Basic Epidemiology Terminology (DD)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
1
New cards
cluster
An aggregation of cases over a particular period closely grouped in time and space, regardless of whether the number is more than the expected number
2
New cards
endemic disease
Present at a continuous level throughout a population/geographic area; constant presence of an agent/health condition within a given geographic area/population; refers to the usual prevalence of an agent/condition.
3
New cards
epidemic
Large numbers of people over a wide geographical area are affected.
4
New cards
etiology
Study of the cause of a disease.
5
New cards
fomite
A physical object that serves to transmit an infectious agent from person to person. An example of this is lice on a comb. The comb is the _ and the lice are the agent that can make your hair itch.
6
New cards
iatrogenic
An illness that is caused by a medication or physician.
7
New cards
incubation period
Time in between when a person comes into contact with a pathogen and when they first show symptoms or signs of disease.
8
New cards
index case/patient zero
First patient in an epidemiological study
9
New cards
morbidity
Rate of disease in a population.
10
New cards
mortatlity
Rate of death in a population.
11
New cards
outbreak
More cases of a particular disease than expected in a given area or among a specialized group of people over a particular period of time.
12
New cards
pandemic
An epidemic occurring over several countries or continents and affecting a large proportion of the population.
13
New cards
plague
A serious, potentially life-threatening infectious disease that is usually transmitted to humans by the bites of rodent fleas. It was one of the scourges of our early history. There are three major forms of the disease: bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic.
14
New cards
nosocomial disease
An infection that is acquired in a hospital.
15
New cards
risk
The probability that an individual will be affected by, or die from, an illness or injury within a stated time or age span. _ of illness is generally considered to be the same as the Incidence and the terms are used interchangeably. Age-span is not usually a consideration in this usage. _ of death from a particular illness is expressed as the Case Fatality Rate CFR (Number OF deaths due to a disease/Number with the disease) or the Cause-specific Mortality Rate CMR (Number of deaths due to a disease/Number in population). Age span is a more common consideration in this last usage.
16
New cards
surveillance
The systematic and ongoing collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data. The purpose of public health _ is to gain knowledge of the patterns of disease, injury, and other health problems in a community so that we can work towards their prevention and control.
17
New cards
vector
An animal that transmits disease but is not the cause of the disease itself. For example, a mosquito is a _ for malaria.
18
New cards
zoonosis
An infectious disease that is transmissible from animals to humans.
19
New cards
symptomatic
Showing symptoms or signs of injury.
20
New cards
asymptomatic
Showing no signs or symptoms, although can be carrier of disease.
21
New cards
incidence (of an illness)
The number of new instances of disease in a population over a given time period; X cases/Y population/ Z time
22
New cards
prevalence (of an illness)
the number of affected persons in the population at any given point in time; X cases/Y population
23
New cards
sporadic
a disease that occurs infrequently and irregularly
24
New cards
ratio
value obtained by dividing one quantity by another. A _ often compares two rates
25
New cards
proportion
the comparison of a part to the whole as the number of cases divided by the total population, does not have a time dimension, can be expressed as a decimal, fraction, or percentage.
26
New cards
normal flora
many microbes have positive symbiotic relationships with other organisms
27
New cards
mutualism
both organisms benefit
28
New cards
commensalism
one organism and the other is not harmed or help
29
New cards
parasitism
the condition (one organism is helped where another is harmed) taking places when humans are invaded by infectious microbes, forming a parasite-host relationship
30
New cards
infectious agent
an agent capable of producing infection
31
New cards
latency period
the stage of subclinical diseases extending from the time of exposure to the onset of disease symptoms (for chronic diseases)
32
New cards
agent
a microbial organism with the ability to cause disease
33
New cards
reservoir
a place where agents can thrive and reproduce
34
New cards
portal of exit
a place of exit providing a way for an agent to leave the reservoir
35
New cards
portal of entry
an opening allowing the microorganism to enter the host
36
New cards
susceptible host
a person who cannot resist a microorganism invading the body, multiplying and resulting in infection
37
New cards
infectious dose
the amount of pathogen (measured in number of microorganisms) required to cause an infection in the host. Usually, this varies according to the pathogenic agent and consumer's age and overall health
38
New cards
period of communicability
the period when you are infectious and can spread your germs (whether bacteria, viruses, or parasites) to an uninfected person
39
New cards
contamination
when a potentially infectious agent exists in the host but has not yet invaded the tissues of the host. The microbe may be destroyed by the body defenses or it may become part of the normal flora
40
New cards
infection
when the infectious agent begins its invasion of the host tissue and its rapid multiplication. The infection may be localized or it may spread to alternative sites as deeper organs or tissues become systemic
41
New cards
disease
when the cumulative effects of the infection cause damage in the tissues
42
New cards
infectivity
refers to the proportion of exposed persons who become infected
43
New cards
pathogenicity
refers to the proportion of infected persons who develop clinical diseases
44
New cards
virulence
refers to the proportion of persons with clinical disease who become severly ill or die
45
New cards
convalescent
(type of vector/carrier) Humans are also capable of spreading disease following a period of illness, typically thinking themselves cured of the disease
46
New cards
incubatory
(type of vector/carrier) When an individual transmits pathogens immediately following infection but prior to developing symptoms
47
New cards
chronic
(type of vector/carrier) Someone who can transmit a disease for a long period of time
48
New cards
genetic
(type of vector/carrier) has inherited a disease trait but shows no symptoms
49
New cards
transient/temporary
(type of vector/carrier) Someone who can transmit an infectious disease for a short amount of time
50
New cards
ecological
(type of study) comparisons of geographical locations
51
New cards
cross sectional
(type of study) a survey, health questionnaire, "snapshot in time"
52
New cards
case control
(type of study) compare people with and without disease to find common exposures
53
New cards
cohort
(type of study) compare people with and without exposures to see what happens to each
54
New cards
randomized controlled trial
(type of study) human experiment
55
New cards
quasi experiments
(type of study) research similarities with traditional experimental design or RCT, but lack element of random assignment to treatment/control
56
New cards
clinical care
prevention, treatment, and management of illness and the preservation of mental and physical well-being through the services offered by medical and allied health professions; health care.
57
New cards
determinant
factor that contributes to the generation of a trait
58
New cards
health outcome
result of a medical condition that directly affects the length or quality of a person's life
59
New cards
hyperendemic
In epidemiology, the term _ disease is used to refer to a disease which is constantly and persistently present in a population at a high rate of incidence and/or prevalence and which equally affects all age groups of that population.
60
New cards
hypoendemic
A disease that is constantly present at a low incidence or prevalence and affects a small proportion of individuals in the area
61
New cards
mesoendemic
endemic disease with some transmission in an area
62
New cards
holoendemic
endemic disease affects most individuals in a population
63
New cards
indicator
a measurable factor that allows decision makers to estimate objectively the size of a health problem and monitor the processes, the products, or the effects of an intervention on the population (for example, the number of new cases of diarrhea, the proportion of children fully immunized in a district, or the percentage of high school students who report that they smoke at least one cigarette a day).
64
New cards
active surveillance
system employing staff members to regularly contact heath care providers or the population to seek information about health conditions. __ the most accurate and timely information, but it is also expensive
65
New cards
passive surveillance
system by which a health jurisdiction receives reports submitted from hospitals, clinics, public health units, or other sources. __ is a relatively inexpensive strategy to cover large areas, and it provides critical information for monitoring a community's health. However, because passive surveillance depends on people in different institutions to provide data, data quality and timeliness are difficult to control
66
New cards
routine health information system
__ is a passive system in which regular reports about diseases and programs are completed by public health staff members, hospitals, and clinics.
67
New cards
health information and management system
__ is a passive system by which routine reports about financial, logistic, and other processes involved in the ad\`ministration of the public health and clinical systems can be used for surveillance.
68
New cards
categorical surveillance
__ is an active or passive system that focuses on one or more diseases or behaviors of interest to an intervention program. These systems are useful for program managers. However, they may be inefficient at the district or local level, at which staff may need to fill out multiple forms on the same patient (that is, the HIV program, the tuberculosis program, the sexually transmitted infections program, and the Routine Health Information System). At higher levels, allocating the few competent surveillance experts to one program may leave other programs under-served, and reconciling the results of different systems to establish the nation's official estimates may be difficult.
69
New cards
integrated surveillance
__ is a combination of active and passive systems using a single infrastructure that gathers information about multiple diseases or behaviors of interest to several intervention programs (for example, a health facility–based system may gather information on multiple infectious diseases and injuries). Managers of disease-specific programs may be evaluated on the results of the integrated system and should be stakeholders. Even when an integrated system is functioning well, program managers may continue to maintain categorical systems to collect additional disease-spe\`cific data and control the quality of the information on which they are evaluated. This practice may lead to duplication and inefficiency.
70
New cards
syndromic surveillance
__ is an active or passive system that uses case definitions that are based entirely on clinical features without any clinical or laboratory diagnosis (for example, collecting the number of cases of diarrhea rather than cases of cholera, or "rash illness" rather than measles). Because *_* is inexpensive and is faster than systems that require laboratory confirmation, it is often the first kind of surveillance begun in a developing country. However, because of the lack of specificity (for example, a "rash illness" could be anything from the relatively minor rubella to devastating hemorrhagic fevers), reports require more investigation from higher levels. Also an increase in one disease causing a syndrome may mask an epidemic of another (for example, rotavirus diarrhea decreases at the same time cholera increases).
for bioterrorism, refers 2 active surveillance of syndromes caused by potential agents used by bioterrorists/refers to alternative measures
for bioterrorism, refers 2 active surveillance of syndromes caused by potential agents used by bioterrorists/refers to alternative measures
71
New cards
behavioral risk factor surveillance system BRFSS
__ is an active system of repeated surveys that measure behaviors that are known to cause disease or injury (for example, tobacco or alcohol use, unprotected sex, or lack of physical exercise). Because the aim of many intervention program strategies is to prevent disease by preventing unhealthy behavior, these surveys provide a direct measure of their effect in the population, often long before the anticipated health effects are expected. These surveys are useful for providing timely measures of program effectiveness for both communicable and noncommunicable disease interventions.
72
New cards
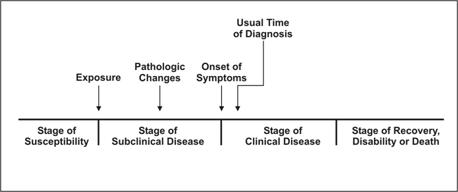
natural history of a disease
__ refers to the progression of a disease process in an individual over time, in the absence of treatment
73
New cards
(direct) direct contact
_ occurs through skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and sexual intercourse. Direct contact also refers to contact with soil or vegetation harboring infectious organisms. Thus, infectious mononucleosis (“kissing disease”) and gonorrhea are spread from person to person by direct contact. Hookworm is spread by direct contact with contaminated soil.
74
New cards
droplet spread
refers to spray with relatively large, short-range aerosols produced by sneezing, coughing, or even talking. Droplet spread is classified as direct because transmission is by direct spray over a few feet, before the droplets fall to the ground. Pertussis and meningococcal infection are examples of diseases transmitted from an infectious patient to a susceptible host by droplet spread.
75
New cards
indirect transmission
refers to the transfer of an infectious agent from a reservoir to a host by suspended air particles, inanimate objects (vehicles), or animate intermediaries (vectors).
76
New cards
airborne transmission
occurs when infectious agents are carried by dust or droplet nuclei suspended in air. Airborne dust includes material that has settled on surfaces and become resuspended by air currents as well as infectious particles blown from the soil by the wind. Droplet nuclei are dried residue of less than 5 microns in size. In contrast to droplets that fall to the ground within a few feet, droplet nuclei may remain suspended in the air for long periods of time and may be blown over great distances. Measles, for example, has occurred in children who came into a physician’s office after a child with measles had left, because the measles virus remained suspended in the air
77
New cards
vehicle transmission
that may indirectly transmit an infectious agent include food, water, biologic products (blood), and fomites (inanimate objects such as handkerchiefs, bedding, or surgical scalpels). A vehicle may passively carry a pathogen — as food or water may carry hepatitis A virus. Alternatively, the vehicle may provide an environment in which the agent grows, multiplies, or produces toxin — as improperly canned foods provide an environment that supports production of botulinum toxin by *Clostridium botulinum*.
78
New cards
vector transmission
such as mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks may carry an infectious agent through purely mechanical means or may support growth or changes in the agent. Examples of mechanical transmission are flies carrying *Shigella* on their appendages and fleas carrying *Yersinia pestis*, the causative agent of plague, in their gut. In contrast, in biologic transmission, the causative agent of malaria or guinea worm disease undergoes maturation in an intermediate host before it can be transmitted to humans (Figure 1.20).
79
New cards
animal reservoir
Humans are also subject to diseases that have animal reservoirs. Many of these diseases are transmitted from animal to animal, with humans as incidental hosts. The term **zoonosis** refers to an infectious disease that is transmissible under natural conditions from vertebrate animals to humans. Long recognized zoonotic diseases include brucellosis (cows and pigs), anthrax (sheep), plague (rodents), trichinellosis/trichinosis (swine), tularemia (rabbits), and rabies (bats, raccoons, dogs, and other mammals). Zoonoses newly emergent in North America include West Nile encephalitis (birds), and monkeypox (prairie dogs). Many newly recognized infectious diseases in humans, including HIV/AIDS, Ebola infection and SARS, are thought to have emerged from animal hosts, although those hosts have not yet been identified.
80
New cards
environmental reservoir
Plants, soil, and water in the environment are also reservoirs for some infectious agents. Many fungasel agents, such as those that cause histoplasmosis, live and multiply in the soil. Outbreaks of Legionnaires disease are often traced to water supplies in cooling towers and evaporative condensers, reservoirs for the causative organism *Legionella pneumophila.*
81
New cards
selection bias
The error introduced when the study population does not represent the target population.7,8 Selection bias can be controlled when the variables influencing selection are measured on all study subjects and either (a) they are antecedents of both exposure and outcome or (b) the joint distribution of these variables (plus exposure and outcome) is known in the whole target population, or (c) the selection probabilities for each level of these variables are known.9 It can be introduced at any stage of a research study7: design (bad definition of the eligible population, lack of accuracy of sampling frame, uneven diagnostic procedures in the target population) and implementation.
82
New cards
information bias
occurs during data collection. The three main types of _ are misclassification bias, ecological fallacy, and regression to the mean. Other information biases are also described.
83
New cards
confounding bias
occurs when a variable is a risk factor for an effect among non-exposed persons and is associated with the exposure of interest in the population from which the effect derives, without being affected by the exposure or the disease (in particular, without being an intermediate step in the causal pathway between the exposure and the effect).1 The counterfactual approach is the current procedure to explain confounding adequately,58 and causal diagrams help to identify it.59 Confounding can occur in every epidemiological study. *Susceptibility bias* is a synonym: when people who are particularly susceptible to development of a outcome are also prone to be exposed; for example, women with threatened abortion have a high probability of delivering a malformed fetus but also have a high probability of receiving hormone treatment. This can yield a spurious association between hormones and congenital malformations.53
84
New cards
primordial prevention
risk factor reduction targeted 2 entire population w focus on social+environment conditions promoted by law, aimed @ children,
85
New cards
Primary prevention
consists of measures aimed at a susceptible population or individual. The purpose of primary prevention is to prevent a disease from ever occurring. Thus, its target population is healthy individuals. It commonly institutes activities that limit risk exposure or increase the immunity of individuals at risk to prevent a disease from progressing in a susceptible individual to subclinical disease. For example, immunizations are a form of primary prevention.
86
New cards
secondary prevention
emphasizes early disease detection, and its target is healthy-appearing individuals with subclinical forms of the disease. The subclinical disease consists of pathologic changes, but no overt symptoms that are diagnosable in a doctor's visit. Secondary prevention often occurs in the form of screenings. For example, a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is a form of secondary prevention aimed to diagnose cervical cancer in its subclinical state before progression.
87
New cards
tertiary prevention
_ targets both the clinical and outcome stages of a disease. It is implemented in symptomatic patients and aims to reduce the severity of the disease as well as of any associated sequelae. While secondary prevention seeks to prevent the onset of illness, _ aims to reduce the effects of the disease once established in an individual. Forms commonly include rehabilitation efforts.
88
New cards
quarternary prevention
According to the Wonca International Dictionary for General/Family Practice, _ is: "action taken to identify patients at risk of overmedicalization, to protect him from new medical invasion, and to suggest to him interventions, which are ethically acceptable." Marc Jamoulle initially proposed this concept, and the targets were mainly patients with illness but without the disease. The definition has undergone recent modification as" 'an action taken to protect individuals (persons/patients) from medical interventions that are likely to cause more harm than good."
89
New cards
aneurysm
excessive enlargement of an artery caused by a weakening of the artery wall
90
New cards
parasitical ascariasis
caused by ascaris lumbricodes, a hookworm/whipworm transmitted by the soil
91
New cards
viral shingles
caused by varicella zoster
92
New cards
anthrax bacteria
caused by bacillus anthracis, gramp-positive bacteria
93
New cards
cat scratch disease, trench fever, and carrion’s bacterial disease
bartonella bacteria
94
New cards
parisitic pediculosis
lice infestation
95
New cards
parasitic scabies
contagious skin disease marked by itching and small raised red spots caused by itch mite
96
New cards
parasitic lyme disease
caused by blacklegged tics
97
New cards
bacterial botulism
food poisoning found on improperly sterilized meat and other foods, caused by clostridium botulinum, rare illness with bacteria produces nerve toxin inducing paraylsis
98
New cards
bovine spongiform encephalopathy
mad cow disease
99
New cards
viral bronchiolitis
infects the lungs and breathing passages
100
New cards
fungal aspergillosis
common mold living in and outdoors, transmits via spores