L7 Natural selection and adaptation
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
mutation
ultimate source of varitation
In a population that has three alleles at locus A (A1, A2, A3) the frequency of allele is 0.4 and the frequency of allele A3 is 0.5 what is the frequency of allele A2
0.1
what do these equations calculate?
A) p + q = 1
B) p² + 2(pq) + q² = 1
A) allele frequency of parents, B) genotype frequency of offspring
Brown fur allele B is dominant to the grey fur allele b. In a population of 100, 75 have brown fur. what is the Allele frequency of b? assume the population is in HW equilibrium
0.3
0.5
0.7
0.25
0.5
p² = B = 0.75
q² = b = 0.25
allele frequency is sqrt 0.25
Though important for some highly social species, cultural evolution is not a major contributor to evolutionary change. Why?
not all species have culture
culture can be variable within species
culture is not consistent across species
culture does not have a genetic component
culture does not have a genetic component
Evolution by natural selection occurs only traits are
disadvantageous
heritable
advantageous
advantageous in a certain environment
Heritable
What is natural selection
differential reproductive success (fitness) of biological entities that differ in one or more characteristics
variation in phenotype
differential fitness associated
heritability of phenotypes
evolution and natural selection
evolution by natural occurs when heritable variations leads to change in populations over generations
natural selection is not synonymous with evolution
change in allele frequency in allele frequencies over time
evolution is change in allele frequency in a population over generations
not number of alleles
Natural selection leads to non random changes in allele frequency
Natural selection and Chance
Natural selection is the nonrandom change in allele frequency over time
other processes cause evolutionary change through chance changes allele frequency
How are neutral alleles affected by selection
Neutral alleles are not affected by selection
Neutral alleles will increase through selection, but only if they are beneficial
Neutral alleles will increase by selection only in certain environments
Neutral alleles will decrease by selection, because they are not beneficial
Neutral alleles are not affected by selection
they don’t affect fitness
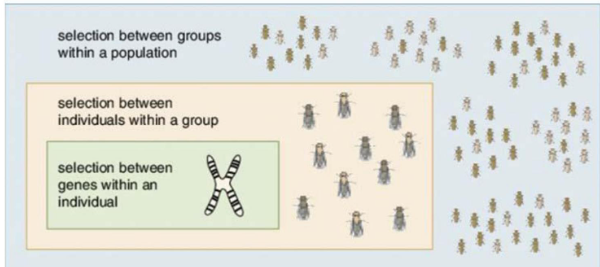
levels of selection
genes
cell types
individual organisms
populations (highly controversial)
Biological fitness
survival and reproductive success
gene fitness
more copies of that allele in the next generation
copies of gene (allele) in the next generation
selfish genetic elements
fitness of gene does not (necessarily) contribute to fitness of the organism the gene is in
wants to be reproduces as often as possible, often at the detriment of organisms the gene is found in
eg transposable elements
meiotic drive/segregation distortion
this occurs when selfish genetic elements segregate into gametes more than expected by segregation
individual fitness
number of offspring in the next generation
occurs at a higher level than selection among genes
however, this can still be considered at a genic level
when an individual experiences reproductive success at least half of their genome is being passed to the next generation
selfish gene hypothesis
fitness at the individual level only serves to propagate the alleles associated with that fitness
Altruism - a fitness conundrum
altruistic behaviors are those that benefit another individual, often at the expense of their own fitness
if altruistic behaviors decreases personal fitness, so how does it evolve
evolves by kin selection
Kin selection
occurs by increasing kin fitness
and individual is increasing the fitness of the alleles that they share with that relative
this reinforces the idea of the selfish gene
group fitness
survival of population to the next generation
group selection
proposes that one population as whole can be more fit than another population of different genetic compostition
Group selection was originally proposed to what
explain altruistic behavior
though individual cheaters have greater fitness, but altruistic population have a greater fitness as a whole
sometimes altruism doesn’t win
this is because individuals selection works much faster than group selection and therefore has a much stronger evolutionary force
it is agreed that group selection
has little impact on evolutionary change
How does kin selection allow for altruism to evolve?
selection is acting on the alleles: alleles than make you altruistic have pleiotropic effects that also make you super fertile.
selection is acting on the individual: the individual who is altruistic is more likely to have higher fitness.
selection is acting on the alleles: related individuals share alleles and when one individual experiences fitness, their shared alleles experience fitness
selection is acting on the individual: individuals who sacrifice for others are protected by the group and get access to more resources
selection is acting on the alleles: related individuals share alleles and when one individual experiences fitness, their shared alleles experience fitness
multilevel selection theory
adaptation is the process
by which, over time, organisms are altered to become better suited to their environmenst - this process is natural selection
an adaptation is a characteristic
that makes organisms better suited for their environment that evolved through natural select
adaptations _____ arise through natural selection; natural selection does ______ result in adaptations
always; not always
Exaptation/preadaptation
adaptation of an existing structure for a different, completely new, adaptive function
many evolve from nonadaptive traits
exaptation vs adaptation
exaptation:
feather evolves an adaptive function other than the original function
not all birds with wings can swim = unique function
adaptation:
a new trait evolves an adaptive function
wings have evolved into unique structures (flippers) for new adaptive function
selection for
selection for a trait implies the feature caused the organism to have higher fitness
the functio of this trait is to incraese fitness
selection of
selection for one trait often causes incidental selection of another trait
the increase of this trait is a side effect or selection for the correlated trait (hitch hiking)
Recognizing adaptations
not every trait is an adaption
a trait could be
a consequence of physics or biochemistry
evolved by another mechanism (eg. genetic drift)
correlated with an adaptation (selection of vs for)
a consequence of phylogenetic history
for this reason, we should not assume a trait is an adaptation unless we have evidence to support this conclusion
The long sharp beak of the kea evolved for cracking seeds. As the kea spent more time exposed to humans it began to use this same beak (no modification) to pick flesh from livestock and wreak all kinds of havoc in human populations.
In this instance the beak of the kea is considered
an adaptation (and nothing more)
an exaptation/preadaptation
none of the above. the beak is not adaptive in this instance.
an exaptation/preadaptation
Which of the following is an example of an exaptation/preadaptation
Cats evolved retractable claws from non-retractable claws, helping them hunt more efficiently.
Angiosperm use modified leaves, called flower petals, to attract pollinators
The giraffe's long neck evolved via male-male competition (sexual selection). They now use their long necks to feed from taller vegetation.
Cacti thorns are modified leaves that serve to protect the cacti from herbivory and reduce water loss.
The giraffe's long neck evolved via male-male competition (sexual selection). They now use their long necks to feed from taller vegetation.
Trade-off
existence of both fitness benefit and fitness cost for a specific trait
can also be though of as a compromise between two traits that cannot be optimized simultaneously
natural selection is constrained by what
genetic variation
without heritable variation, new and potentially beneficial traits cannot arise and be selected for
lack of genetic variation also explains the retention of non-adaptive traits
which of the following is a fitness trade-off
In some hornbill species, the male helps seal the female in a tree with her nest until the young are ready to fledge.
Hummingbirds are the best pollinators of certain flowers, but bees are the best pollinators for orchids.
The strong, thick beak of a woodpecker helps it find insects in trees.
Turtle shells provide protection but are heavy and burdensome when moving.
Turtle shells provide protection but are heavy and burdensome when moving.