Containment - lecture 10 - National immunisation program
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
history NIP
1957 first vaccinations implemented → polio, tetanus, diptheria, pertussis
1974 rubella
1976 measles
1987 mumps
1993 heamophilus influenzae
2002 meningococcal disease
2006 pneumococcal disease
2009 HPV (13 year old girls)
2011 hepB
2018 MenACWY
2019 maternal pertussis
2022 HPV age 10 boys and girls
2023 maternal flu
2024 rotavirus
2025 rsv
all the vaccinations in the netherlands
1957 - diptheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio
1974 - rubella
1976 - measles
1987 - mump
1998 - h3qmophilus influenza type B
2002 - meningococcal C
2006 - pneumococcal disease
2009 HPV (13 year old girls)
2011 hebB
2017 - menACWY
2019 - maternal pertussis
2022 - HPV at 10 year boys and girls
2023 - maternal flu
2024 - rotavirus
2025 - RSV
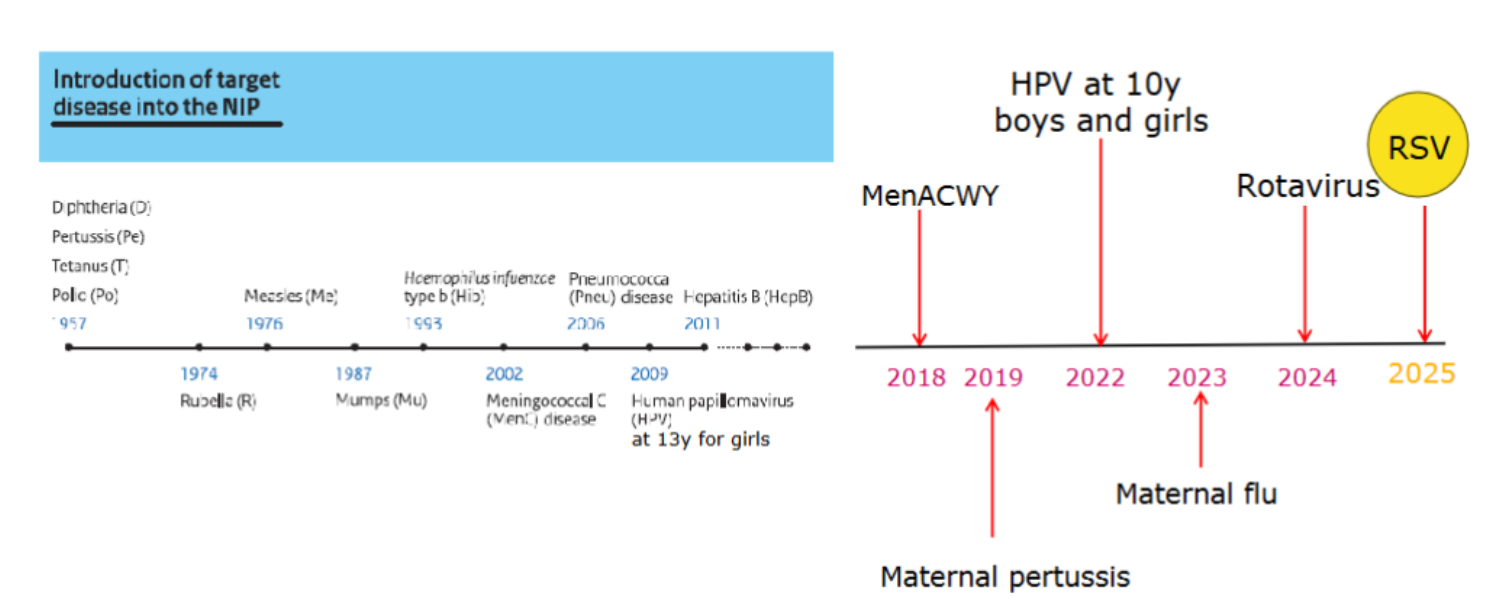
facts about NIP in the Netherlands
children 0-18 years
pregnant women
14 infectious diseases
15 vaccinations and 2 oral doses
over 2 million vaccination per year
costs 90million / year
NIP principles
equal access
central organization (so you know when something goes wrong, which batch)
central registrations
individual invitationsd
reminder
public information, education, campaigns
expertise of professionals
monitoring of safety and effectiveness
assurance of quality and continuity
cose effective, advantages of scale
3 head principles
qualitatively strong programme
based on voluntary participation
aiming at high coverage of the target group
ingredients vaccine
active substances → parts of the virus or bacteria against which immunity is built up. (Antibodies in case of immunization)
after production, these residues are removed from the vaccine as much as possible but very small quantities could still be present.
excipients → substances added to the vaccine to improve effectiveness/ immune response, extend shelf life and make it easier to administer the vaccine.
residues → trace amounts of substances used in the production of the vaccine.
3 different vaccines
1. inactivated vaccines fragments of pathogens toxin (difteria/tetanus) recombinant RNA methode (HPV)
2. live attenuated vaccines a weakened virus (measles rotavirus)
3. immunisation antibodies (RSV)
NIP in other countries
all different in different countries (different rules and regulations)
vaccine logistics
distribute vaccines to 250 locations each week
delivered in cold chain fridge and monitor stock
the vaccines are distributed to group vaccination sessions
all very specific and registered!! → batch number connected to the child.
different stakeholders
vaccine manufacturers → develop, make and sell vaccine
(local) medicine agency → give registration/permission for the vaccine to be sold
health council → advice on making the vaccine part of NIP
minister/state secretary of health → final decision on the content of the NIP (decide in 3 months)
youth health care facilities
big stakeholder in vaccines in the netherlands
consultatiebureau → unique in the netherlands that they combine the consultatie with also vaccine advice / administration.
they do individual consultation
vaccination
registration
sometimes there are also mass group vaccination days
other important stakeholders
IGJ (inspection) → quality of health care, first done by RIVM but better to have objective party
Lareb → monitoring side effects
midwifes → refer pregnant women to the youth health care centre for maternal vaccination
pediatricians → medical risk groups, children hospitalized.
cooperation of ministery, NHI, and medical professionals
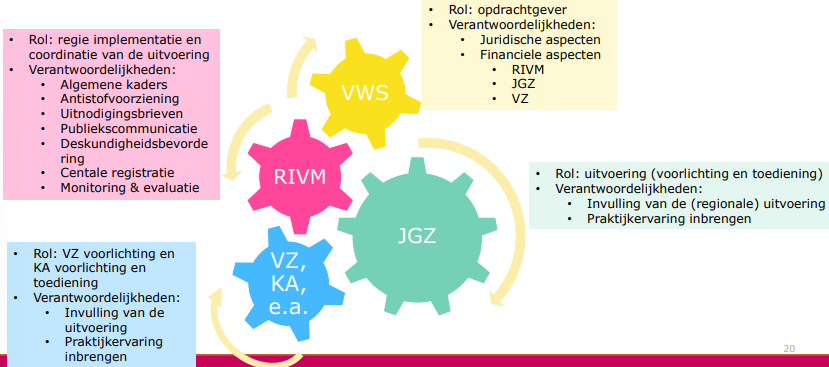
RIVM structures the implementation
takes 6 months
risks of lawsuits so needs to be done well
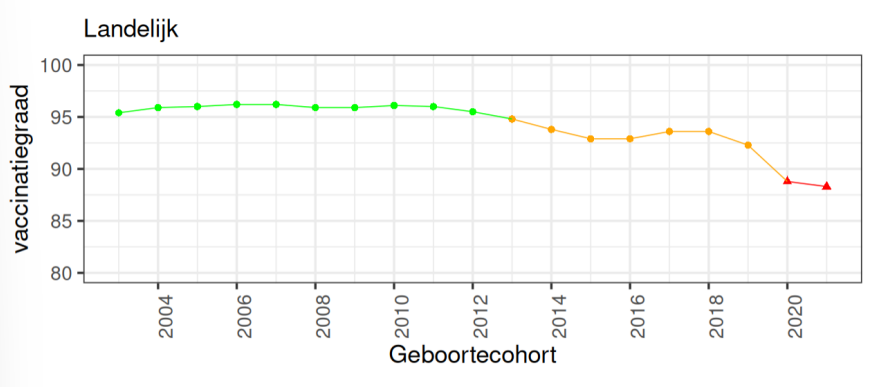
vaccinatiegraad
above 90% is considered ideal for herd immunity (for some even >95%
right now nothing is over 90% in the netherlands
measles outbreak
very problematic
high R number
has went down through the years
important to know where the people are that are not vaccinated (cities, bible belt etc.) → clustering, serotypes and genotypes of the measles are different between these clusters.
health inequity → in certain areas less vaccine uptake, might be due to the people there not having there questions answered. They might not have all the information needed.
vol vertrouwen in vaccinaties
politiek innitiatief om vaccinatiegraad omhoog te krijgen in Nl.
every year (jan, juni) there is a kamer brief where all information about vaccination is send
WHO has a tool → Tailooring Immunization Programmes.
TIP
define underserved groups and communities → detervax
what are barriers and drivers → sociovax
design intervention → done together with people in the neighbourhood and people working there. e.g. midwives betrekken bij vaccineren.
evaluate and implement
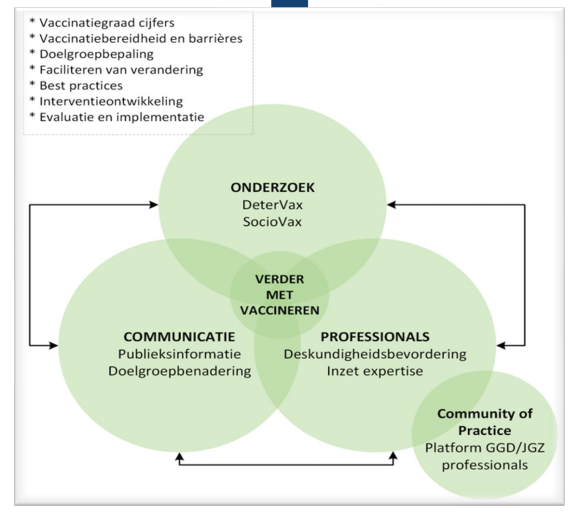
detervax
epdiemiological study
determines coverage national and regional
stap 1 in TIP; what and where coverage is low.
connects to CBS data and RIVM data
look at trends over time.
coverage by sociodemographic denomination.
sociovas, social scientific research
how do people think about the NIP
investigate changes in attitudes in time
how to inform people
design interventions and pilot them
RSV
newest vaccination (immunizatin)
needs to be given immediately after birth (mostly done in hospital, but not in Nl).
oktober to march children are infected.
global burden very high → in low and middle income countries children often die.
nirsevimab → langwerkend antistof tegen RS. → binds to F protein so the virus can not bind. this antibody works for 6months do protects for the whole season. (only need to give once).
data RSV vaccination spain
effectiviteit 82%
but uptake is super high here (above 90%) this adds to this high effectiviteit.