Photosynthesis
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Autotrophs OTHER THAN plants
Protists and some bacteria
What do plants make as their source of food?
Plants make carbohydrates as their source of food, NOT energy
Carbohydrates are in the form of what for plants?
Simple sugars (like glucose)
What in the chloroplast traps the sun?
Chlorophyll
What is the chemical energy stored as?
Starches or polysaccharides
What else is needed in photosynthesis other than light?
Carbon dioxide and water
Where does photosynthesis occur in the plant?
Chloroplast- these are found in green plants and protista
What is the series of disks in the chloroplast called?
Thylakoids (contains chlorophyll and is the site of light dependent photosynthesis reactions)
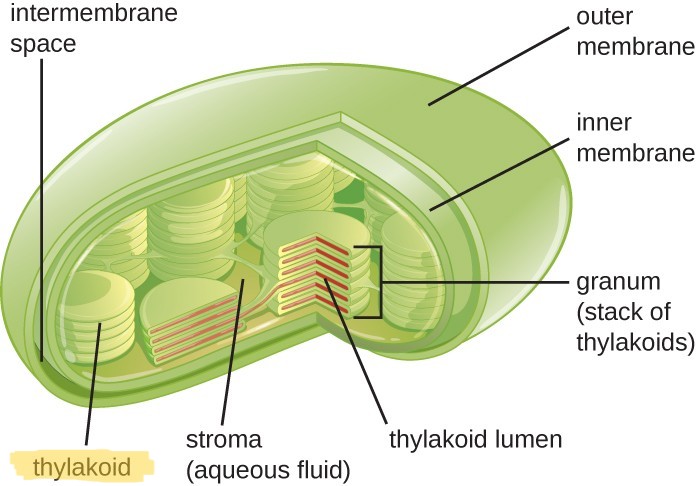
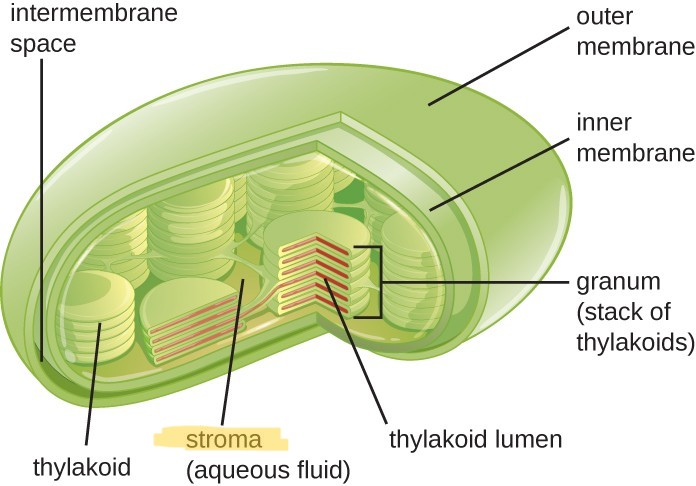
What is the fluid surrounding the thylakoids called?
Stroma
What is the chemical formula for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H20 —> 6O2 + C6H12O6
What do the coefficients tell us?
How many molecules there are
What do the subscripts tell us?
The # of atoms
What is the difference between chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b?
a = absorbs red-violet wavelengths more and reflects blue-green.
b = absorbs more violet-blue light and reflects red-orange light.
What does chemosynthesis mean?
Chemo = chemical. Synthesis = to make.
Chemosynthesis is the synthesizing of organic compounds
What color is sunlight?
White (a fusion of equal amounts of ROYGBV light).
Why are plants green?
The color green is mostly reflected upon hitting a plant- all other colors are absorbed
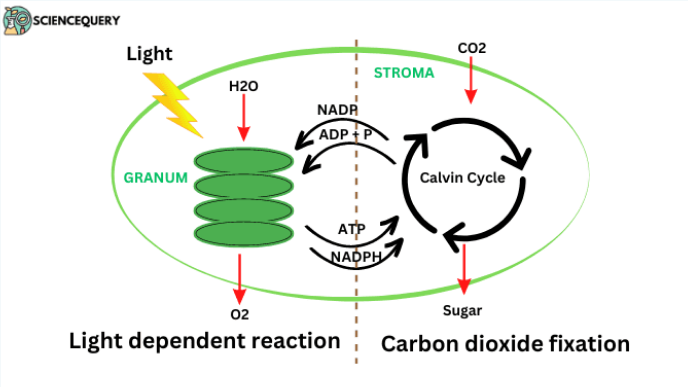
Stage 1: Light Dependent Reactions
Sunlight splits H2O into hydrogen and oxygen molecules
Oxygen releases into atmosphere
Hydrogen is added to NADP+ to synthesize NADPH, an energy carrier
ATP is made
This process happens in the thylakoids
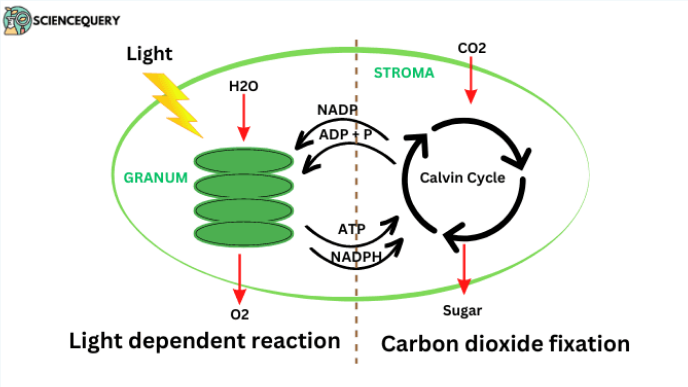
Stage 2: Light Independent Reactions, aka the Calvin Cycle
CO2 + H combines to form C6H12O6
ATP is used
This process happens in the stroma
What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Light Intensity
Temperature
Amount of CO2
Amount of H2O
All reactions of photosynthesis are controlled by enzymes. Temperatures below optimum will slow down photosynthesis.
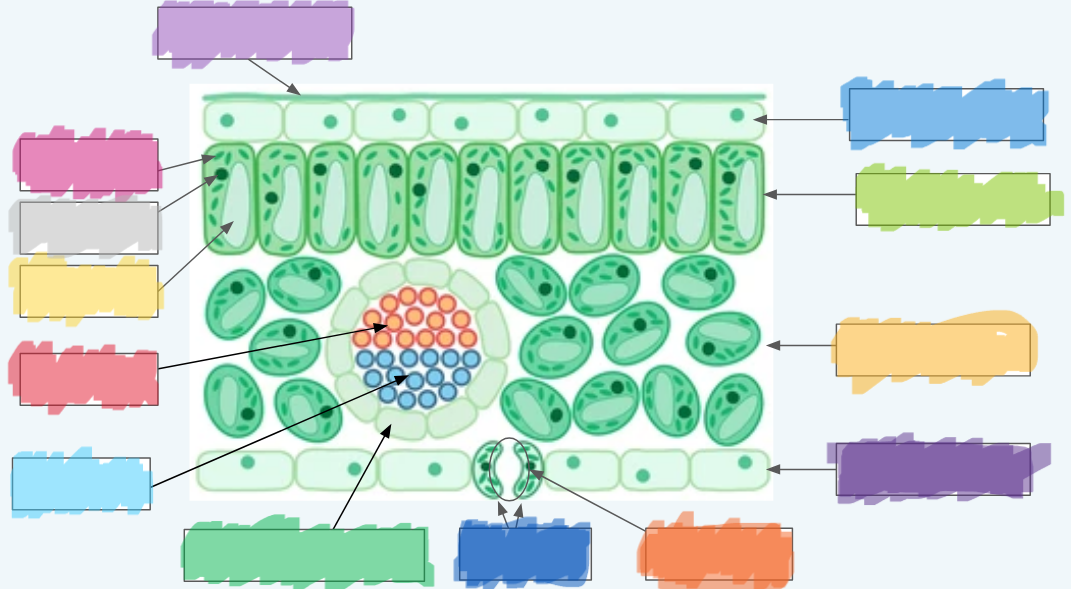
What is the (lighter) purple?
Cuticle
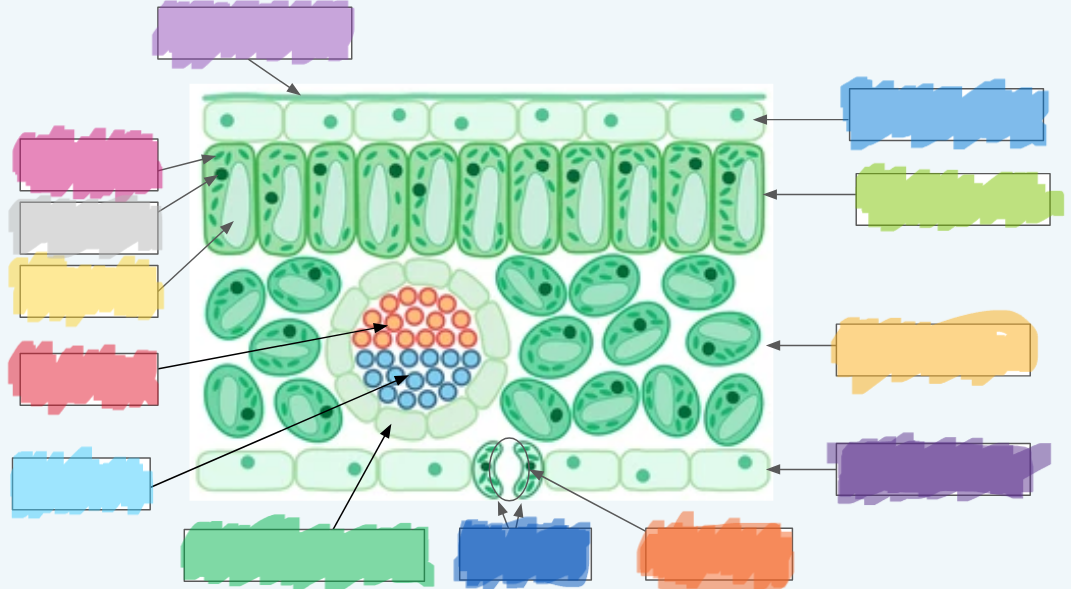
What is the (normal) blue?
Upper epidermis

What is the lime green? (hint: not the chloroplast lol)
Palisade layer
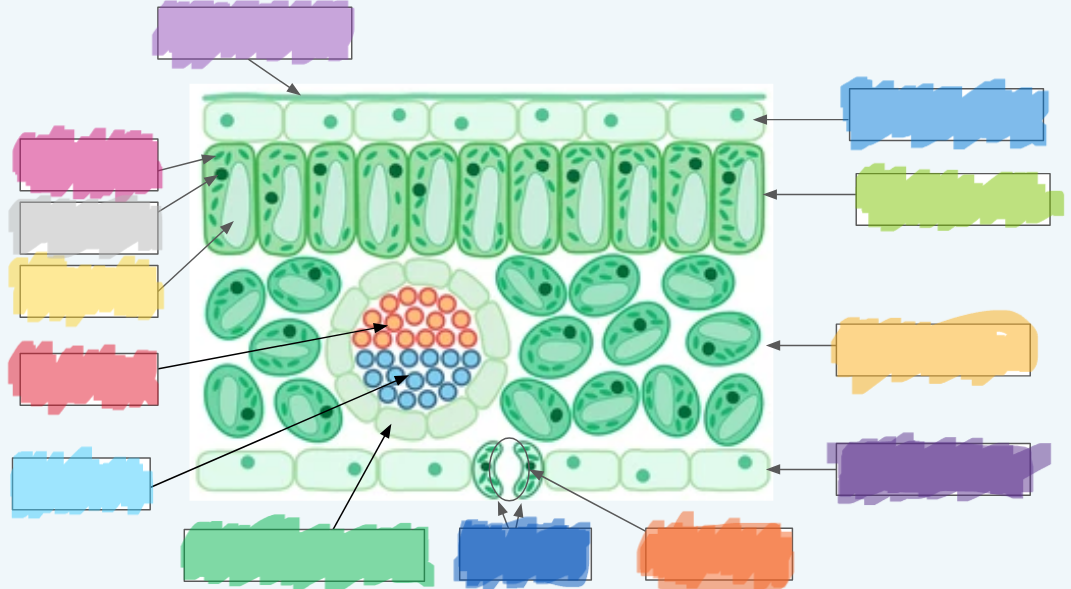
What is the golden-yellow?
Spongy layer
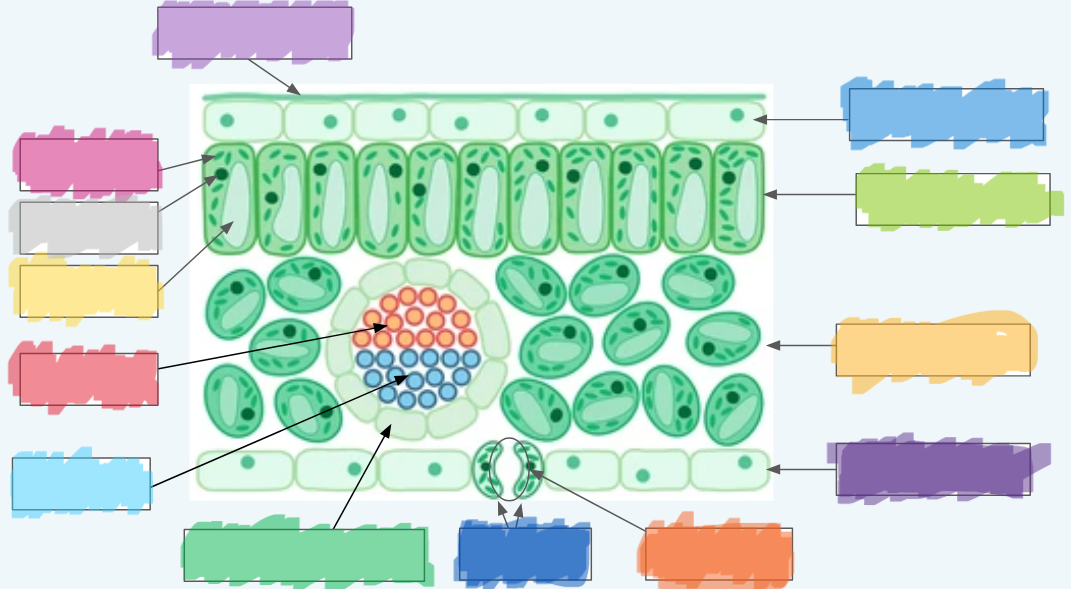
What is the dark purple?
Lower epidermis
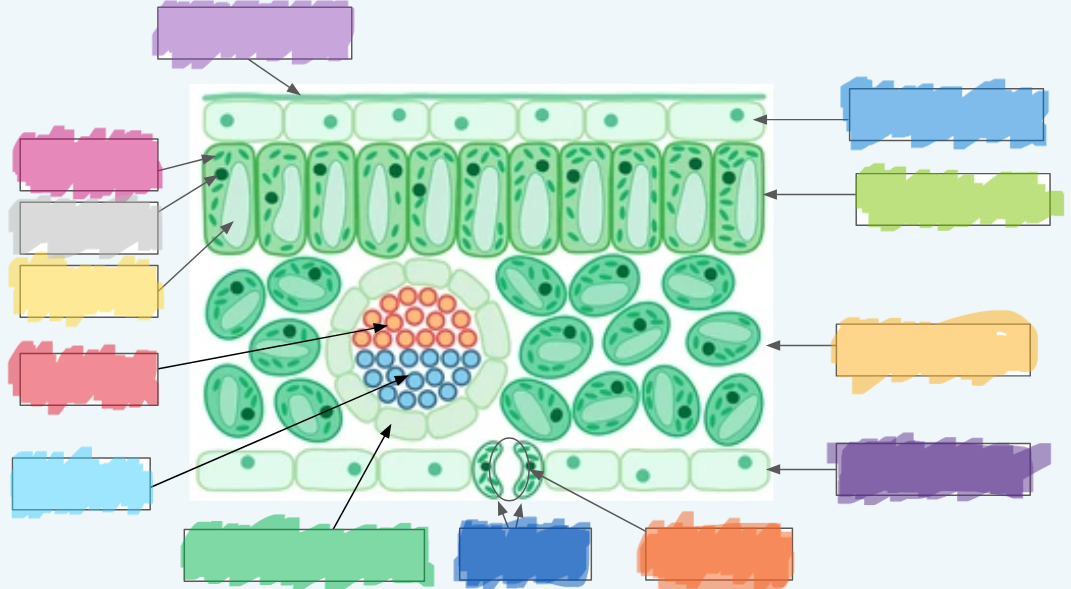
What is the orange?
Stoma
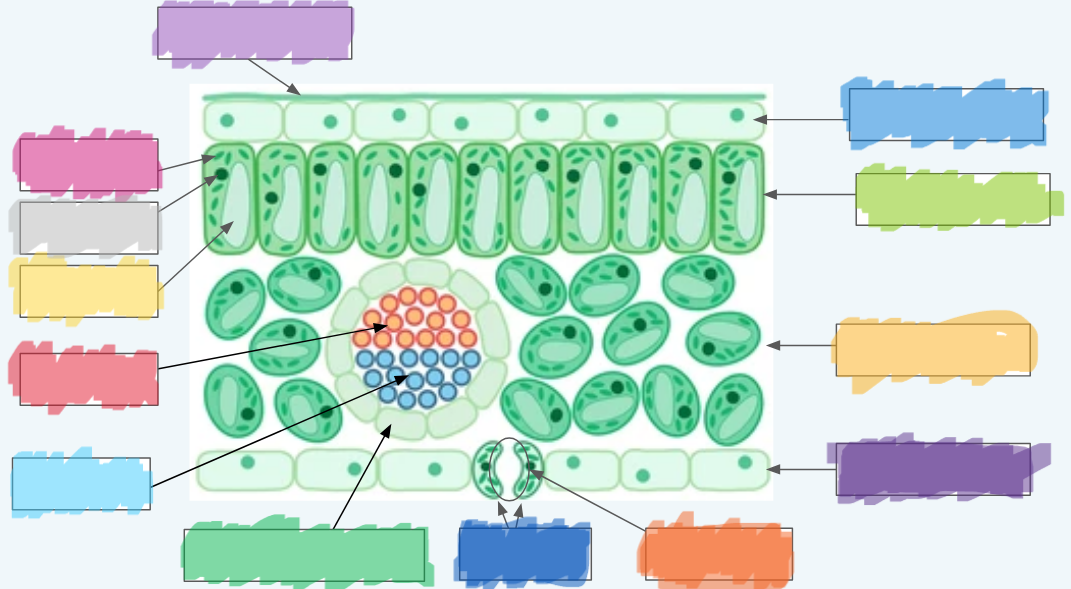
What is the dark blue?
Guard cells
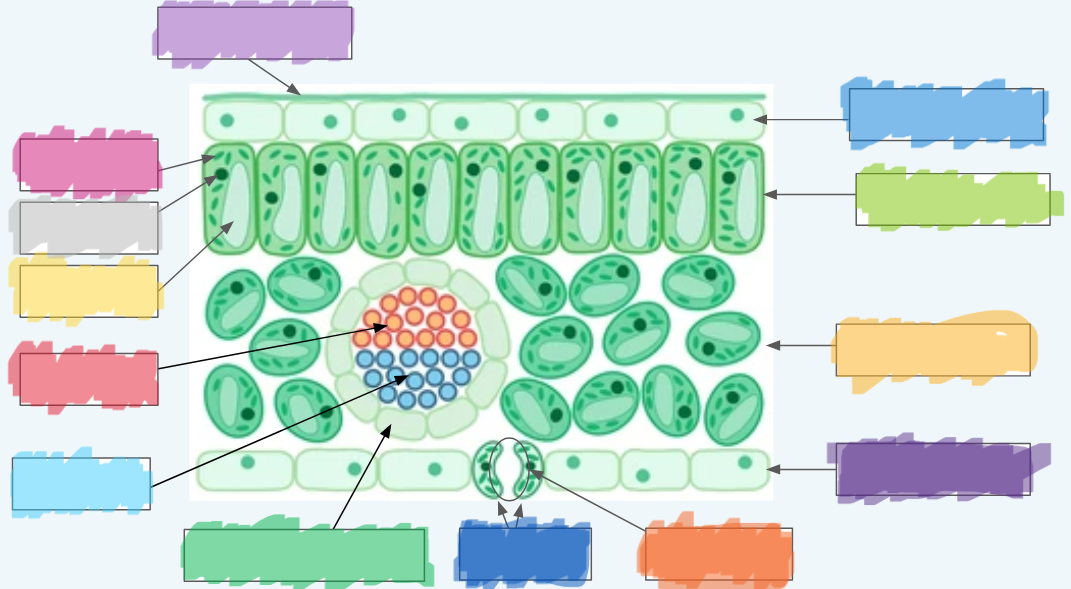
What is the normal green? (hint: not the chloroplasts)
Vascular bundle (Vein)
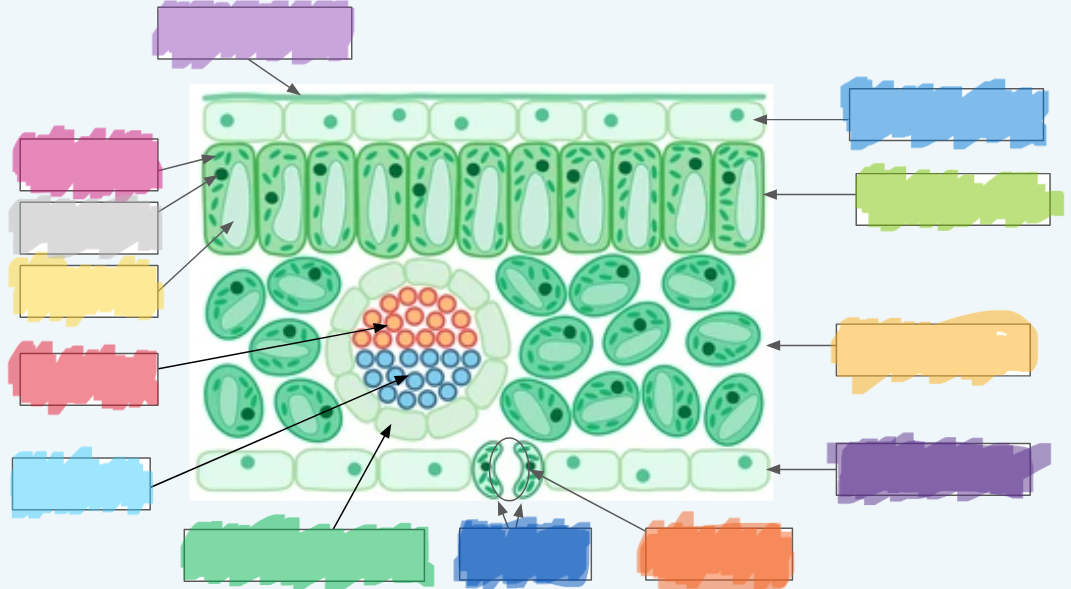
What is the sky blue?
Xylem
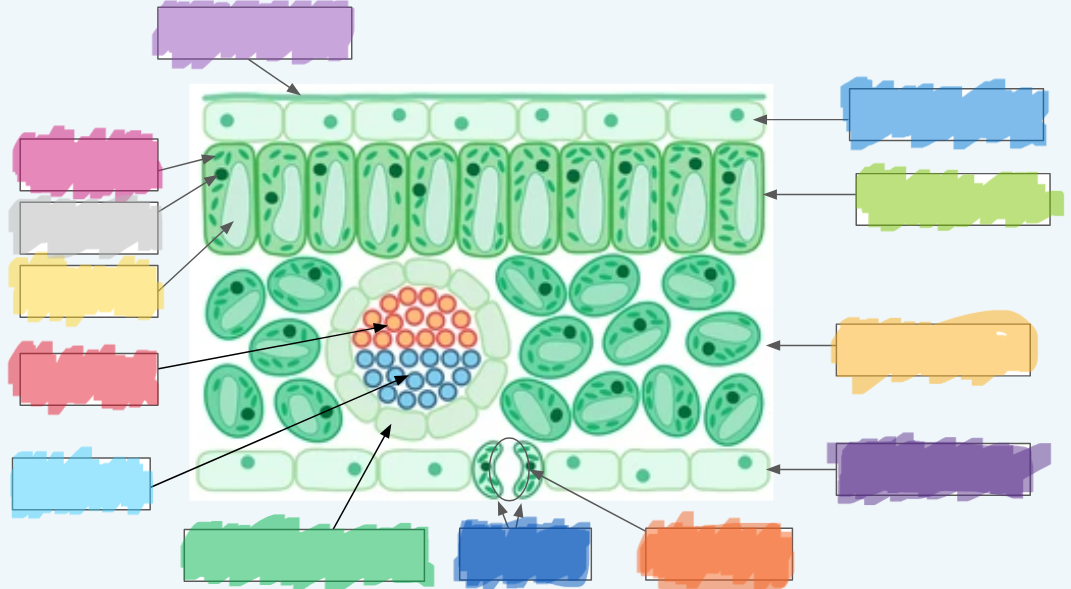
What is the red?
Phloem
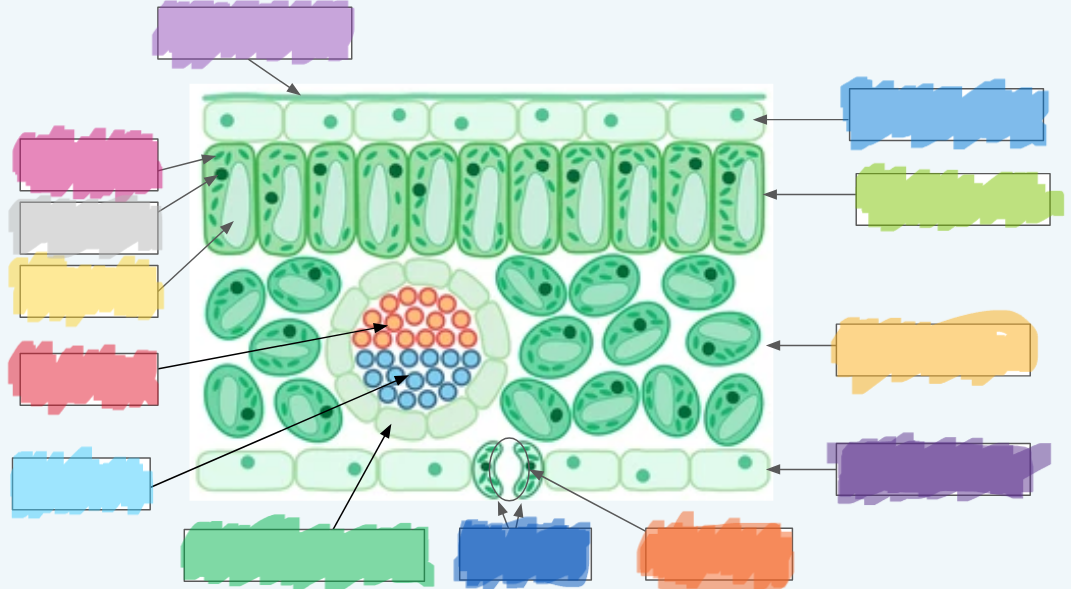
What is the yellow?
Vacuole
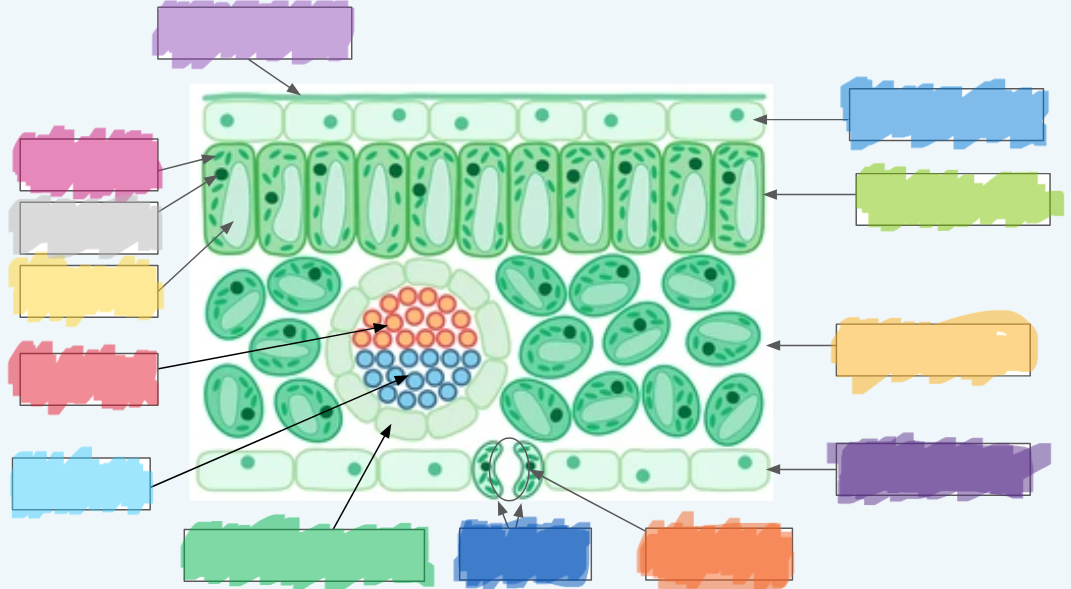
What is the light gray?
Nucleus
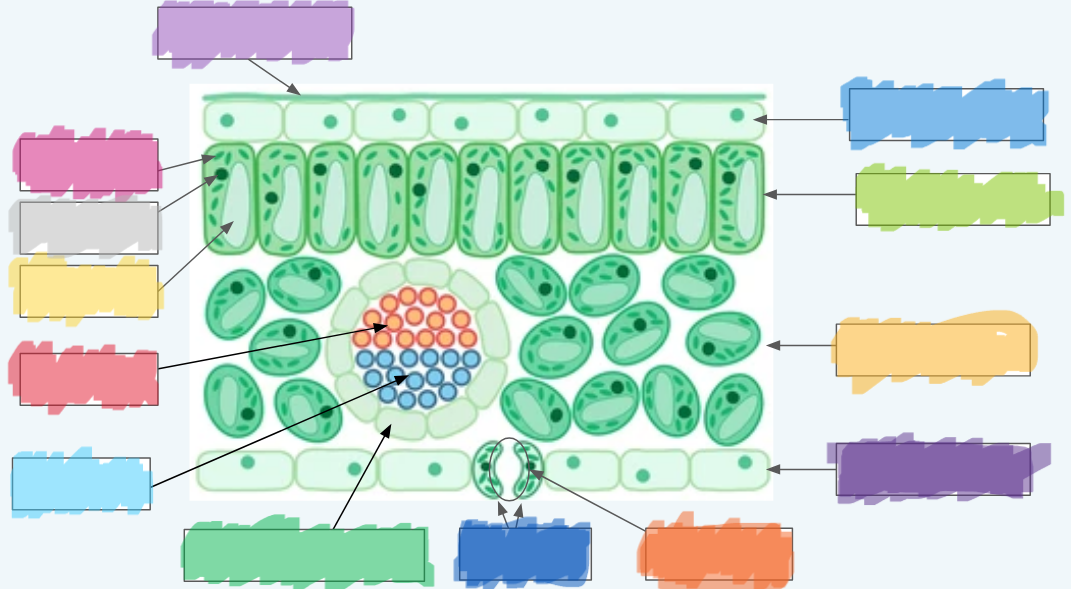
What is the hot pink?
Chloroplasts (sorry lol ^-^)
Cuticle
Waxy layer that covers the epidermis, prevents water loss
Upper epidermis
Brick-like clear cells, allows light to pass, prevents water loss
Palisade layer
Columnar cels tightly packed, contains chloroplasts and main cells to carry out photosynthesis
Spongy layer
Loosely packed cells that hold water and allow gas exchange
Lower Epidermis
Bottom layer responsible for gas exchange
Stoma
Diffusion of gases in and out of the leaf (CO2 and O2 cycling in and out)
Guard cells
Regulates the opening and closing of the stoma
Vascular bundle
Group of tissues in the roots and stem that transports necessary materials throughout the leaf
Xylem
Pumps water throughout the leaf
Phloem
Transfers sugar throughout the leaf