spine - TMJ
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
TMD signs/sxs
- jaw/ear pain
- jaw clicking/locking
- pain with chewing
- facial pain
- headaches
- dizziness
- tinnitus/hearing loss/ear fullness
microtrauma to the jaw
- nail biting
- pencil chewing
- chewing gum
- teeth clenching
- bruxism (grinding)
what systemic disease may contribute to TMD
Marfans syndrome
temporalis action
- elevation
- ant fibers: protrude
- post fibers: retrude
- ipsilateral lateral deviation
masseter action
- elevation
- protrusion
- ipsilateral lateral deviation
medial pterygoid action
- elevation
- protrusion
- contralateral lateral deviation
lateral pterygoid action
- protrusion
- contralateral lateral deviation
- superior head: eccentrically controls disc with closing
- inferior head: assists with opening
suprahyoids assist with
depression and retrusion
suprahyoids can only work is
infrahyoidd are stabilizing the hyoid bone
hyoid is at the same level of what vertebrae
C3
superior vs inferior articulation of TMJ
- superior: superior disc/articular eminence
- inferior: condyle and inferior aspect of disc
articular disc attachments anterior vs posterior
- anterior: superior head of lateral pterygoid and joint capsule
- posterior: bilaminar retrodiscal tissue
during phase 1 of opening the condyle ______. during phase 2 the condyle ______
- rotates
- translates
kinematics of mandibular retrusion/protrusion
translates posterior/anterior
R lateral deviation kinematics
- R condyle rotation
- L condyle anterior translation
(ipsilateral rotation, contralateral translation)
what muscles are working during opening
- lateral pterygoid (inferior head)
- digastric
- suprahyoids
what muscles are working during closing
- temporalis
- masseter
- medial pterygoid
*lateral pterygoid superior head eccentrically controls disc with closing
muscles working during lateral deviation
- ipsilateral: temporalis & masseter
- contralateral: lateral & medial pterygoid
muscles during protrusion
- bilateral medial & lateral pterygoids
- anterior fibers of temporalis
muscles during retrusion
- posterior fibers of temporalis
- digastric
- hyoid muscles
what branch of trigeminal innervates muscles of mastication?
mandibular
what questions should you ask during hx for TMD?
- does moving the jaw alter sxs
- jaw locking or catching?
- clicking, popping?
- crepitus?
reciprocal click suggests
anterior disc dislocation that is relocating
if someone has reciprocal click the opening click occurs because of _____. the closing click occurs because of ______
- open: disc back on condyle
- close: disc dislocates anteriorly
what is "closed lock"
severe limited opening due to abnormal position of disc being in front of the condyle (anterior disc displacement without reduction)
- progression of anterior disc dislocation w/ relocation
retrodiscal tissue can remodel to become
a pseudodisc
what is "open lock"
- extreme mouth opening
- disc is POSTERIOR
observation for TMJ pt
- facial asymmetry (distance from eye to mouth = distance from nose to chin)
- malocclusions (crossbite, overbite, overjet)
- posture (resting position, FHP)
what is the resting position of TMJ
- tongue on roof of mouth
- opening btwn teeth (freeway space: 2-4 mm)
FHP causes a ____ force on the jaw
retrusive
what causes C-curve
joint hypomobile on side of deviation
what causes S-curve
muscular imbalance or displacement of condyle around disc, or pain
normal mandibular lateral deviation
8-11mm (up to 15mm)
mandibular distraction
- head stabilized against PT
- thumb placed intra-orally on bottom molars
- hand under chin serving as pivot point
- gently apply downward force
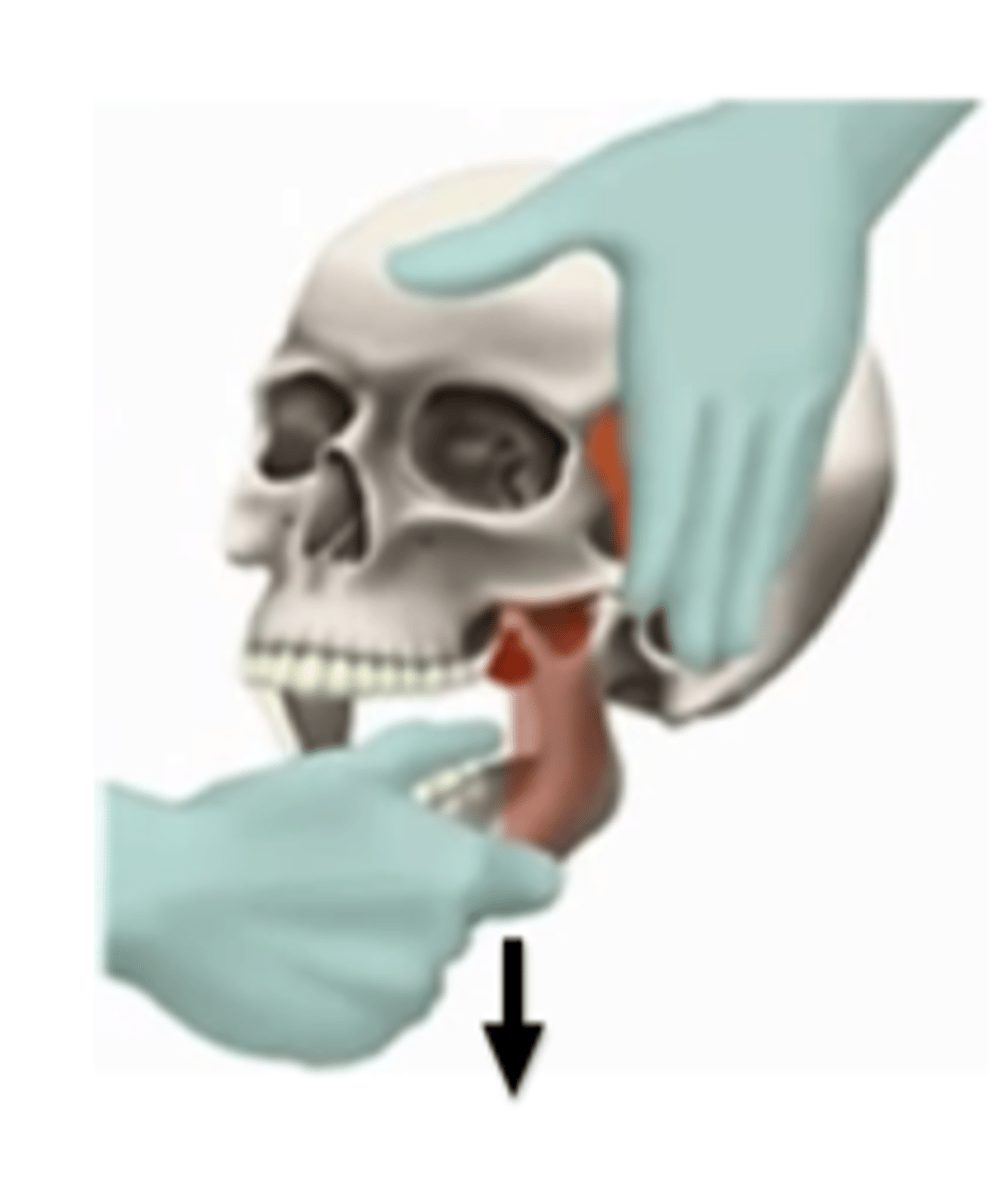
mandibular anterior glide
- head stabilized against PT
- thumb placed intra-orally on bottom molars
- gently distract then pull anteriorly
(opening, protrusion)
mandibular medial glide
- mouth is open
- stabilizing hand on limited side
- mobilizing hand on normal side
bite test/dynamic loading
- patient bites down on tongue depressor or cotton roll unilaterally
- pain on ipsilateral side = muscle
- pain on contralateral side = jointq
disc displacement without reduction is characterized by opening of --mm or less
40
arthritis in TMJ
- joint pain and crepitus
- bite test positive contralaterally
- pain/stiffness
- capsular pattern [limited opening]
what will you find if someone has a 1 sided capsular adhesion
- opening less than 40 mm (C-curve)
- limited contralateral lateral excursion/translation
- protrusion with with deflection toward affected side
what will you find if someone has a masseter or temporalis problem
- palpation reproduces sxs
- bite test is positive same side
- mouth opening painful because of stretch
- pain with resisted iso of closing
*confirm lateral excursion and protrusion not limited
if lateral pterygoid is the problem then pain is reproduced with resisted
protrusion
does someone have an upper or lower cervical problem if they have cervicogenic headaches
upper
with cervicogenic headaches, there may cervical trigger point referral from
- suboccipitals
- scalenes
- SCM
what motion do you lose if you have a TMJ replacement
lateral deviation
rocobado's 6x6 progrsm
1. tongue resting position
2. controlled TMJ rotation on opening
3. mandibular rhythmic stabilization
4. upper cervical distraction
5. cervical axial extension
6. shoulder girdle retraction
1. tongue resting position
2. controlled TMJ rotation on opening
3. mandibular rhythmic stabilization
4. upper cervical distraction
5. cervical axial extension
education for TMD
- "rest" the TMJ
- soft foods, chew on affected side
- protected yawn
- habit awareness and modification
- avoid prone (compresses TMJ & cervical stress)
education - RTTPB
- relax
- tongue up
- teeth apart
- posture
- breath
occlusal appliances change the contact of
the posterior teeth
if someone is having neurological sxs in jaw then consider...
trigeminal neuralgia
jaw jerk reflex tests what
masseter & temporalis - closing