Human reproduction
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Sex gland
Produces semen that contains sperm cells
2
New cards
Sperm duct
Sperm passes through
3
New cards
Testes
Produce sperm and testosterone- contained in scrotum
4
New cards
Penis
Passes urine and semen in and out of body
5
New cards
Urethra
Tube that carries semen or semen- a ring of muscle stops the two mixing
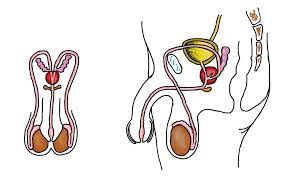
6
New cards
5 male reproductive structures
Sex gland
Sperm duct
Testis
Penis
Urethra
Sperm duct
Testis
Penis
Urethra
7
New cards
Ovary
Contains ova that develop when FSH is released
8
New cards
Oviduct/fallopian tube
Contains ovary to uterus
9
New cards
Uterus
Has thick lining so fertilised cells can be inplanted
10
New cards
Cervix
Ring of muscle at lower end or uterus to ensure foetus remains in place during pregnancy
11
New cards
Vagina
Muscular tube that leads into body
12
New cards
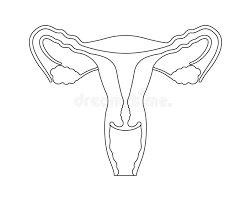
5 structures of female reproductive system
Ovary
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
Fallopian tube
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
13
New cards
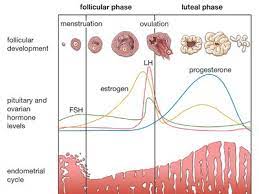
Menstrual cycle
Every 28 days lining of the uterus thickens and is prepared for pregnancy, if no fertilisation occurs lining is shed
14
New cards
What is the day of ovulation
Day 14
15
New cards
Oestrogen
Released by uterus
Causes thickening of uterus lining
Levels peak on day 10
Causes thickening of uterus lining
Levels peak on day 10
16
New cards
Progesterone
Maintains uterus lining
Inhibits the release of LH and FSH
Inhibits the release of LH and FSH
17
New cards
FSH & LH
FSA released by pituitary gland causes maturation of egg in ovary
LH stimulated the release of the mature egg
LH stimulated the release of the mature egg
18
New cards
Decrease in oestrogen…
LH & FSH start increasing
19
New cards
Describe levels of hormones throughout menstrual cycle
20
New cards
Placenta
Allows glucose, oxygen and amino acids from mother’s blood to diffuse into developing foetus
21
New cards
Amniotic fluid
Liquid contained in a bag in the uterus that surrounds foetus and protects it