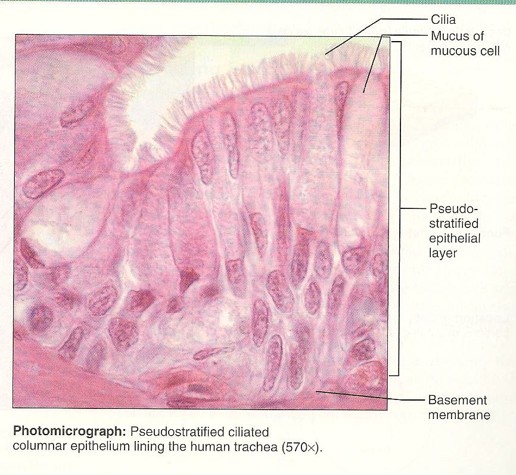
Pseudostratified
10
New cards
Stratified Squamous
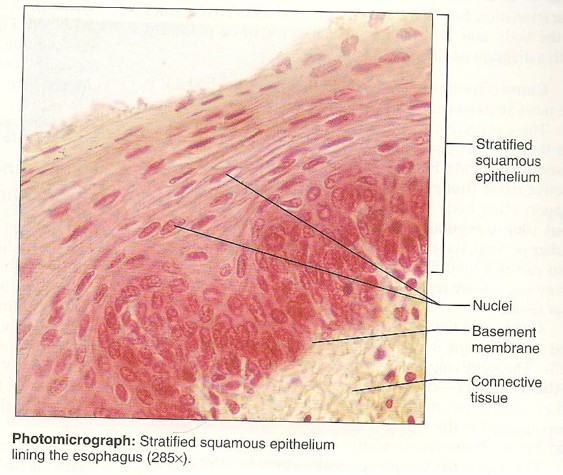
11
New cards
Stratified Cuboidal
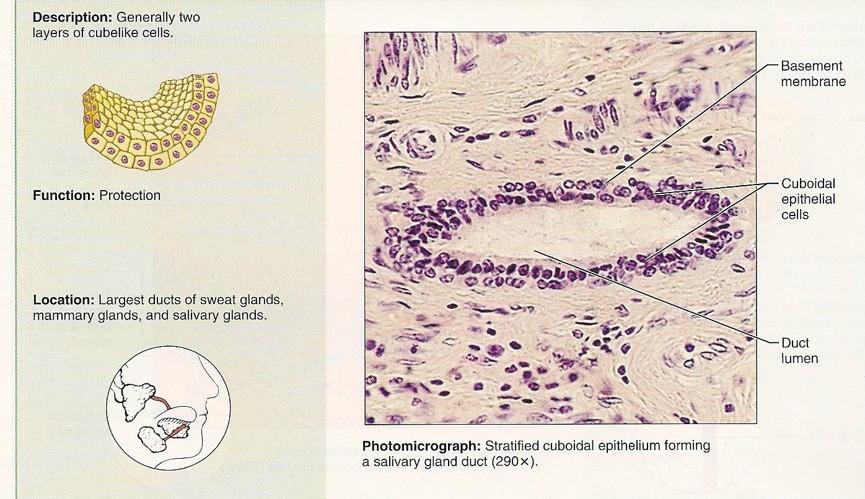
12
New cards
Stratified Columnar
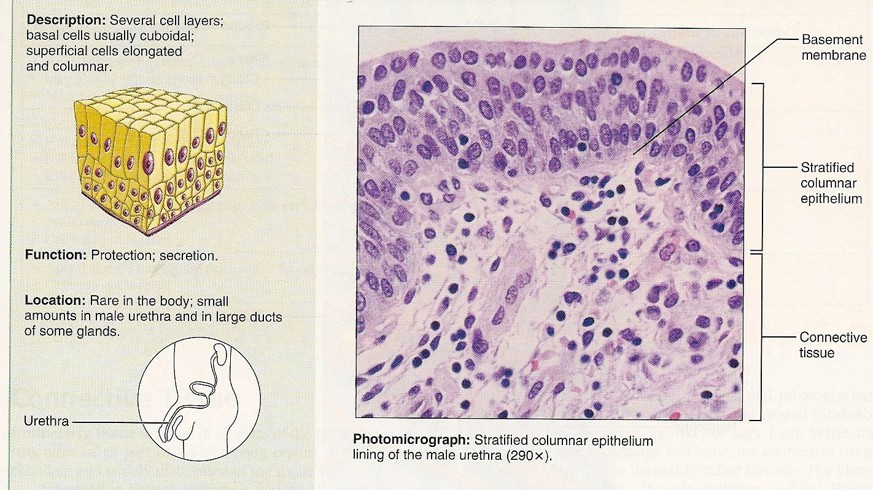
13
New cards
Transitional (urinary bladder)
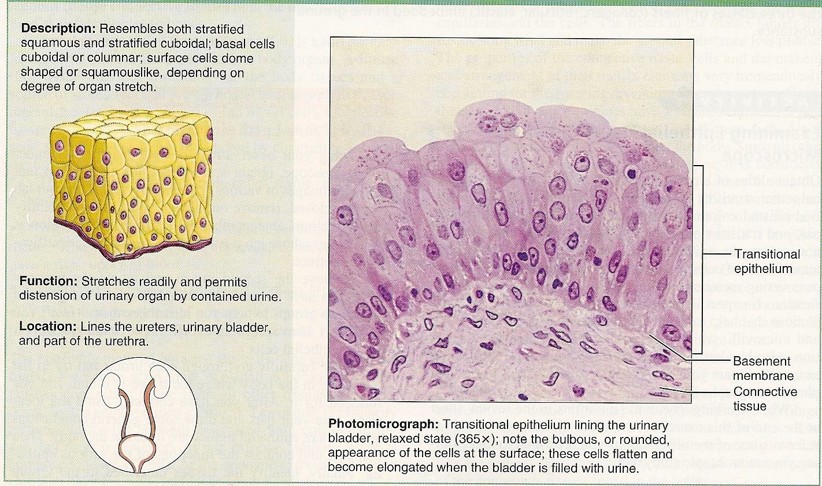
14
New cards
Connective Tissue
Support
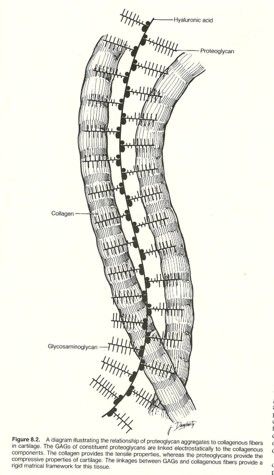
15
New cards
Extracellular matrix
secreted with ground substance (glycoproteins and polysaccharides) and fibers - GAGs, proteoglycan and adhesive glycoproteins
16
New cards
Proteoglycans
Help hold tissues together like a net to attract the immune system
17
New cards
Loose and Dense
Connective Types
18
New cards
Areolar, Adipose, Reticular
Loose Types
19
New cards
Areolar
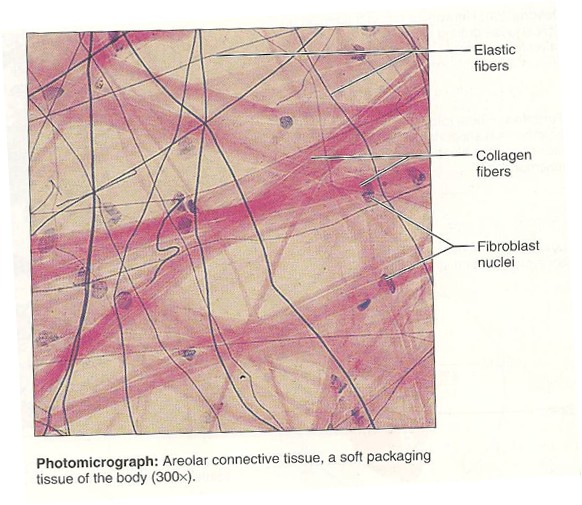
20
New cards
Adipose
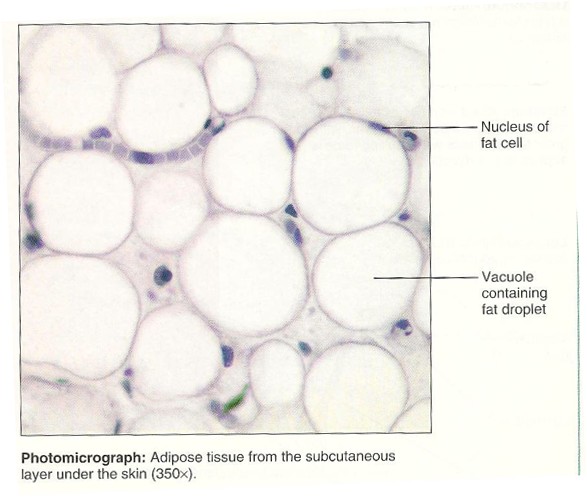
21
New cards
Reticular
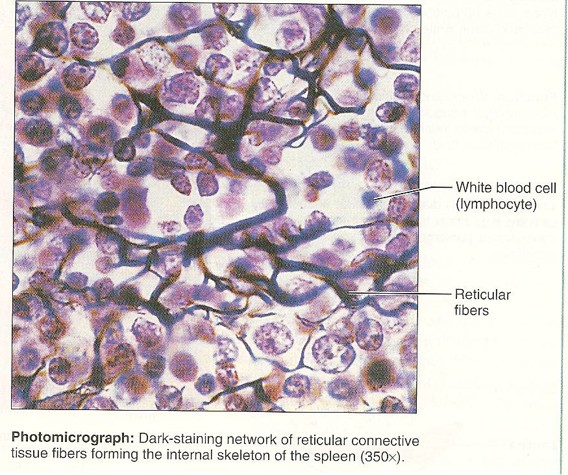
22
New cards
Regular and Irregular
Dense types
23
New cards
Dense Regular
Tendons and ligaments and Yellow Elastic Tissue
Found in wavy sheets - tends to tear
Found in wavy sheets - tends to tear
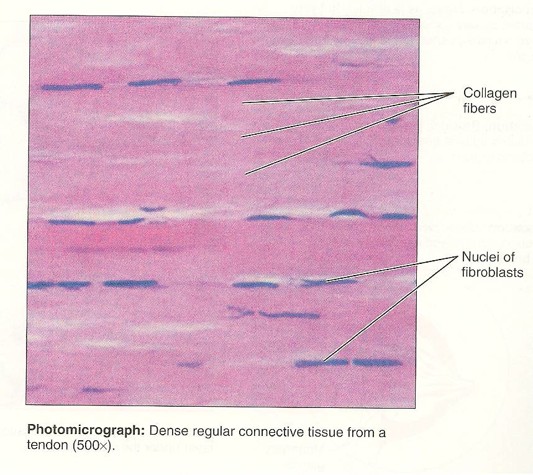
24
New cards
Dense Irregular
More free movement - no tearing - resist stretching
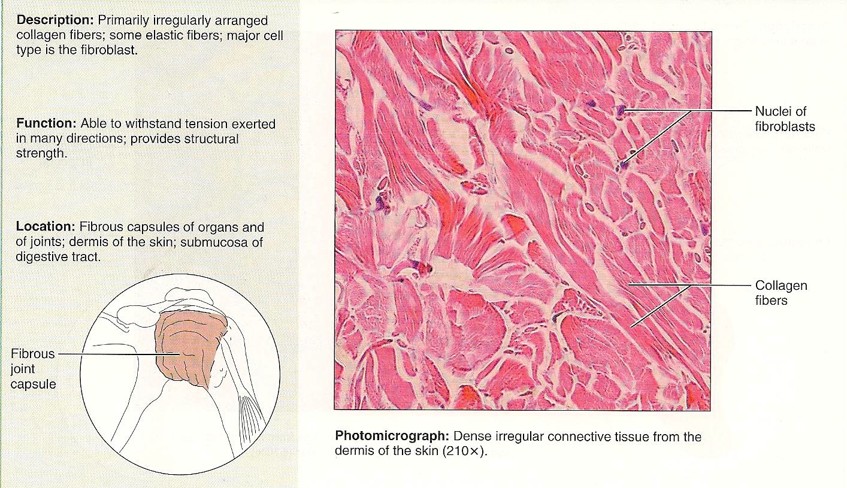
25
New cards
Hyaline, Fibro, Elastic
Cartilage types
26
New cards
hyaline cartilage
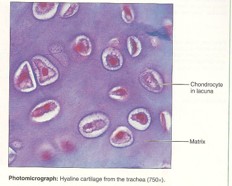
27
New cards
fibro cartilage
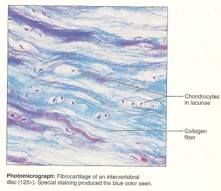
28
New cards
elastic cartilage
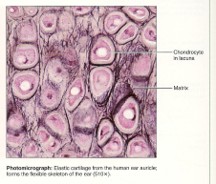
29
New cards
Compact and spongey
Bone types
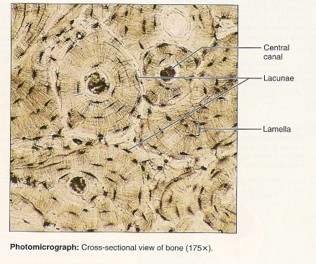
30
New cards
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Muscle types
31
New cards
Skeletal
has thin striations
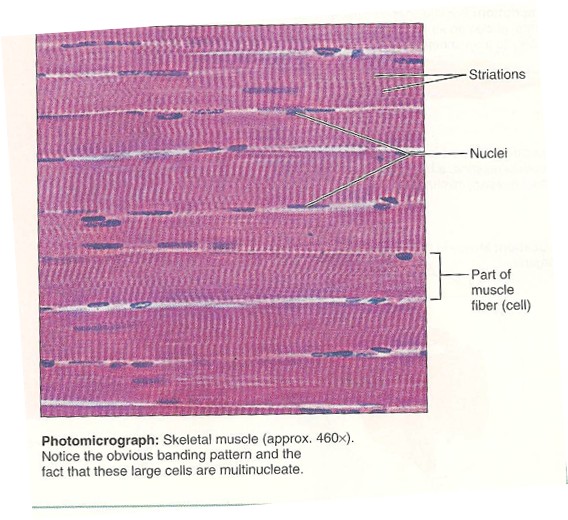
32
New cards
Cardiac
striation not long but branching - dark striations and one or two nuclei
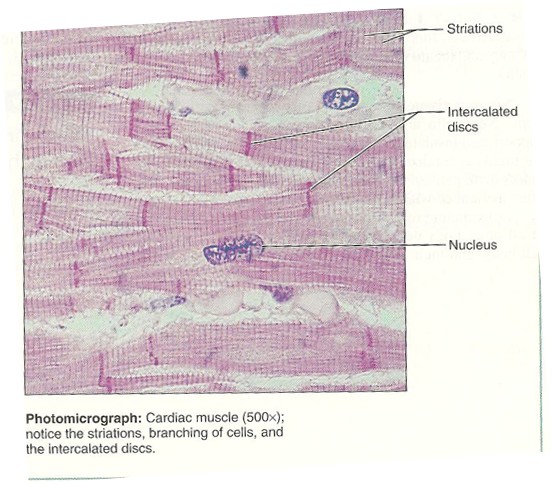
33
New cards
Smooth
No striation - spindle and fuseform shape
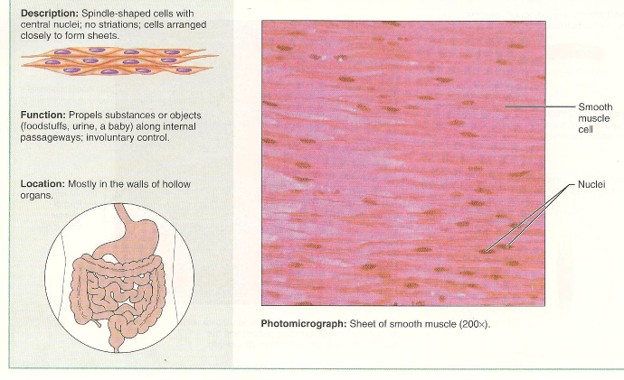
34
New cards
Nervous Tissue
Neurons and Neuroglia
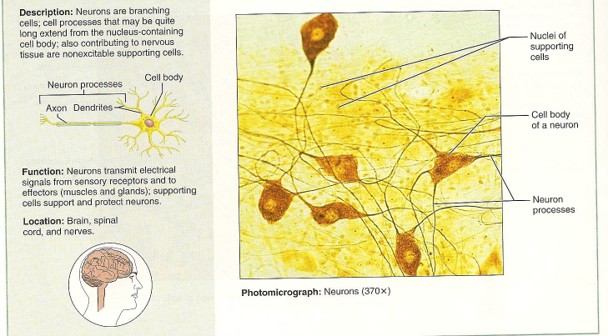
35
New cards
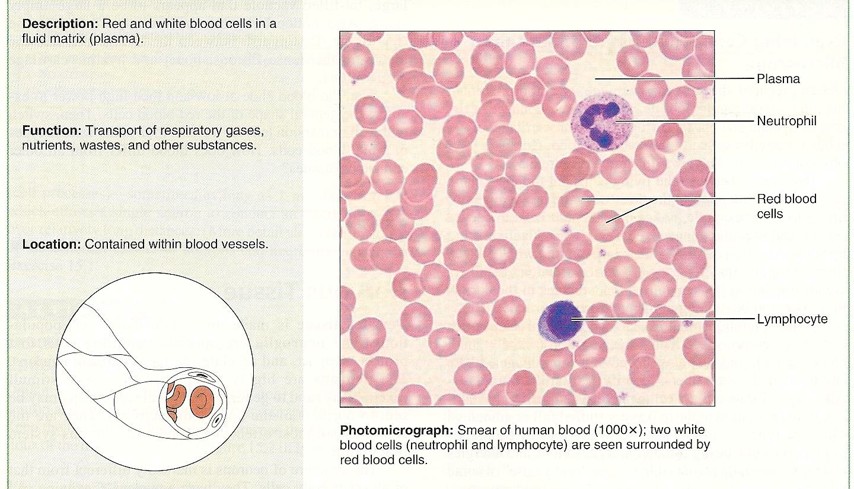
Blood Tissue