Unit 1- Biology- B1- [Cell structure and function]
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is B1 of biology unit 1 in the applied science foundation diploma series of Pearson edexcel
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is the cell-surface membrane in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Phospholipid bilayer
What is the bilayer responsible for?
controlling the passage of substances across exchange surfaces
What is a cell?
The smallest unit of a living thing
What is a prokaryotic cell?
single celled organisms like bacteria (no nucleus)
What is a eukaryote?
cell with a nucleus
How do prokaryotic cells multiply?
binary fission
How do eukaryotic cells multiply?
mitosis or meiosis
What do most animal cells have?
- mitochondria
- ribosomes
- endoplasmic reticulum
- golgi
- lysosomes
-nucleus
- cell membrane
What is flagella used for?
locomotion
What is pili?
used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation
What is fimbriae?
used by bacteria to attach to a host cell
What does the capsule enable prokaryotic cells to do?
stick to surfaces
What do most prokaryotes have?
a peptidoglycan cell wall
What are ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
70s- thus means that the subunit is 50s large and 30s small
What are vesicles
sacs made of membrane
What is the function of the cell wall?
Provides the cell with support and protection, mainly made with cellulose fibres and water dissolved substances
What is the cell wall made of?
made of cellulose forming a sieve-like network
What is the function of the capsule?
Prevents desiccation (water loss) and stops digestion by phagocytosis
What is the structure of the capsule?
slippery layer outside the cell wall
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Its a fluid of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. it is semi-permeable
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
it has a phospholipids bilayer with proteins embedded in the layer
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Maintains cell shape and stores chemicals needed by the cell for metasolic reactions
What is the function of the nucleoid?
Contains DNA, which is the store of genetic information.
What is the function of plasmids?
small rings of DNA
What is the function of chromosomes?
carry genetic information
What is the function of membrane bound organelles?
acts as a diffusion barrier, but also provides each organelle with its unique morphology that contributes to its function
What is the function of the nucleolus?
produce ribosomes and makes RNA
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes and the newly synthesised proteins are transported to the Golgi apparatus.
What is the function of the ribosome?
Protein synthesis occurs at the ribosomes.
What is the function of the the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Responsible for synthesis and transport of lipids and carbohydrates.
What is the structure of the SER?
Responsible for synthesis and transport of lipids and carbohydrates.
What is the function of the Golgi body?
Newly made proteins are received here from the rough ER. The Golgi apparatus modifies them and then packages the proteins into vesicles to be transported to where they are needed.
What is the structure of the golgi body?
Newly made proteins are received here from the rough ER. The Golgi apparatus modifies them and then packages the proteins into vesicles to be transported to where they are needed.
What is the function of lysosome?
They can be used to digest invading cells or to break down worn out components of the cell.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
produce ATP and responsible for aerobic respiration
What is the structure of the mitochondria?
They have two membranes. The inner membrane is highly folded to form cristae. The central part is called the matrix. They can be seen as long in shape or spherical depending on which angle the cell is cut at.
What is the function of vesicles?
Transport vesicles are used to transport materials inside the cell and secretory vesicles transport proteins that are to be released from the cell, to the cell surface membrane.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
site of photosynthesis. Light energy is trapped by the chlorophyll and used to produce carbohydrate molecules from water and carbon dioxide.
What is the structure of the chloroplast?
Has a double membrane and is filled with a fluid called stroma. The inner membrane is a continuous network of flattened sacs called thylakoids. A stack of thylakoids is called a granum (grana is plural). Grana contain chlorophyll pigments.
What is the purpose of a vacuole?
to store water, food, or waste products. Maintains turgor to ensure a rigid framework in the cell.
What is the function of the tonoplast?
It controls what enters and leaves the vacuole
What is the function of the Amyloplasts?
Responsible for the synthesis and storage of starch granules.
What is the structure of the amyloplast?
A double membrane-bound sac containing starch granules.
What is the function of the plasmodesmata?
Enable transport and communication between individual plant cells.
What is the function of pits?
Allow water to enter and leave xylem vessels.
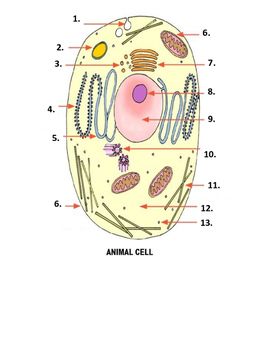
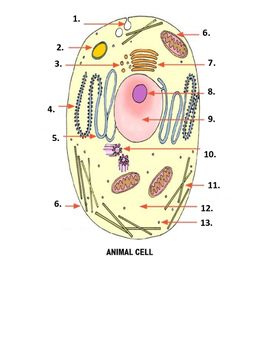
What is number 5 on the image?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
What is number 6 on the image?
mitochondria
What is number 7 on the image?
Golgi apparatus
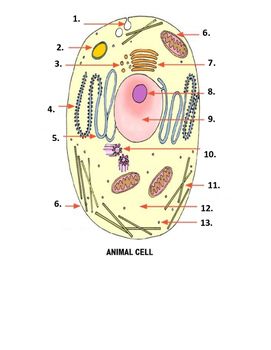
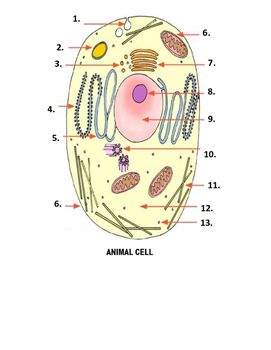
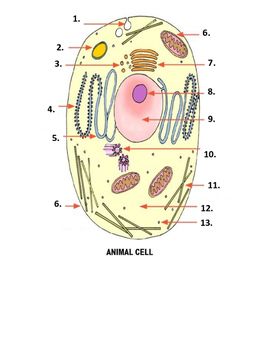
What is number 1 on the image?
Pinocytonic vesicle
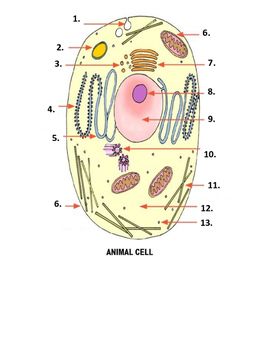
What is number 3 on the image?
Golgi vesicle
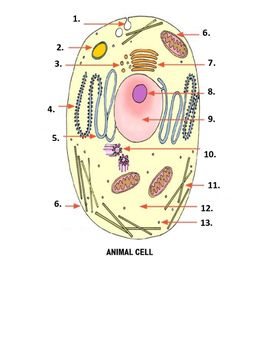
What is number 4 on the image?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
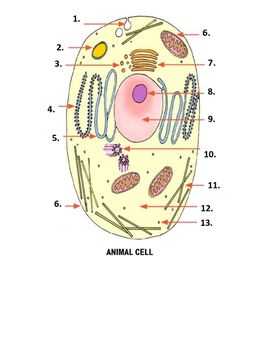
What is number 8 on the image?
Nucleolus
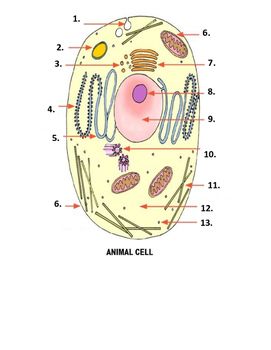
What is number 9 on the image?
nucleus
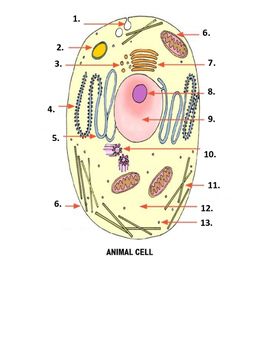
What is number 10 on the image?
Centrioles
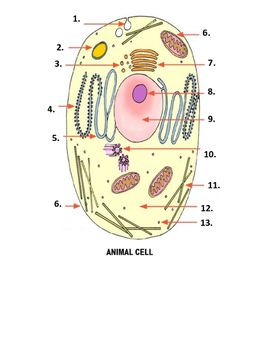
What is number 11 on the image?
microtubles
What is number 12 on the image?
Cytoplasm
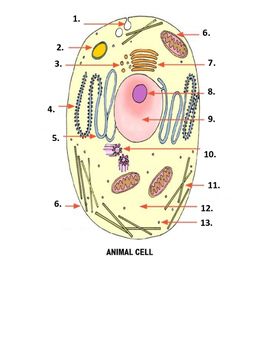
What is number 13 on the image?
ribosome
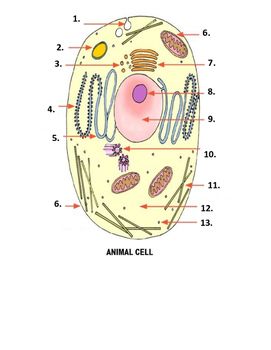
What is number 2 on the image?
Lysosome
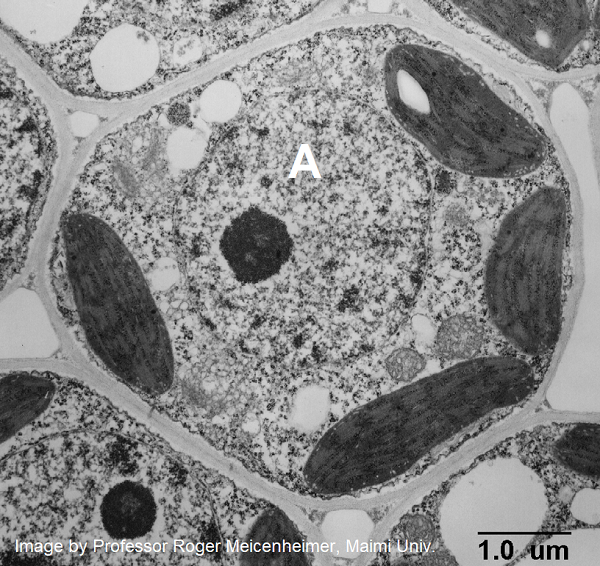
What is the structure A used for?
to store genetic material
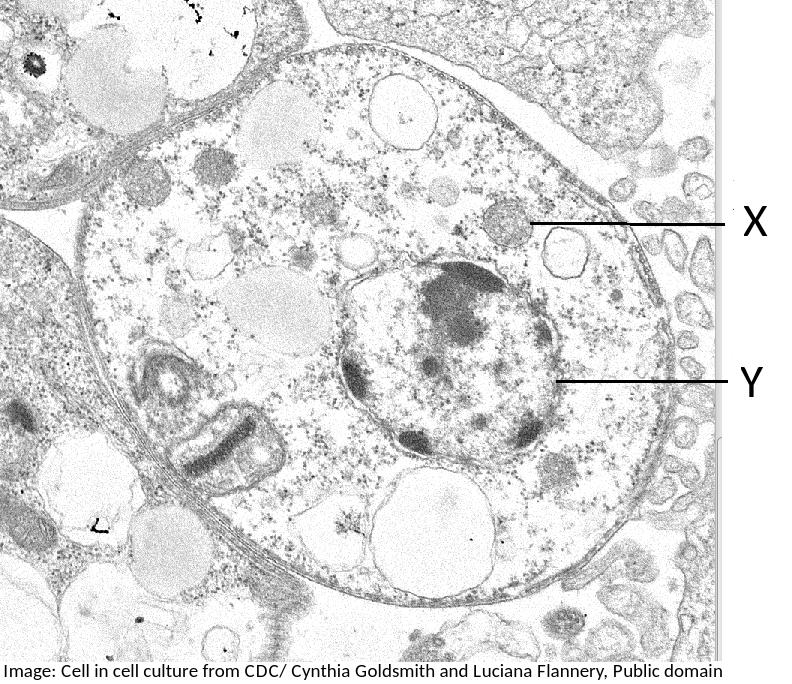
What are the structures X and Y likely to be?
X is mitochondrion and Y in the nucleus
What is the difference between gram positive and gram negative bacterial cell walls?
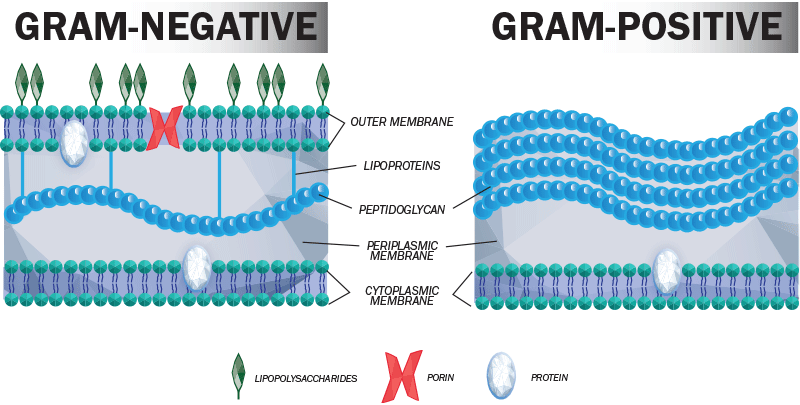
Gram-negative bacteria are surrounded by a thin peptidoglycan cell wall, which itself is surrounded by an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide. Gram-positive bacteria lack an outer membrane but are surrounded by layers of peptidoglycan many times thicker than is found in the Gram-negatives.
Why do they react differently to antibiotics?
Gram-negative bacteria tend to be more resistant to antimicrobial agents than Gram-positive bacteria, because of the presence of the additional protection afforded by the outer membrane.
What is the equation for magnification?
Magnification= Image size / actual size
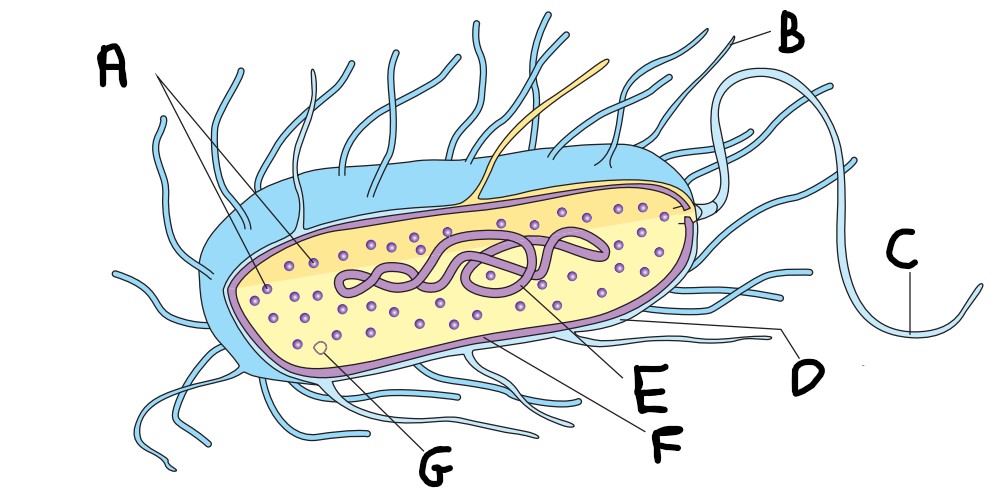
What is A on the image?
ribosomes
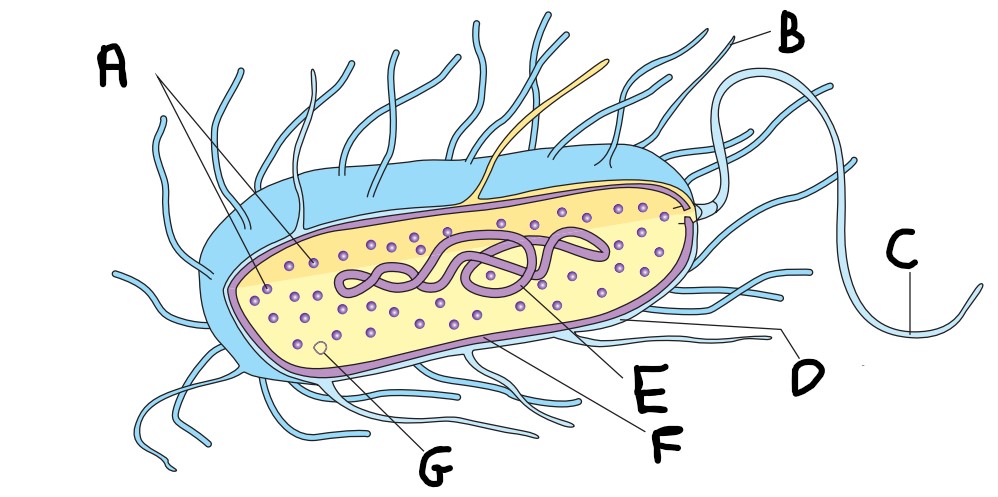
What is B on the image?
pilus
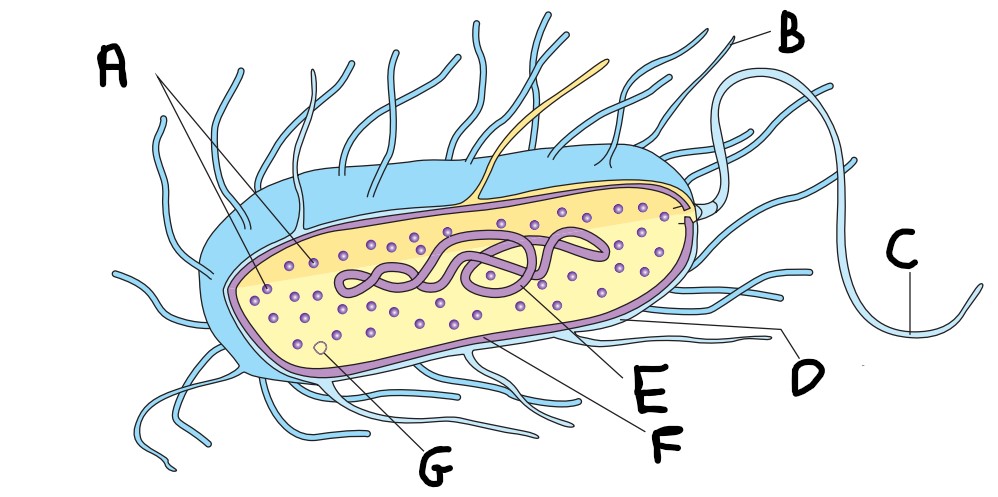
What is C on the image?
flagellum
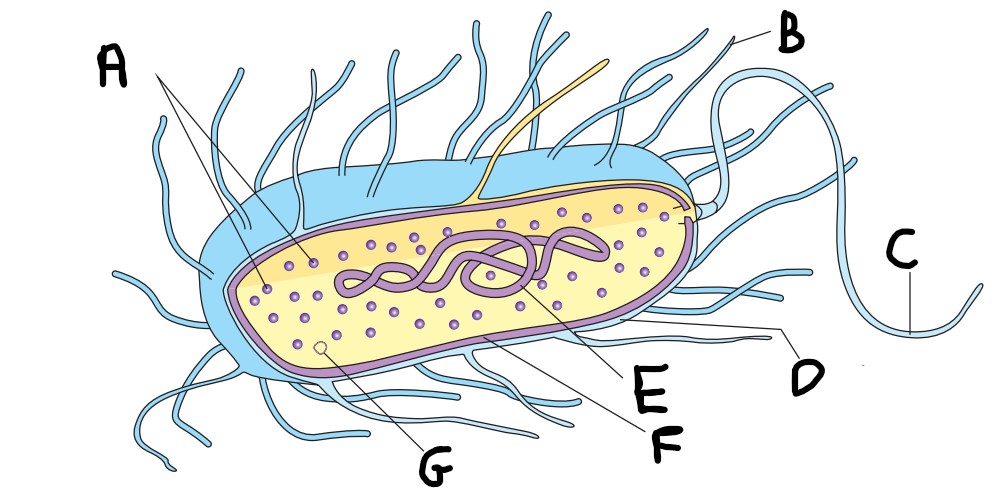
What is D on the image?
capsule
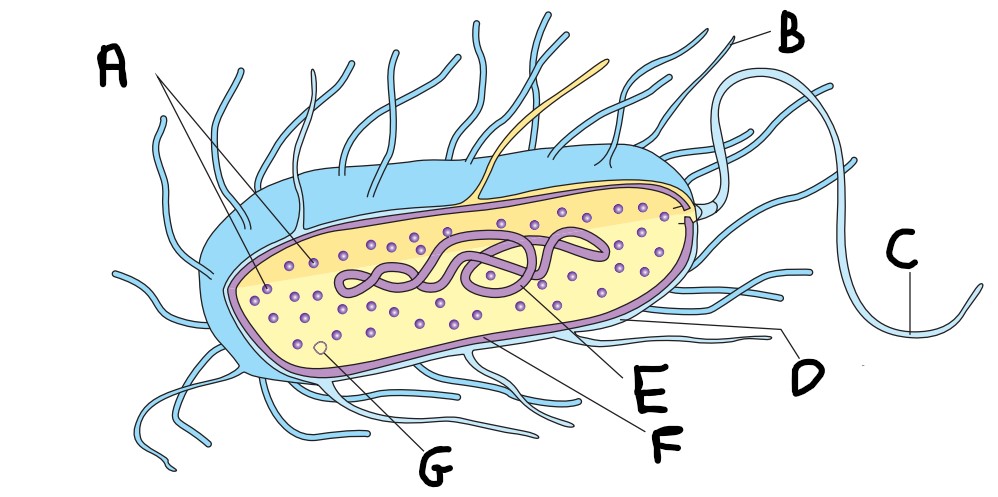
What is E on the image?
nucleoid
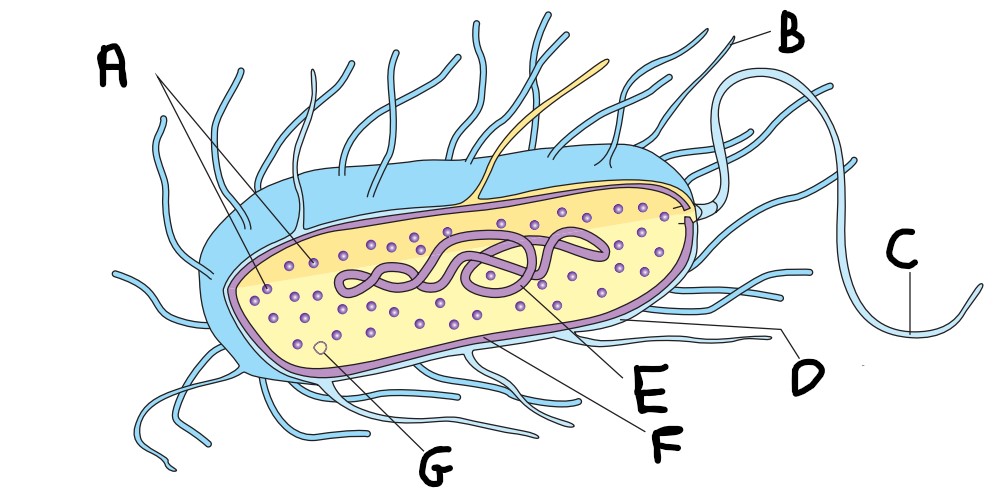
What is F on the image?
cell wall

What is G on the image?
plasmid