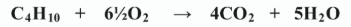13 - Fuels and Heats of Reaction
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To be accompanied with past exam questions. CALCULATIONS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is a hydrocarbon?
Compound containing hydrogen and carbon only
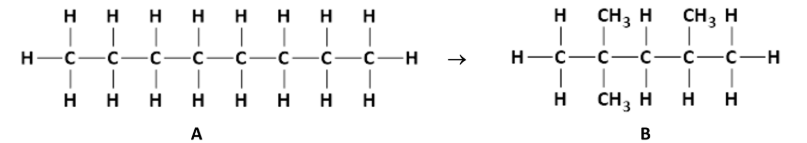
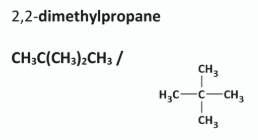
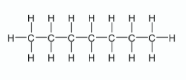
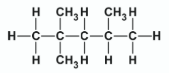
State the systematic IUPAC names of compounds A and B
A: Octane
B: 2,2,4 - trimethylpentane
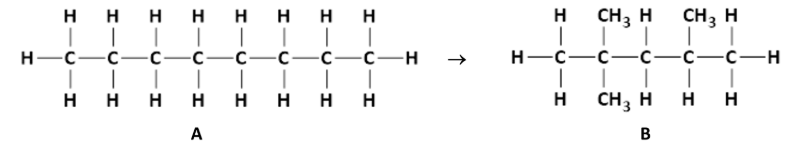
Explain why compounds A and B are referred to as saturated alkanes
Only contain single bonds
Draw the molecular structure of methylpropane, including all atoms and bonds
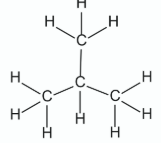
A molecule of octane can undergo catalytic cracking to produce a molecule of methylpropane and a molecule of compound C.
State the systematic IUPAC name of three of the possible isomers of compound C. In each case, draw the molecular structure of the isomer, including all atoms and bonds.
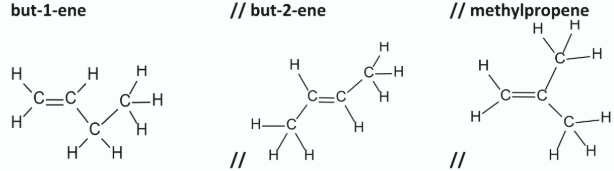
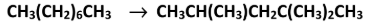
Give the systematic IUPAC name for the product in the equation
2,2,4 - trimethylpentane
Pentane and 2-methylbutane are structural isomers of C5H12. Give the systematic IUPAC name of the other structural isomer of C5H12 and draw its molecular structure
A molecule of C15H32 was converted into a molecule of 2-methylbutane, a molecule of but-1-ene and one other molecule during catalytic cracking. What was the molecular formula of the third molecule formed?
C6H12
What is the difference in the molecular formulae of two successive members of the alkane homologous series?
CH2
Explain the term fractionation of crude oil
Separation into components according to size by distillation
With the aid of labelled diagram explain how crude oil is fractionally distilled
Separation on basis of boiling point /
smaller or lower b.p. at top /
larger or higher b.p. at base
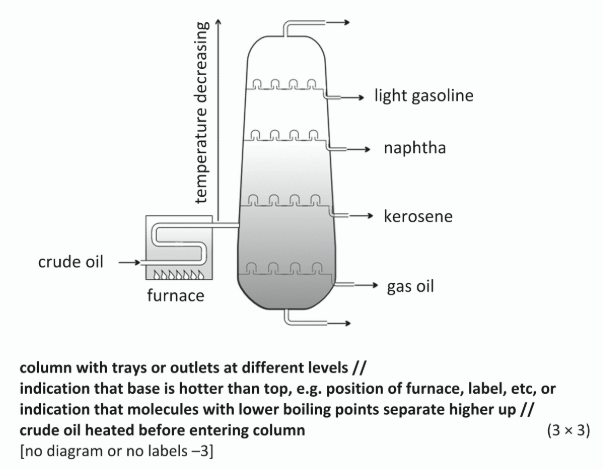
Show on your diagram where the refinery gas and oil fractions separate
Refinery gas (LPG) above gas oil (diesel) shown
What property of kerosene allows it to be separated from the other constituents of crude oil?
Boiling point / molecular mass
What is the purpose of adding mercaptans to natural gas or to LPG?
Safety / to give gas a smell / to enable leaks to be detected
Give a major use for
i) kerosene
ii) residue / bitumen
i) Aviation fuel / home heating oil
ii) roofing / road making
Explain the term structural isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
Compare petrol (a mixture of light gasoline and naphtha) and diesel (gas oil) in terms of
i) average molecular mass of the hydrocarbons present,
ii) boiling point.
i) petrol has smaller average Mr / diesel has greater average Mr
ii) petrol has lower boiling point / diesel has higher boiling point
Explain the term octane number of a fuel
Measure of the tendency of a fuel to auto-ignite or cause knocking
Give the systematic IUPAC name and draw the structure of a molecule of the alkane fuel assigned an octane number of zero
Heptane
Give the systematic IUPAC name and draw the structure of a molecule of the alkane fuel assigned an octane number of 100
2,2,4 - trimethylpentane
What molecular characteristics are required to create a hydrocarbon fuel with a high octane number?
Short chain //
branched chain //
cyclic structure
[any two]
List three methods commonly used in oil refining to increase the octane number of a fuel
Isomerisation //
reforming / dehydrocyclisation //
catalytic cracking //
adding oxygenates
Give an example of an oxygenate used in petrol
MTBE, methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol
What is the advantage of adding tetraethyllead to petrol?
To reduce auto-ignition /
To increase to octane rating
Why was the use of tetraethyllead in car engines discontinued?
Toxic / poisonous / harmful / carcinogenic / damages catalytic converters / pollutant
Name the process that can convert compound A to compound B
Isomerisation
Why is isomerisation carried out?
Increase octane number / reduce auto-ignition / increase branching
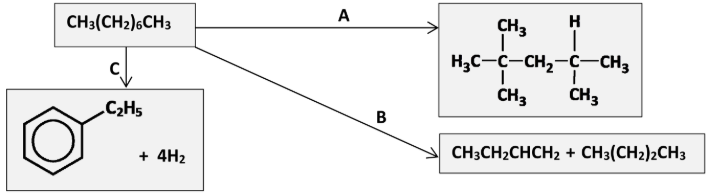
Identify the processes B and C
B: Catalytic cracking //
C: Dehydrocyclisation
Why is catalytic cracking carried out in oil refining?
Gives useful products in higher demand / gives products with higher octane rating
Explain the term knocking in the engine
Auto-ignition: tendency to premature ignition
How is hydrogen gas manufactured on an industrial scale?
Steam reforming of natural gas /
electrolysis of water
Give two advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel
High kilogram calorific value / non-polluting products / can be piped / can be produced from water / does not contribute to global warming etc
Suggest a disadvantage of hydrogen as fuel
Explosive / fire risk / difficulty storing fuel
Suggest a reason why elemental hydrogen (H2) does not occur in nature on Earth as a fuel source
Too reactive (explosive, flammable, combustible) / too light
What are the two main hydrocarbon components of LPG?
Propane //
butane
Define heat of reaction
The heat change when the number of moles of reactants indicated in the balanced equation for the reaction, react completely
Define heat of combustion
Heat change in KJ when one mole of the substance is completely burned in excess oxygen
Define heat of formation
Heat change in KJ when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in their standard states
Heat of neutralisation
Heat change in KJ when one mole of H+ ions from an acid reacts with one mole of OH- ions from a base
Explain why the same amount of energy is released when one mole of hydrogen is used up in a fuel-cell as when one mole of hydrogen is burned in excess oxygen
Same reaction / Hess’ law
What apparatus is used to accurately measure the heat of combustion of a fuel?
Bomb calorimeter
Give one use made of the kilogram calorific values of various fuels
Compare efficiencies of fuels
Suggest one advantage of using bioethanol as a motor fuel
Bioethanol is renewable / environmentally friendly / reduces knocking / cheaper
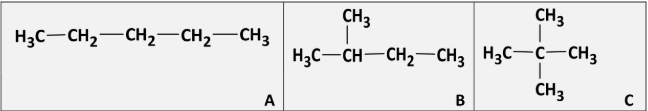
Why to A, B and C separate in the same fraction in the distillation of crude oil?
[note: they are structural isomers]
Same number of carbons / same molecular masses / same molecular formulae
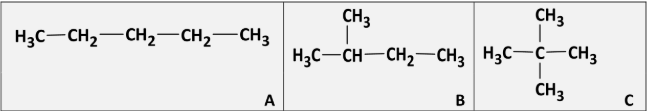
Explain which of A, B and C is most likely to auto-ignite in a petrol engine
A because it has the longest chain / A because it is least branched /
A is straight chained / A has lowest octane number rating
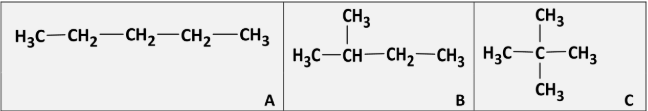
Give the systematic IUPAC names for A, B and C
A: pentane
B: 2-methylbutane
C: 2,2-dimethylpropane
Identify the hydrocarbon gas produced by anaerobic decomposition of either animal waste or vegetation
Methane (CH4)
Explain why high molecular mass alkanes have high boiling points
Stronger intermolecular bonds (forces) / more electrons present
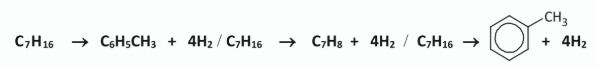
Write a balanced equation for the dehydrocyclisation reaction in which heptane is converted into methylbenzene and hydrogen
State Hess’ Law
If a reaction takes place in a number of stages, the sum of the heat changes in the separate stages is equal to the heat change if the reaction was carried out in one stage
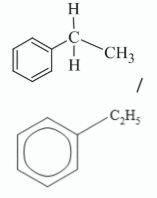
Draw the molecular structure of ethylbenzene
What are the two reference hydrocarbons used to assign octane numbers to fuels?
heptane //
2,2,4 - trimethylpentane
Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of butane in an adequate supply of oxygen