Catchments/Watersheds and Fluid Flow Pathways
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
28/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is a watershed?
Any surface area from which runoff resulting from rainfall is collected and drained through a common point
also known as drainage basins or catchment area
What is a subwatershed?
Larger watershed divided into smaller watersheds
What is drainage area (A)?
is a measure of the the volume of water on a watershed from rainfall
What is watershed length (L)?
distance measured along the main channel from the watershed outlet to the basin divide
measure of the travel time of water through a watershed
What is the watershed slope (S)?
reflects the rate of change of elevation along the principle flow path. S affects momentum of runoff, which in turn has an impact on flood magnitudes
How can you calculate watershed slope?
using this equation
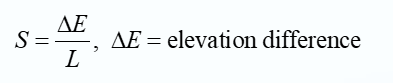
What is elevation difference (E)?
The elevation difference is usually taken along the principle flow path L and is therefore not necessarily the maximum elevation difference in the watershed
What is channel length?
measured along the main channel from the watershed outlet to the end of the channel
What is the channel slope?
elevation difference measured between points defining the upper and lower ends of the channel.
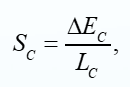
What is drainage density?
ratio of the total length of all streams within a watershed to the watershed’s area A.
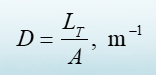
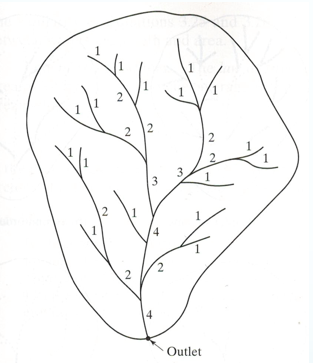
How do we use stream order?
it is a measure of the degree of stream branching
Order 1 = first order stream = unbranched tributary
Second order stream = tributary formed by two or more first order streams
Third order = formed by two or more second order streams
Order n = a tributary formed by two or more streams of order n-1.
Principal order = order of the channel at the watershed outlet
If two streams of the same order merge, the resulting stream is given a number which is one higher
What are scaling laws?
their purpose is to describe the organization of landscapes
Scale
characteristic length or time of a process or observation
Scaling
transfer of information across scales
What are the two functional relationships two hydrologic variables can have?
scale independent
scale invariant
What is the bifurcation ratio?
ratio of streams of order n-1 to the order n
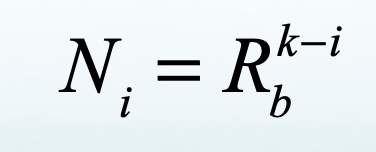
What are the other average scaling laws we can have?
law of average stream lengths of order i L_i
law of average drainage area of streams of order i A_i
law of average stream slopes of order i S_i

What is hack’s law?
L is proportional to A^c where 0.5<c<0.6