Monopolistic Competition: Market Structure, Firm Behavior, and Long-Run Outcomes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is monopolistic competition?
A market structure where many firms produce similar goods or services but maintain some independent control over their prices.
What is the primary goal of firms in monopolistic competition?
To maximize profits while maintaining brand loyalty and product differentiation.
What characterizes the demand curve for firms in monopolistic competition?
The demand curve is downward sloping, indicating that firms can set prices above marginal cost.
What is the significance of brand loyalty in monopolistic competition?
Brand loyalty allows firms to increase prices without losing customers, as consumers perceive their product as unique.
What happens to economic profits in the long run in monopolistic competition?
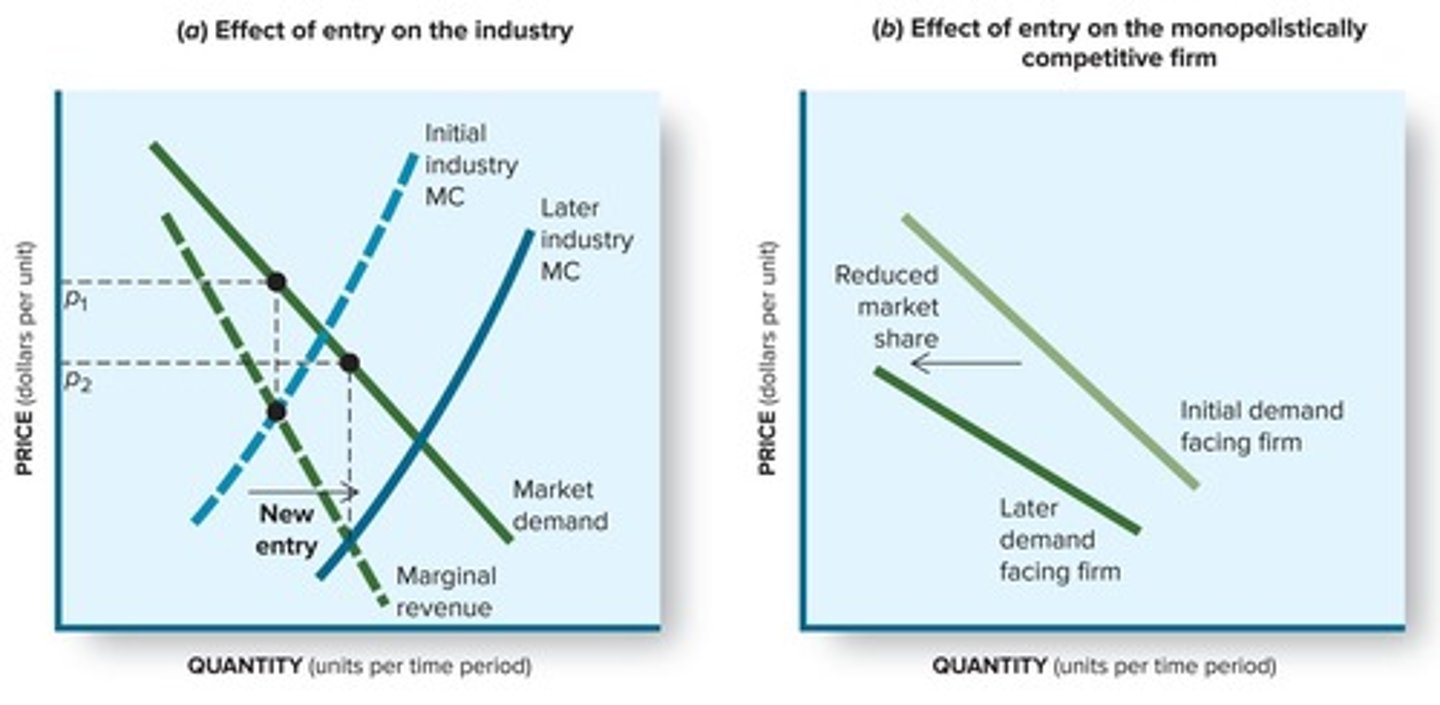
Economic profits tend to zero as new entrants enter the market, increasing supply and driving down prices.
What is excess capacity in monopolistic competition?
Excess capacity occurs when firms produce at a rate below their minimum average total cost (ATC), leading to inefficiency.
How do firms in monopolistic competition engage in non-price competition?
They use product differentiation, advertising, and promotions to enhance their product's image and attract brand-loyal customers.
What are the long-run consequences of entry into a monopolistically competitive market?
Entry of new firms shifts the market supply curve to the right, reducing prices and eliminating economic profits.
What is the relationship between market power and price in monopolistic competition?
Firms have some market power, allowing them to set prices above marginal cost due to product differentiation.
What are concentration ratios in monopolistic competition?
Concentration ratios are low, indicating that no single firm dominates the market.
What is the impact of advertising on prices in monopolistic competition?
Advertising increases marketing costs, which are reflected in higher prices for advertised brands compared to generic brands.
What is productive inefficiency in monopolistic competition?
Productive inefficiency occurs when firms do not produce at the minimum average total cost, leading to wasted resources.
What is allocative inefficiency in monopolistic competition?
Allocative inefficiency occurs when the mix of output is not optimal, leading to a misallocation of resources.
What is the role of product differentiation in monopolistic competition?
Product differentiation helps firms create a distinct identity, fostering brand loyalty and allowing for price increases.
What is the effect of brand-loyal consumers on a firm's market share?
Brand-loyal consumers have high repurchase rates, which helps firms maintain their market share and profitability.
How does the entry of new firms affect existing firms in monopolistic competition?
New entrants increase market supply, shift demand curves inward for existing firms, and drive down prices.
What are the unique features of monopolistic competition?
Many firms, product differentiation, some market power, and low barriers to entry.
What is the significance of low barriers to entry in monopolistic competition?
Low barriers allow new firms to enter the market easily, increasing competition and reducing economic profits.
What is the effect of consumer perception on a firm's pricing strategy in monopolistic competition?
If consumers perceive a product as unique, firms can charge higher prices without losing sales.