Energy in Cells and Photosynthesis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Energy
The ability to do work
ATP
a molecule made of 3 smaller molecules bonded together, used to store energy in cells
ADP
the result of losing a phosphate group, can be recharged; used for energy in a cell
Photosynthesis
The process in which light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen
Evolution of Photosynthesis
The development of photosynthesis in prokaryotic organisms, which later became the basis for eukaryotic photosynthesis
Leaves
The major photosynthetic organs of plants, with a large surface area to absorb light and stomata for gas exchange
Chlorophyll
A pigment in plants that absorbs light for photosynthesis, with two types (A and B) that absorb different wavelengths
Light Intensity
The level of light energy, which affects the rate of photosynthesis - higher intensity leads to a higher rate
CO2 Concentration
The amount of carbon dioxide, which affects the rate of photosynthesis - higher concentration leads to a higher rate
Temperature
The level of heat, which affects the rate of photosynthesis - optimal temperature increases photosynthesis, while extreme heat denatures enzymes and decreases photosynthesis
Light Dependent Reaction
The part of photosynthesis that converts sunlight into chemical energy
Light Independent Reaction
The part of photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle) that uses carbon dioxide to produce glucose
releases energy
when ATP breaks apart, releasing a phosphate group
recharged
when ADP gains an extra phosphate
energy is stored in _?_
in the bonds of chemical compounds
parts of ATP
adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups
parts of ADP
adenine, ribose, 2 phosphate groups
ATP stands for
adenosine triphosphate
ADP stands for
adenosine diphosphate
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water --light--> glucose + oxygen
Where does CO2 come from?
atmosphere
where does the water come from?
ground via the roots
where does the oxygen go?
into the atmosphere
Reactions for photosynthesis
water, CO2 (and light for energy - not matter)
products for photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
organisms that carry on photosynthesis
plants, algae, and some bacteria
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to make glucose
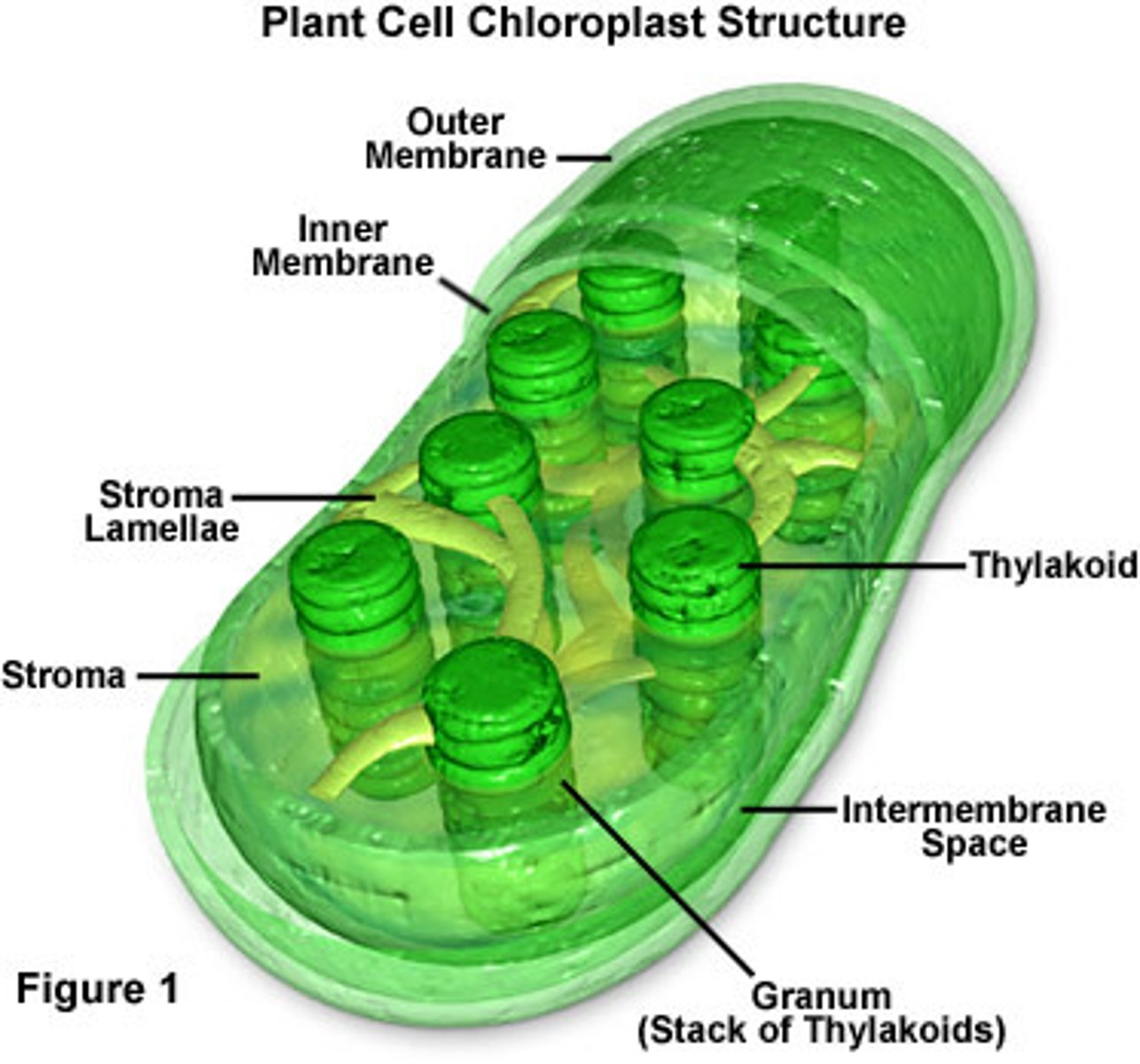
Location of Light Dependent Reaction
Thylakoid Membrane (inside chloroplast)
Location of Photosynthesis
Chloroplast
Location of Light independent Reaction
stroma
light-dependent reactions reactants
Light, water, NADP+, ADP and phosphate
Light Independent Reactions reactants
ATP, NADPH, CO2
light-independent reaction is also called -?-
Calvin Cycle
Chlroplast
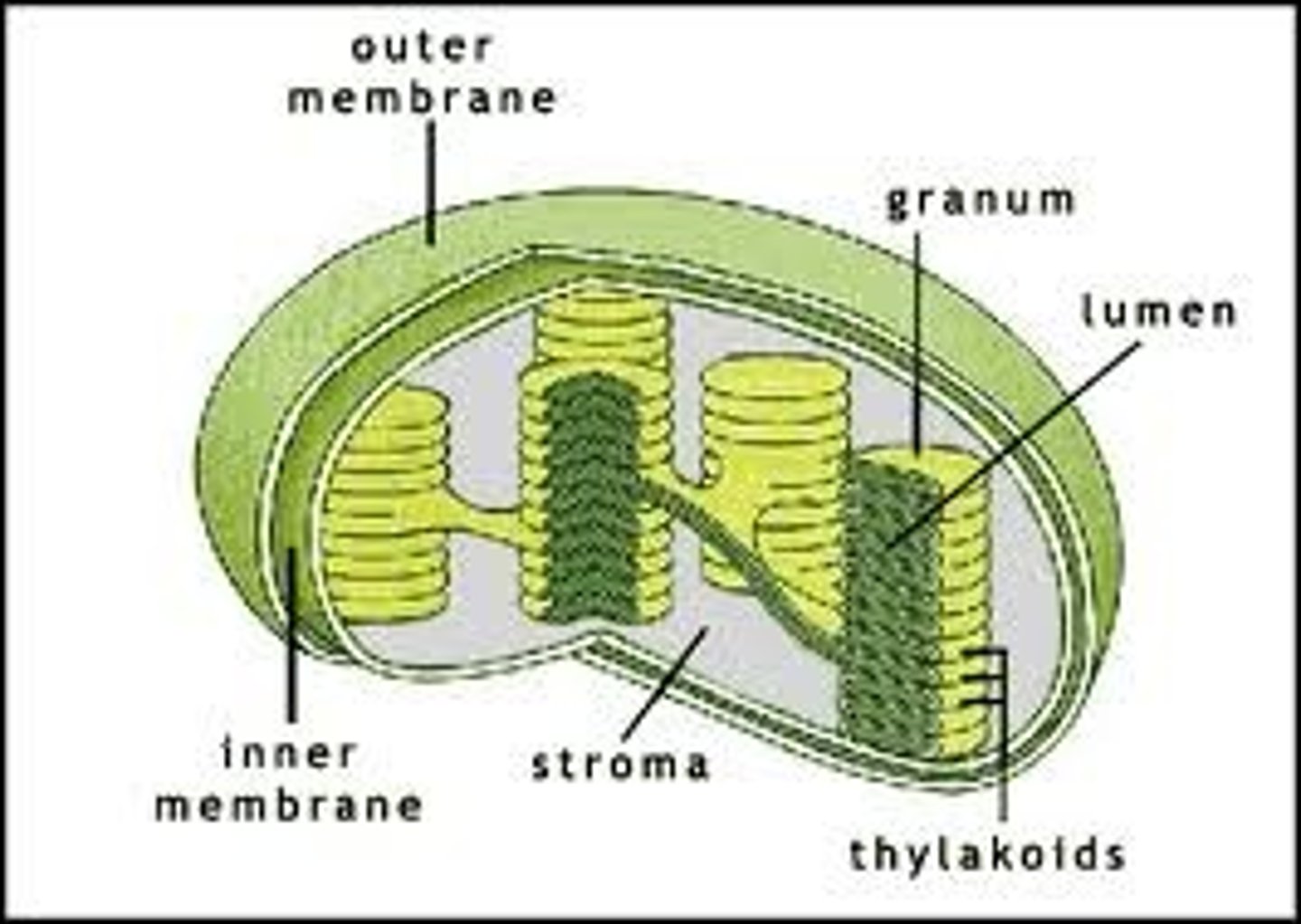
Lamella (in Chloroplasts)