Basic Tissues
1/58
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
The types and functions of the cells that make up these tissues
The characteristics of the matrix that surrounds the cells
Relative amount of space occupied by cells versus matrix.
Epithelial Tissue
a type of body tissue that forms the covering on all internal and external surfaces of your body
Characteristics of the Epithelial Tissue
Consists of a flat sheet of closely attached cells
it is avascular
it gains its nourishment from a loose layer of connective tissue it is supported by.
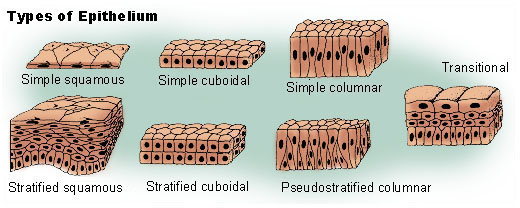
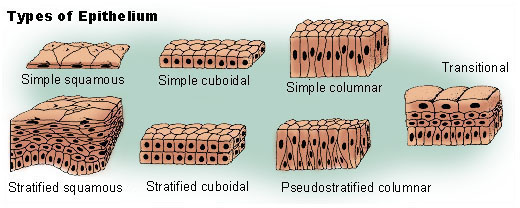
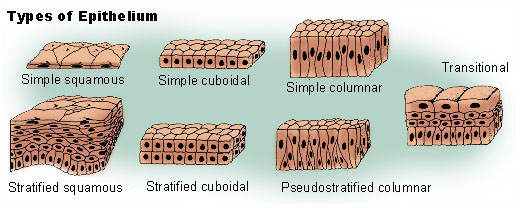
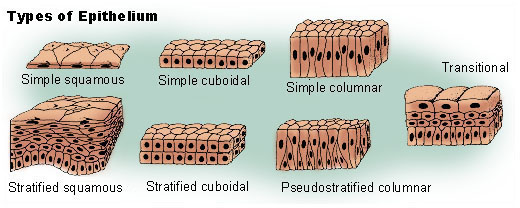
Types of Epithelial tissues based on Cell shape
Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Types of Epithelial Tissues based on Layers
Simple Squamous Epithelial tissue
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial tissue
Simple Columnar epithelial tissue
Stratified Squamous Epithelial tissue
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelial tissue
Stratified Columnar Epithelial tissue
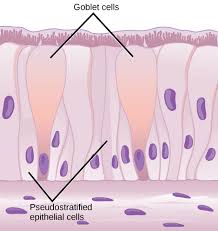
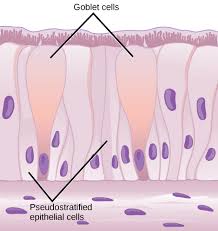
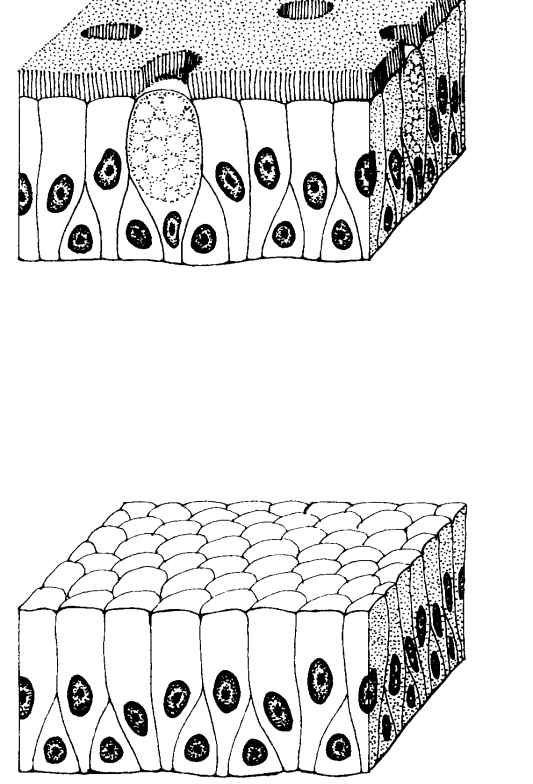
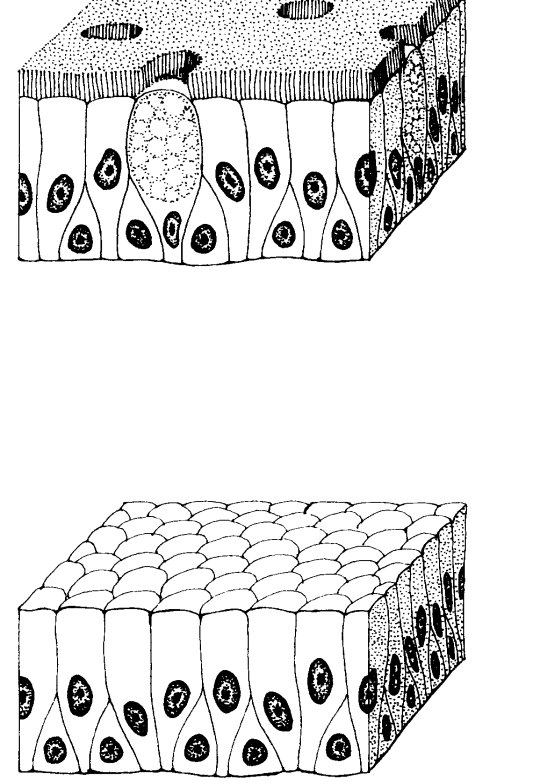
Pseudostratified epithelial tissue
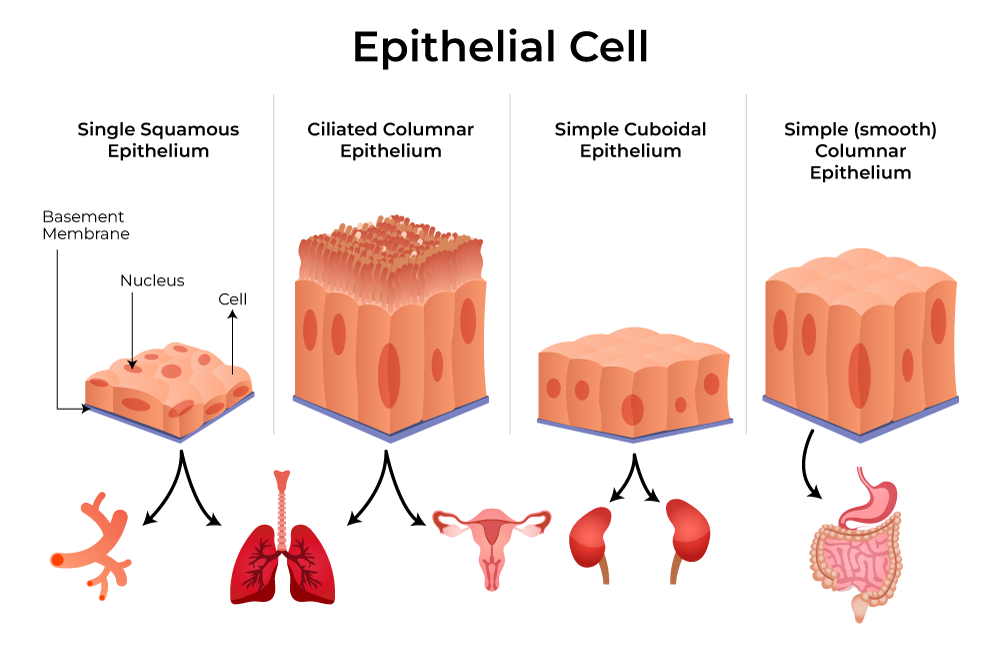
Simple Epithelium tissue
This means the epithelium cells occurs in just one cell layer
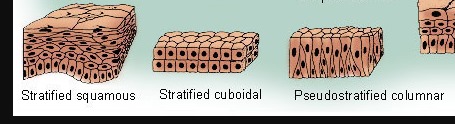
Stratified epithelial tissue
this means that the epithelium cells occurs in multiple layers
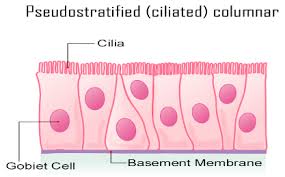
Pseudostratified Epithelial tissue
This is made up of epithelial cells that appear to occur in multiple layers
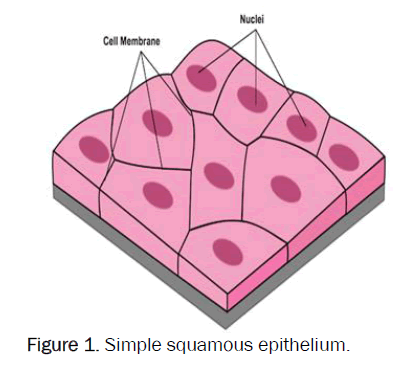
Epithelial Tissue that is made up of flat cells, and due to this they’re used for diffusion and absorption of nutrients
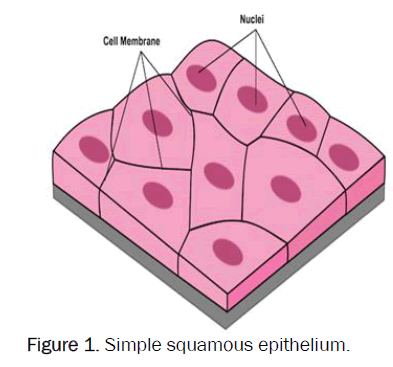
Structures where squamous tissues are present
Lining of the mouth
Esophagus
Blood vessels
Alveoli
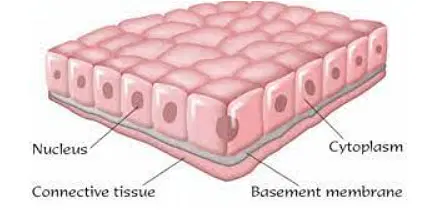
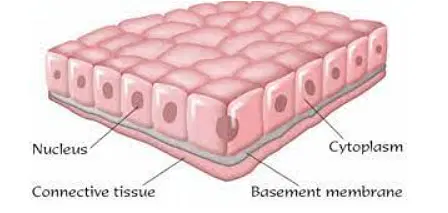
Responsible for all body movements, composed of cells that have the special ability to contract in order to produce movement of the body parts.
Types of Muscle Tissues
Cardiac Muscle tissue
Skeletal Muscle tissue
Smooth Muscle tissue
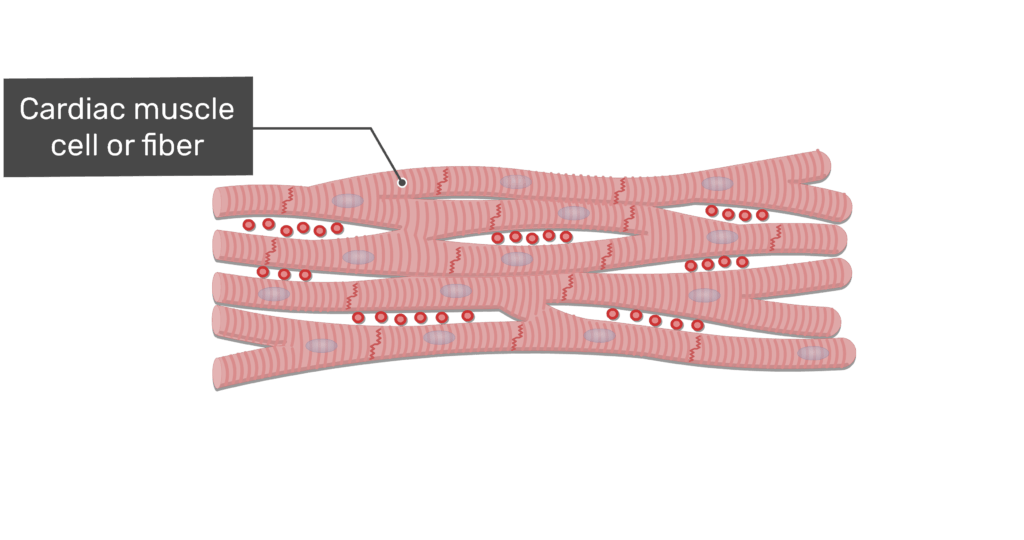
Cardiac Muscle tissue
This muscle tissue is involuntary and is striated and is located in only the heart
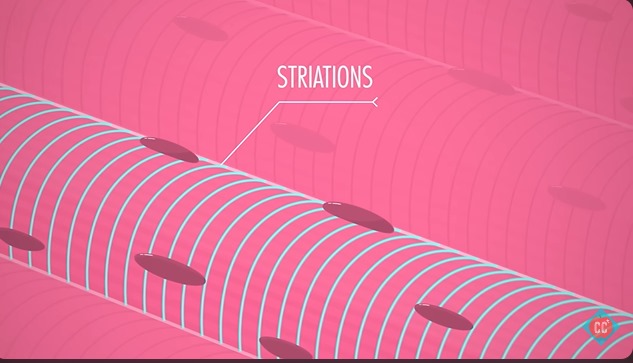
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
These are voluntary muscle tissues that contract and relax to facilitate movement. they are striated
Tendons
Extensions of the muscle tissue that attaches them to the skeleton.
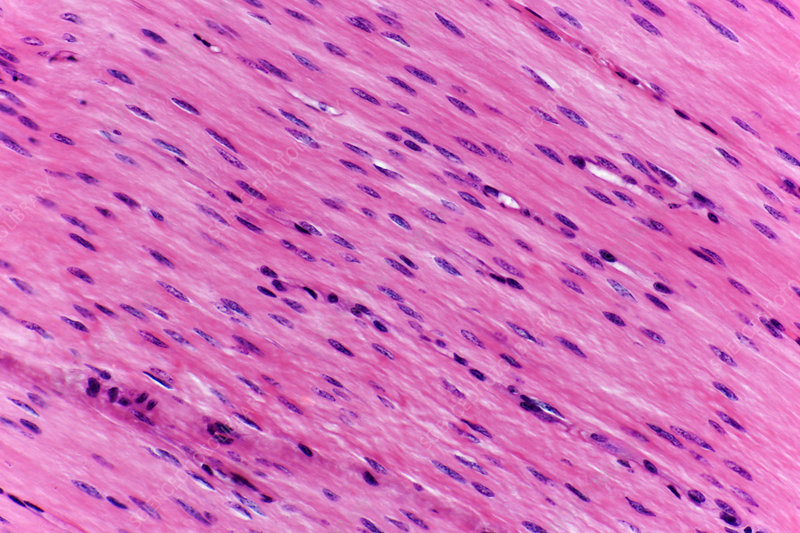
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissues that are involuntary and not striated. The are found in hollow organs such as intestines and blood vessels
The primary tissue that composes the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
Organization of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
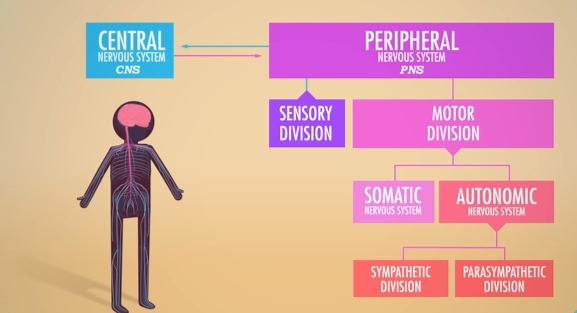
Parts of the Peripheral nervous system
Somatic and autonomic nervous systems
Somatic nervous systems
This is the nervous system responsible for voluntary movements
Autonomic Nervous system
the nervous system responsible for involuntary actions
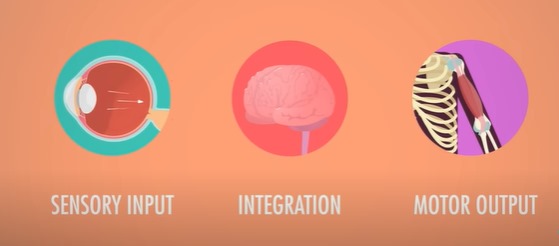
Principal Functions of the nervous system
Sensory input, integration, motor output
Types of Nervous Tissues
Neurons
Glial cells
Neurons
nerve cells that send messages all over your body to allow you to perform various functions
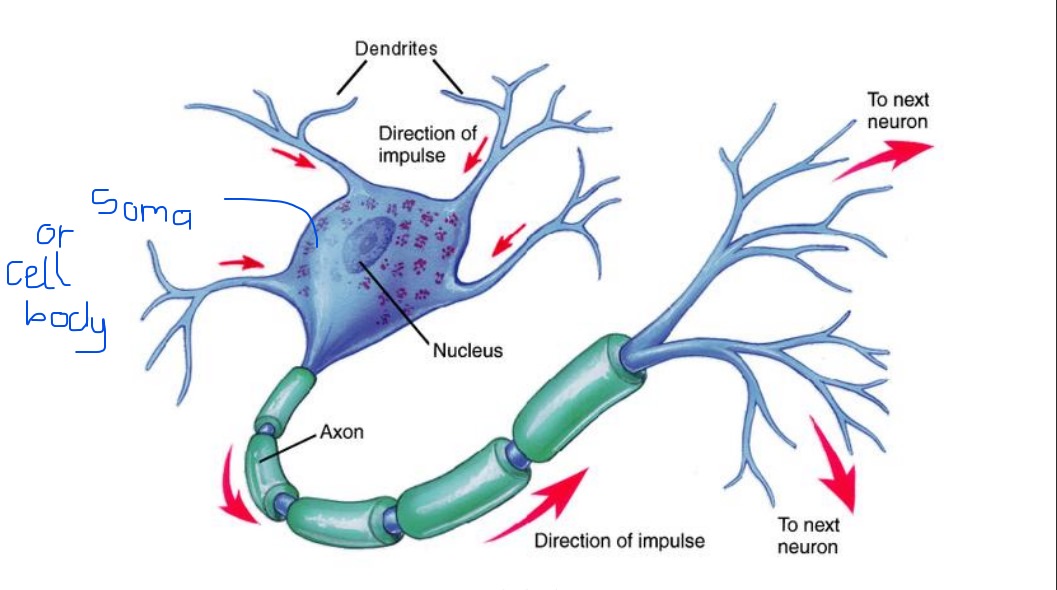
Part of a Neuron
Dendrites: Inputs impulse into the cell
Axons: Transmits impulse out of the cell
Glial Cells
They support and protect neurons
Which tissue is the most diverse
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
These tissues support other tissues. They also provide fuel storage
Types of Connective Tissues
Loose connective tissue
Dense connectuve
Cartilage connective tissue
Bone connective tissue
Blood connective tissue
Adipose connective tissue
Adipose connective tissue
body fat, is a connective tissue that extends throughout your body
Common characteristics of conective tissues
They are all develop from mesenchyme
They have different degrees of vascularity
They are made up of a non living layer called the extracellular matrix.
Macrophage
A class of connective tissue that defends the body against pathogens.
Components of the Extracellular Matrix
Fibers and Ground Substance
Ground Substance
A watery unstructured material that fills in the spaces between cells. It protects the external surroundings of cells.
Compositioni of the ground substance
It is made up of proteins called Proteoglycans. Out of these proteoglycans are strands called glycosaminoglycans.
Blast Cells
Immature connective tissue cells that secretes the ground substance and fibers that form the matrix
Suffix for mature connective tissue cells
Cyte
Chondroblast
The blast cells of cartilage tissues
Osteoblast
The blast cell of bone tisues
Epithelial tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle tissue
Nervous Tissue.
Types of Fibers in the extracellular matrix
Collagen Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Elastic fibers
Collagen Fibers
The most abundant fibers that provide support, structure and connection between other tissues and organs
Reticular Fibers
Thin branching fibers that form a delicate supporting network around organs and structures such as the liver.
Elastic Fibers
These are yellow springy fibers that allow tissues to stretch and recoil
Types of Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
The most abundant cartilage which covers the ends of bones and joints for smooth movemet. It can be found in the nose, trachea and ribs
Elastic Cartilage
These cartilage provide support to structures that need flexibility such as the external ear (pinna) and epiglottis
Fibrocartilage
This cartilage absorbs shock and provides cushoining in areas like the joint capsules
What is the function of intercalated discs
Allows for rapid transmission of nerve impulses between cardia muscle cells
what is the function of the enteric nervous system
Regulates the functions of the gut wall
what type of connective tissue surrounds the entire muscles
Epymysium
Fibroblast
These are cells tha produce collagen fibres in connective tissues
what type of epithelium adapted to protect underlying tissues from abrasion and friction
stratified squamous epithelium