Unit 4.5 - Managing Inventory and Supply Chains
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Mass customisation
Offering individually tailored goods or services to customers on a large scale
Factors required for mass customisation
Market which values variety and individuality
Quick responses to market changes
Ability to provide customisation
Scope for economies of scale
Benefits of mass customisation
Cost reductions
Higher revenue
Customer loyalty
Greater understanding of wants
Greater protection from market changes
Improved employee motivation
Drawbacks of mass customisation
Requires sophisticated systems
Expensive - equipment and training
Difficult to resell rejected products
Unsuitable supply chains - requires flexibility
Matching supply to demand - managing demand
- Widen product range to overcome issues of spare capacity
- Off peak special offers for periods of low demand
- Increasing prices to reduce overly high demand
Matching supply to demand p managing supply
- Producing to order
- Use of temporary and part time employees
- Outsourcing
Producing to order
Only ordering or manufacturing a product when an actual purchase has been made
- Ranges from small scale, tailor made products such as suits to large scale one off planes where the basic layout is modified
- Adopt a modular approach to manufacturing:
Basic element
Then an element which can be customised
Benefits of producing to order
Meets customers exact requirements
Reduced costs of holding inventory
Higher prices
Targeting markets becomes easier
Production planning is easier (no need to forecast demand)
Drawbacks of producing to order
Higher costs of production
Can't take advantage of sudden interest
Unpredictable fluctuations of demand
Factors to consider when producing to order
Value to the customer
Willingness of customers to wait
Nature of the product and relative costs
Cost of holding inventory i.e needs refrigeration
Impact of having no stock - loss of sale
Part-time workers
limited number of hours, such as 15 hours per week
Temporary workers
contract of employment has an end date. Can be full or part time
When temporary or part time are likely to be used
More flexible than full time staff
Seasonal demand - temporary workers to cover busy periods
Saves wage costs - no need to pay them all year round
Part time staff usually used for predictable variations in demand
Pubs employing more people on a weekend
Benefits of part time or temporary workers
Lower costs
More flexible - respond to changes in demand
Higher customer service
Employees may be motivated if part time suits them
Can retain valued employees i.e parents
Outsourcing
transfer of activities which were previously conducted by the business, to a third party. The business get another business to produce some or all of its product for it or perform part its operations
Benefits of outsourcing
React to changes in demand
Increased specialisation - higher quality
Less disruptive to production
Is sometime cheaper than having to get skilled workers or train own employees
Drawbacks of outsourcing
Loss of control - lower quality
Overall price could rise - everyone needs to make a profit
factors influencing decision to outsource
- Available capacity - high capacity utilisation = likely to outsource
- Expertise - lower skill level = likely to outsource
- Quality considerations - if USP isn't quality = likely to outsource
- Nature of demand - unpredictable = likely to outsource
- Cost - not benefiting from economies of scale = likely to outsource
Inventories/stock
Goods or stock a business holds to use in production or sell to customers
Inventory/stock control
management of levels of raw materials, work in progress and finished goods
3 forms of inventory
Raw materials - components or ingredients
Work in progress - part finished products
Finished goods - completed products that are owned by the business until the sale has been agreed
Inventory control key features
- Can be used to ensure production matches demand
- By holding high levels of inventory, can meet growing demand
- During low demand periods, business can produce to replenish inventory sold in high demand
- The ideal level of inventory depends on circumstances
Benefits of high inventory levels (JIC)
- Customer demands are met
- There is no loss of goodwill caused by running out of inventory
- Sudden increase in demand can be met
- Production lines not halted because of shortages of raw materials
- Companies can benefit from bulk buying
Benefits of low inventory levels (JIT)
- Reduced warehouse costs are possible
- Opportunity cost is low (cash)
- Security costs are lower
- Perishable products are less likely to deteriorate and less likely for products to become obsolete
- Less cash flow issues due to cash not being tied up in inventory
Inventory control chart
A diagram that is used to register levels of stock/inventory over a period of time.
Inventory control chart (diagram)
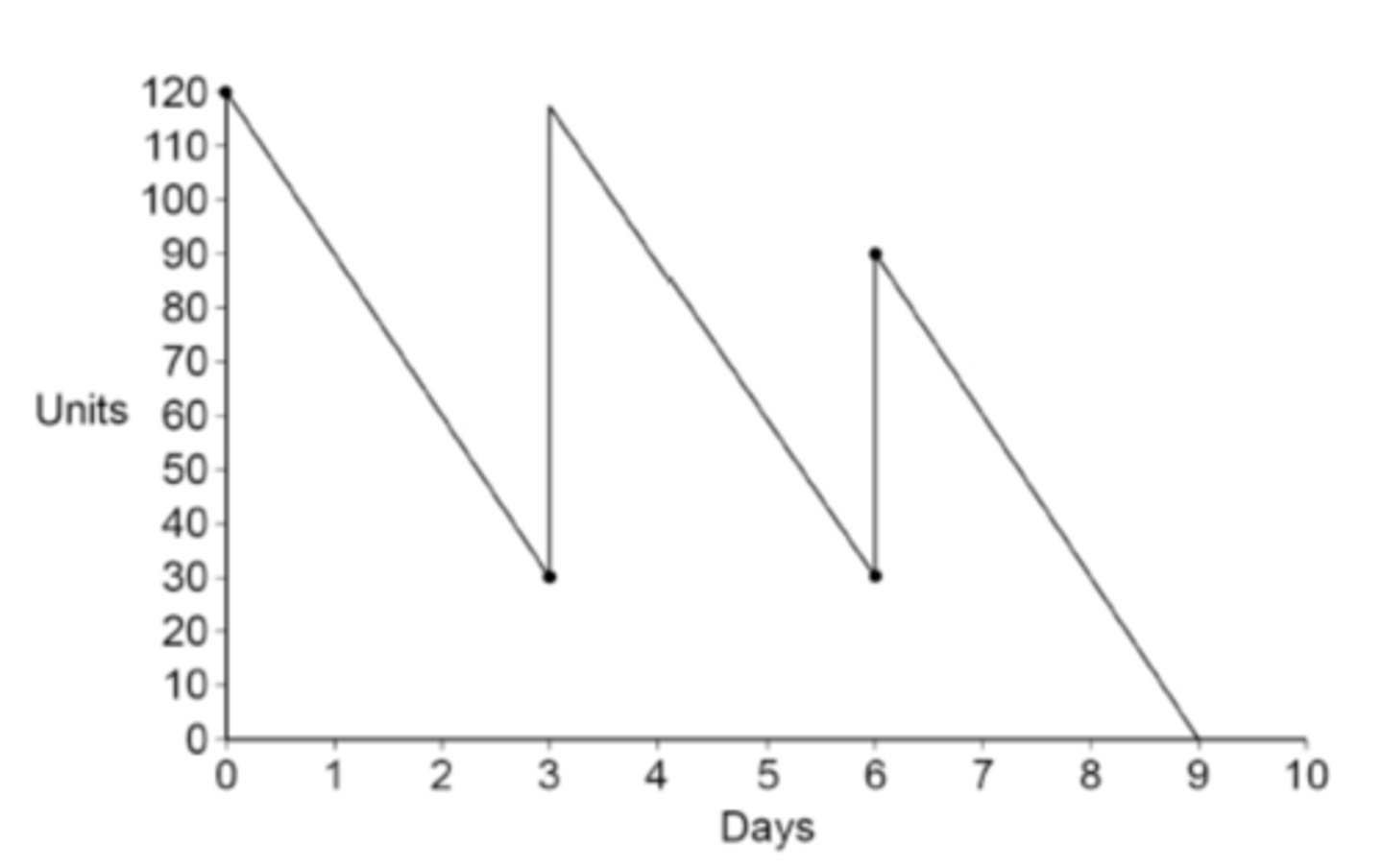
Buffer levels/inventory/stock
minimum amount of inventory held by a business
Re-order level
the inventory level at which an order is placed for new inventory
Re-order quantity
the actual number of products purchased from the supplier in a particular order
Lead time
how long the supplier takes to deliver an item once the order has been placed
What does re-order quantity and level depend on
Suppliers lead time
Demand for the product
Consequences of running out of inventory
Inventory wastage
Measure the loss of inventory within a business
Inventory rotation
using old inventory before new to make sure that wastage is kept to a minimum
Improving the efficiency of inventory control
- Traditionally, businesses kept high levels of inventory ‘just in case’ they were needed
- Led to businesses selling inventory at cheap prices to avoid complete wastage
- Japanese firms led the way in arguing that this was a waste of space and inventory
- This lead to the introduction of just in time inventory control
Just in time stock control (JIT)
An inventory-management approach in which supplies arrive just when needed for production or resale
Benefits of JIT
- Low inventory holding costs
- Less space needed to hold inventory
- Less cluttered environment - safer
- Less chance of inventory going out of date or going unsold
Drawbacks of JIT
- Cannot not benefit from purchasing economies of scale
-Relies on suppliers, may be unreliable
- May require more frequent deliveries
- May be less able to meet sudden increases in demand/fluctuating demand
- Will have to pay whatever the price is for materials when you need them as there is no buffer stock
Supplier
An organisation that provides a business with materials or finished goods needed to carry out activities
Factors influencing choice of suppliers
Prices
Payment terms
Quality
Capacity
Reliability
Flexibility
Price (choice of suppliers)
- Reduce the final selling price - gain competitive advantage
- Keep selling price the same but enjoy extra profit
But may be trade-off in other areas such as quality
Payment terms (choice of suppliers)
Arranged made about the timings of payments (and other conditions)
It is normal for credit to be offered (no need to pay for 28 or 30 days) for two reasons:
Helps improve cash flow cycle
Order supplies - make product - sell product - gain revenue - use revenue to pay suppliers
Helps suppliers to be competitive
Businesses will prefer to use them over other suppliers
Trade credit
Period of time given by suppliers where the business is proved with resources needed but does not have to pay until a later date
Quality (choice of suppliers)
Must match customer expectations
Price trade off
How important is quality?
Capacity (choice of suppliers)
Can the supplier provide the quantity needed?
Particularly relevant if the resource can't be obtained elsewhere
Reliability (choice of suppliers)
% of deliveries made on time
If the business is manufacturing, this could be detrimental to production
Important if the business uses just in time production
Flexibility (choice of suppliers)
Sudden changes in demand
Negative publicity around an ingredient / component
Transport difficulties preventing deliveries from other sources
Value of contingency plans: PLAN B can be used in an emergency
How to manage supply chain effectively
Different businesses will have different operational objectives:
Low costs
High quality
Speed of response
Flexibility
Dependability
Environmental objectives
Added value
But will likely all require
- getting the right suppliers, supplies arriving on time, getting a fair price, product being priced in a way that is acceptable to the business, good communication with suppliers, coordinating other functional areas