Y12 Psych - Genetics and Behavior
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:33 AM on 11/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Gene
A unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring, contained on a chromosome
2
New cards
Allele
A variant form of a gene. For example, the 5HTT gene, the serotonin transporter gene
3
New cards
Chromosomes
Your genetic makeup (who you are genetically which controls things like eye color, hair color, bone structure, organ size, etc.) is controlled by the paring of these; 23 from the female egg, and 23 from the male sperm
4
New cards
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
The carrier of the genetic material that determines who you are (genetically). --- Each molecule of this is made up of thousands of genes, which determine your "genetic makeup"
5
New cards
Diathesis-stress theory of depression
Theorize that people’s reaction to stress depends on their genetic make-up , interaction with the environment cause these genes to be expressed
6
New cards
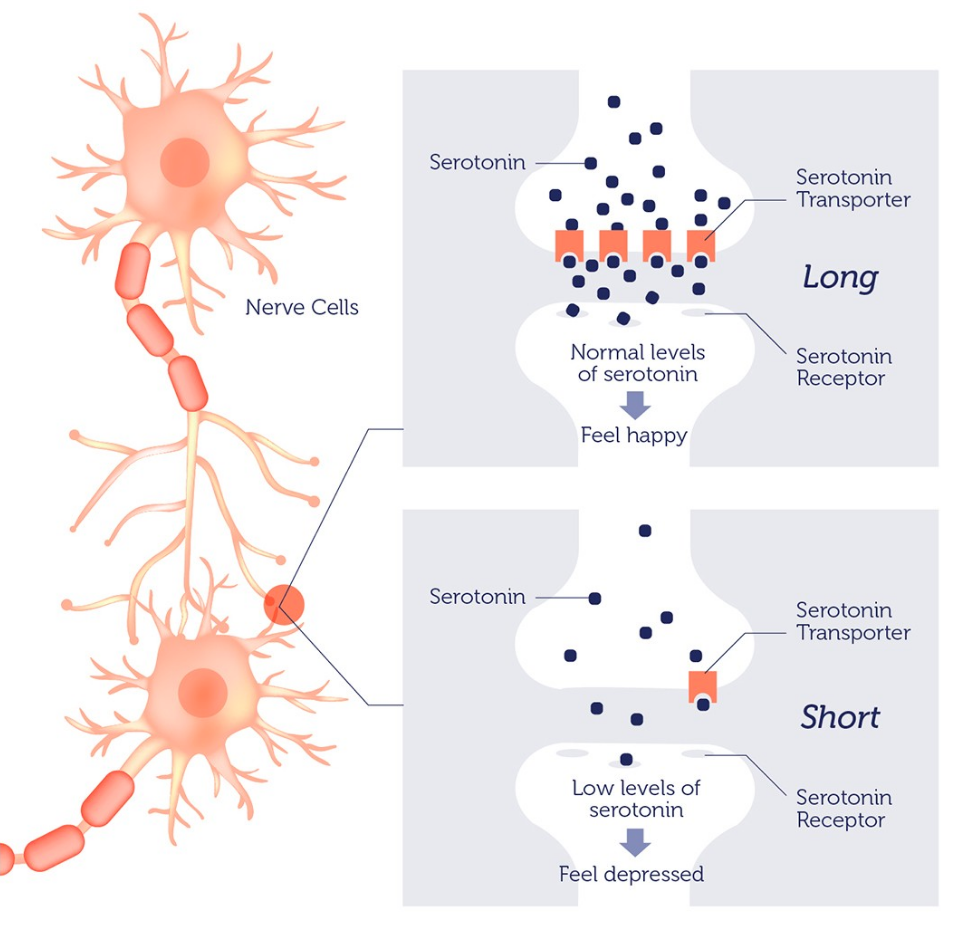
5HTT (Serotonin transporter)
The serotonin transporter that is involved in the reuptake of serotonin in brain synapses.
7
New cards
Caspi et al (2003) 5-HTT vs. depression
!! GENES STUDY !!
A - To investigate whether a change on the 5HTT gene is linked to a higher or lower risk of depression in an individual.
M - Correlational analysis of looking at Life-history calendar (LHC) and Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS) --- Looked at a sample of 1037 New Zealand 26 year olds --- All members of a cohort assessed for mental health every two years from age 3.
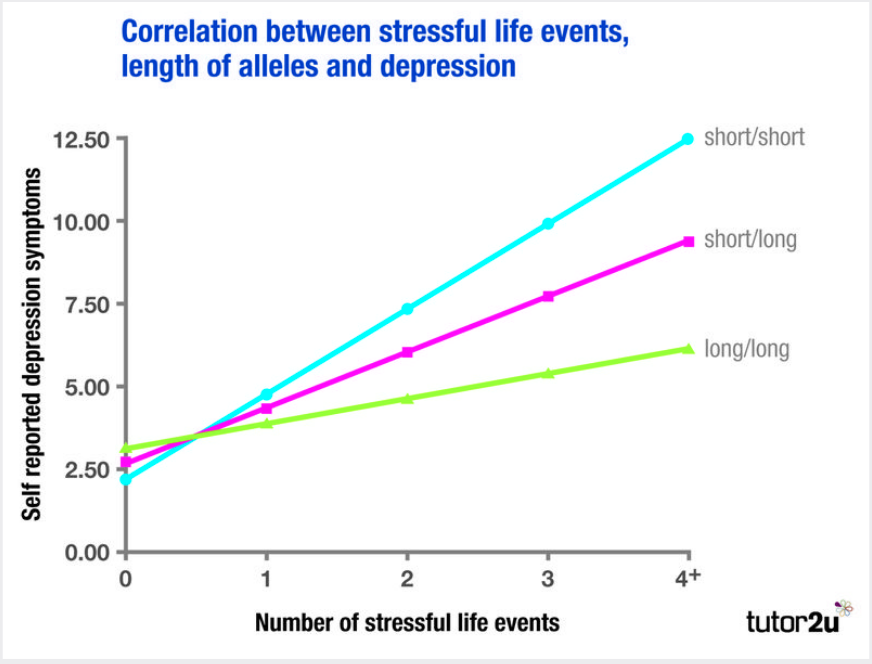
P - Divided into three groups based on their 5-HTT alleles: Group 1 had two short alleles, 2 had one short + one long, 3 had two long.
Participants were asked to fill in a "Stressful life events" questionnaire which asked them about the frequency of 14 different events - including financial, employment, health and relationship stressors - between the ages of 21 and 26. They were also assessed for depression.
R - People with one or two short alleles exhibited more depressive symptoms, diagnosable depression and suicidal ideation in relation to stressful life-events than individuals who carried the long allele of 5-HTT.
C - No direct relation between short alleles on the 5HTT gene and depression, but a correlation between these and instances of depression linked to stressful life events. --- The long alleles seem to protect against suffering depression as a result of stress. The effects of the gene adaptation are dependent on environmental exposure to stress (Genetic vulnerability, Gene-environment interaction)
E - ✓ Longitudinal study, from age 3 (reliability), High sample size (Population validity / generalizability), Holistic, considered environmental factors, not just genes as the cause
⨉ Correlational, no cause-and-effect, self-reporting (low reliability), studies (see Risch) could not replicate results (low replicability), some people without the mutation still developed depression
A - To investigate whether a change on the 5HTT gene is linked to a higher or lower risk of depression in an individual.
M - Correlational analysis of looking at Life-history calendar (LHC) and Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS) --- Looked at a sample of 1037 New Zealand 26 year olds --- All members of a cohort assessed for mental health every two years from age 3.
P - Divided into three groups based on their 5-HTT alleles: Group 1 had two short alleles, 2 had one short + one long, 3 had two long.
Participants were asked to fill in a "Stressful life events" questionnaire which asked them about the frequency of 14 different events - including financial, employment, health and relationship stressors - between the ages of 21 and 26. They were also assessed for depression.
R - People with one or two short alleles exhibited more depressive symptoms, diagnosable depression and suicidal ideation in relation to stressful life-events than individuals who carried the long allele of 5-HTT.
C - No direct relation between short alleles on the 5HTT gene and depression, but a correlation between these and instances of depression linked to stressful life events. --- The long alleles seem to protect against suffering depression as a result of stress. The effects of the gene adaptation are dependent on environmental exposure to stress (Genetic vulnerability, Gene-environment interaction)
E - ✓ Longitudinal study, from age 3 (reliability), High sample size (Population validity / generalizability), Holistic, considered environmental factors, not just genes as the cause
⨉ Correlational, no cause-and-effect, self-reporting (low reliability), studies (see Risch) could not replicate results (low replicability), some people without the mutation still developed depression
8
New cards
McDermott (2009) MAOA gene vs. aggression
!! GENES STUDY !!
A - To investigate whether the MAOA gene predicts aggressive behavior when provoked.
M - Laboratory quasi-experiment (participants were not randomly allocated to conditions thus not a true experiment)
78 male subjects (a mix of MAOA-H and MAOA-L)
MAOA-L is the variant (hypothesized to be more aggressive)
P - Participants did a simulation in which they were asked to administer hot sauce to fictional opponents who they were told don’t like hot sauce (supposed aggressive behavior)
In each round they were told that their opponent had taken a portion of their earnings/money. They could then punish their opponent by administering hot sauce. The money taken was 0%, 20%, then 80% in each round (3 rounds)
R - Individuals with MAOA-L were significantly more likely to administer the hot sauce compared to MAOA-H when 80% of their earnings were taken. When it was only 20% taken the difference between MAOA-H and MAOA-L was minimal.
C - Evidence of a gene-environment interaction
Individuals with MAOA-L (genetic variation) are more likely to demonstrate aggressive behavior when provoked through the environment.
E - ✓ Gene-environment interaction, Cause-and-effect relationship
⨉ Mundane realism (low generalizability), Construct validity (low internal validity)
A - To investigate whether the MAOA gene predicts aggressive behavior when provoked.
M - Laboratory quasi-experiment (participants were not randomly allocated to conditions thus not a true experiment)
78 male subjects (a mix of MAOA-H and MAOA-L)
MAOA-L is the variant (hypothesized to be more aggressive)
P - Participants did a simulation in which they were asked to administer hot sauce to fictional opponents who they were told don’t like hot sauce (supposed aggressive behavior)
In each round they were told that their opponent had taken a portion of their earnings/money. They could then punish their opponent by administering hot sauce. The money taken was 0%, 20%, then 80% in each round (3 rounds)
R - Individuals with MAOA-L were significantly more likely to administer the hot sauce compared to MAOA-H when 80% of their earnings were taken. When it was only 20% taken the difference between MAOA-H and MAOA-L was minimal.
C - Evidence of a gene-environment interaction
Individuals with MAOA-L (genetic variation) are more likely to demonstrate aggressive behavior when provoked through the environment.
E - ✓ Gene-environment interaction, Cause-and-effect relationship
⨉ Mundane realism (low generalizability), Construct validity (low internal validity)
9
New cards
Meta-analysis
A research strategy where instead of conducting new research with participants, the researchers examine the results of several previous studies
10
New cards
Risch et al (2009) 5-HTT vs. depression
!! GENES STUDY (Counter-argument to Caspi) !!
A - Investigate possible interactions between stressful life events, depression and the serotonin 5HTT gene.
M - Meta-analysis, ~14,000 participants
C - No correlation between 5HHT gene and major depressive disorder.
E - ✓ Meta-analysis, shows low reliability of the Caspi study, large sample size
⨉ ?
A - Investigate possible interactions between stressful life events, depression and the serotonin 5HTT gene.
M - Meta-analysis, ~14,000 participants
C - No correlation between 5HHT gene and major depressive disorder.
E - ✓ Meta-analysis, shows low reliability of the Caspi study, large sample size
⨉ ?
11
New cards
Gene-environment interaction
A different effect of an environmental exposure on behavioral patterns in persons with different genotypes
12
New cards
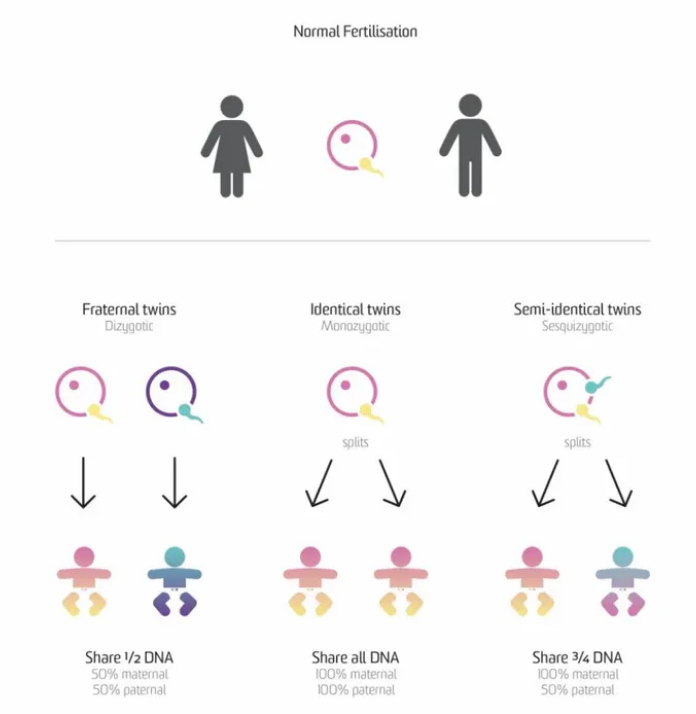
Genetic Similarity
The degree to which individuals share a certain amount of genetic material
13
New cards
Why genetic similarity is studied
Comparisons between the genetic similarity of individuals and their likelihood to display a specific behavior offer researchers valuable information on the potential genetic nature of specific behaviors
14
New cards
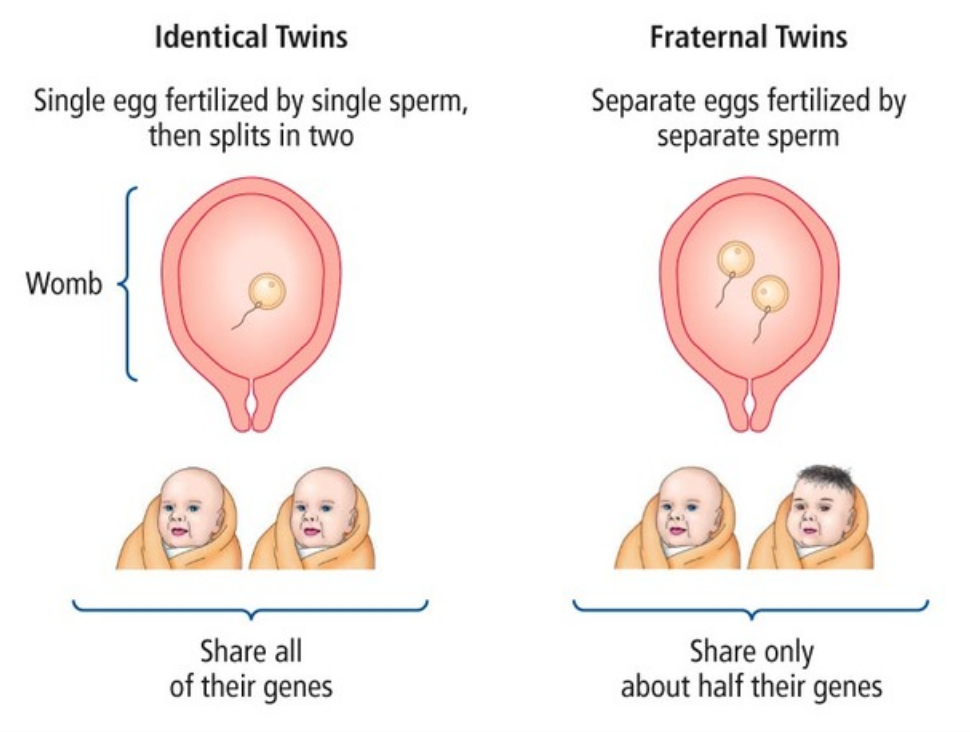
Twin Study
Used to compare the concordance rates for behaviors of monozygotic twins with dizygotic twins to try to establish the extent of the genetic component of the behavior. They feel they can do this as all participants, monozygotic and dizygotic, have shared the same environment. Hence, any differences we see could be attributed to genetics
15
New cards
Kinship Study
The study of family history and genealogy as a means of tracing traits that might be inherited
16
New cards
Family study
17
New cards
Monozygotic twins
When a single fertilized egg splits into two separate embryos which then implant into the uterus. Share identical DNA at birth
18
New cards
Dizygotic twins
When a female's ovary releases two eggs into the uterus that are both fertilized. These two separate gametes differentiate into two separate fetuses that mature into fraternal (non-identical) twins
19
New cards
Concordance Rate
A term that is used to describe the rate of probability that two people with shared genes will develop the same behavior.
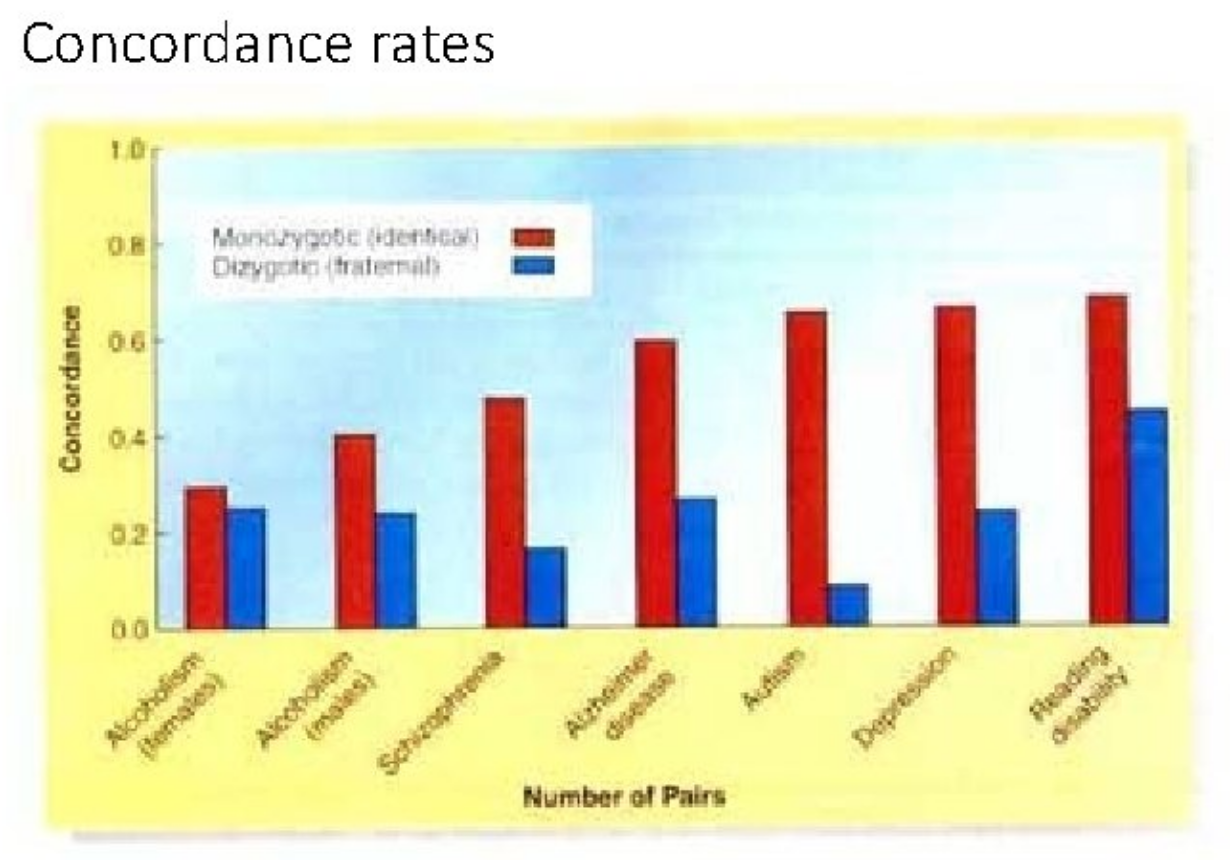
20
New cards
Equal environment fallacy
states that identical twins and fraternal twins are treated quite differently by parents, teachers, friends, etc.
21
New cards
Prospective Study
Select and observe a family before certain behaviors are observed (i.e. if it is suspected depression is genetic within a family). The researchers watch for outcomes, such as the development of a disorder.
22
New cards
Genetic Vulnerability
A genetic predisposition toward a behavior, but an appropriate environmental stimuli is required for it to be manifested
23
New cards
Kendler et al (2006) Genetics vs. Major Depressive Disorder
A - To investigate the role that genetics plays in major depressive disorder
M - Twin study - Sample of 15,493 complete twin pairs listed in the national Swedish Twin Registry born between 1886 and 1958. Only twins whose zygosity could be verified were used in the study.
P - A team of trained interviewers carried out telephone interviews that were carried out between March 1998 and January 2003, and assessed lifetime major depression by using modified DSM-IV criteria.
8056 twins met the criteria for a diagnosis of major depressive disorder at some point in their life - and 322 twins voluntarily discussed a history of antidepressant treatment.
In addition to this information, the interviewers also asked questions about the twins' "shared environment" - that is, when they were living in the same household - and their "individual-specific environment" - that is, adult personal life events that may make members of the twin pair more susceptible to depression.
R - The results indicate that correlations were significantly higher in monozygotic (MZ) than in dizygotic (DZ) twins. In addition, the heritability of major depression was significantly higher in women than men. The estimated heritability of major depressive disorder was 0.38, in line with previous research.
They also found no correlation between the number of years that the twins had lived together and lifetime major depression.
C - The study suggests that there must be a substantial genetic component to MDD as MZ twins were more likely to both have MDD than DZ twins. However, the results suggest that the heritability of major depression is higher in women than in men and that some genetic risk factors for major depression are sex-specific. The results also indicate that environmental factors do not play a significant role in MDD.
Genetic similarity seems to play a more substantial role.
E - ✓ Confirms previous research (reliability), large sample size (generalizability)
⨉ No particular genes were isolated and tested; no cause and effect (correlational), self-reported (reliability), twins diagnosed over the phone, not official (validity)
M - Twin study - Sample of 15,493 complete twin pairs listed in the national Swedish Twin Registry born between 1886 and 1958. Only twins whose zygosity could be verified were used in the study.
P - A team of trained interviewers carried out telephone interviews that were carried out between March 1998 and January 2003, and assessed lifetime major depression by using modified DSM-IV criteria.
8056 twins met the criteria for a diagnosis of major depressive disorder at some point in their life - and 322 twins voluntarily discussed a history of antidepressant treatment.
In addition to this information, the interviewers also asked questions about the twins' "shared environment" - that is, when they were living in the same household - and their "individual-specific environment" - that is, adult personal life events that may make members of the twin pair more susceptible to depression.
R - The results indicate that correlations were significantly higher in monozygotic (MZ) than in dizygotic (DZ) twins. In addition, the heritability of major depression was significantly higher in women than men. The estimated heritability of major depressive disorder was 0.38, in line with previous research.
They also found no correlation between the number of years that the twins had lived together and lifetime major depression.
C - The study suggests that there must be a substantial genetic component to MDD as MZ twins were more likely to both have MDD than DZ twins. However, the results suggest that the heritability of major depression is higher in women than in men and that some genetic risk factors for major depression are sex-specific. The results also indicate that environmental factors do not play a significant role in MDD.
Genetic similarity seems to play a more substantial role.
E - ✓ Confirms previous research (reliability), large sample size (generalizability)
⨉ No particular genes were isolated and tested; no cause and effect (correlational), self-reported (reliability), twins diagnosed over the phone, not official (validity)
24
New cards
Weissman et al (2005) Genetics vs. Major Depressive Disorder
A - To investigate potential genetic nature of Major Depressive Disorder.
M - Longitudinal kinship study - sample of 161 grandchildren and their parents and grandparents.
P - The study took place over a 20-year period, looking at families at high and low risk for depression. The original sample of depressed patients (now, the grandparents) was selected from an outpatient clinic with a specialization in the treatment of mood disorders. Here we can see how the study was prospective in nature. The non-depressed participants were selected from the same local community. The original sample of grandparents (1st generation) and parents (2nd generation) were interviewed four times during this period. The children (3rd generation) were evaluated by two experienced clinicians - with one being a child psychiatrist and the other a psychologist.
R - The researchers found high rates of psychiatric disorders in the grandchildren with two generations, parents and grandparents, showing symptoms of major depression.
By the age of 12, 59.2% of these grandchildren were already showing signs of a psychiatric disorder - most commonly anxiety disorders.
Children had an increased risk of any disorder if depression was observed in both the grandparents and the parents, compared to children where their parents were not depressed.
On the other hand, if a parent was depressed but there was no history of depression in the grandparents, there was no significant effect of parental depression on the grandchildren.
C - This is the first study of its kind, in that it has three generations of family members, and seems to indicate that psychiatric disorders are more likely to occur in people with a family history of mental illness that goes back two or more generations.
The fact that children were more likely to display symptoms of psychiatric disorders when both a grandparent and parent also did, indicates a strong case for a genetic component.
E - ✓ Longitudinal study (reliability), triangulation (validity), large sample (generalizability)
⨉ Kinship studies indicate a potential genetic link to behavior; no actual genotype was studied (correlational), amount of time that a child spent with a healthy grandparent may be a confounding variable (reliability)
M - Longitudinal kinship study - sample of 161 grandchildren and their parents and grandparents.
P - The study took place over a 20-year period, looking at families at high and low risk for depression. The original sample of depressed patients (now, the grandparents) was selected from an outpatient clinic with a specialization in the treatment of mood disorders. Here we can see how the study was prospective in nature. The non-depressed participants were selected from the same local community. The original sample of grandparents (1st generation) and parents (2nd generation) were interviewed four times during this period. The children (3rd generation) were evaluated by two experienced clinicians - with one being a child psychiatrist and the other a psychologist.
R - The researchers found high rates of psychiatric disorders in the grandchildren with two generations, parents and grandparents, showing symptoms of major depression.
By the age of 12, 59.2% of these grandchildren were already showing signs of a psychiatric disorder - most commonly anxiety disorders.
Children had an increased risk of any disorder if depression was observed in both the grandparents and the parents, compared to children where their parents were not depressed.
On the other hand, if a parent was depressed but there was no history of depression in the grandparents, there was no significant effect of parental depression on the grandchildren.
C - This is the first study of its kind, in that it has three generations of family members, and seems to indicate that psychiatric disorders are more likely to occur in people with a family history of mental illness that goes back two or more generations.
The fact that children were more likely to display symptoms of psychiatric disorders when both a grandparent and parent also did, indicates a strong case for a genetic component.
E - ✓ Longitudinal study (reliability), triangulation (validity), large sample (generalizability)
⨉ Kinship studies indicate a potential genetic link to behavior; no actual genotype was studied (correlational), amount of time that a child spent with a healthy grandparent may be a confounding variable (reliability)