The National Judiciary
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Article III
Establishes the Judicial Branch

Federalist No. 78
Hamilton addresses the scope of power of the judicial branch- the judicial branch is created to protect the Constitution and maintain separation of powers and checks and balances; he proclaims that the judicial branch is the weakest of the three branches and that judges shall have life tenure; and he hints at the power of judicial review

Marbury v. Madison (1803)
Established judicial review; "midnight judges;" John Marshall; power of the Supreme Court.

Judiciary Act of 1789
In 1789 Congress passed this Act which created the federal-court system. The act managed to quiet popular apprehensions by establishing in each state a federal district court that operated according to local procedures.

writ of mandamus
Court order directing an official to perform an official duty.

judicial review
Allows the court to determine the constitutionality of laws

jurisdiction
The authority of a court to hear a case

original jurisdiction
The jurisdiction of courts that hear a case first, usually in a trial. These are the courts that determine the facts about a case.

appellate jurisdiction
The authority of a court to review decisions made by lower courts

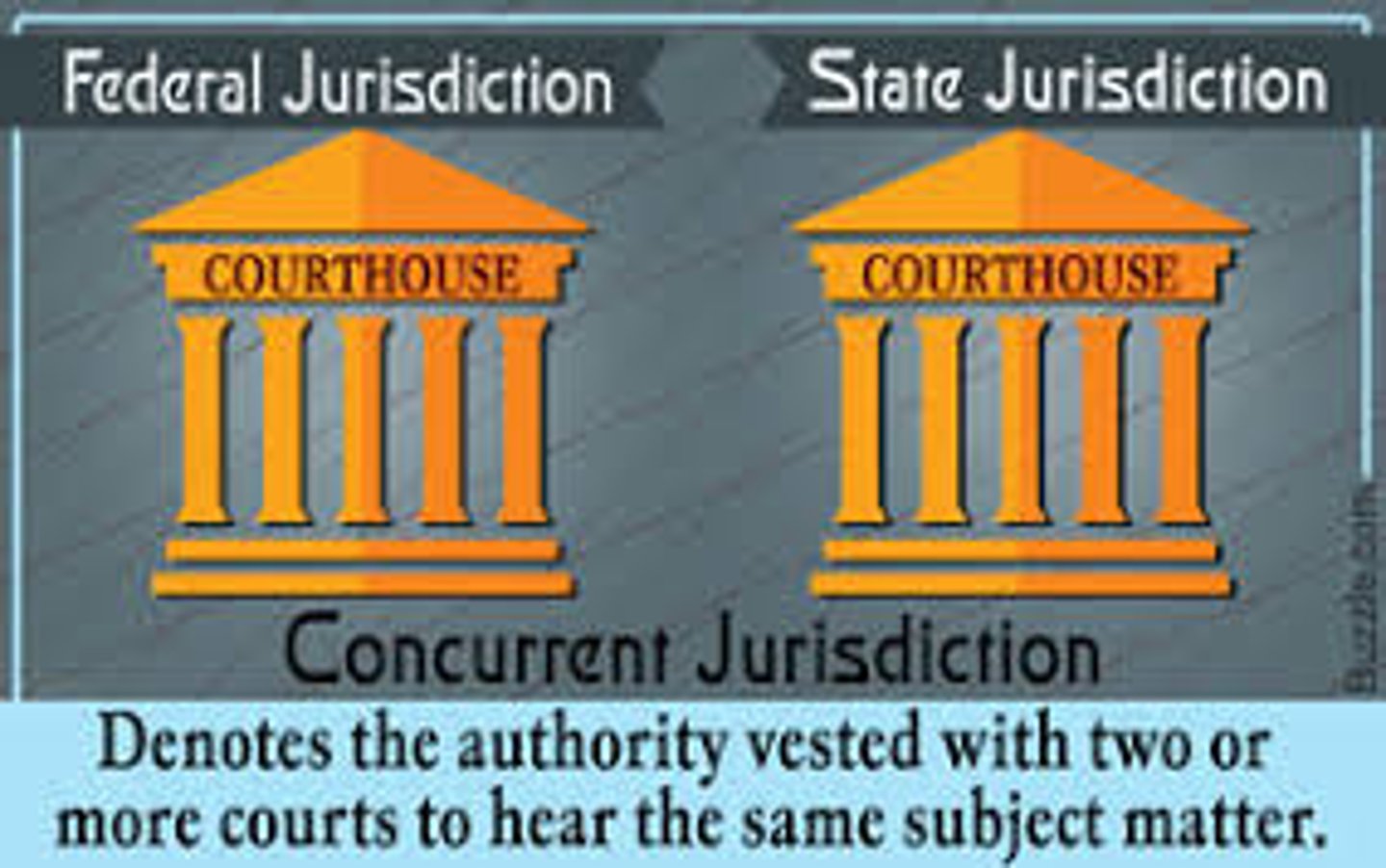
concurrent jurisdiction
authority for both state and federal courts to hear and decide cases
constitutional courts
Federal courts specifically created by the U.S. Constitution or by Congress pursuant to its authority in Article III.

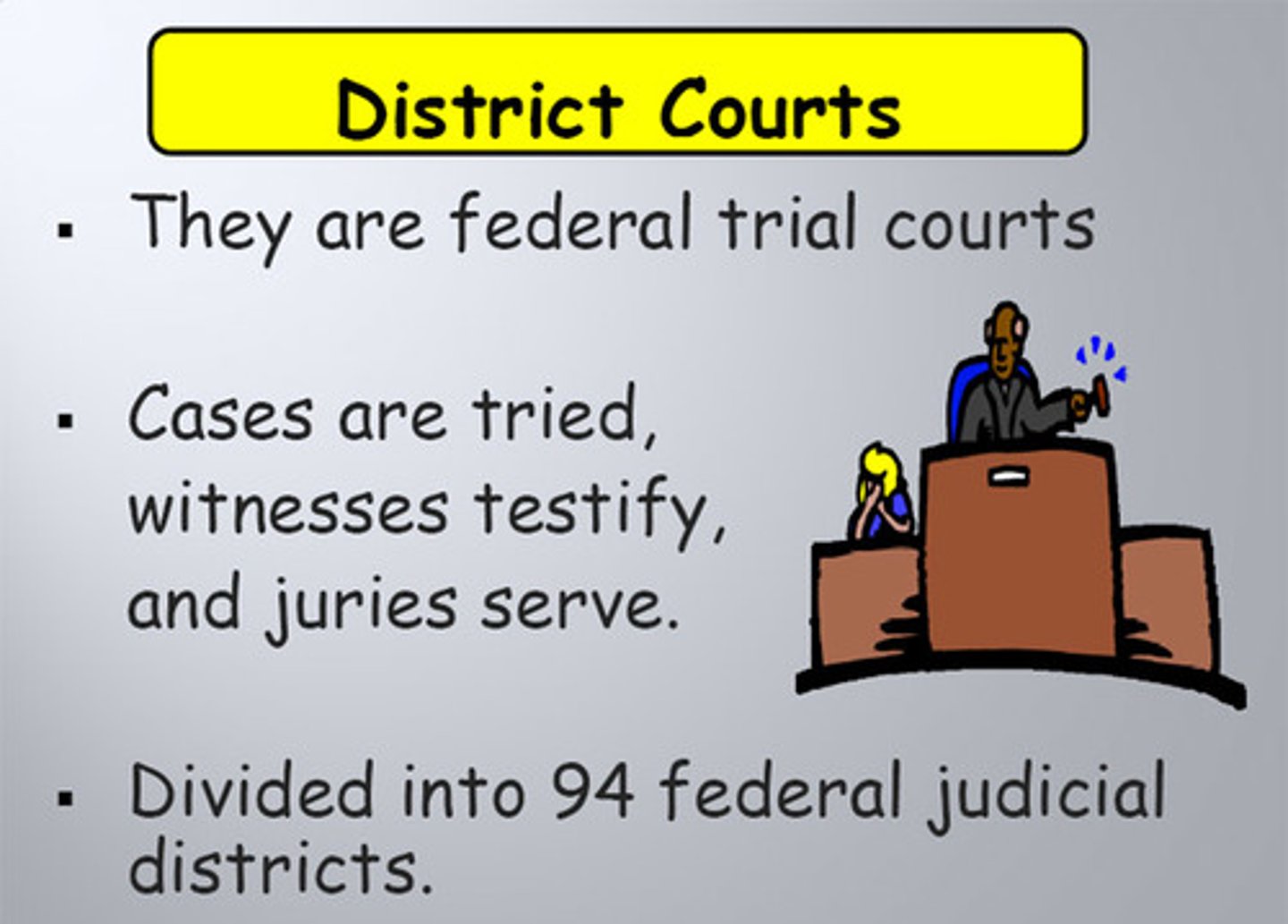
district courts
the lowest federal courts; federal trials can be held only here
Courts of Appeals
Federal courts that review decision of federal district courts, regulatory commissions, and other federal courts.
legislative courts
Courts created by Congress for a specialized purpose with a narrow range of authority.

Supreme Court
the highest federal court in the United States. Consists of nine justices, each appointed by the President and confirmed by Congress. Appointment is for life. Supreme Court exercises the power to determine constitutionality of statutes

senatorial courtesy
Presidential custom of submitting the names of prospective appointees for approval to senators from the states in which the appointees are to work.

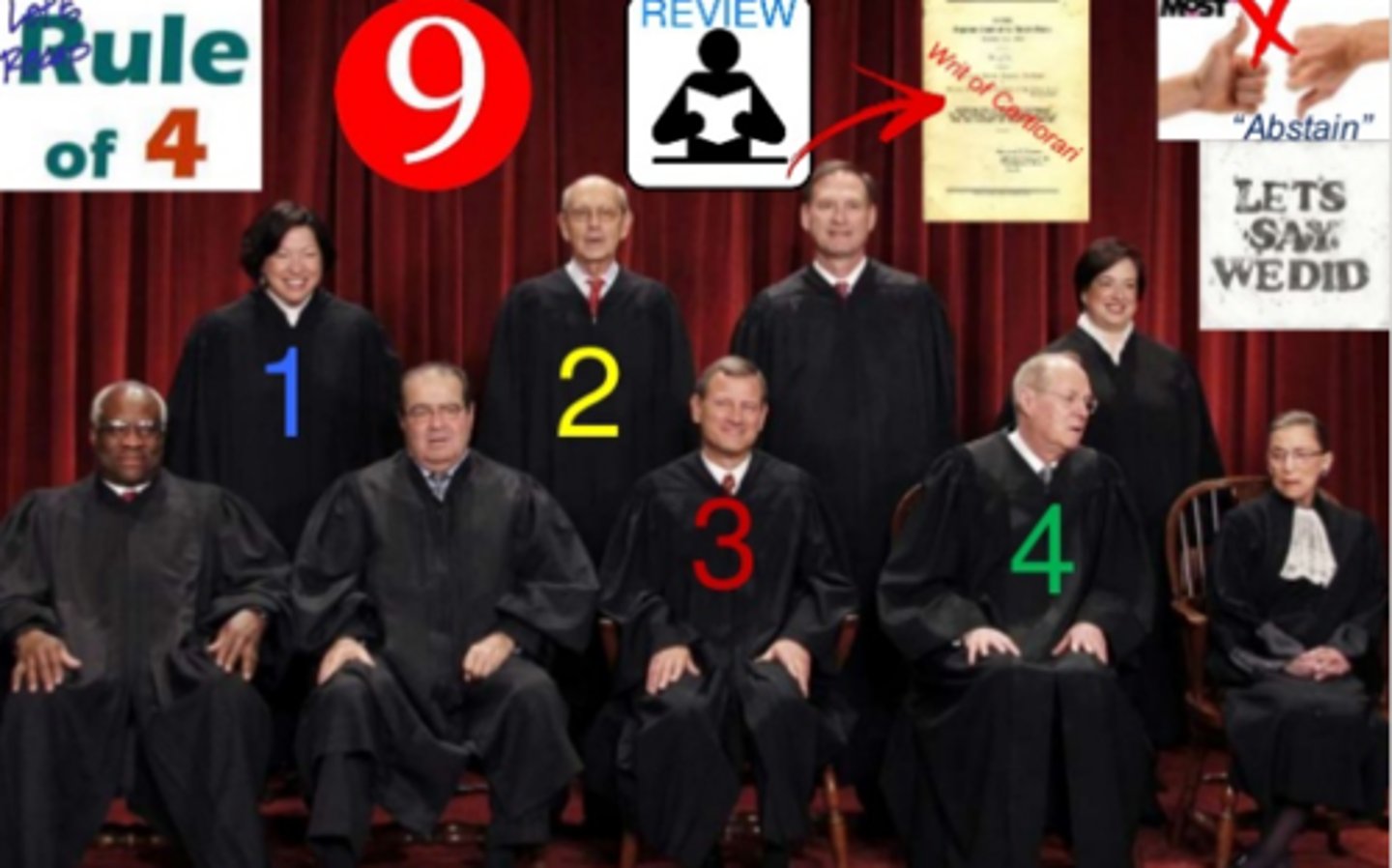
rule of four
At least four justices of the Supreme Court must vote to consider a case before it can be heard

brief orders
the returning of a case to a lower court because a similar case was recently decided

writ of certiorari
An order by a higher court directing a lower court to send up a case for review

solicitor general
Justice Department officer who argues the government's cases before the Supreme Court

certificate
a lower court asks the Supreme Court about the rule of law or procedure

brief
A written statement by an attorney that summarizes a case and the laws and rulings that support it

amicus curiae briefs
Friend of the court; interested groups may be invited to file legal briefs supporting or rejecting arguments of the case.

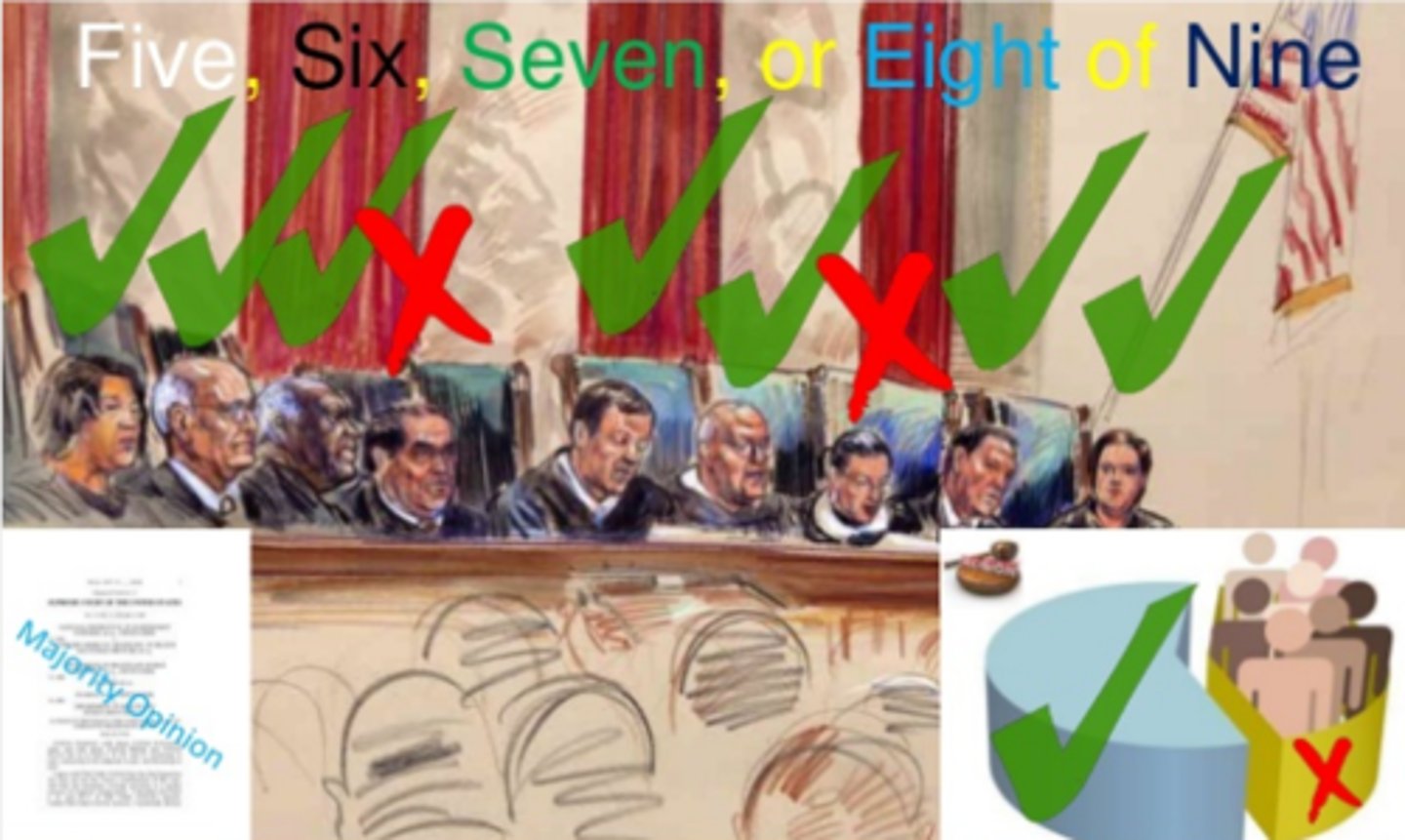
majority opinion
a statement that presents the views of the majority of supreme court justices regarding a case

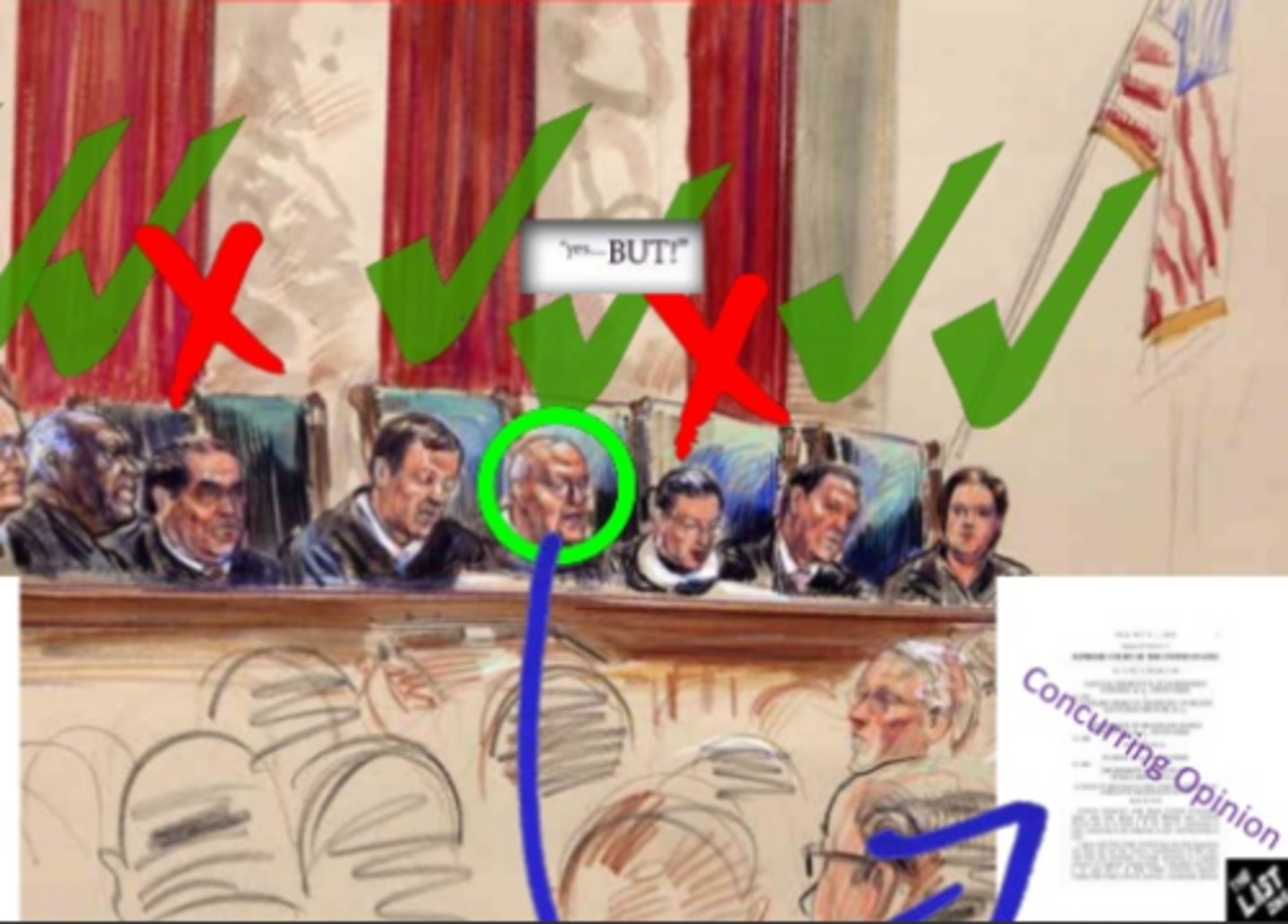
concurring opinion
An opinion that agrees with the majority in a Supreme Court ruling but differs on the reasoning.

dissenting opinion
a signed opinion in which one or more justices disagree with the majority view

precedents
prior cases whose principles are used by judges as the bases for their decisions in present cases
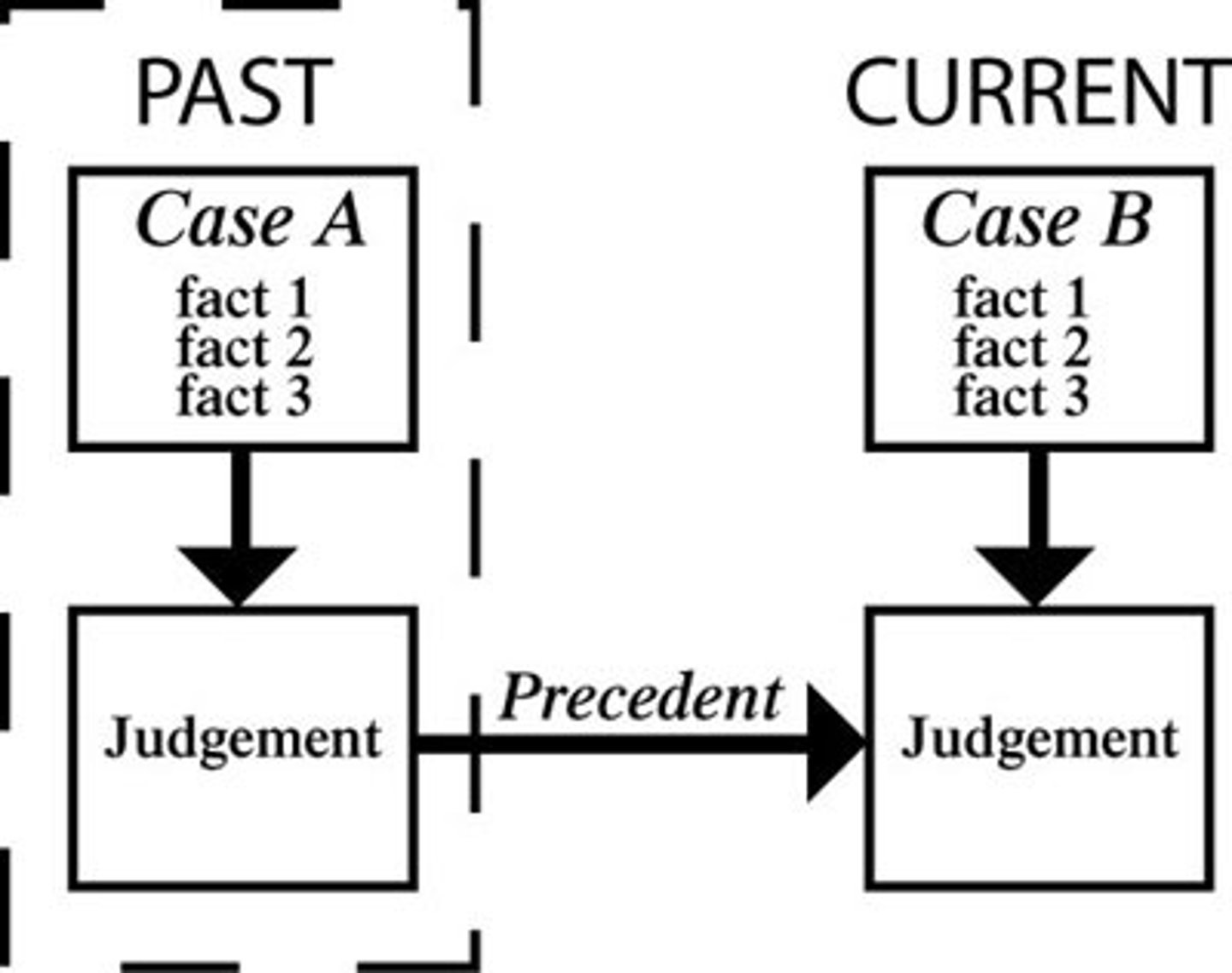
stare decisis
Let the decision stand; decisions are based on precedents from previous cases

executive privilege
The right of the president to withhold information from Congress or refuse to testify; limited by the Supreme Court in U.S. v. Nixon

judicial activism
An interpretation of the U.S. constitution holding that the spirit of the times and the needs of the nation can legitimately influence judicial decisions (particularly decisions of the Supreme Court)

judicial restraint
A judicial philosophy in which judges play minimal policymaking roles, leaving that duty strictly to the legislatures

loose constructionist
The belief that judges should have freedom in interpreting the Constitution

strict constructionist
an approach to constitutional interpretation that emphasizes the Framers' original intentions
