Radiology Lecture 4: Film Imaging - Image Receptors, Latent Image Formation, Processing, Errors
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is film covered by?
Gelatinous emulsion with crystals
What is the makeup of the crystals?
- Mostly (95%) silver bromide (AgBr)
- Some (5%) silver iodide (AgI)
What are crystals called collectively?
Silver halide
The silver halide matrix in the emulsion has the same functions as the ________________
- Barium fluorohalide phosphor layer in DR
- Europium ions and silicon
Latent image site or sensitivity speck
A sulfur containing compound
Interstitial silver ions
Non-bound silver ions that can move within the crystal; these ions are positively charged
Remnant radiation
X-rays that pass through the patient (transmitted photons) expose crystals in the emulsion
Interstitial silver ions migrate to the _________ in exposed crystals and become neutral silver atoms
Latent image site
What does the latent image site have the same function as?
F-centers in PSP imaging and electrons in the charge packets
Latent image
Invisible change produces on film, resulting from the differential exposure of the film by x-rays passing through the patient
What is the latent image analogous to?
Latent image in digital radiology created by electrons in the F-centers in PSP or voltage patterns on solid-state sensor after exposure
What is the latent image made visible by?
Processing the film
Crystals that have been exposed to more x-rays have _______________
Large amounts of neutral silver at the latent image site
Crystals that have been exposed to fewer x-rays have _______________
Fewer silver atoms at the latent image site
Crystals that have not been exposed to x-rays have ___________
Unchanged structure
What does the pattern of exposed and unexposed crystals result in?
Varying amounts of neutral silver at the latent image sites, is the latent image
T/F: F-speed (fastest) intraoral film requires the same exposure as solid-state sensors
False
- Same exposure as PSP sensors
Exposure time can be reduced by 60% when changing from ______ to _____ speed film
D to F
- No loss of diagnostic accuracy
How is latent image made visible?
Processing in a darkroom (or other light-safe area) with chemicals
- Same as sampling and quantizing voltage, then applying the gray scale
What are darkroom requirements?
Exclude white lights bc light leaks cause dark or black areas (fog) on film
In PSP digital radiography, white light _______ the latent image, and the visible image is too _________
- Erases, light
- Opposite of film
Exposure to white light makes the film _______
Dark
How do you explain the localized black area?
Light leak
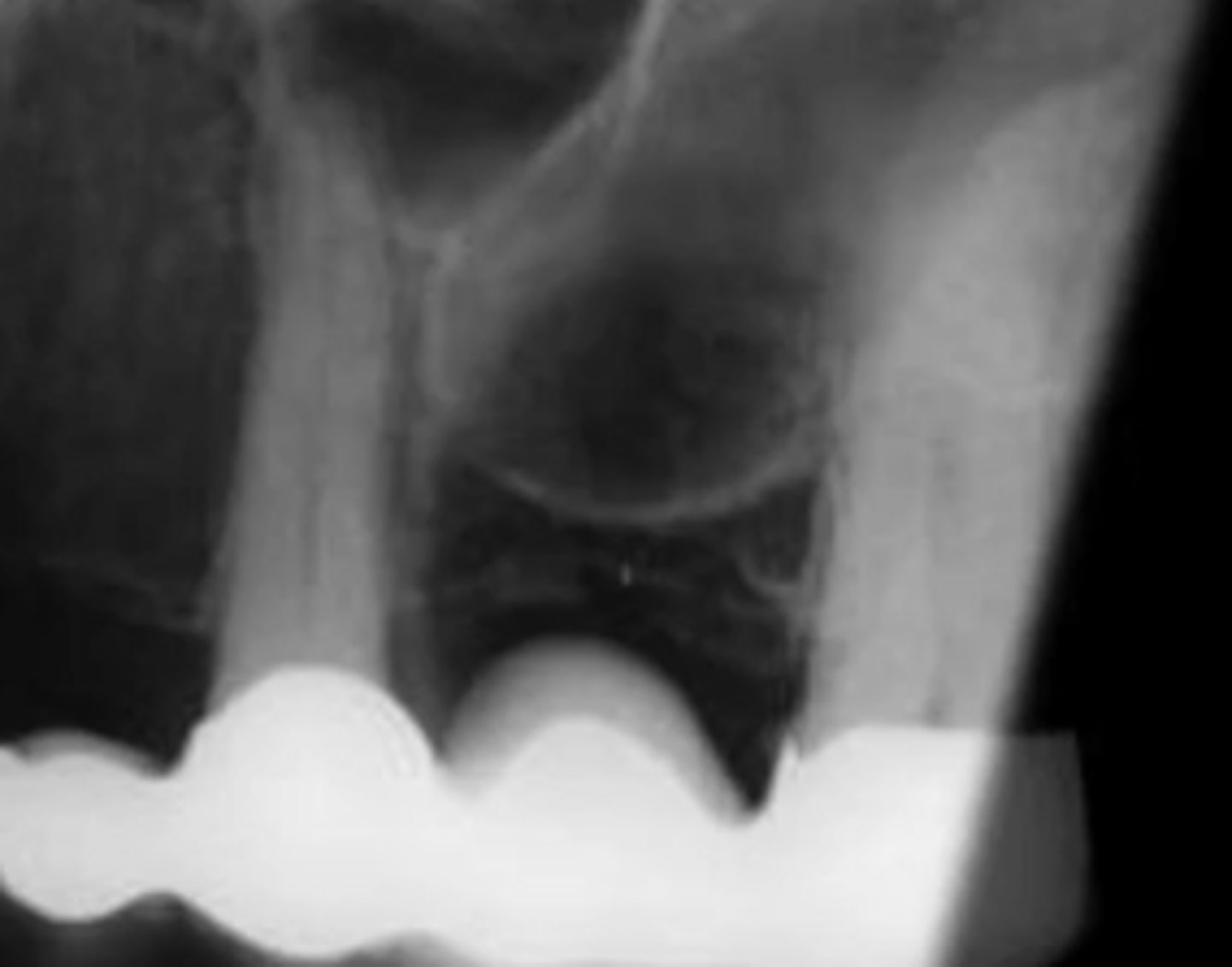
What is this?
Film fog

What is film fog?
Unwanted darkness on the image, decreases value of radiograph
What does developer reduce exposed crystals into?
Converted into solid black silver atoms
What does developer do?
Darkens (blackens) the film
- Exposed crystals look dark
Time-temperature processing
Must stop developer at proper time and must use proper temperature to avoid blackening the unexposed crystals
What does a fixer do?
Clears (lightens) the image
- Unexposed parts of film look light or clear
What happens if developer time or temperature is too low?
Too light
What happens if developer time or temperature is too high?
Too dark
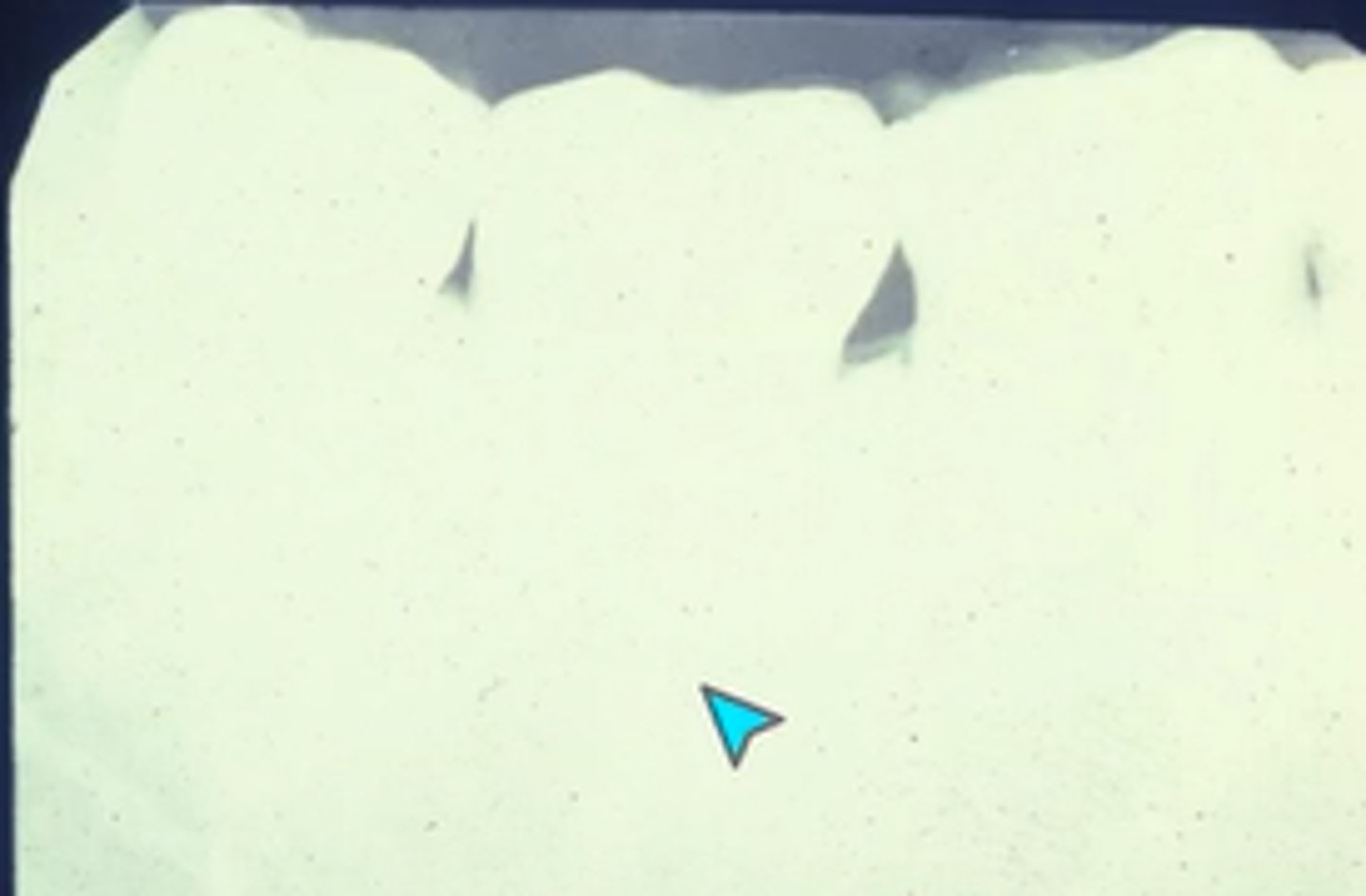
What error occurred here?
Developer time or temperature is too low

What error occurred here?
Developer time or temperature too high
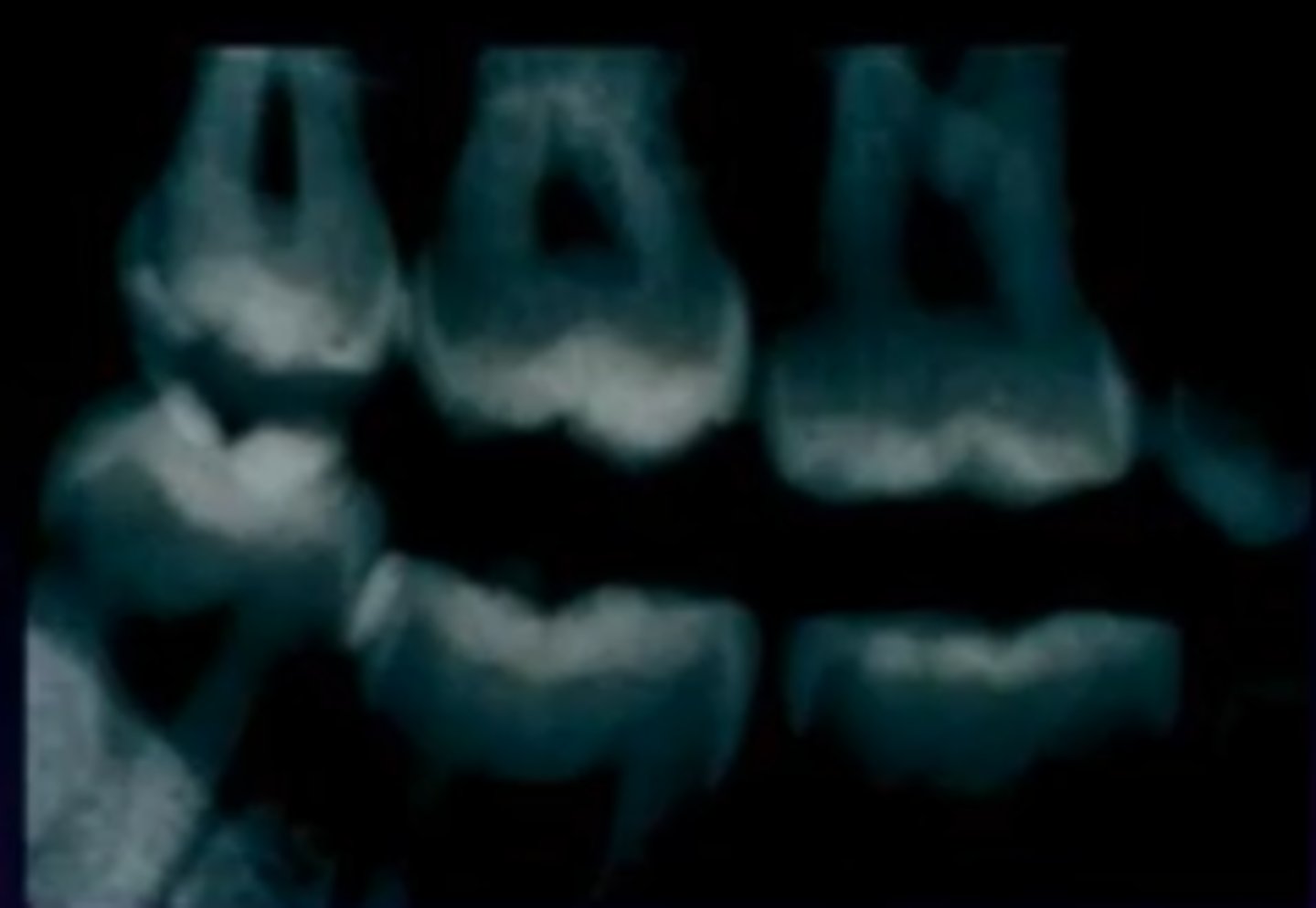
What happens if developer becomes exhausted?
Too light, contrast is poor
What does a brown appearance of radiograph indicate?
Old oxidized developer
What does a green appearance of radiograph indicate?
Inadequate developing and fixing
What happens when fixer time or temperature is too low?
Image is opaque
What happens when fixer time or temperature is too high?
Image may be light
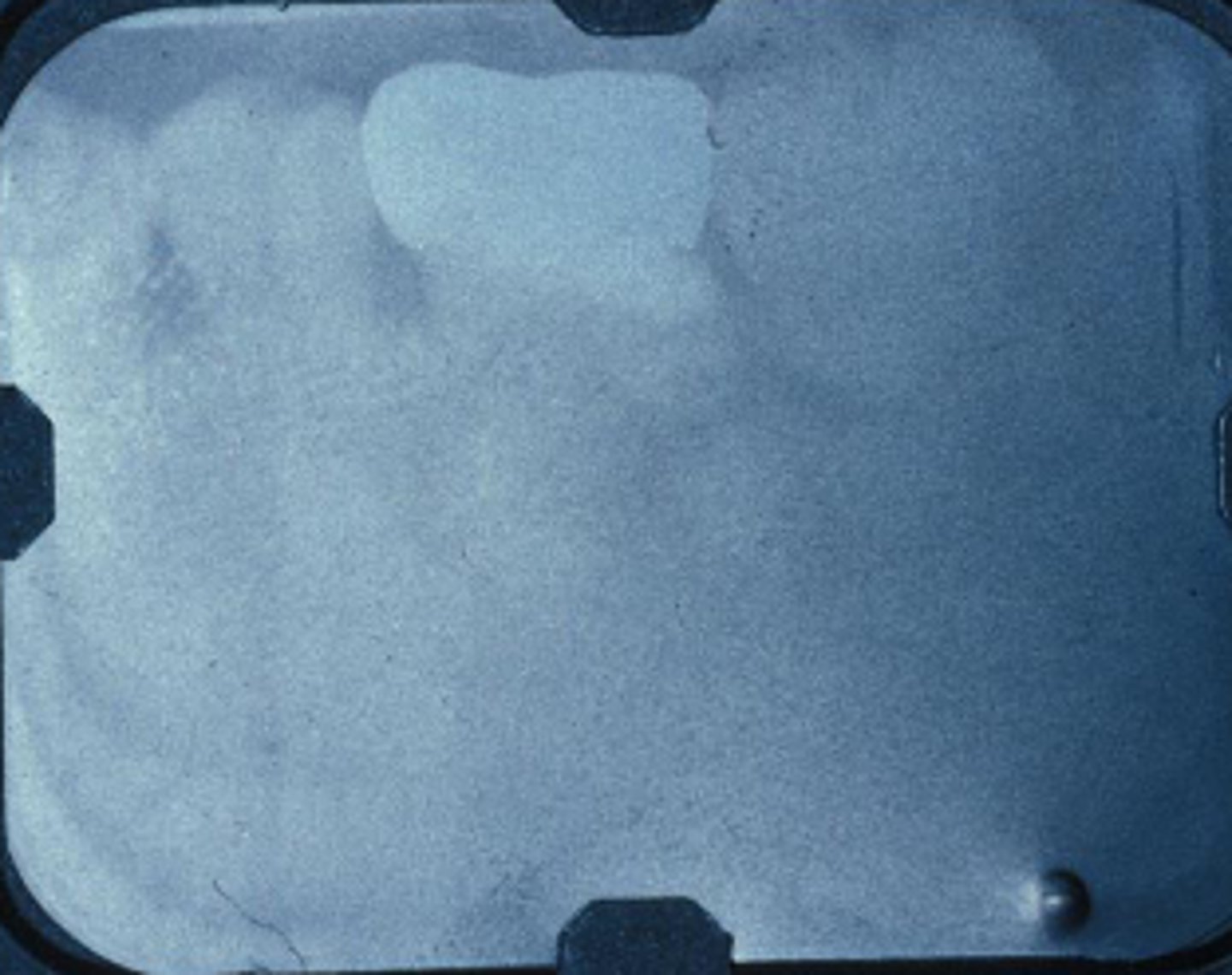
What error occurred here?
- Fixer time or temperature too low
- Radiograph opaque
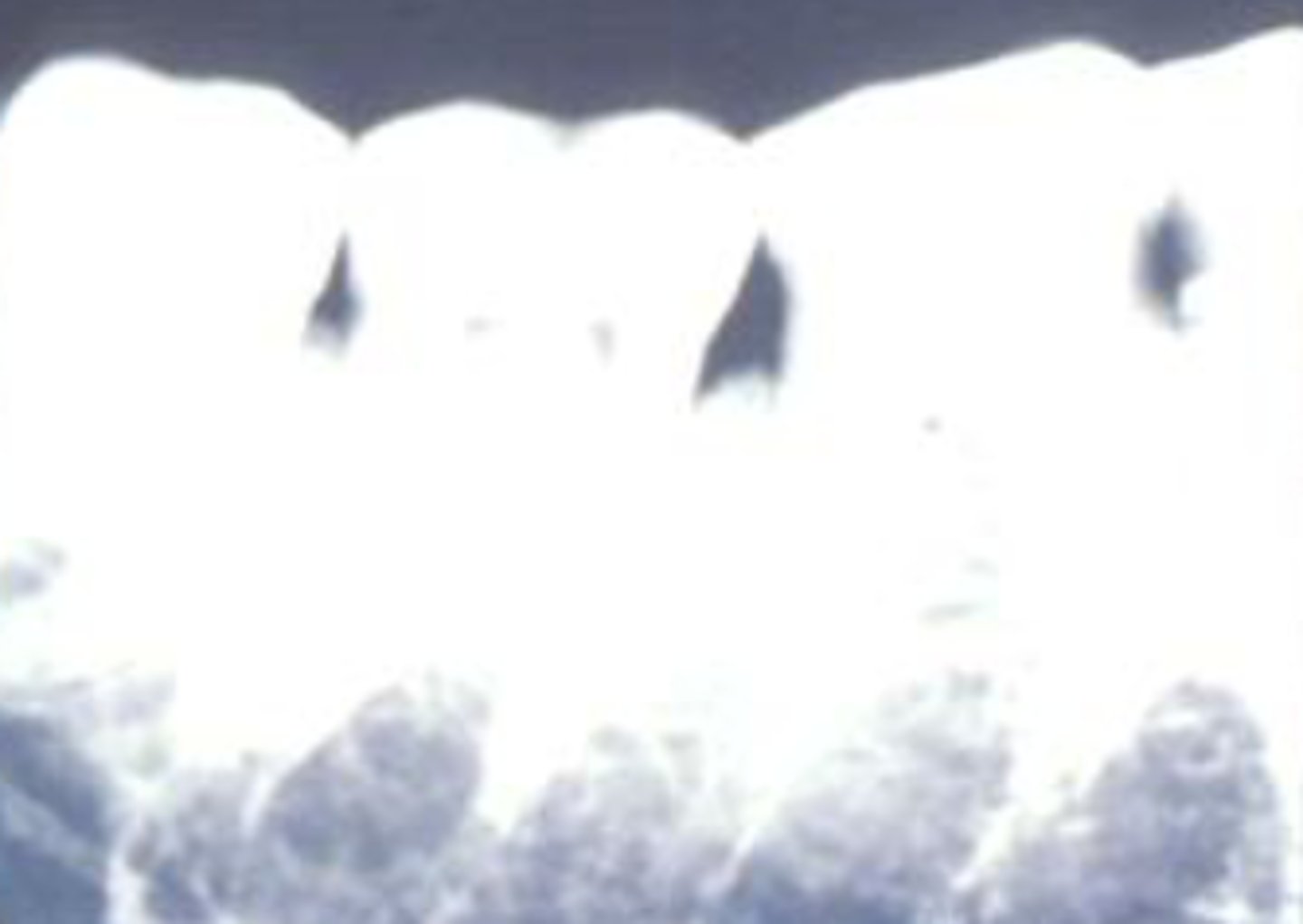
What error occurred here?
- Fixer time or temperature too high
- Radiograph light
What is produced from the film handling errors static electricity pattern?
Static charge produces lighting bolt patterns
What error occurred here?
Static electricity
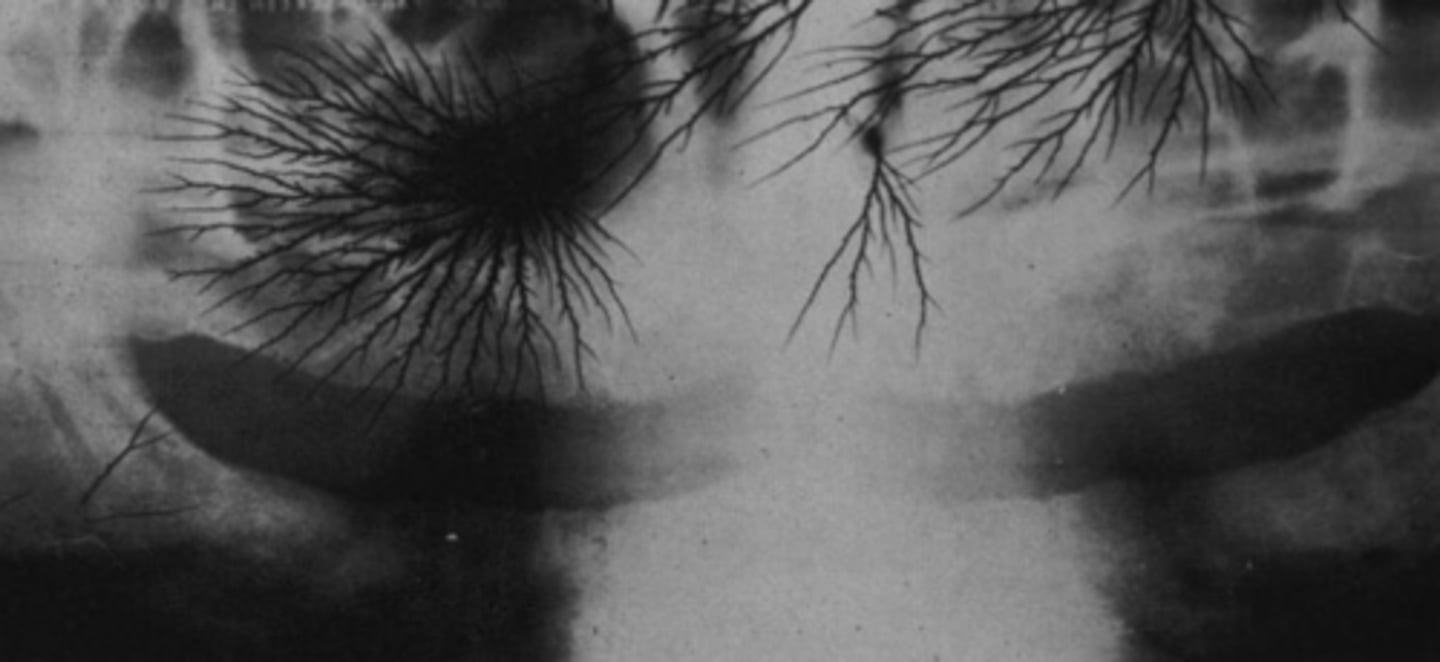
T/F: Films is a double film packet
True
What does the lead strip do?
Absorbs scatter from inside the mouth
If the film is backwards in the mouth, where is the lead strip? What does it result in?
In front of films
- Light film, circular embossed pattern
What error occurred here?
Film exposed backwards
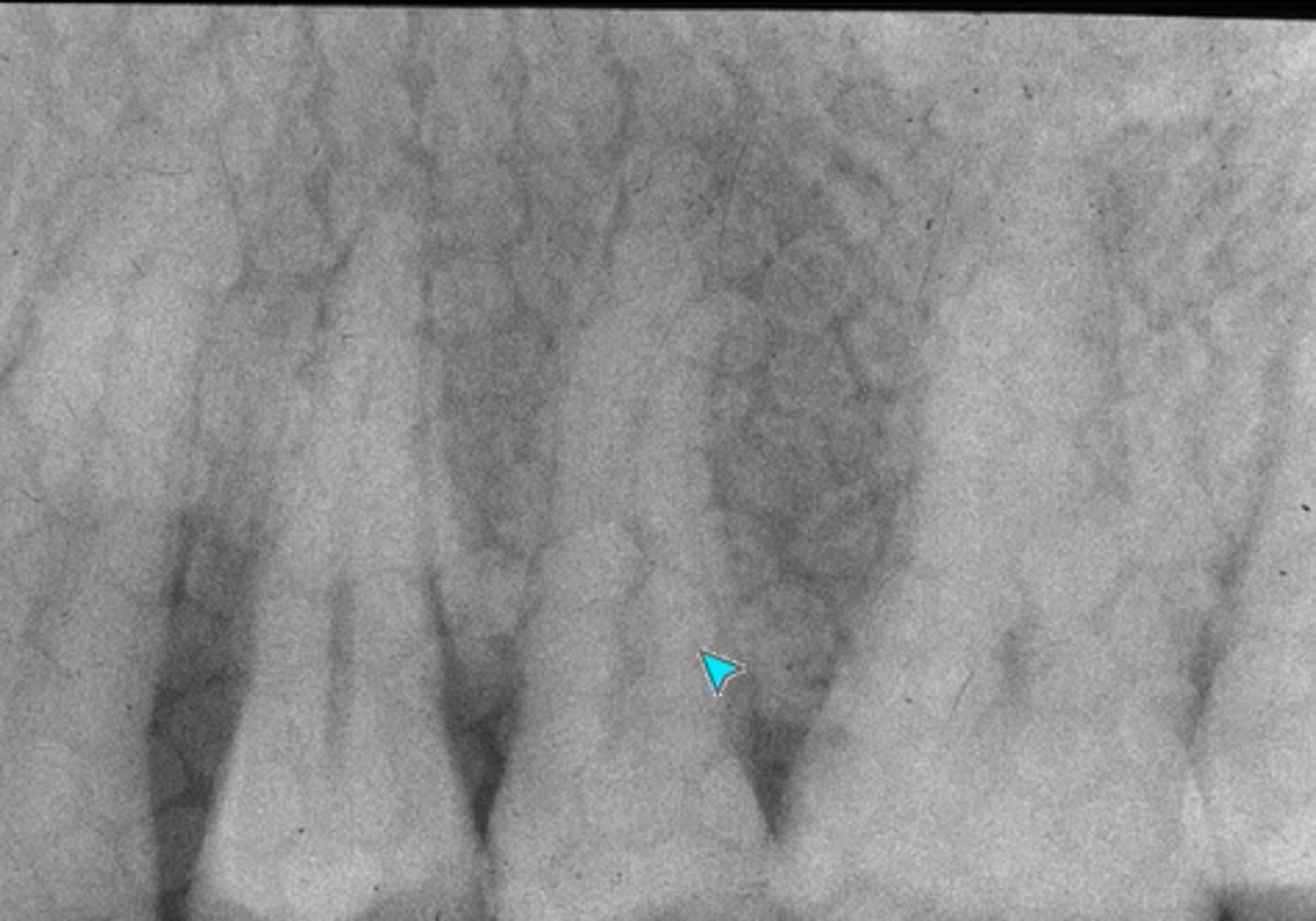
Which sensors can double exposure occur in? Which can it not occur in?
- PSP sensors
- Solid-state sensors
What error occurred here?
Double exposure
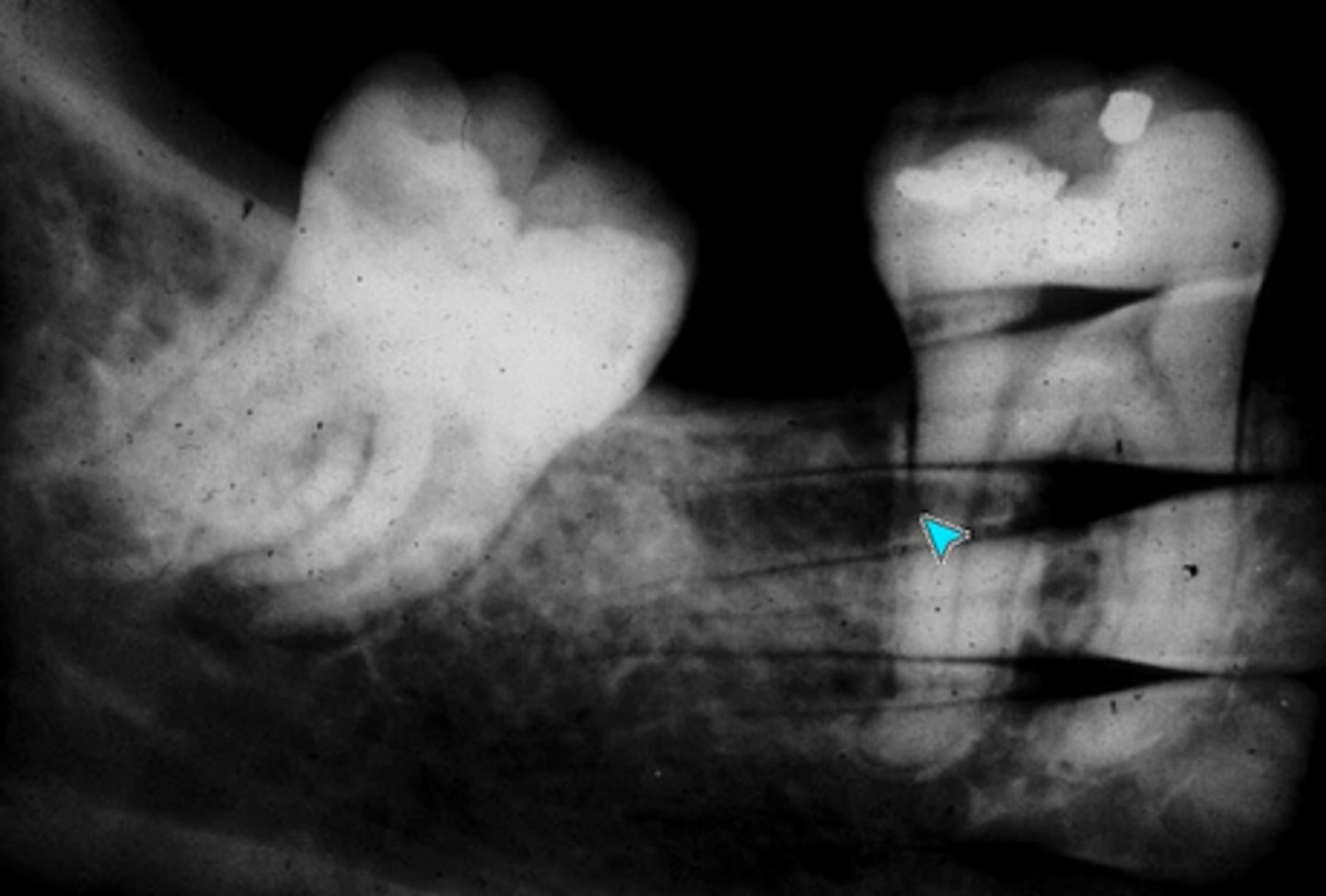
What are the types of errors?
- Exposure errors
- Processing errors
- Technique errors
- Film handling errors
What can be the results of exposure errors?
- Totally clear
- Too light
- Too dark
- Totally black
- Double exposure
What can cause a totally clear digital image?
- No exposure
- PSP sensor flooded with white light→ removes latent image signal by moving all electrons out of the F-centers
What exposure error is this?
Too light
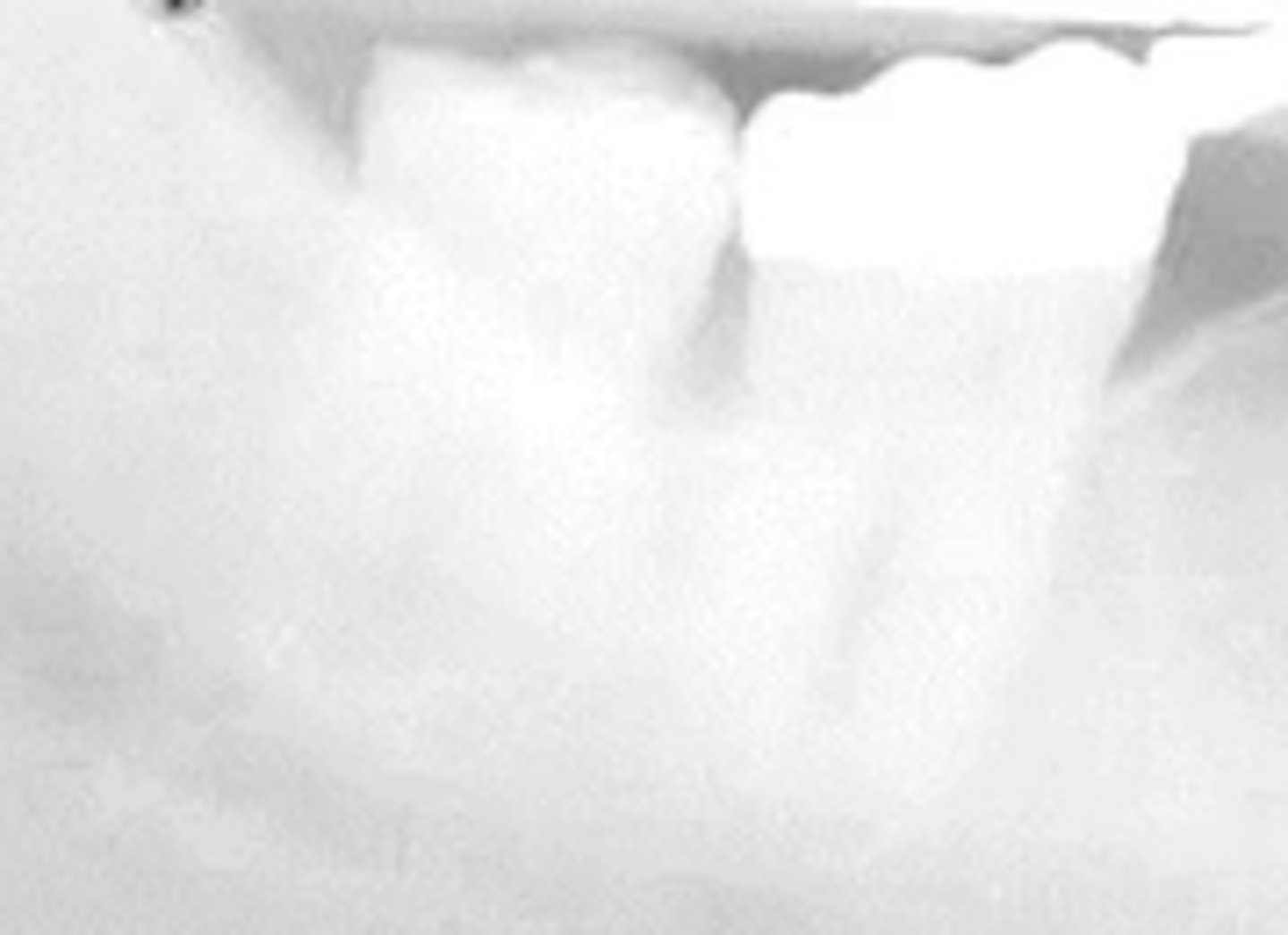
What exposure error is this?
Too dark
What is the effect of white light exposure to PSP and Film?
- PSP= too light
- Film= too dark
T/F: Exposure error leading to a totally black digital image is very common
False - almost never happens
What exposure error is this?
Double exposure
In what sensor is placing it in the mouth backward impossible?
Solid-state
T/F: Image sensor/film can be corrected if it's placed in the mouth backward
False; it cannot