L10 Globalization: Economic, culture, and physical aspects
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Is Globalization good or bad?
depends on the person you are asking
what is the world economic forum?
an annual meeting held in Davos, Switzerland.
Participants typically:
- champion free trade
- represent large corporations
what is the goal for the world social forum?
The goal is to promote social and environmental justice by advocating for policies that address inequality and sustainability.
world social forum examples
Korean farmers demonstrate- December 2005 WTO Meeting in Hong Kong.
• World Trade Organization’s
• The World Bank
• International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Globalization in geographer Andrew Kirby’s perspective
explains that with globalization, we are living “not so much in a world without boundaries, or
in a world without geography– but more literally, in a world, as opposed to a neighborhood or a region.”
some questions on globalization
• A political-economical system, therefore a matter of choice (or imposition)? A social phenomenon or one with a natural background?
• A new phenomenon? Or the reoccurrence of an older one in a new more intensive form? Is it reversible?
addition to globalization definition
• Variety of definitions, centering around the world becoming “smaller” and more interconnected in the areas of commerce, culture, and politics
• Causes: technological advances in communication, travel, and
computational power, expansion of trade
what role do networks play in globalization?
the are the set of interconnected notes without a center. They facilitate communication and the flow of information, goods, and culture across global boundaries.
Some examples of networks
• Financial
• trade
• Communication
• Media
• Kinship
• Corporate
• government
• NGOs
• Education
functions of geography of the internet
creates a virtual place
maintain social and family ties
might amplify disparities between regions
use remains arrested at an early phase of hierarchical diffusion
the years of the stages of globalization
• Globalization 1.0 (from 1492 to 1800)
• Globalization 2.0 (from 1800 to 2000)
• Globalization 3.0 (from 2000 to the present)
globalization 1.0
• Occurred from 1492 until about 1800.
• Globalization was centered around countries.
• It was about how much horsepower, wind power, and steam power a country had and how creatively it was deployed.
• The world shrank from size “large” to size “medium.”
globalization 2.0
• Occurred from about 1800 until 2000.
• Interrupted only by the two World Wars.
• The dynamic force driving change was multinational companies.
• The world shrank from size “medium” to size “small.”
globalization 3.0
• Current era
• The convergence of the personal computer, fiber-optic Internet
connections, and software has created a “flat-world platform.”
• This platform allows small groups and individuals to go global.
• The world has shrunk from size “small” to size “tiny.”
main characteristics of globalization as a widely accepted view
• Political and Economical plexus covering and affecting the whole planet
• Worldwide movement of goods, people, and information (in a capitalistic economy)
• Science and Technology have lead us to this point
4 dimensions of globalization
• Space - extensiveness of global networks
• Regularity- intensity of global interactions
• Speed- velocity of global flows
• Depth– impact of global interconnections on quality of life
5 aspects of globalization
• ECONOMIC
• TECHNOLOGICAL
• CULTURAL
• POLITICAL
• MILITARY
All connected
Globalization consequences/effects
Consequences cited by various scholars and activists
Terrorism/asymmetric warfare made easier
Economic crises spread more rapidly
Increased trafficking of humans and drugs
Diseases spread more rapidly
western culture dominating traditional cultures
facing backlash if you want to maintain traditional culture
what is Homogenization
The process by which diverse cultures and societies become more similar, often due to globalization. This often results in the dominance of Western culture over local traditions and practices.
lead to a loss of cultural diversity as local customs and identities are overshadowed.
As global interactions increase, unique traditions may be transformed or diminished.
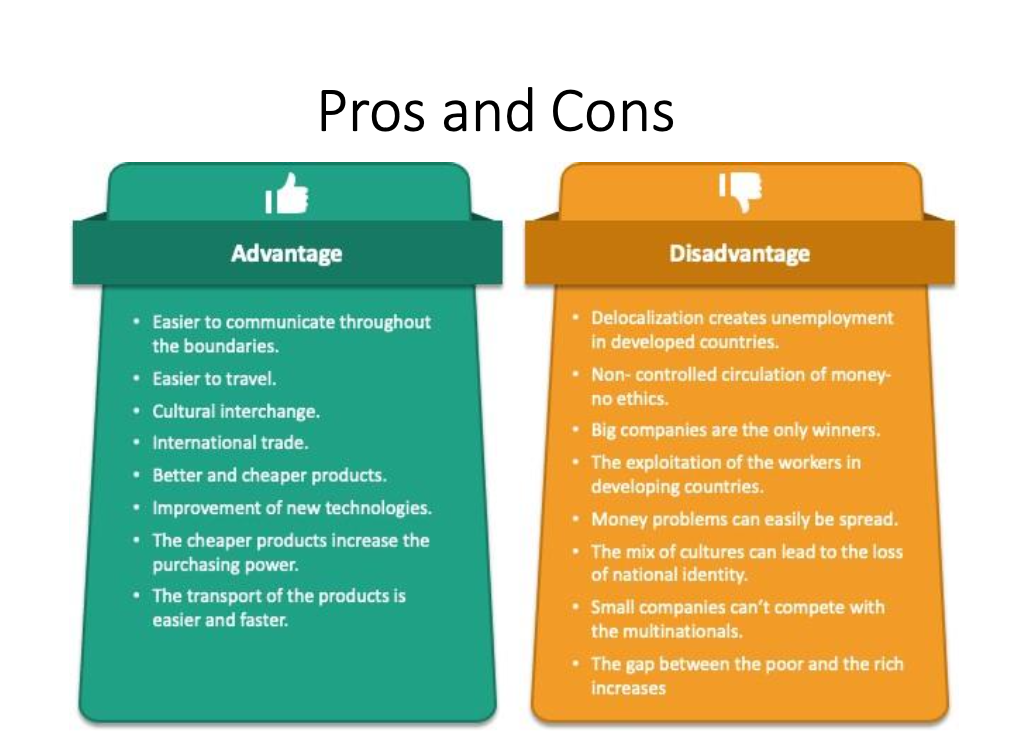
Pros and cons