physics, forces and acceleration test
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is a FBD (free body diagram)
simplified representations in a problem of an object (the body), and the force vectors acting on it.
Which way does gravity point in a FBD
down
Which way does normal force point in a FBD
up
What is gravity
(Fg) Pulls objects down towards the earths core
what is applied force
(Fa) Force exerted by another object/actor
what is force of friction
(Ff) Force that resists motion when objects are moving in contact with on another. Ex. the reason a chair stops if you push it across the floor.
what is normal force
(Fn) The force that solids exert on one another to prevent objects from passing each other. Equal and opposite force. Ex you and your chair.
what is force of tension
(Ft) Occurs if the object exerting the force is a string
Which way does force of friction point in a FBD
opposite of movement
Which way does applied force point in a FBD
The direction the object is moving. EX. A car moving to the right- arrow pointing to the right.
Which way does force of tension point in a FBD
up (replaces normal force)
What is newtons first law?
Inertia - an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by another force.
What is newtons second law?
F= M x A - Acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object.
What is newtons third law?
Action reaction - If a force is exerted on an object an equal and opposite force will be exerted back from that object. (for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction)
How are inertia and mass related?
More mass = More inertia
How does mass affect acceleration
More mass = Less acceleration
At what speed to objects fall?
9.8 m/s2
What is mass measured in?
Kilograms (KG)
What is force measured in?
Newtons (N)
What is acceleration measure in?
m/s2
What is 1N?
1 kg/s2
What 3 formulas describe the relationship between mass, force and acceleration?
F=M x A
M = F/A
A = F/M
Difference in speed vs Velocity
Speed = How fast, no direction
Velocity = How fast, direction ( can be + or -)
How to calculate change in
Initial - Final
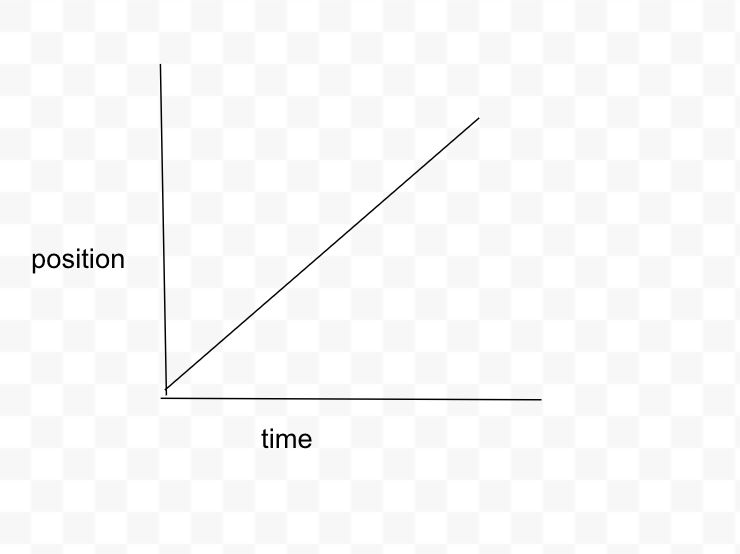
What is the position vs time graph for the car traveling on a straight highway at constant velocity for 10 seconds?
Constant slope - straight diagonal line upwards
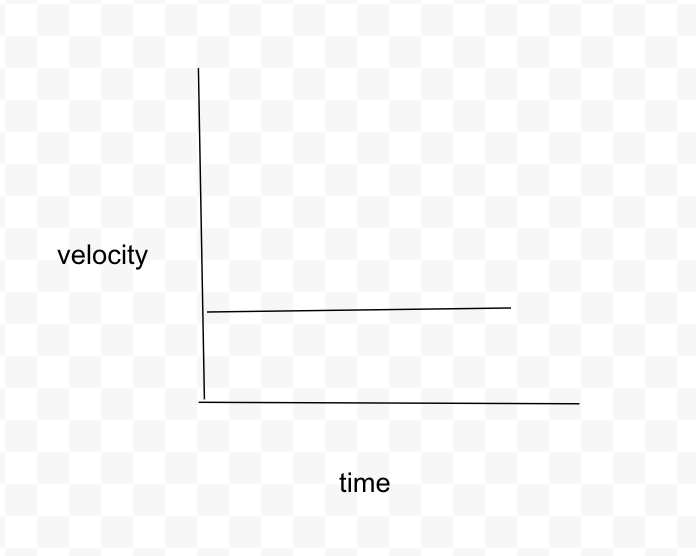
What is the velocity vs time graph for the car traveling on a straight highway at constant velocity for 10 seconds?
straight line - slope not changing
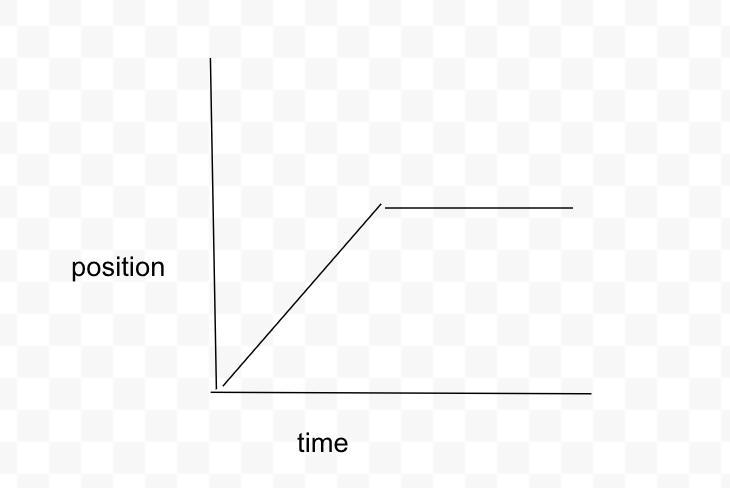
What is the position vs time graph for the car traveling on a straight highway at constant velocity for 10 seconds and then it stops for 5 seconds?
Constant slope, diagonal line upwards until it stops then it becomes a straight flat line
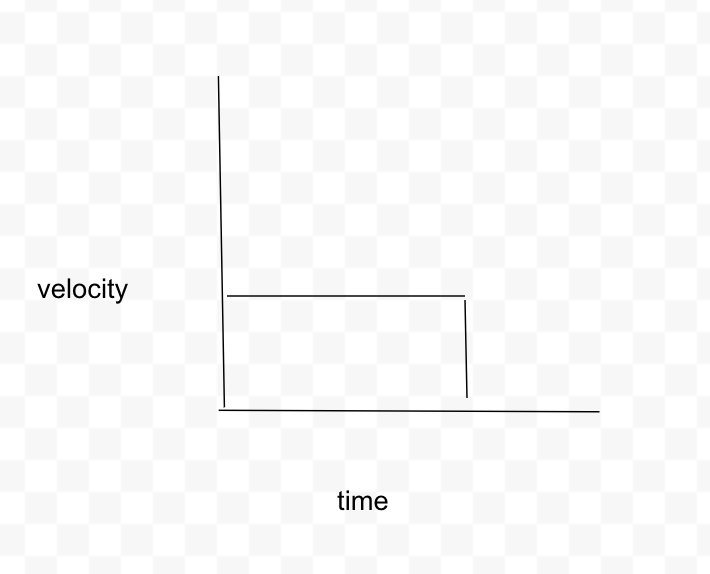
What is the velocity vs time graph for the car traveling on a straight highway at constant velocity for 10 seconds and then it stops for 5 seconds?
Straight line then when the car stop the line goes straight down.
What is the position vs time graph for the car constantly accelerating for 3 seconds?
Curved line going upwards
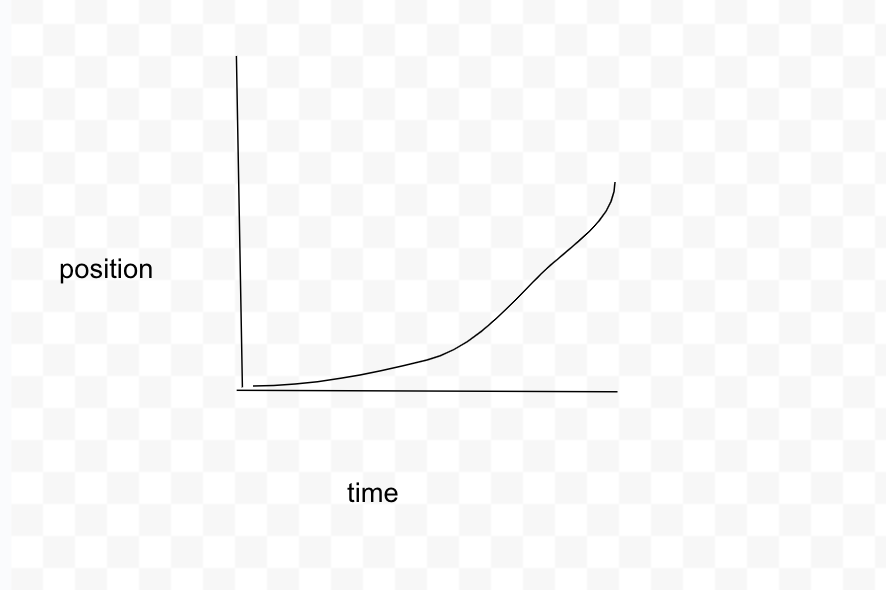
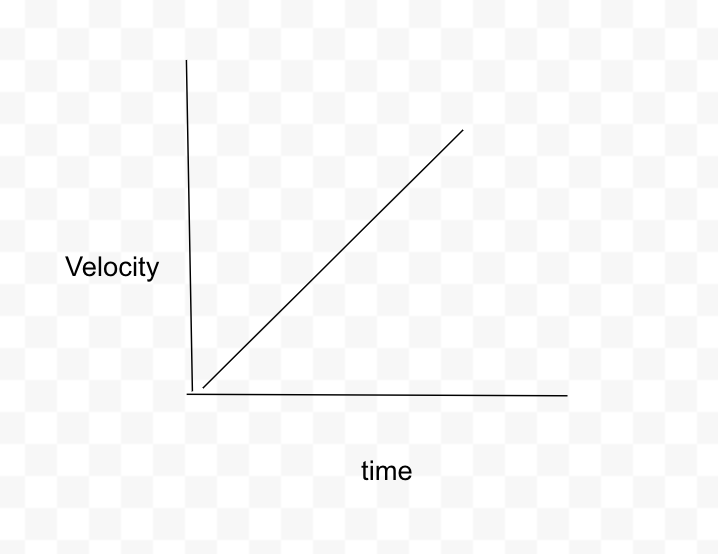
What is the velocity vs time graph for the car constantly accelerating for 3 seconds?
Straight diagonal line upwards, constant slope
What direction is the force during circular motion?
inward
What direction is the acceleration during circular motion?
inward
What direction is the velocity during circular motion?
outward
how do you draw a circular FBD?
draw a circle, and make an L shape with one point going inward and one going outward. The point going inward is acceleration and the force and the point going outward is velocity
If there are 80n of applied force going to the right and 40n of force of friction going to the left, what will happen?
it will move to the right and the net force is 40n
If there are 40n of applied force going to the right and 40n of force of friction going to the left, what will happen?
it wont move at all
If there are 80n of applied force, on an object that has a mass of 80kg, going to the right and 40n of force of friction going to the left, what will happen?
it will be going to the right at ½ m/s²
What 3 things does gravitation force between two objects depend on?
Mass (of the first object) mass (of the second object) and the distance between those two objects
What is mass?
The amount of matter/stuff that is containe in an object
Is the gravitational force between two ordinary objects big or small?
Very small, ignorable
Does your mass change depending on what planet your on?
No
When do you use Fg= m x g
When you want to find the gravitational force of an object, but this equation only works for planet earth.
What is (g)?
Gravitational acceleration (9.8)
What is (G)?
univeral gravitational constant (6.67×10-11)
What units are used for (g)?
N/Kg (gravitational field strength of earth)
What is another word for Fg?
weight
What does r2 stand for?
distance between the objects (squared)
Does your gravitational force change depending on what planet your on?
yes