Ancient Near East & Ancient Egypt Test Reflection
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms

Palette of Narmer
is from the very beginning of ancient Egypt (it shows the unification of ancient Egypt). Know that it was created around 3100 BCE.
Transatlantic trade
(that involved slaves and alcohol) influenced El Anatsui’s decision to make works like Old Man’s Cloth (especially the medium)

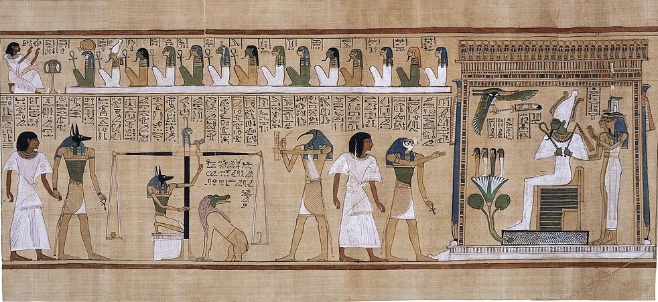
Hu-Nefer was not a pharaoh
he was a royal scribe - which is exactly why they emphasize the fact that Thoth is writing down what happens during the weighing of the heart. It shows the importance of written records in ancient Egypt.

Hatshepsut’s Mortuary Temple
originally had a lot of exotic plants and trees on the terraces. Some came from as far away as Somalia. There are paintings that show this and archaeologists found seeds on the terraces.
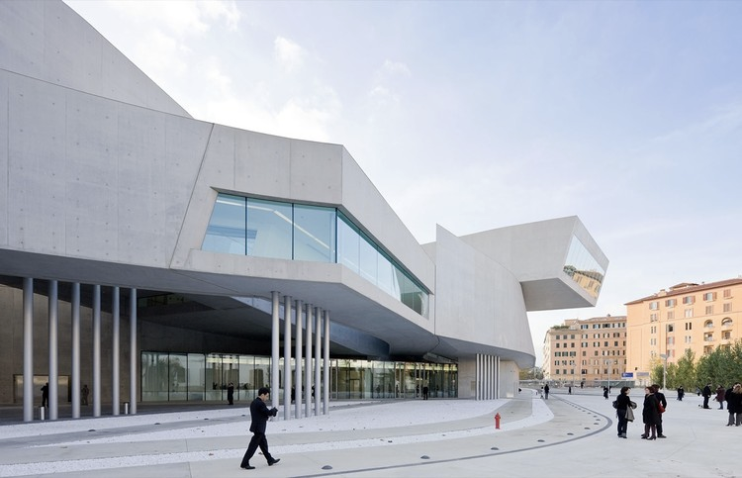

MAXXI
references the ancient past in Rome by the use of concrete (the Romans invented concrete). Be able to ID this work of art.

Be able to ID the subject
Virgin Mary and know why she was so popular during the Gothic Period.
because she represented purity, motherhood, and was often associated with miracle stories
life was getting better

St. Foy was a what type church
Romanesque church: a type of church characterized by architectural elements like rounded arches, heavy walls, and stone vaults, reflecting Roman architectural styles
Lucas Cranach the Elder’s Allegory of Law and Grace
Propaganda?
Two halves, difference, and meaning?
Protestant Church and how they try to convince people to be Protestant instead of Catholic
The Prodistants criticizes the Catholics for only focusing on god, Prodistants achieve through faith alone
Chathlioc (order and law). Prodistants (want to be different and simpler)
Left side- human sinfulness and judgment under law
adam and eve under the tree of knowledge
punishment of sin under law through the skeleton
moses is giving the ten comandments
right side- salvation through the faith of Jesus
on cross with blood
divine mercy not human effort
cloisonne
decorative work in which enamel, glass, or gemstones are separated by strips of flattened wire placed edgeways on a metal backing
repousse
a metalworking technique where a malleable metal is shaped by hammering from the reverse side to create a raised or high relief design on the front
Know that the Merovingian Looped Fibulae were from
the Early Medieval Period (just after the Fall of Rome) - they are considered Migratory Art or Art of the Warrior Lords.
before romanesque. sixth century

Know that the Rucellai Palace was influenced by… HOW?
Colosseum (a large theater or stadium)- its use of classical orders and symmetry in design.
How are the how the Bayeux Tapestry and Trajan’s Column are similar.
scroll- wide and short wrap around the colum and continous narative
They both depict significant historical events through detailed narrative reliefs and illustrations. By using sequential scenes and figures, they tell the story of battles and conquests, showcasing the importance of these events in their respective cultures.
Know what historical event is depicted on the Bayeux Tapestry.
The Norman Conquest of England in 1066, specifically the events leading up to the Battle of Hastings. William sailed from Normandy to England.
Know the medium of the Bayeux Tapestry.
embroidery on linen
Maria and Julian Martinez reference their ancestral past by using
the black on black coloration - it is complex, they had to figure out how to get the pot itself to be a matte black, then paint glossy black over it. That is what the ancestral Puebloans did.
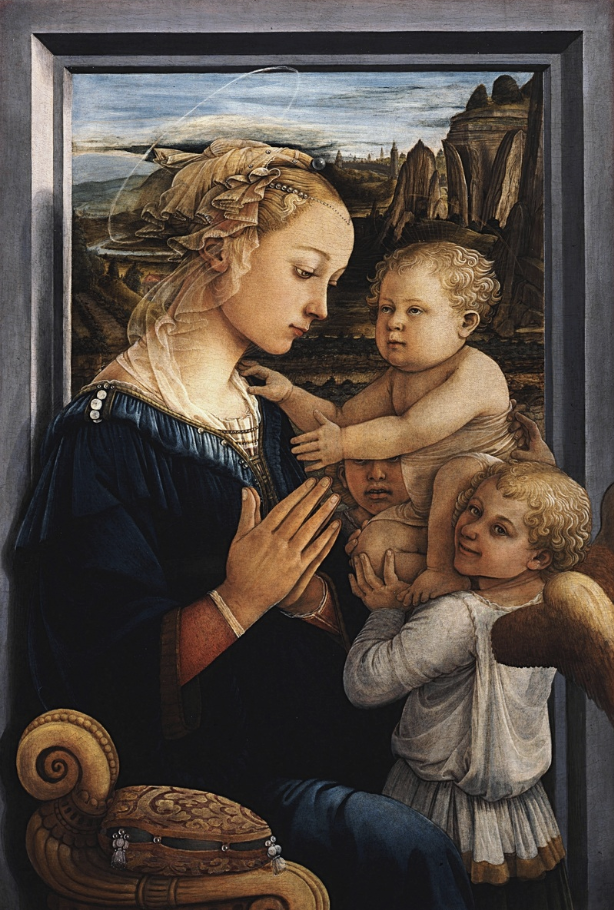

know that in the Italian Renaissance, they were trying to be more…_____ It had not been like that during the Medieval Period for the most part.
How does Lippi achieve naturalism?
naturalistic again- like in the classical greek and roman art. It had not been like that during the Medieval Period for the most part.
naturalism through the human emotion and realism. Childlike Jesus and light and space
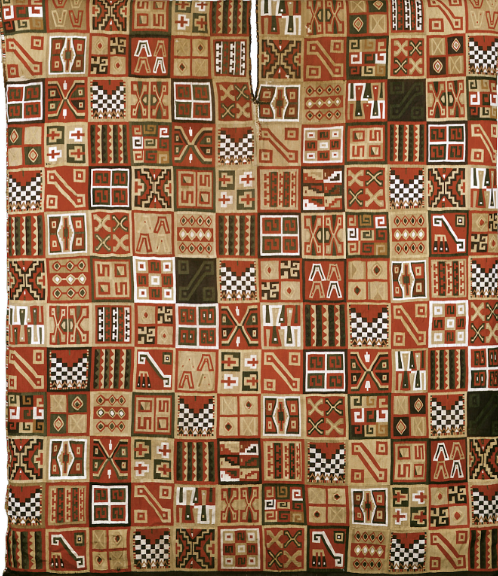

Know that the All-T’oqapu Tunic was made specifically for the…
How does it represent his power?
Sapa Inka.
Made by skilled craftsmen. not traded to spain because made specifically for the sapa inka (unique)
Luxury medium of alpaca.
Know the difference between centrally planned and basilica plan.
centrally planned- San Viatale. circle, square, octagon, equal distant walls to center
Basilica plan- long
Know that the big Romanesque cathedrals were
pilgrimage churches
Know that the Hagia Sophia was
originally Christian and was built in the 6th century CE - it was definitely classically influenced.
Know that the Great Mosque at Cordoba and the Hagia Sophia both were built by
one religion and then used by others.
Hagia Sophia- origiannlu christian, covered mosque and add minerates

Know that the Birth of Venus (image) was
painted by Botticelli
Know that the Hagia Sophia was made in the
6th century CE (shortly after the fall of Rome).
Know that the interior of the Hagia Sophia was originally decorated with
mosaics - that is true of San Vitale as well. They are both Byzantine - that’s typical for Byzantine churches.
Know characteristics of Early Christian art (content/style)
Content Characteristics:
Biblical Themes: Focused on stories from the Old and New Testaments (e.g., Jonah and the whale, Daniel in the lion’s den, the Good Shepherd, and scenes from the life of Christ).
Symbolism: Heavy use of symbols such as the fish (Ichthys), the anchor, the Chi-Rho, and the lamb to convey spiritual ideas in coded ways, especially during periods of persecution.
Typology: Use of Old Testament figures as prefigurations of Christ or Christian salvation (e.g., Jonah as a symbol of resurrection).
Salvation and Afterlife: Emphasis on hope, eternal life, and resurrection, often seen in catacomb art and funerary imagery.
Style Characteristics:
Simplified Forms: Less concern for anatomical accuracy or naturalistic perspective compared to Classical art; figures are stylized and frontal.
Hieratic Scale: Important religious figures like Christ are often depicted larger or more prominently than others.
Narrative Composition: Artworks often tell a story in a single scene or through a series of small vignettes.
Abstract and Spiritual Focus: Moved away from realism to emphasize spiritual ideals over physical perfection.

Also be able to ID the Last J tympanum from St. Foy as
Romanesque
Know approx. dates for Early Christian, Romanesque - and what was going on around 1350 (Gothic in some places, Renaissance in others).
Early Christian art (200–500) used simple symbols about Jesus. Romanesque art (1000–1150) had rounded arches and church carvings. Around 1350, Gothic art continued in the north, while the early Renaissance began in Italy with more realistic style.
Jan van Eyck likely invented
oil paint - rich colors - longer drying time. Became popular in Northern Ren. art.
Know the original function (possibly) and later function of the Mamluk Basin
The Mamluk Basin was first used for washing at fancy dinners. Later, it was used in France to baptize babies.
Know that the Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut is a
temple to honor her but NOT a tomb. In the New Kingdom, pharaohs were buried in rock cut tombs (often in the Valley of the Kings) so that their stuff for the afterlife would remain hidden. The mortuary temple, though, was supposed to be a place where people could go and worship her (so definitely not hidden).
This is different from Old Kingdom practices where the mortuary temple would be with the tomb (pyramid).

Be able to ID a lukasa and know what its function is.
symbolic design, materials, storytelling (beads, shells, metal in patterns representing a person or place or concept.
map of history
Know the order and dates for the different Greek Periods.
Archaic – 7th to early 5th century BCE (700s–480s)
Classical – 5th to 4th century BCE (480s–323)
Hellenistic – late 4th to 1st century BCE (323–30)
Know the characteristics of Archaic Greek sculptures - and Classical.
Archaic: stiff
Classical: man is the measure of all things, perfection, natural/idealized
Hellenistic: emotion and human, and real

Know the different parts of Trajan’s Forum. Know that the Basilica Ulpia is part of Trajan’s Forum.
Trajan's Column – A tall column with reliefs depicting Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars.
Basilica Ulpia – A large, grand hall for meetings and legal proceedings.
Trajan's Market – A multi-level shopping center and administrative complex.
Temple of Trajan – A temple dedicated to the emperor Trajan.
Library of Trajan – Two libraries, one for Greek texts and one for Latin.

Be able to ID the Anavysos Kouros and know that it influenced
the Statue of Apollo from Veii (later question) - and that its function was a grave marker.
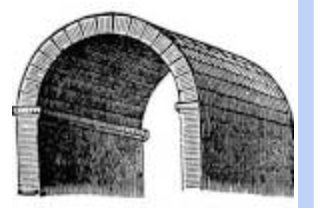
Be able to ID barrel vaulting
and know that the Colosseum had it.

Know why there is a baby next to Augustus’s leg.
Cupid, the son of Venus.
he claimed divine right to rule through divine heritage
Aneus was a son of Venus and cupid son and he is desent from venus
how anavysos Kouros is similar to the Statue of Apollo from Veii
both come from early Greek art and reflect similar stylistic trends:
Both are life-sized: Both statues are large, standing figures meant to represent idealized human forms.
Pose: Both statues feature a similar frontal, rigid pose (called the "kouros pose" for the Anavysos Kouros), with one leg slightly forward and arms at the sides.
Stiffness: Both statues have a certain stiffness in their posture, a characteristic of early Greek art, showing little natural movement.
Idealized Anatomy: Both feature idealized male bodies, with well-defined muscles and a youthful, athletic appearance.
The Taj Mahal was Mughal, not Persian (it is located in India, not Iran).
The Great Mosque at Isfahan IS Persian.
iwans- big arches, both have 4: 4 rivers of paradise

Be able to ID the Ndop of King Mishe.
Remember that the Great Mosque at Djenne is made primarily out of mudbrick - so it needs to be replastered yearly.

Know what a clerestory is- clear row of windows
and that the Basilica Ulpia had one. for light and symbolism
Romans put mosaics on the floor. They decorated the walls with frescoes.
Fresco- WALLS: mural painting technique
Mosaic: ROMAN ON FLOOR: small materials aranged to create patterns or images