water, pH, and carbon (quizlet #3)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Water
Essential to life, abundant, 60-70% of human body/cells. Polarity of water and the resulting hydrogen bonds makes it unique and special
What are the special properties of water?
High heat capacity, heat vaporization, ability to dissolve polar molecules, cohesive and adhesive properties, dissociation into ions that leads to generating pH
Polarity of water
It is composed of H and O which form polar covalent bonds. It does not have a net charge, but there is partial positive on H and partial negative on O because of it's polarity
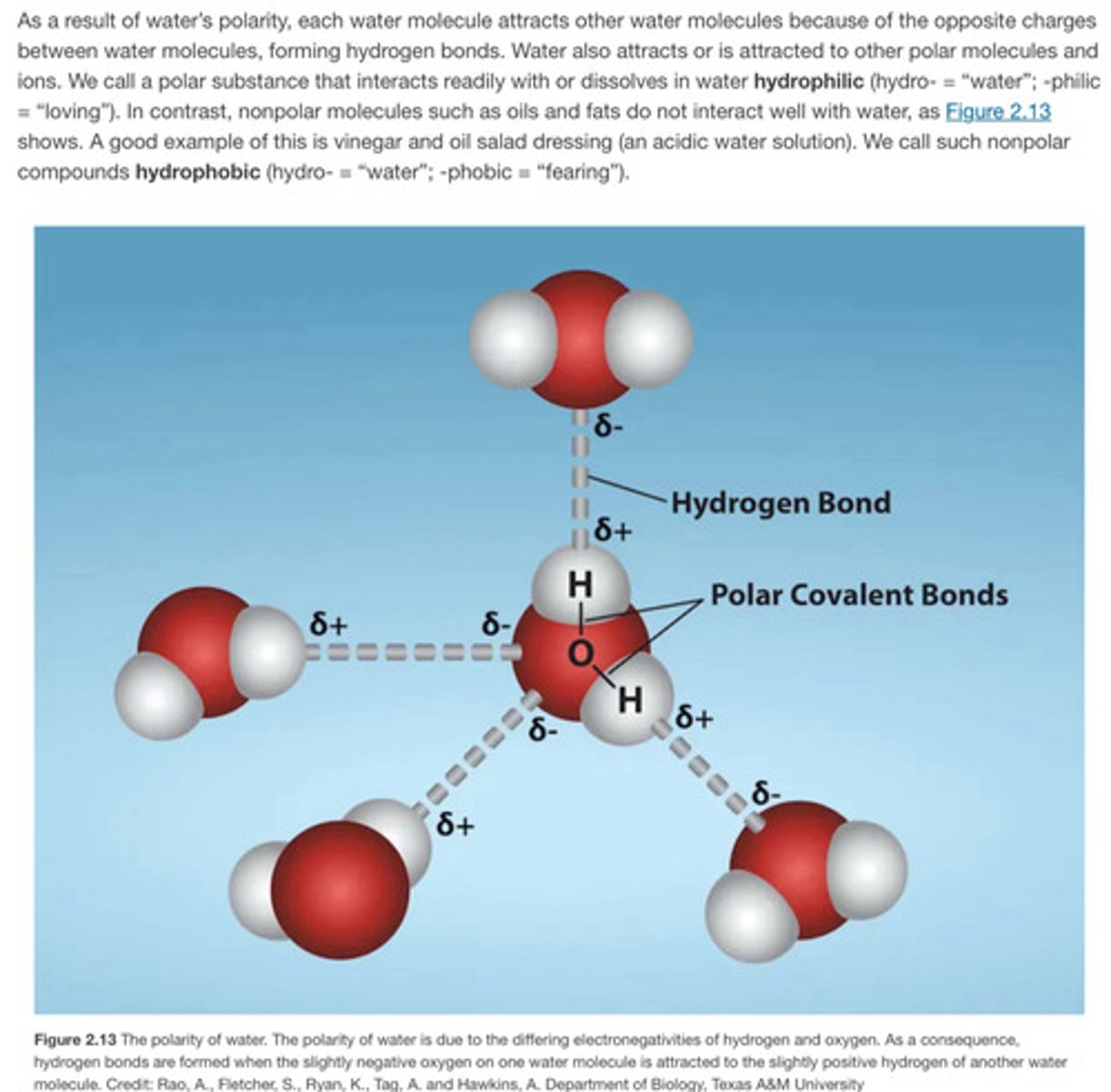
What states can water be found in? Properties of each
Liquid
- formation of hydrogen bonds important quality. they are constantly forming and breaking as water slides around. the sliding creates kinetic energy that breaks bonds due to heat it creates
Gas (steam or water vapor)
- When heat gets high and water boils the kinetic energy makes h bonds completely break and water molecules to escape into air as gas
Solid (ice)
- Freezing forms crystalline structure maintained by h bonding
- Ice is less dense than liquid water because of how the h bonds orient (this allows ice to float in water)
Is water a solvent?
It is polar with partial positive and partial negative so it is very capable of dissolving other polar molecules and ionic compounds
DO I NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CAPILLARY ACTION
idk but it can happen cuz of waters special properties idk maybe smth abt kinetic energy
What is pH?
pH of a solution indicates is acidity or basicity
What is an acid?
Substance that increases hydrogen ions (H+) concentration in a solution (usually by ionization of one of its hydrogen atoms)
What is a base?
Provides either hydroxide ions (OH -) or other negative charged ions that combine with H ions, reducing their concentration in solution, thereby raising pH
How does a solution become more acidic or basic?
Changing the concentration of H+ ions relative to OH- ions. Two H2Os into an H3O+ (hydronium ion) and OH - (hydroxide ion) REVIEW THIS SLIDE
In aqueous solutions, acids donate H+. Why does this happen and what does this do to pH and why?
(NEED TO UNDERSTAND WHY BETTER), pH goes down because overall concentration of H+ is increasing
In aqueous solutions, bases donate OH- or accept H+. Why does this happen and what does this do to pH and why?
(NEED TO UNDERSTAND WHY BETTER), pH goes up because overall concentration of H+ is decreasing
Why does Carbon show up in lots of biologically relevant molecules?
Can make four bonds that are equidistant (consistent angles) from each other. This makes it a great building block. Is the backbone for many larger molecules
What is an organic molecule?
Any molecule that contains carbon
What is a hydrocarbon?
Organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen
What shapes can carbon molecules exist in? Include bonding too
Linear carbon chains, carbon rings, or combinations of both. Individual C to C bonds can also be single, double, or triple covalent bonds.
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures (differ in placement of their atoms and/or chemical bonds)
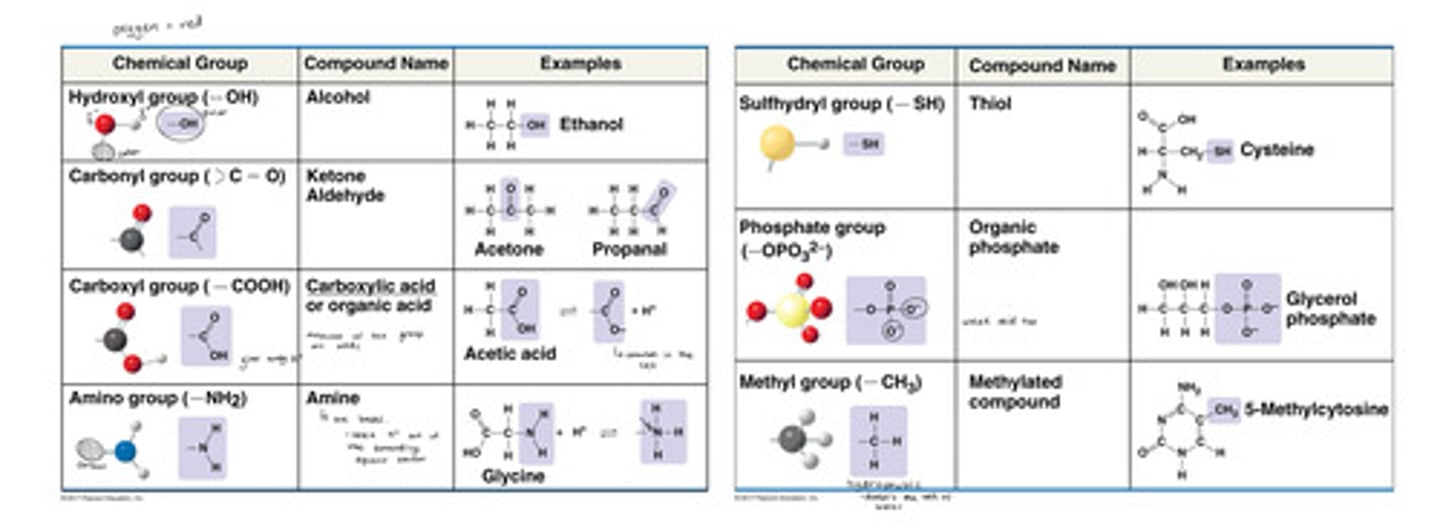
What are functional groups?
Groups of atoms that occur within molecules and confer specific chemical properties to those molecules. They attach to carbon and lend their chemical properties to molecules
The functional groups are