AP Bio Unit 1 Chemistry Of Life
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Organic
Needs to have hydrogen and carbon
biological organization (smallest to largest)
Atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organ, organ systems, organism
ecology levels (Smallest to biggest)
organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biosphere
Organ
2 or more tissues working together
Abiotic
Non-living
6 characteristics of life
1. All organisms reproduce
2. All have DNA
3. All require energy
4. All respond and adapt to their environment
5. All are made up of cells
Sexual Reproduction
-two cells from different parents unite to form the first cell of the new organism
Asexual Reproduction
-involves one parent
-offspring is genetically identical to parent
-most common method is binary fission
-unicellular organism divides in half to form two new organisms
Autotroph
self feeder
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
3 domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Discovery of cells
Robert Hooke
-observed sliver of cork
-coined term cell
Cell Theory
-All living things are made of ells
-Smallest unit of structure and function of all organisms is the cell
-All cells come from pre-existing cells
Electronegativity
"thirst for electrons", for covalent bonds
non polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
Ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Essential Elements of Life
CHON (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen)
Trace elements
required by an organism in only minute quantities
Mass, Atomic, and Neutron #
Mass # (top) = # of protons + neutrons
Atomic # (bottom) = # of protons, # of electrons in neutral atom
# of Neutrons = mass # - atomic #
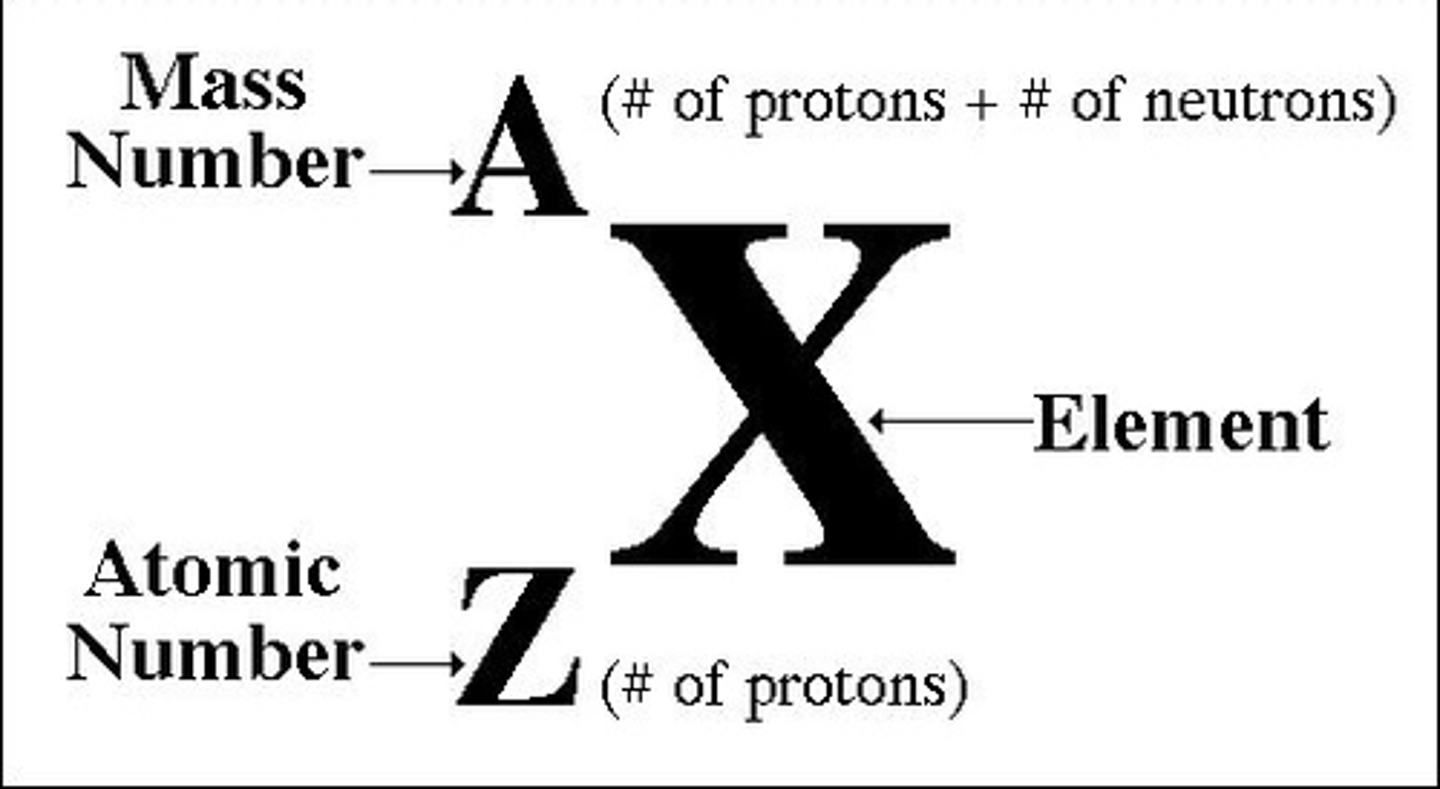
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Radioactive Isotope
An isotope whose nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy.
Electron Shells
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
Valence Electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
-chemical behavior depends on this
Valence Shell
outermost electron shell
ions
extra positively or negatively charged atoms because they have gained or lost an electron
cation
positively charged ion
anion
negatively charged ion
ionic compounds/ salts
a compound resulting from the formation of an ionic bond
hydrogen bonds
-when hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom it has a partial positive charge, attracting electronegative atoms
-van der waals interactions
-basis of property of water
Water Molecules
-covalent bonds
-partially negative O, partially positive H
-hydrogen bonds (weak)
-water properties
Properties of water
-cohesion
-adhesion
-high specific heat
-high heat of vaporization
-Ice is less dense than water
-universal solvent
Cohesion (Strong & High surface tension)
-attraction between other water molecules (Water & water)
-surface tension: how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
-bonded by hydrogen bonds
-transport of water and dissolved nutrients against gravity in plants
adhesion
-clinging of one substance to another such as water
-connected by hydrogen bonds
-water molecules stick to other surfaces
-ex. capillary action
high specific heat
-water resists changes in temperature (requires a lot of energy to cool or heat)
-Specific Heat: amount of het that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temp by 1 degree C
-waters specific heat is 1cal/g*c
-helps regulate climate and body temp
high heat of vaporization
-Hydrogen Bonds have to be broken before evaporation can occur
-heat of vaporation: quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1g of it to be converted from liquid to gas
Floating of Ice/Ice is less dense than liquid Water
-ice floats on liquid water
-when in ice form the hydrogen bonds spread out
- >4*c, water expands as it warms
-at 0*c water freezes, each molecule bonded to 4 partners making ice less than 10% more dense than a liquid
-waters greatest density is at 4*c
Universal Solvent
- water can dissolve many polar or charged substances bc water is polar
Aqueous Solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
hydrophillic molecules
Attracted to water
Hydropobic molecules
substances that repel water because they are non-ionic or non polar (can't form hydrogen bonds)
Ex. Oil
Formulas H, H3O conversion
HCl= H+ + Cl-
NH3 + H+ = NH4+
NaOH= Na+ + OH-
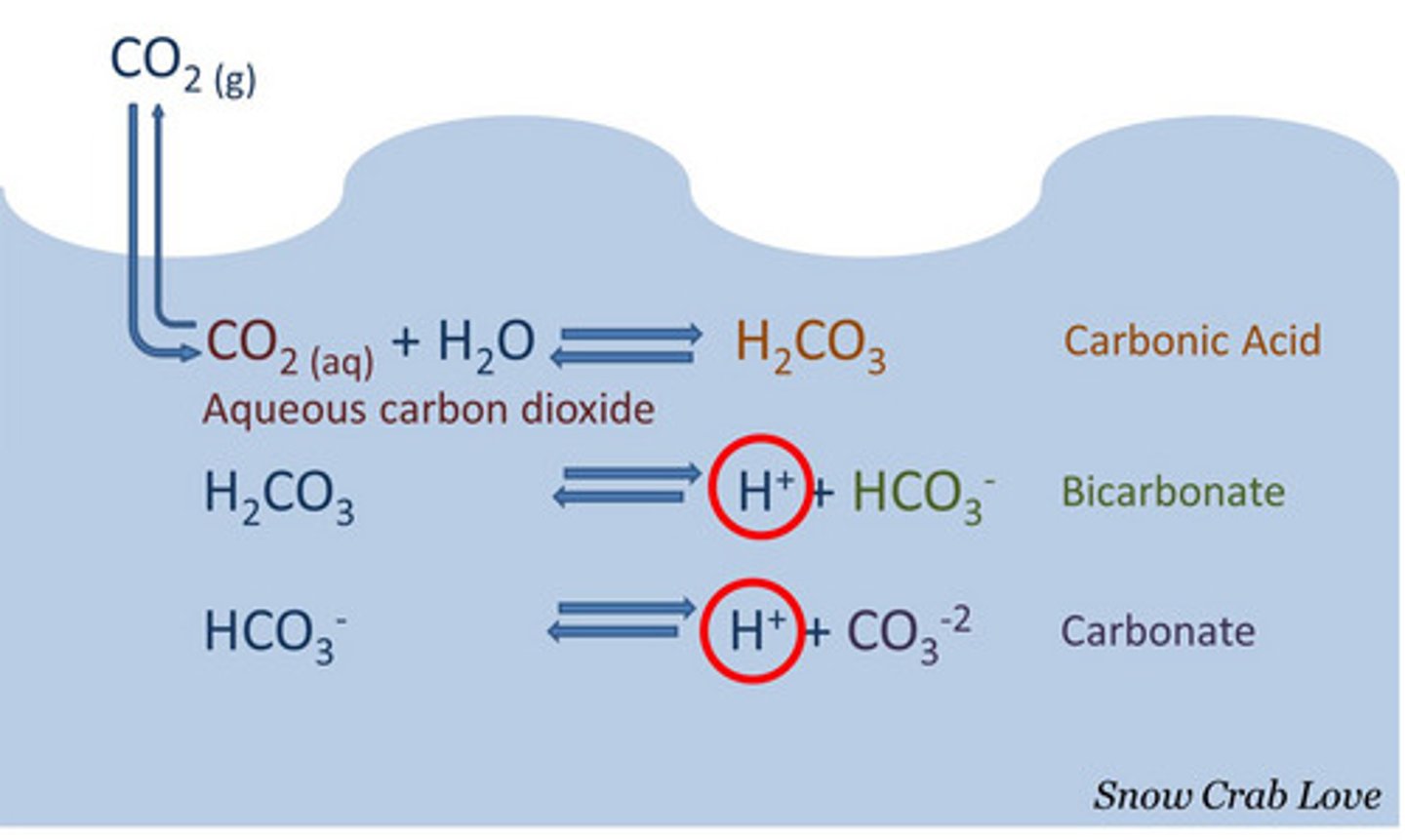
H2CO3 = HCO3- + H+
[H+][OH-]= 10 ^-14
pH= -log[H+]
-log 10^-7 = -(-7) = 7
Van der Waals interactions
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges.
Acids
-excess of H+ ions and a pH below 7.0 [H+] > [OH-]
bases
- excess of OH- ions, pH above 7.0 [H+] < [OH-]
buffers
substances that minimize changes in pH, accept H+ when depleted
carbonic acid (H2CO3)
important buffer of living systems it moderates pH changes in blood plasma and the ocean
Carbon
-usually completes valence shell by sharing 4 electrons with other atoms so 8 electrons are present
-tetrahedron shape
-carbon bonds to other molecules forming carbon skeletons
-forms up to 4 covalent bonds
carbon skeletons
the chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule
hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
Isomers are
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
functional group
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
4 Macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
number of unpaired electrons in an atom =?
amount of bonds it can form
cis-trans isomer
carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of double bonds
enatiomer
One of two molecules that are mirror images of each other.
Hydroxyl Group
polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
-large carbohydrates, proteins, etc are polymers
monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
-form larger molecules by dehydration synthesis
-enzymes speed up process
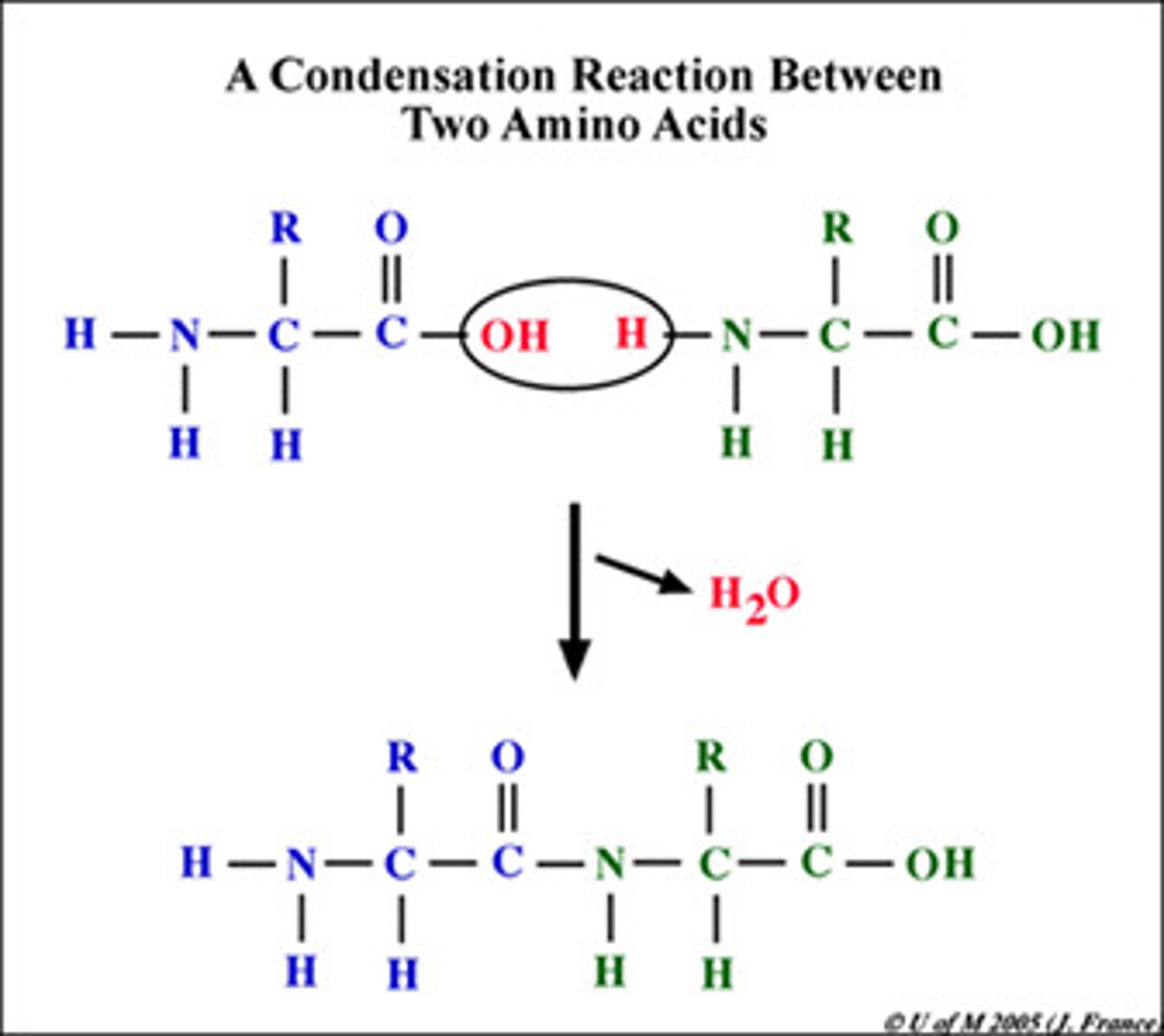
dehydration synthesis/condensation
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
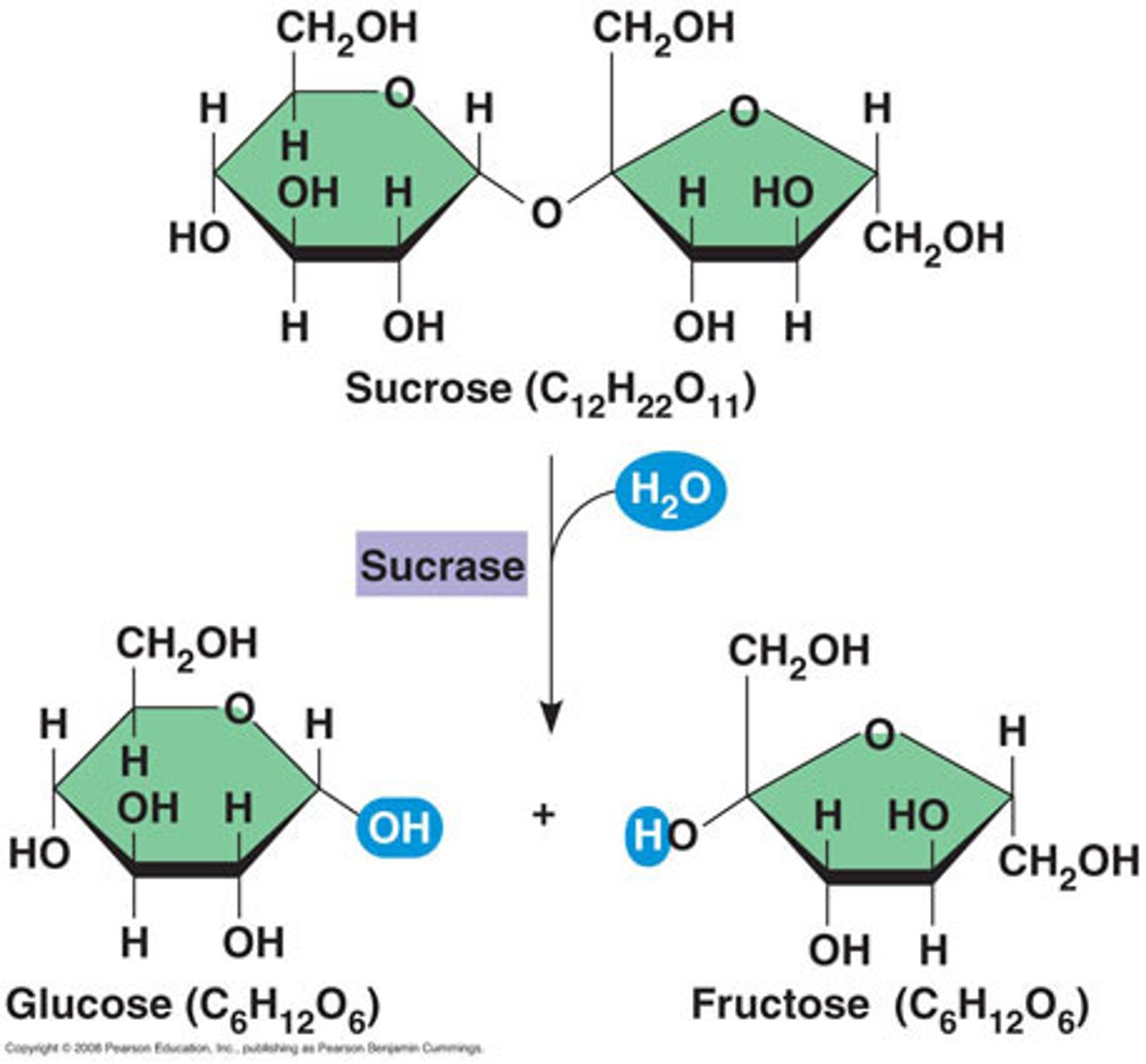
Hydrolysis reaction
A chemical reaction that breaks apart a larger molecule by adding a molecule of water
-reverse reaction
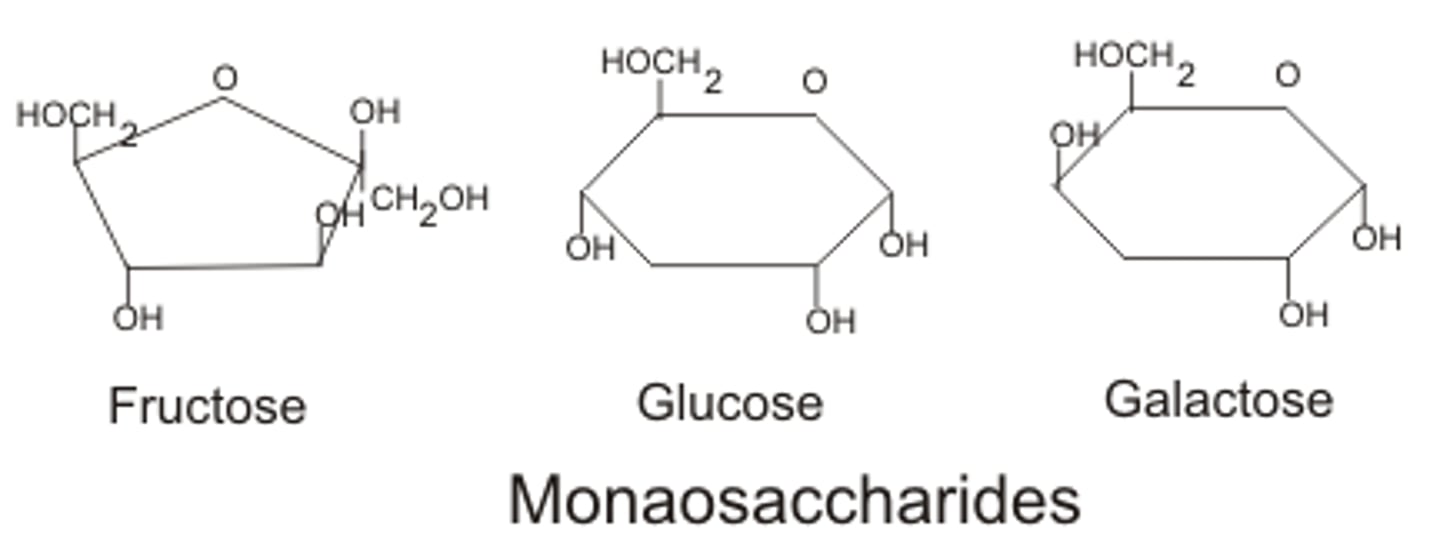
Carbohydrates
-include simple sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose, etc)
-ratio of 1 carbon: 2 hydrogen: 1 oxygen or CH2O (1:2:1)
-consist of monosaccharides
monosaccharides
monomers of carbohydrates; simple sugars
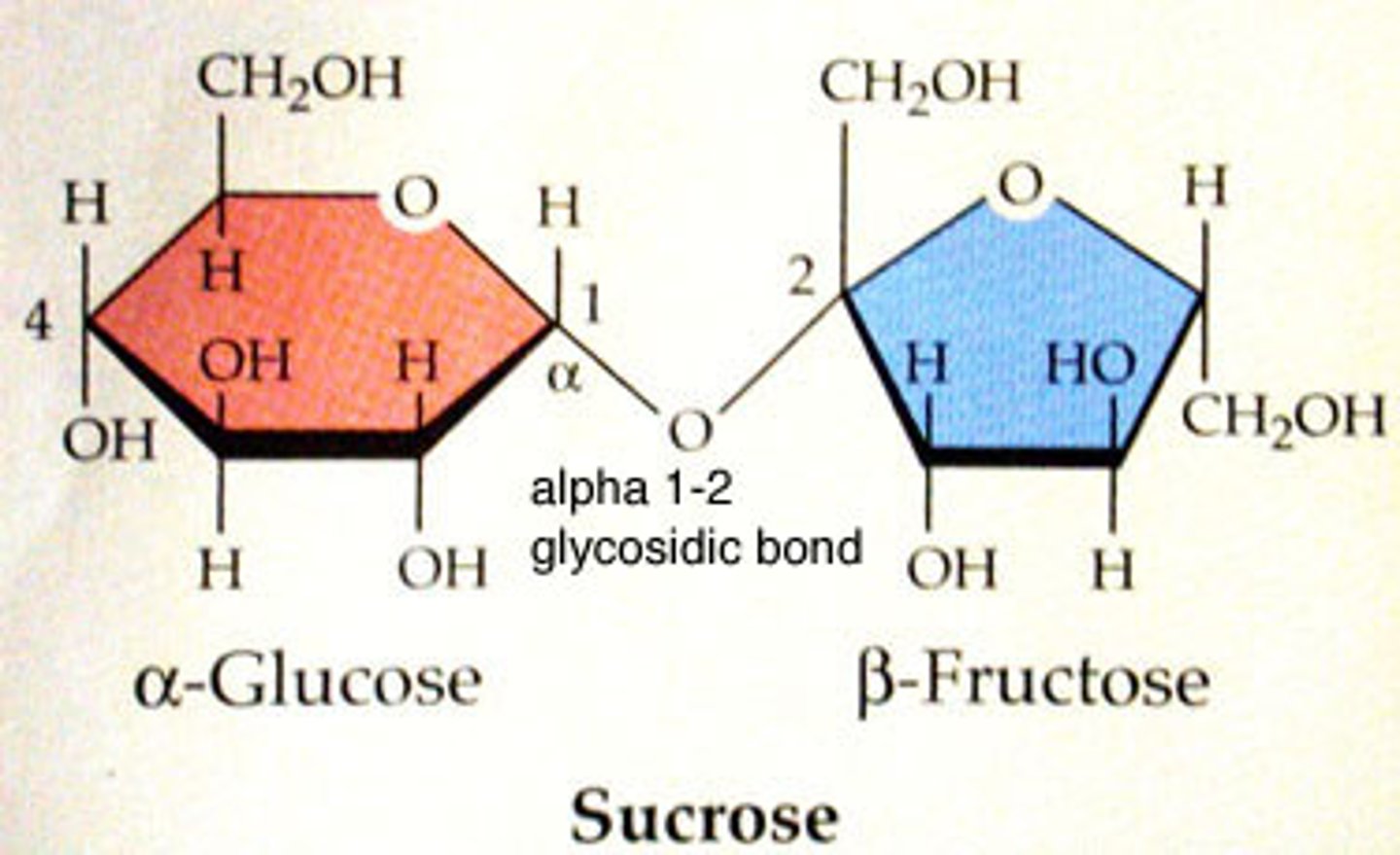
disaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides
-joined by covalent bond called glycosidic linkage
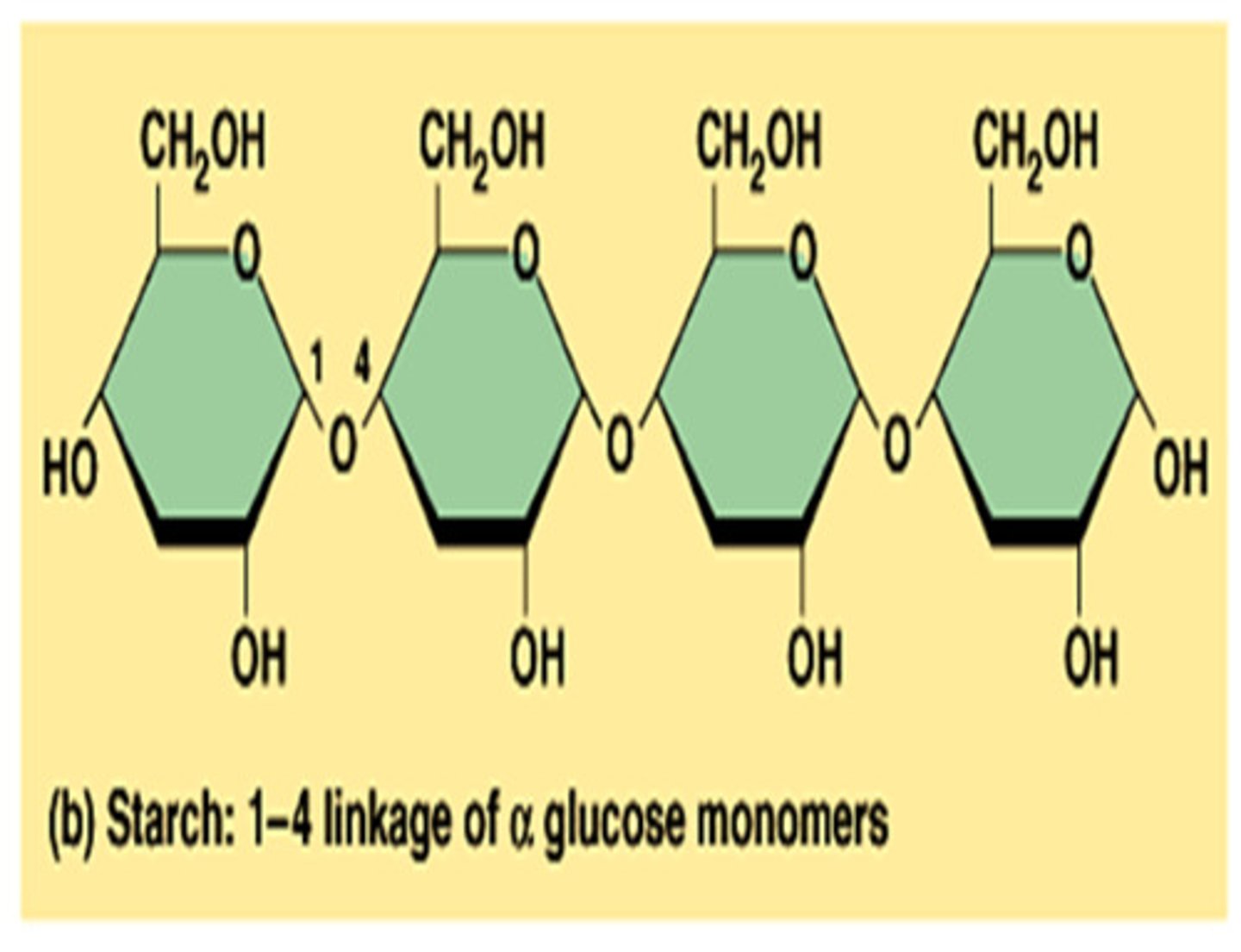
polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
-joined by dehydration synthesis (covalent glycosidic linkages)
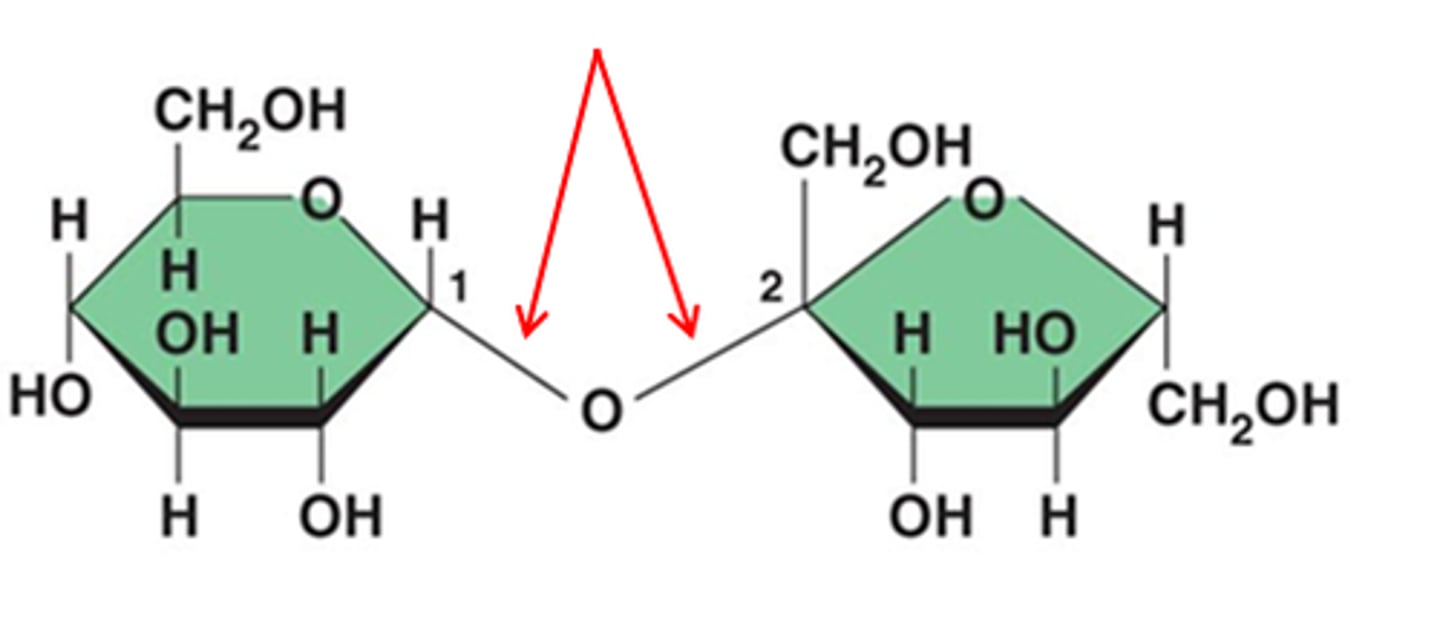
glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose, polymer
cellulose
Carbohydrate component of plant cell walls.
-polysaccharide
-glucose monomers joined by glycosidic linkages
microfibrils
strong fibres that hold together cellulose nolecules
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.
lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- all HYDROPHOBIC
fats (triglycerides)
LIPIDS
composed of 3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol
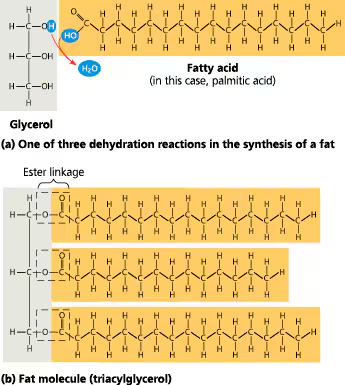
fatty acids
chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms (hydrocarbons)
-non polar (hydrophobic)
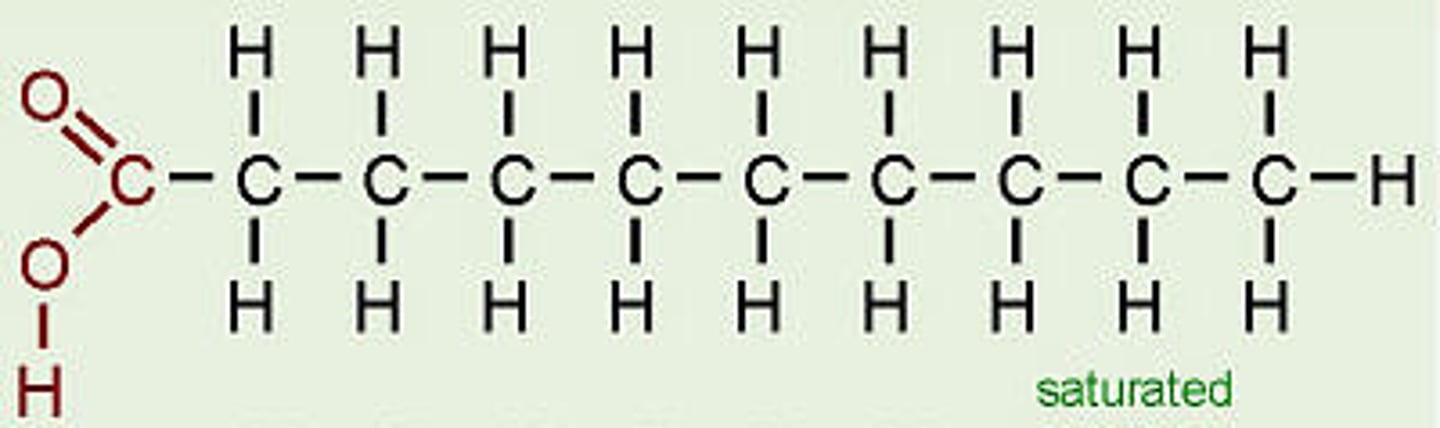
saturated fatty acids
have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
-pack solidly at room temp
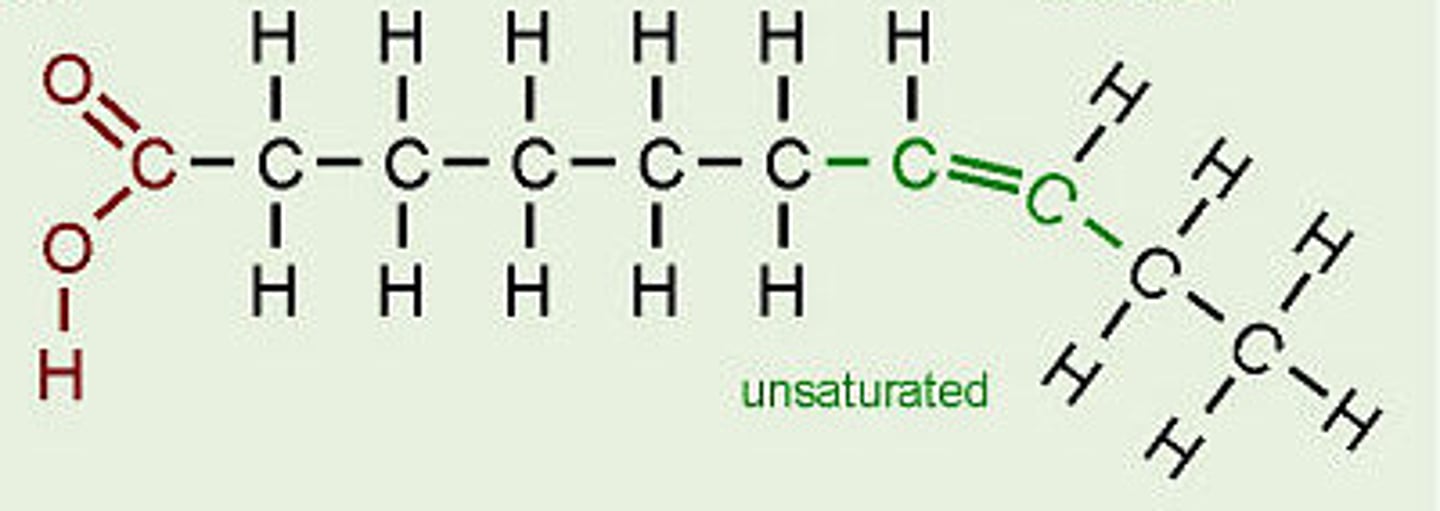
unsaturated fatty acids
-A fatty acid possessing one or more double bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail
-double carbon bonds
-Such bonding reduces the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton.
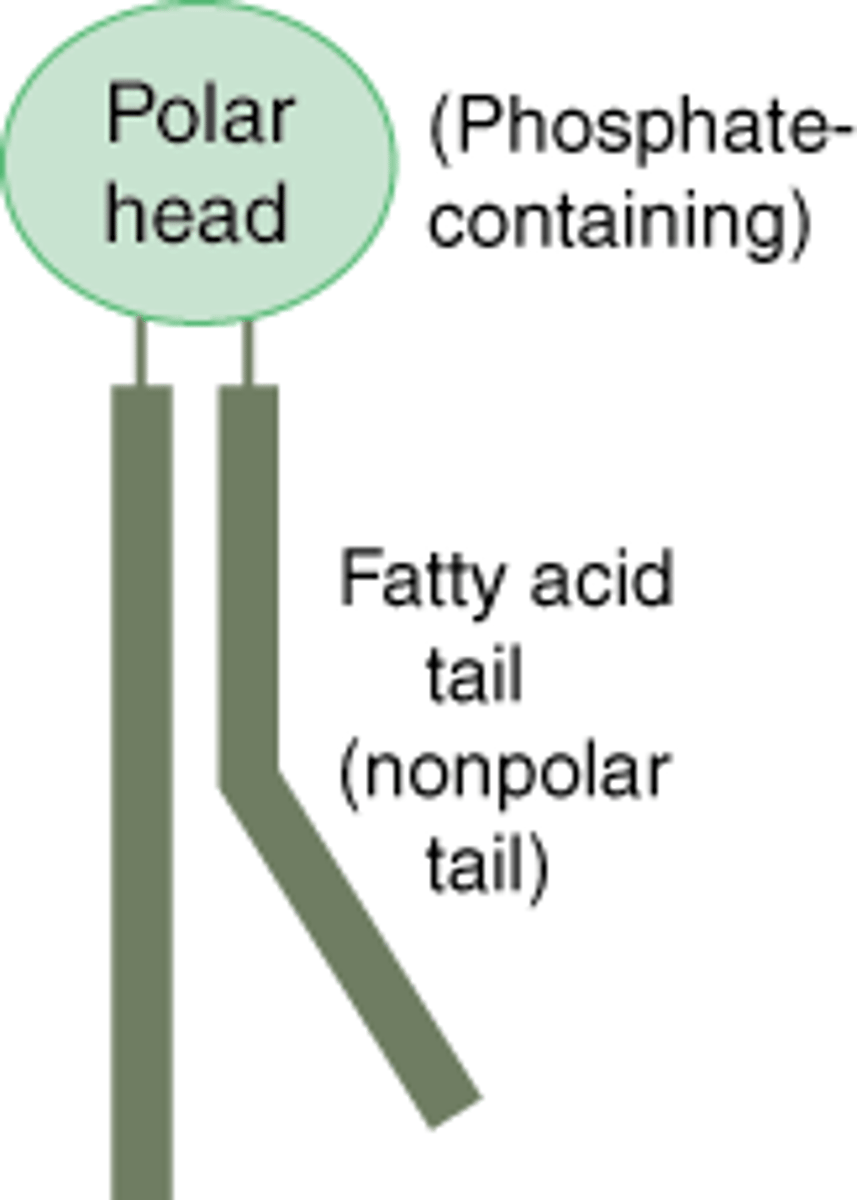
phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes
-are polar,
-2 fatty acids
-have a glycerol backbone (hydrophilic head )a nonpolar
-hydrophobic tail.
-neither phobic or phillic which allows them to form bilayers in cell membranes
steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
-cholesterol is a steroid, so are estrogen and testosterone
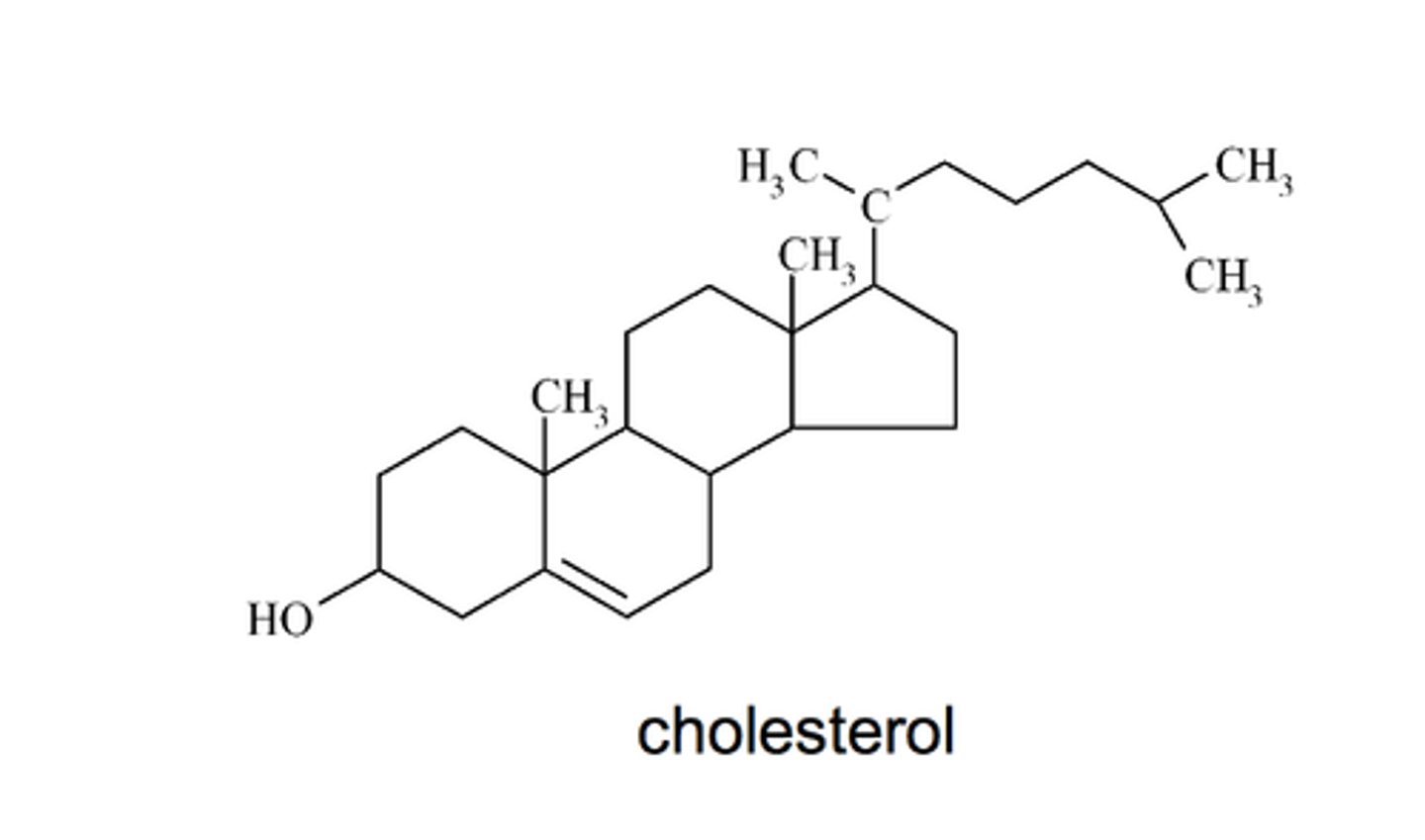
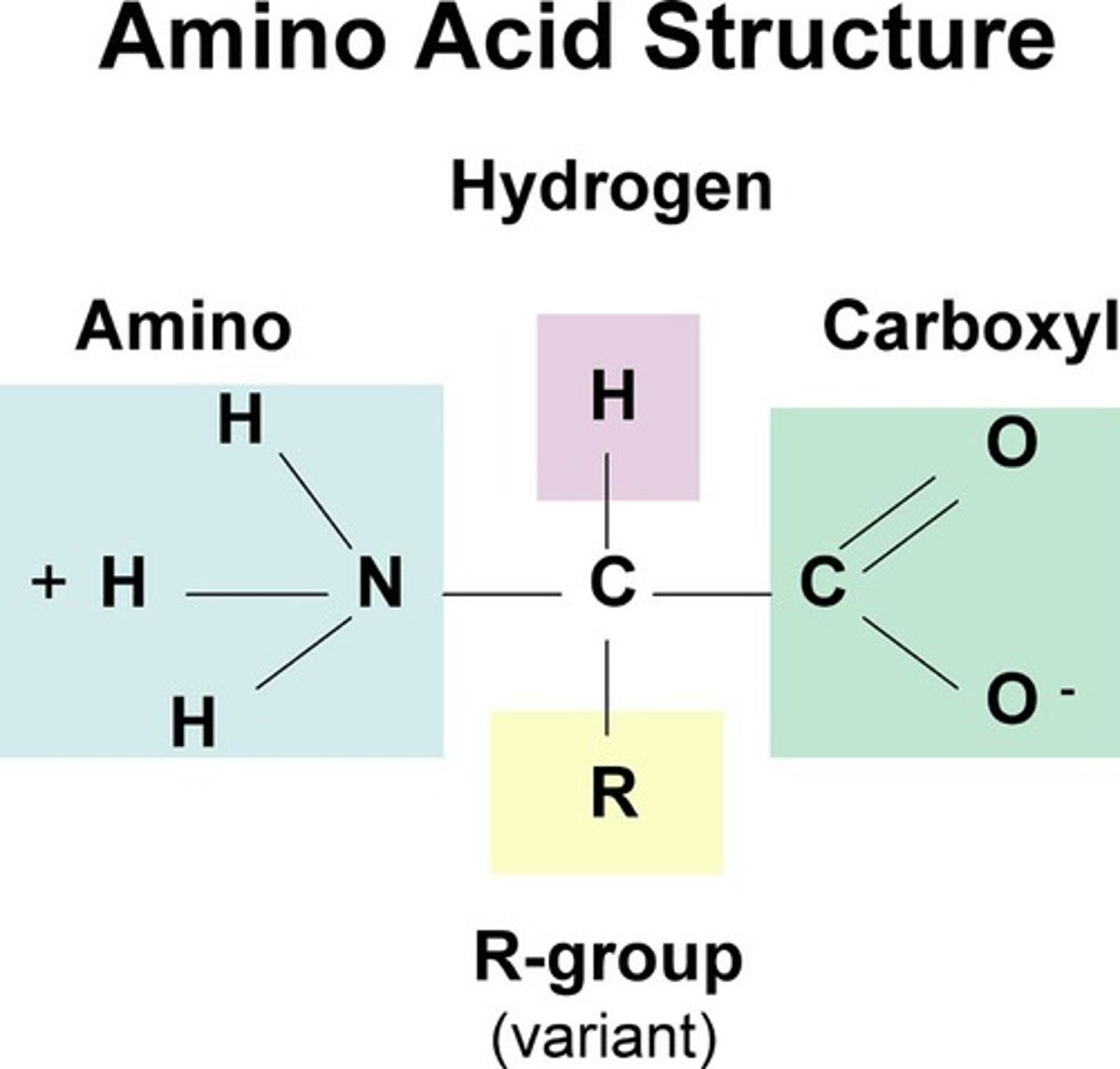
Proteins
polymers made up of amino acid monomers
amino acids
contain a central carbon bonded to a carboxyl group, an amino group, a hydrogen atom, and a R group
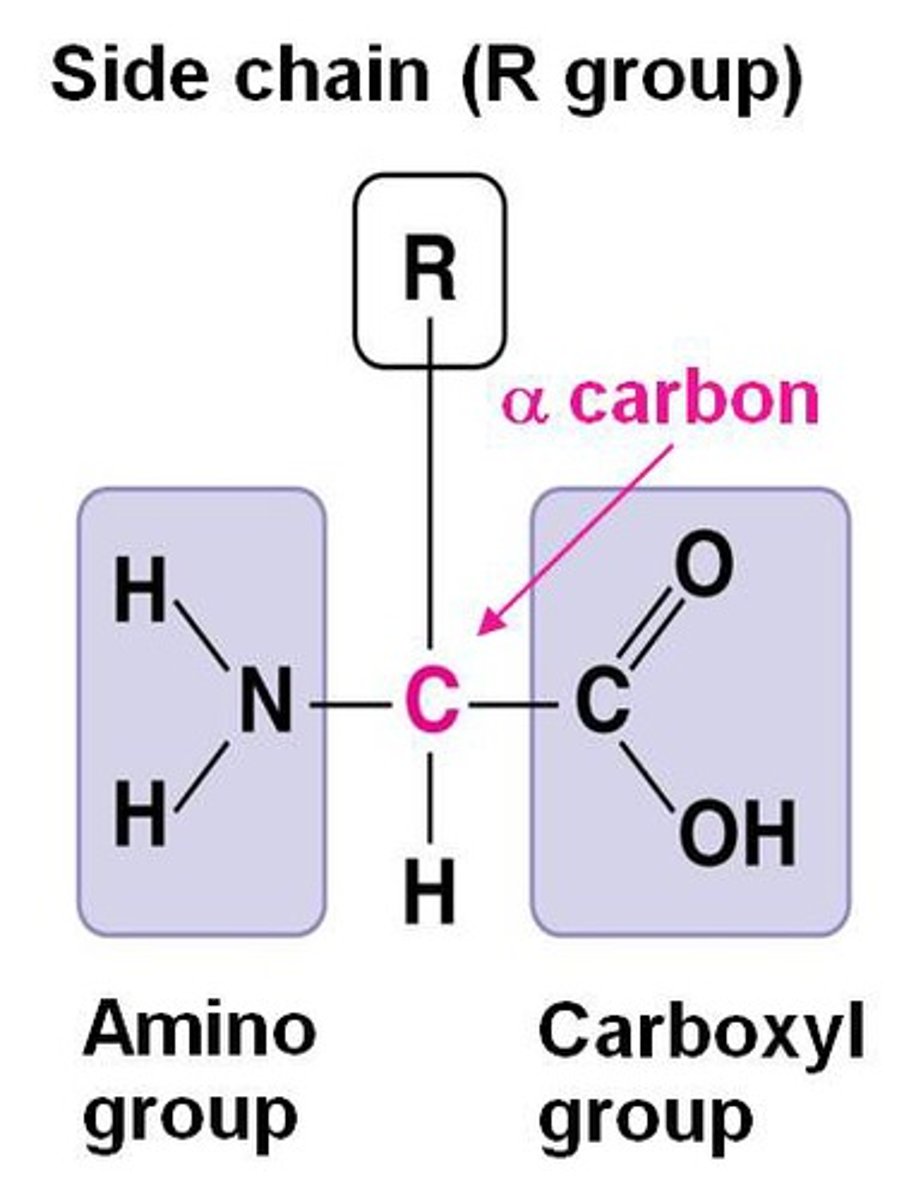
R group
An R-group is any group in which the carbon or hydrogen is attached to the rest of the molecule.
used to represent one of 20 possible side chains found in amino acids of living systems
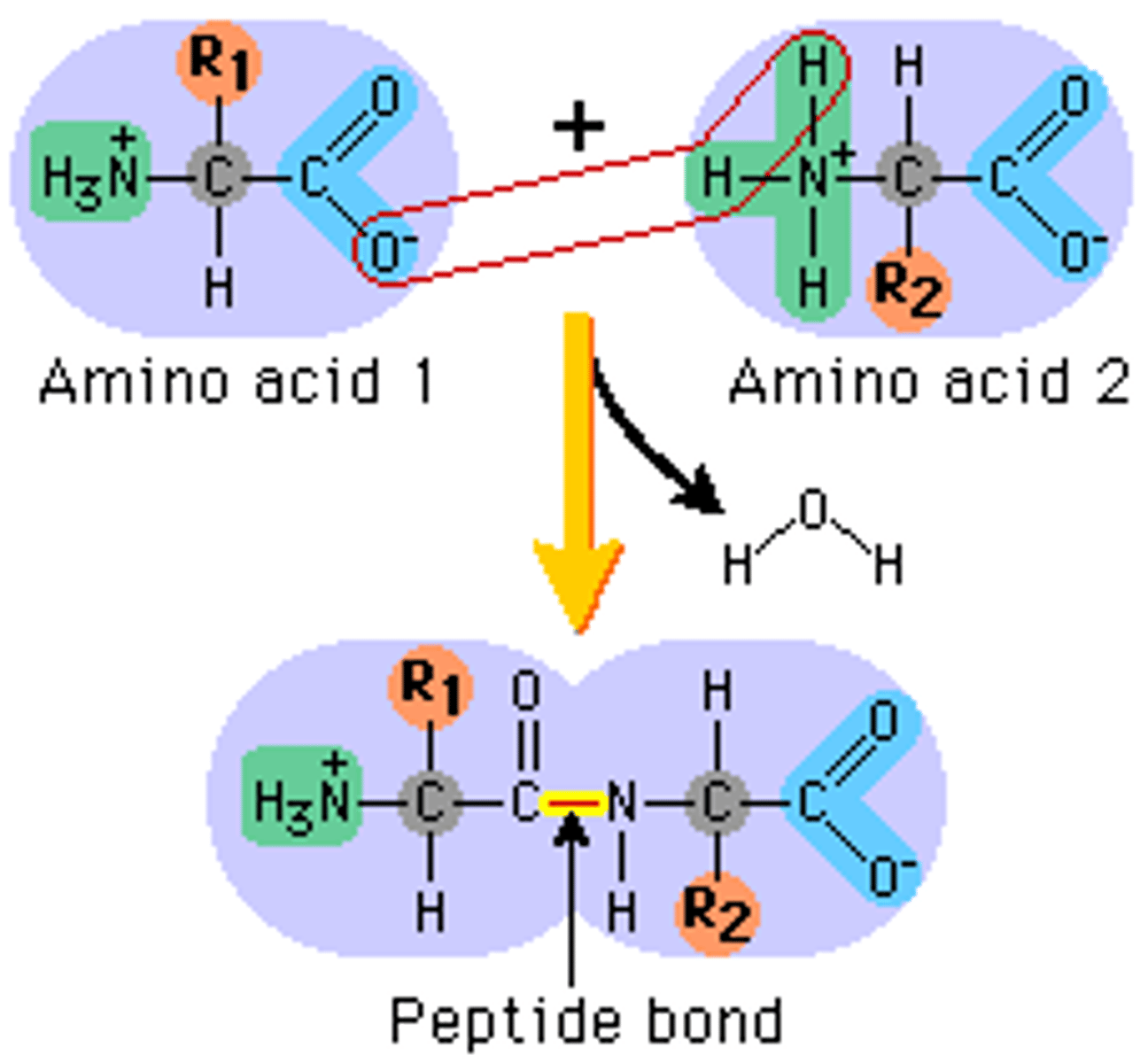
Peptide bonds
Covalent bonds linking amino acids in proteins
-formed by dehydration synthesis
-function depends on order and # of amino acids
- R group determines characteristics of each amino acid
Protein functions
1. Enzymatic
2. Storage
3. Hormonal
4. Contractile/Motor
5. Defensive
6. Transport
7. Receptor
8. Structural
4 Levels of Protein Structure
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
4. Quaternary
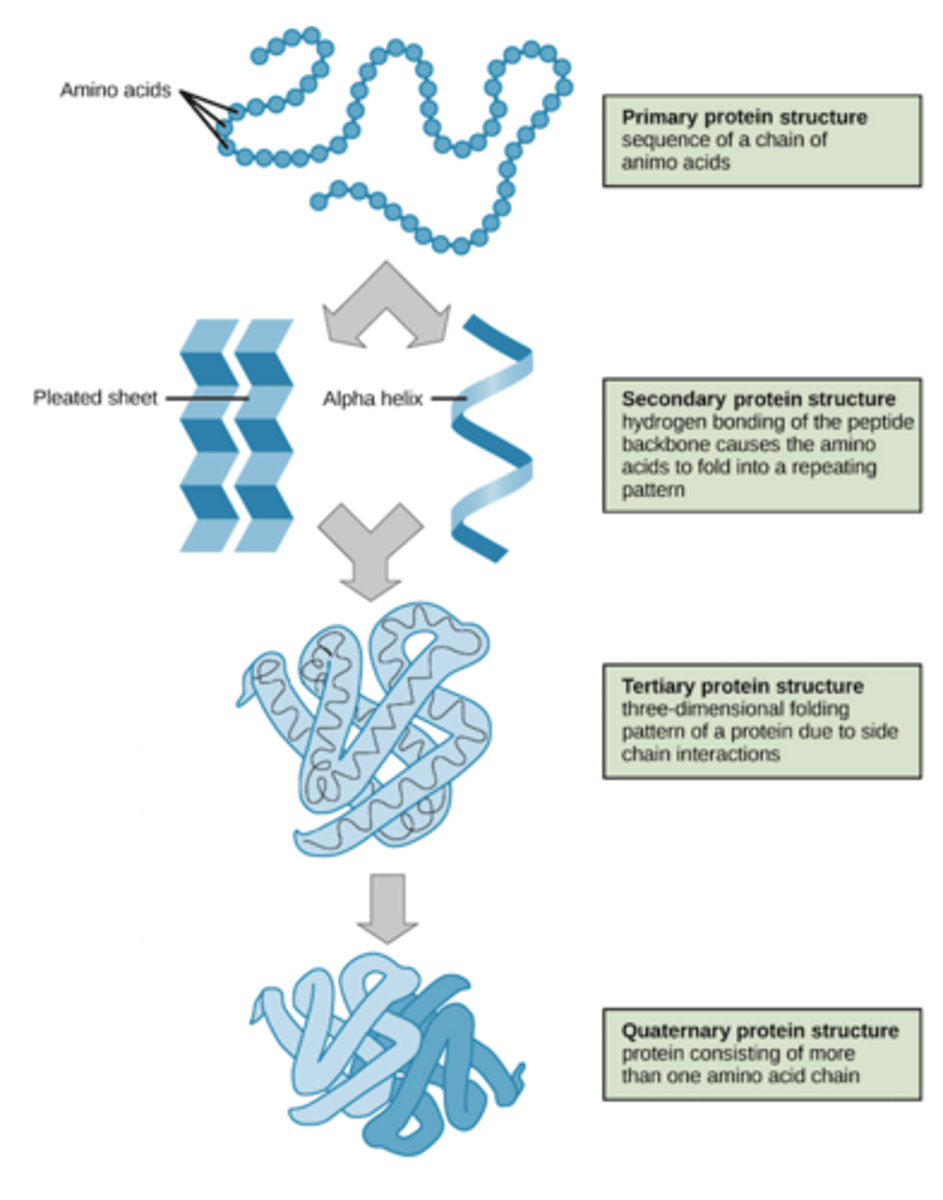
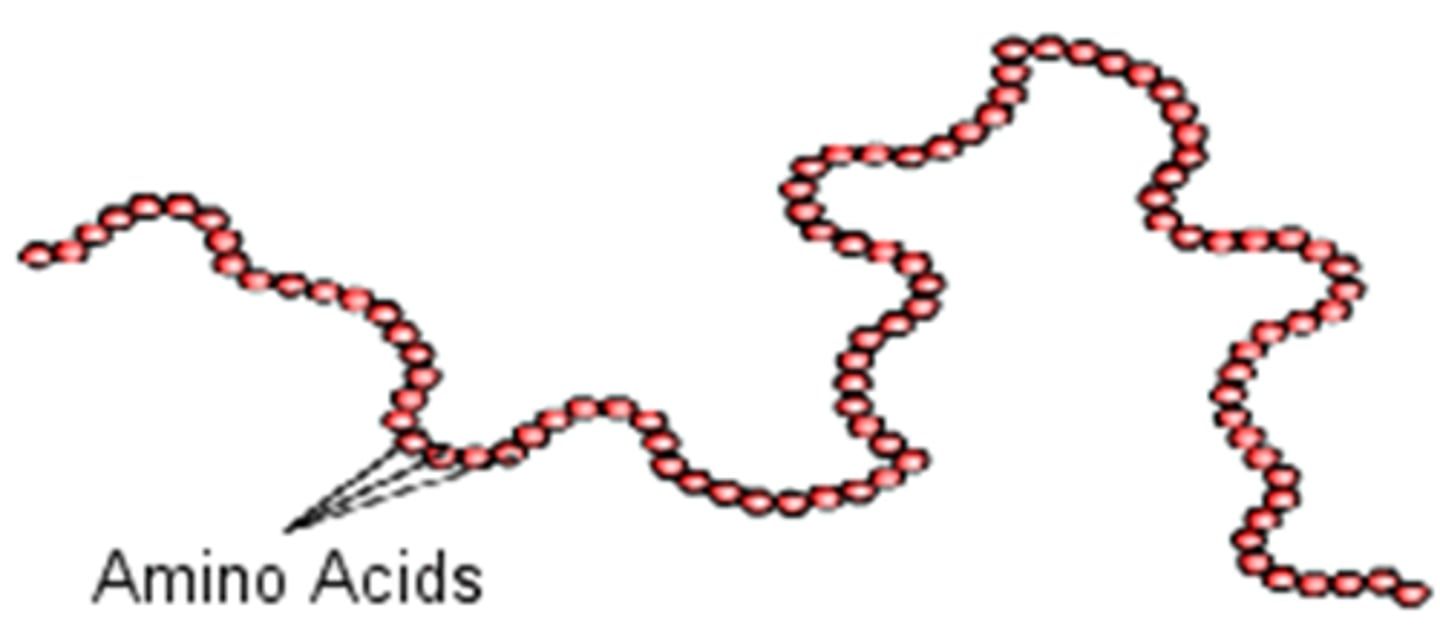
Primary Structure
sequence of amino acids
-covalent bonds

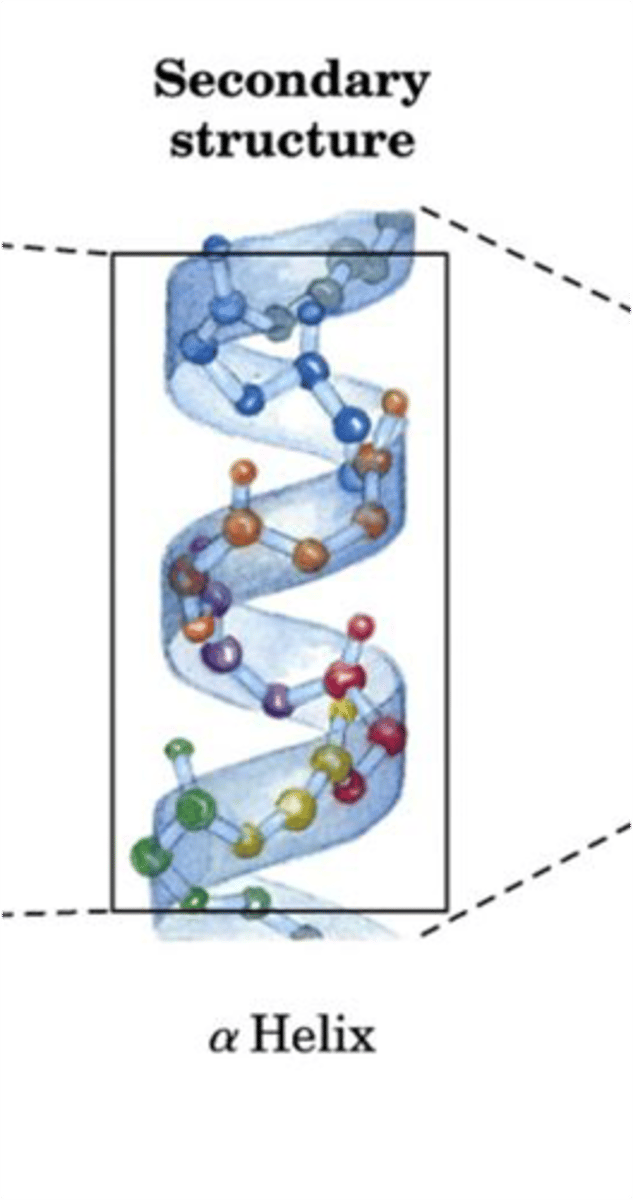
Secondary Structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
- Alpha Helix is a coiled shaped (DNA-like)
- Beta pleated sheet is an accordion shape
-hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms
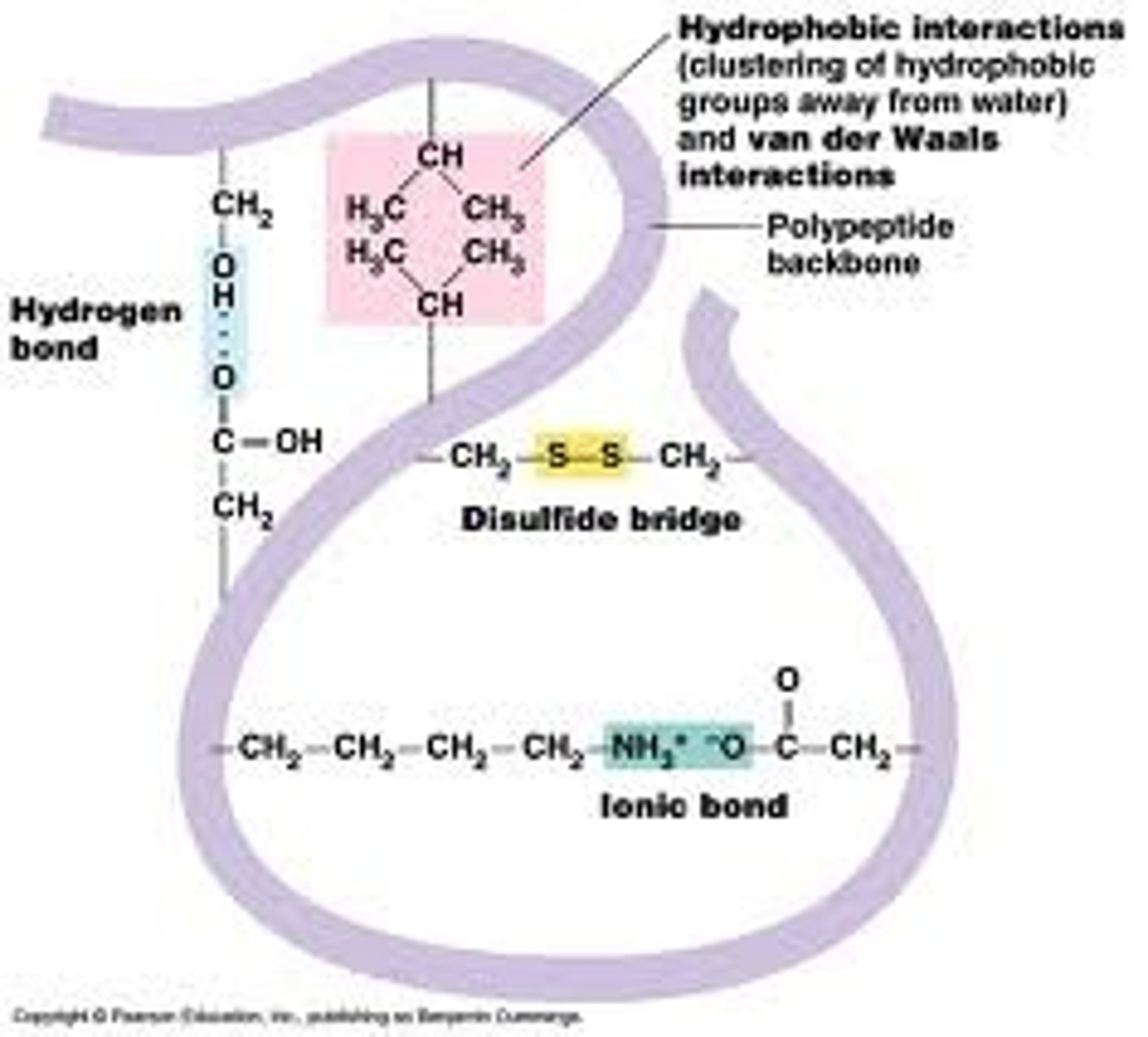
Tertiary structure
-the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain
-complex globular shape
-van der Waals interactions
-hydrogen bonds, ionic, hydrophobic,
-disulfide bridges
-enzymes are held in place by R-group interactions
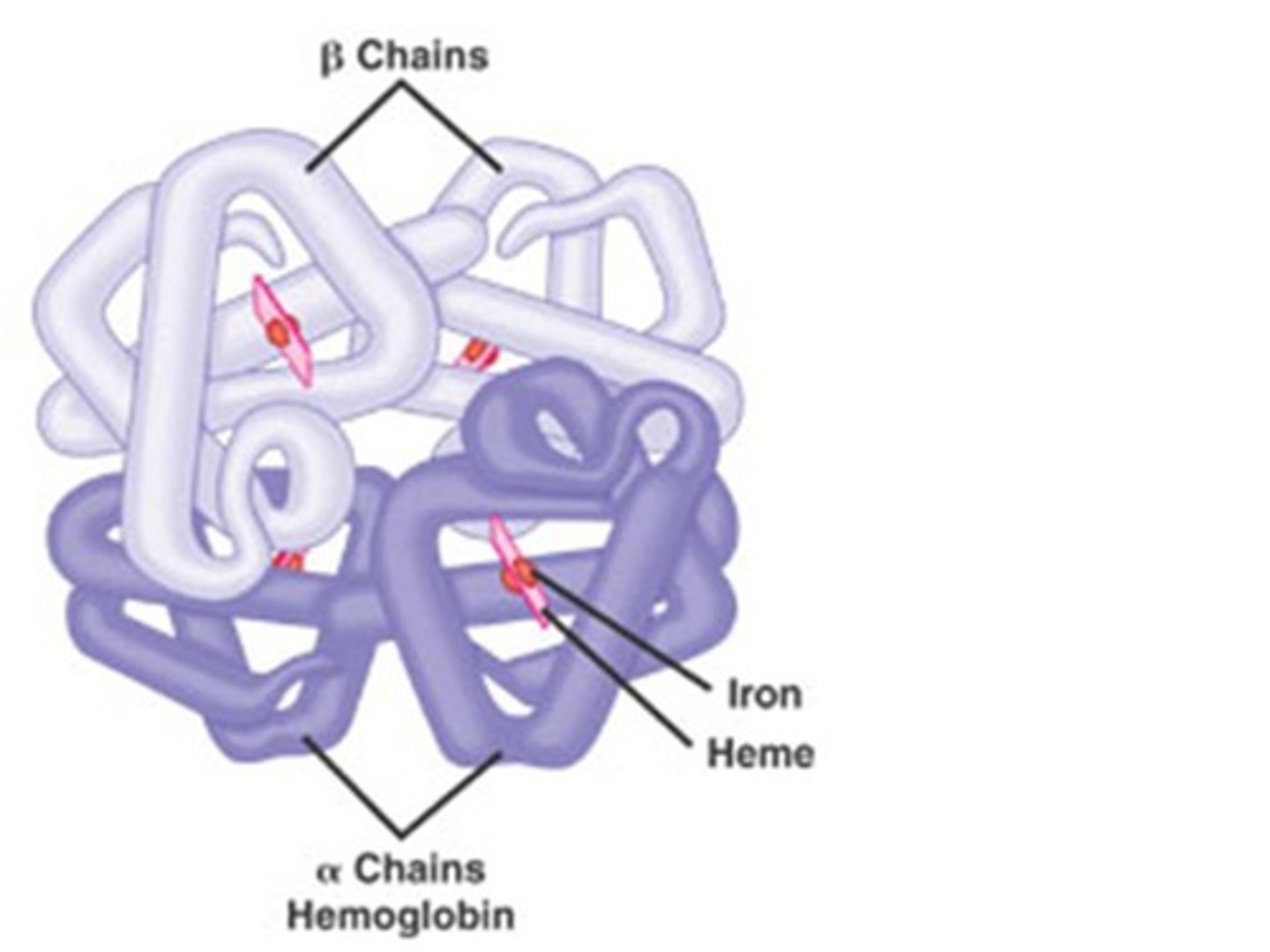
quarternary structure
The overall protein structure that results from the aggregation of two or more polypeptide subunits.
-same bonds as tertiary
protein shape determines
protein function
-misfolds cause function changes
-amino acid substitutions cause misfolds
chaperonins
protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins
denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factor
DNA
-deoxyribonucleic acid
-double-stranded helix
-nucleotides include adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine
-A=T, C=G
(Think: apples in trees, cars in garages)
RNA
-ribonucleic acid
-single stranded
-protein synthesis
-Nucleotides are adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine
- A=U , C=G
(U replaces T)
Monomer of each macromolecule
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharide
Proteins: Amino acid
Nucleic Acids: Nucleotide
Lipids: (no repeating monomer units) Glycerol, fatty acids
Elements Associated with Carbohydrates
C- Always
H- Always
O- Always
N- Never
P-Never
S-Never
Remember: CHO
Elements Associated with Lipids
C- Always
H- Always
O- sometimes
N- Never
P-Sometimes
S-Never
Remember: CH and sometimes OP
Elements Associated with Proteins
C- Always
H- Always
O- Always
N- Always
P-Never
S-Sometimes
Remember: CHON, sometimes S
Elements Associated with Nucleic Acids
C- Always
H- Always
O- Always
N- Always
P-Always
S-Never
Remember: CHONP
Compounds that can be composed of CHO ALONE
Only carbohydrates and lipids
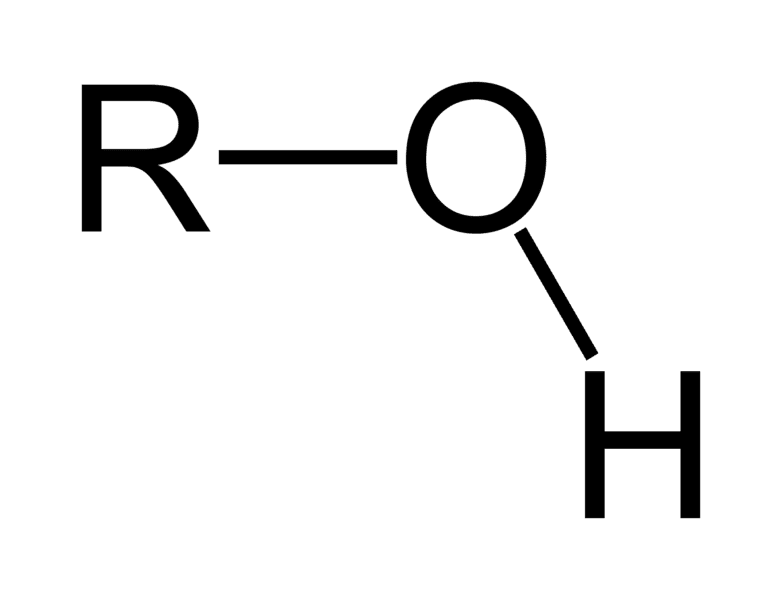
Which Functional Group is this?
Hydroxyl
-OH
Alcohol