Module 6- The Earth's Crust and Natural Resources-Learning Objectives
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
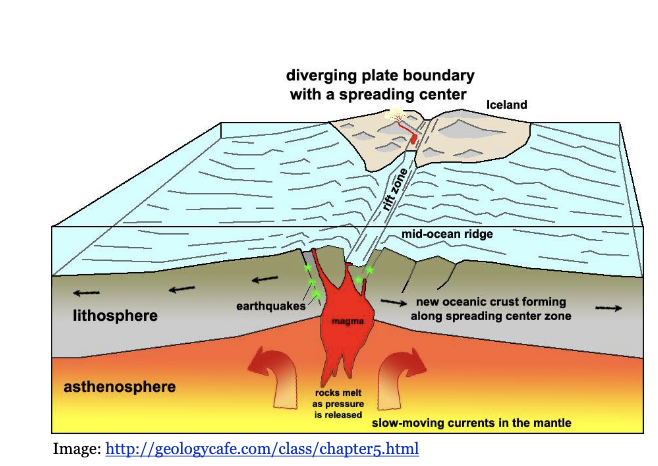
Describe how oceanic crust has differentiated from the mantle and where this occurs
mid-ocean ridges through seafloor spreading
decompression melting occurs at mantle material upwells, reducing pressure and triggering partial melting
produces mafic magma, crystalizes into basalt
homogenous, thin, young
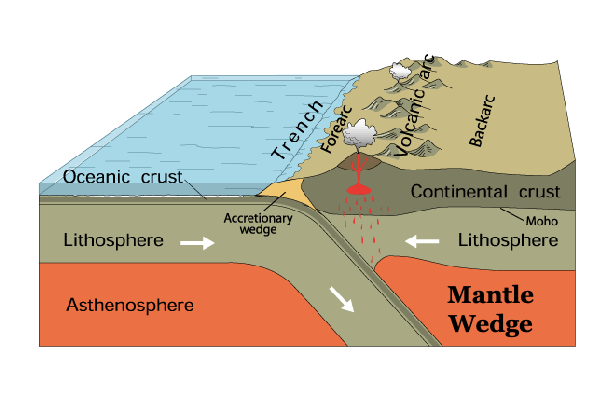
Describe how continental crust has differentiated from mantle and where it occurs
forms at subduction zones
flux melting (partial melt producing mafic magma)
mafic magma ponds at base of less dense crus and undergroes fractional crystallization make more SiO2 magma rocks
heat from ponded magma partially melts overlying continental crust forming felsic magma
Determine if element will be higher in the crust or mantle and what data you’ll need to determine this
Kd(partition coefficient)
compatible if Kd>1, means solid at the mantle
will it sub into olivine SiO4-
explain general trend in oxygen sharing
silicates with more shared oxygens crystallize at cooler temps;
later forming have increasing oxygen sharing, forms sheets and frameworks;
early forming have tetrahedra or single chains
Fe and Mg concentration
early crystallizing minerals → high in Fe and Mg (mafic)
later crystallizing minerals → low in Fe and Mg, high in Si (felsic)
incompatible element abundances
remain in melt and crystallize heat
Goldich’s weathering series
Minerals that crystallize at high temps weather quickly at surface, igneous materials least stable
4 most Common types of chemical weathering
Dissolution: dissolve mineral into its ions with water
acid dissolution: acid water dissolves minerals
oxidation: reduction electron transfer
hydrolysis: water splitting, important for silicate minerals, irreversible, form new mineral from reaction of silicate minerals with water and acid
differential weathering
one rock weathers faster than other on the same rock,
felsic silicates weather slower, intermediate silicates weather faster

how hydrocarbons are formed
source rock wwith abundant carbon buried deep where high T converts orgo matter to petroleum
diagenesis: change orgo matter to waxy kerogen w/ hight T and P
Catagenesis: thermal cracking of kerogen to produce crude oil
metamorphism: complete reakdown of crude oil methan using high T and P
good hydrocarbon quality
high H to C ratio, low sulfur+heavy metal/other impurities, high porosity and permeability
Magmatic ore deposits
chromitite: formed by fractional crystallization of ultramafic or mafic magma
pegmatites: late crystallizations of felsic magmas
sulfide deposits: sulfur rich, sink to bottom
hydrothermal ore deposits
hot, saline brines dissolve and transport metals, lower T and P, Au, Ag, sulfides