Biology Exam 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Hypotonic
Having more water than the cell, causes water to move inward causing cell to swell.
Characteristics of life
Potential to reproduce,
gas exchange,
grow and/or develop,
adapt and evolve,
react to stimuli,
one or more cells,
genetic info,
requires energy source.
First person to draw a cell
Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek
independent variable
the variable that is changed in order to experiment; (ex. amount of water, color of lighting, change in diet, temperature.)
dependent variable
The variable that shows the outcome; the results of the independent variable on the experiment; Any changed feature as result of what was changed.(ex. Growth as result of the change of fertilizer; the vitality of a plant as result of the lighting)
control group
a group that ensures accurate results and is used to be able to see the effect of the independent variable in comparison to the experimental group. All factors remain the same in this group except for the independent variable.
Schwann
all animals are made of cells
schleiden
All plants are made of cells
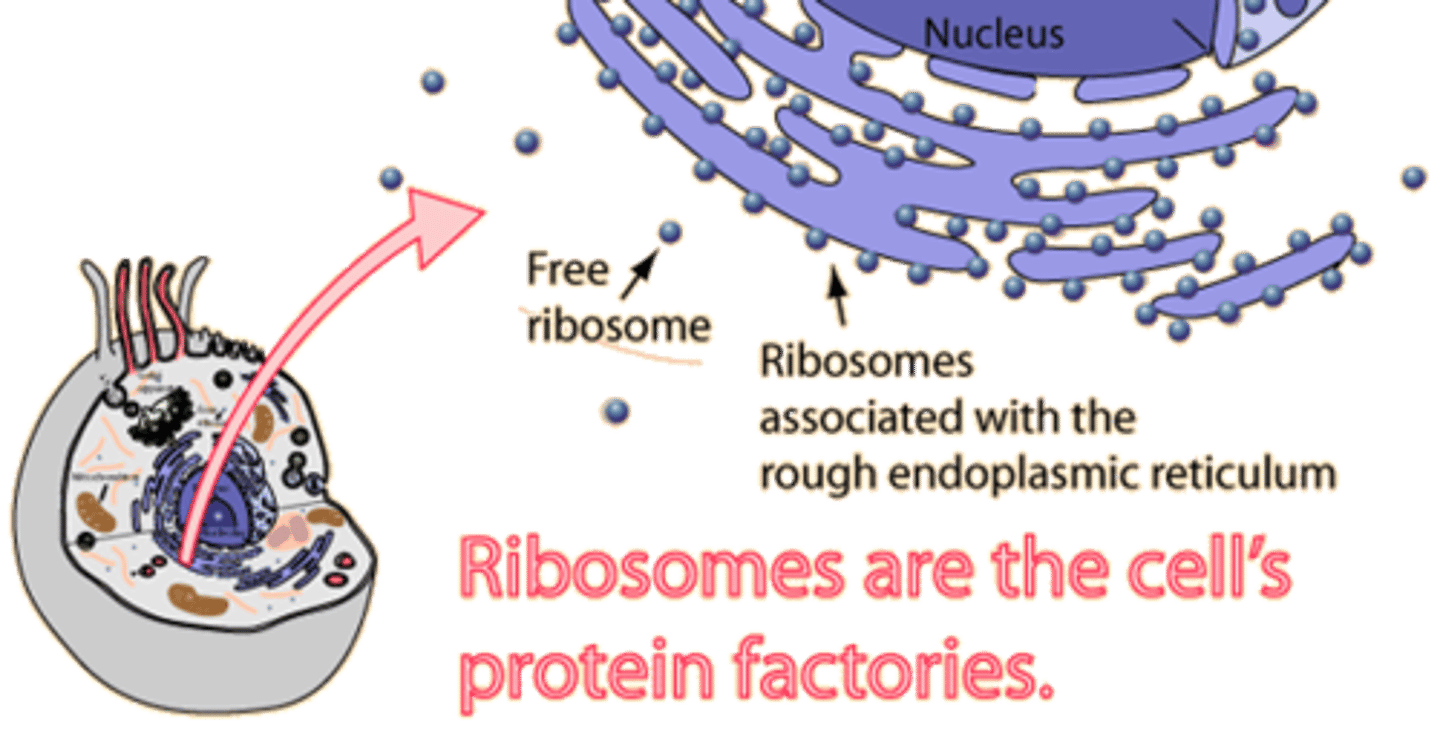
Ribosomes
protein synthesis; can be free or bound to ER; uses RNA to assemble protein.
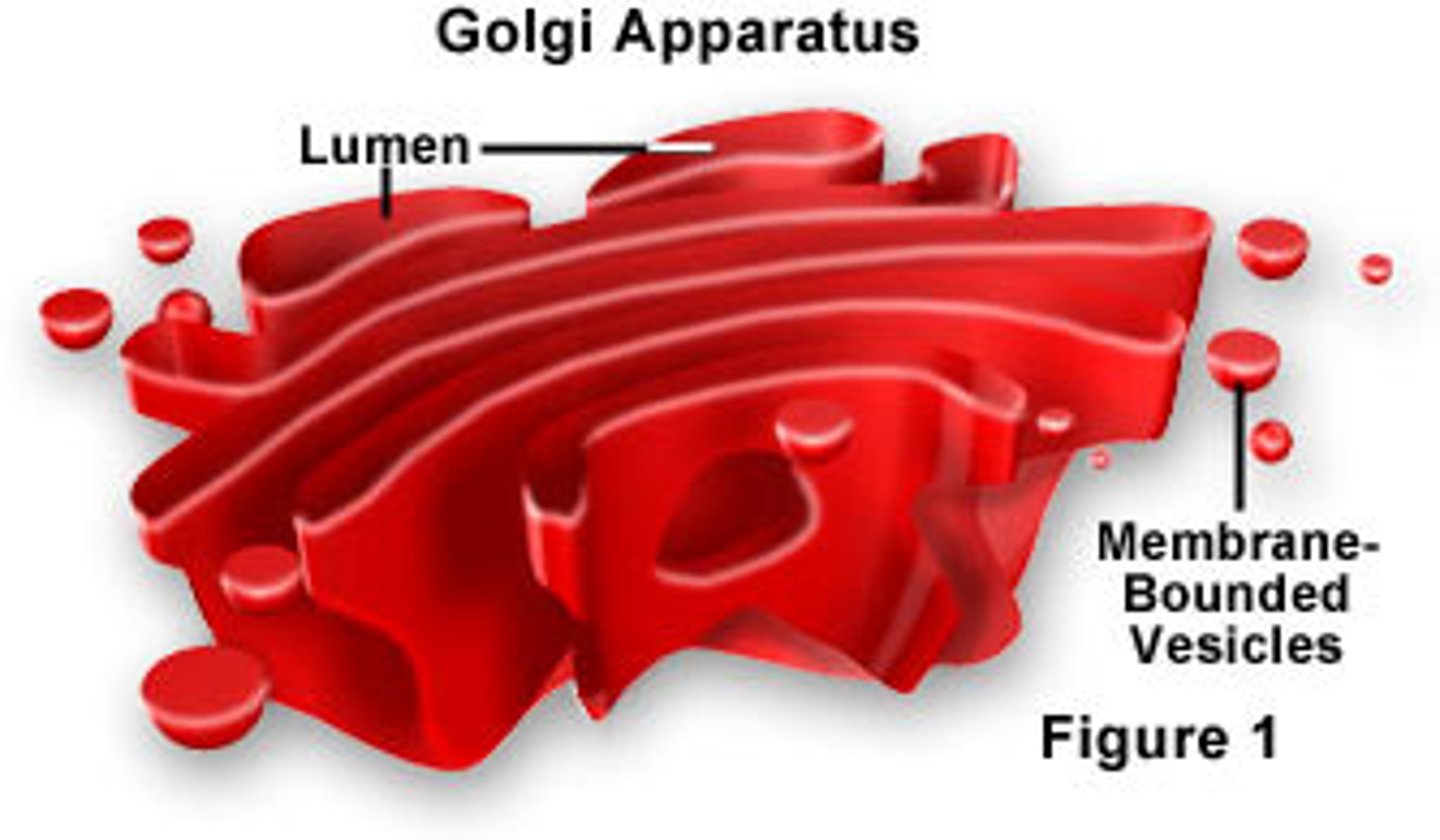
Golgi apparatus
flattened sacs; packages, stransports, and temporarily stores proteins inside and out of the cell not domestically; transports cells by pinching and fusing vesicles to and from the golgi and sometimes to the ER as well.
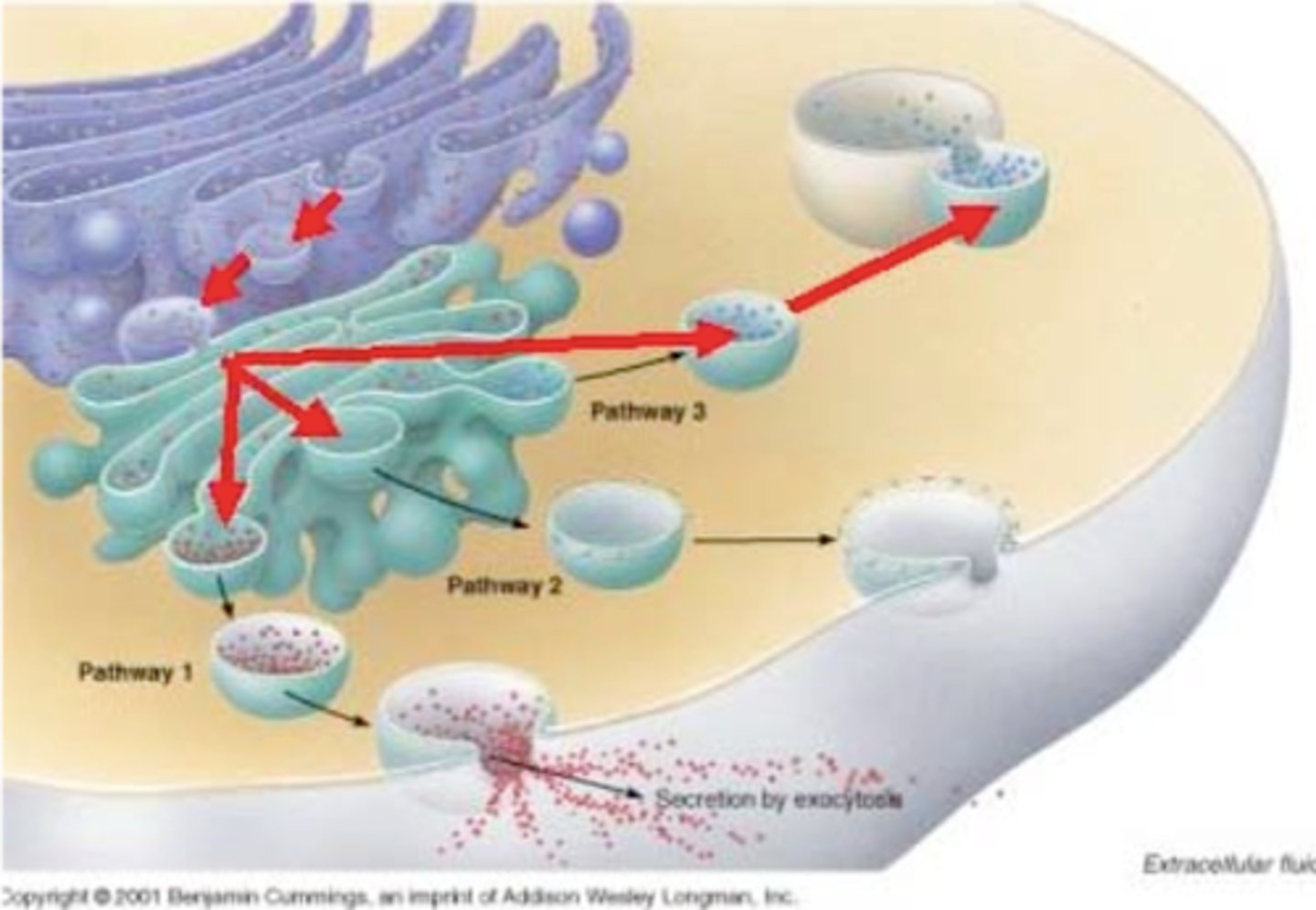
vesicle
membranous sacs for transporting cellular products and wastes; fuses and pinches off ER and golgi apparatus; motor proteins move them throughout the cytoskeleton.
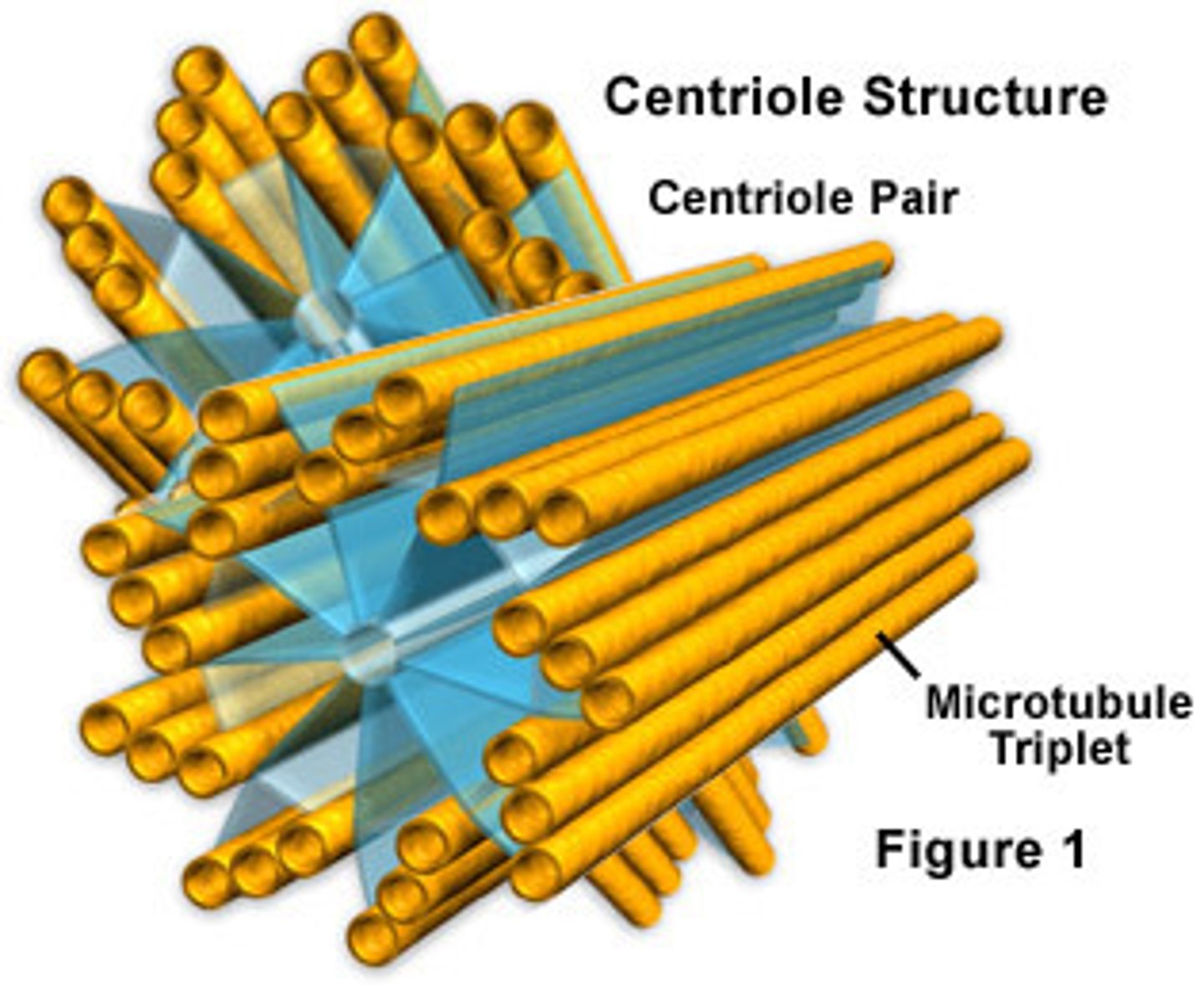
Centrioles
found in pairs only in animal cells; cylindrical ring of microtubules; important in cell division; anchors for spindle apparatus.
peroxisome
similar to lysosomes but digest toxins by stripping hydrogen ions off them and holding onto the removed hydrogen peroxide product until it can be disposed
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended; aka cytosol
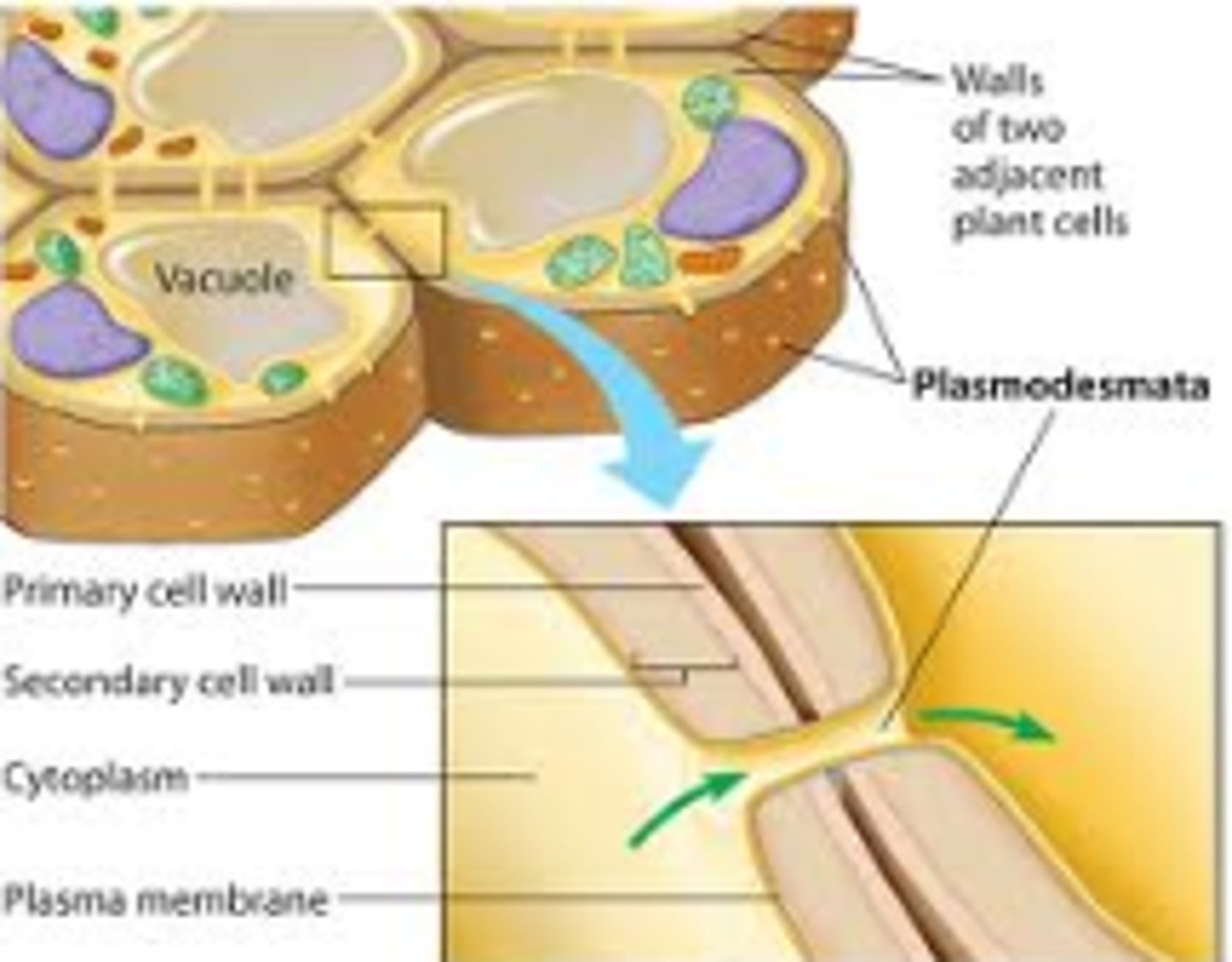
Cell wall
not in animals; outside of the plasma membrane and provides extra protection and rigidity; plants made of cellulose with plasmodesmata..
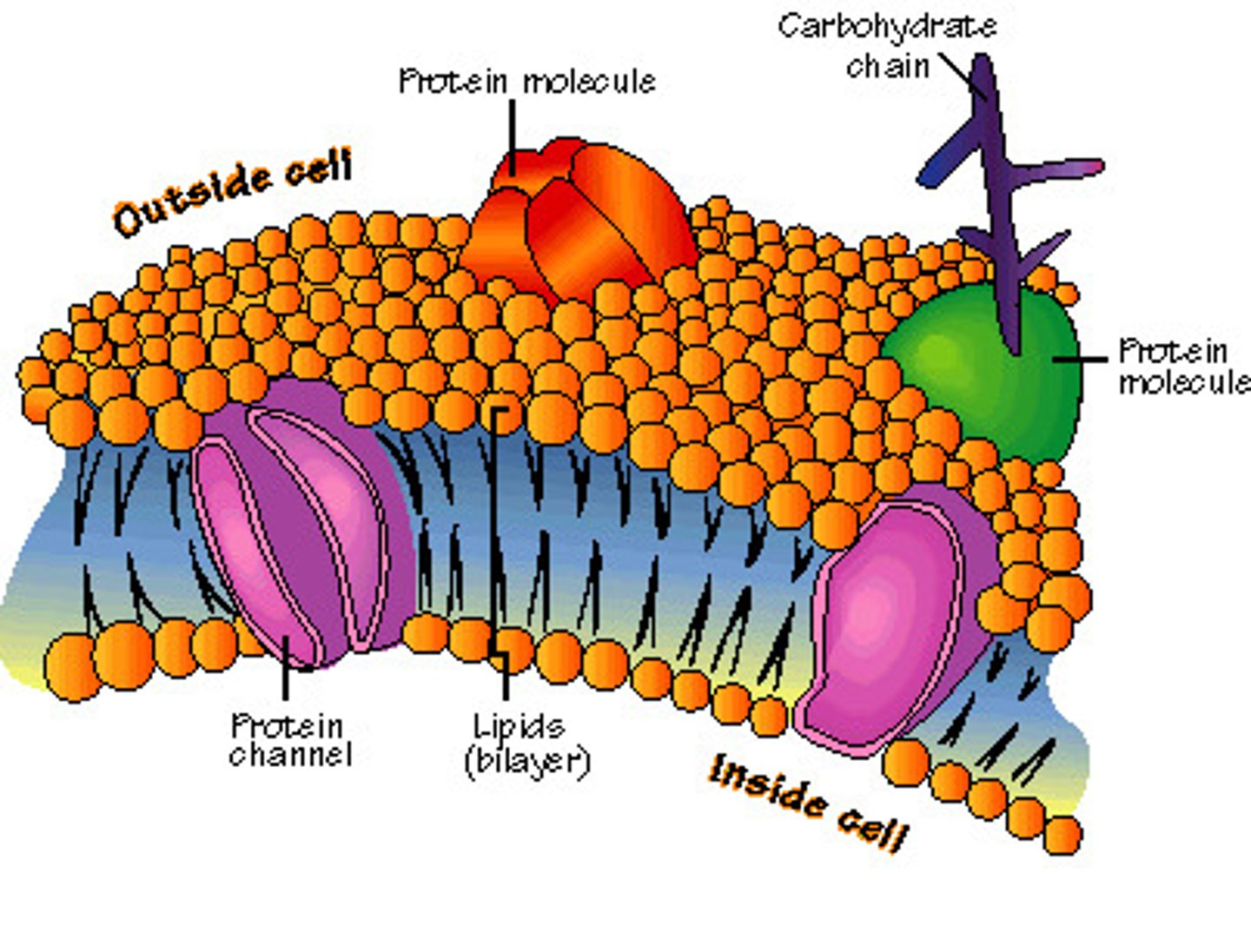
how does the plasma membrane help transport?
Semi-permeable, has proteins which help in
passing larger materials, and uses facilitated diffusion.
Passive transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient.
Exocytosis
when particles are enclosed in a vesicle and released from a cell
experimental group
Factors remain the same as well except for the independent variable: but this variable is applied to the group
scientific method
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem
Steps of the Scientific Method
Identify problem, Form Hypothesis, Collect Data, Analyze Data, Form Conclusions
Hypothesis
A prediction or proposed explanation to what will happen, especially to answer a question in the scientific method.
law
Statements that currently describe and predict a range of phenomena; describes what will happen.
Theory
A group of proven propositions made to explain facts or phenomena in the natural world; has to do with trying to answer why and something happens
Cell theory
all living things are of one or more cells, all cells are the building blocks of life, all new cells are derived from previous cells.
Who coined the term "cell"?
Robert Hooke
Diiference of Eukaryotic over prokaryotic cells
larger, complex structure, membrane bound organelles, able to be motile, can be multicellular, more chromosomes.
plasma membrane
semi-permeable phospholipid bilayer; each phospholipid consists of one hydrophilic phosphate head and 2 fatty acid lipid hydrophobic tails inside; also contains carrier and channel proteins for facilitated diffusion and to move larger particles.
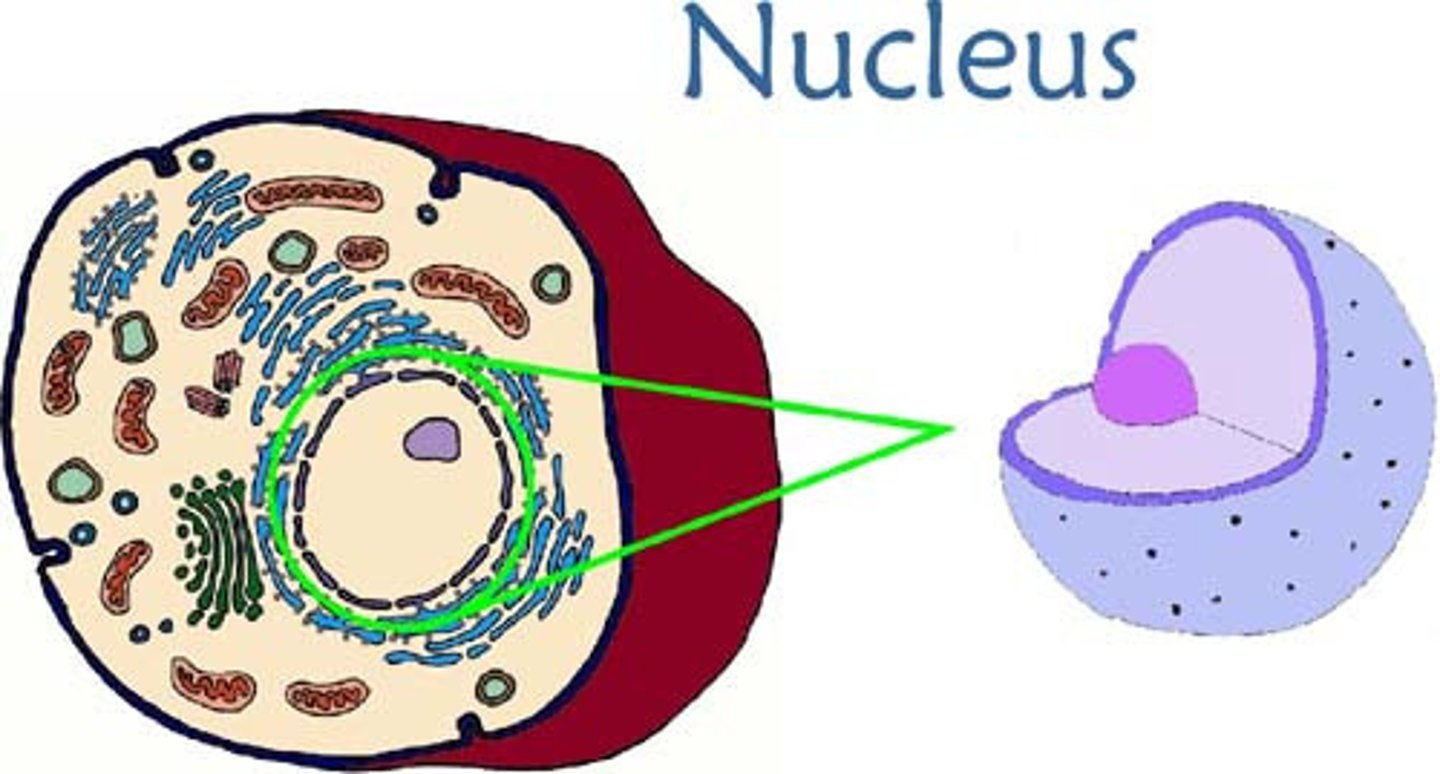
Nucleus
brain of cell, contains DNA which codes the proteins.
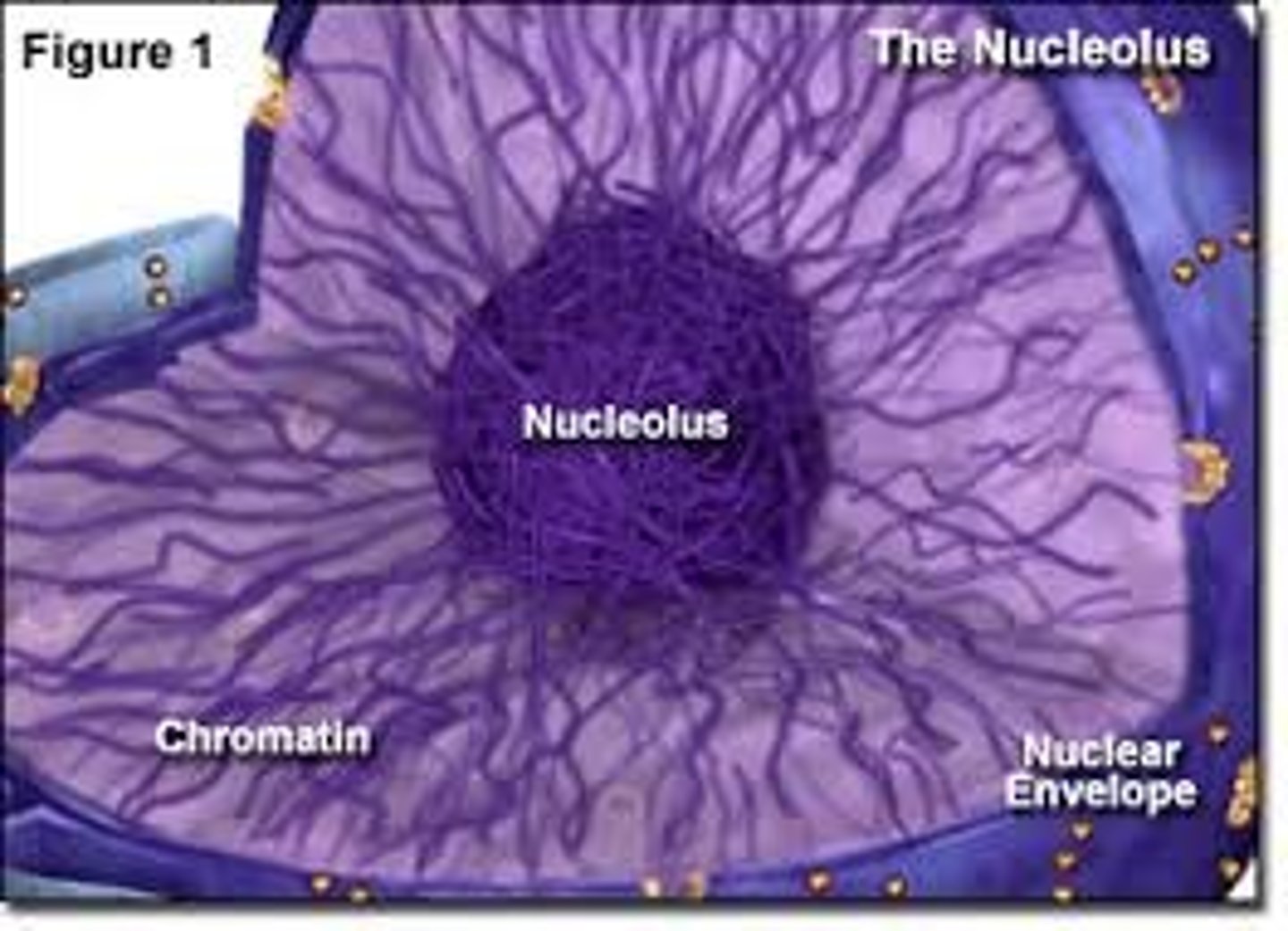
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Rough ER
part of Endoplasmic Reticulum with Ribosomes attached which makes its use for protein synthesis, transports "domestically" within the cell.
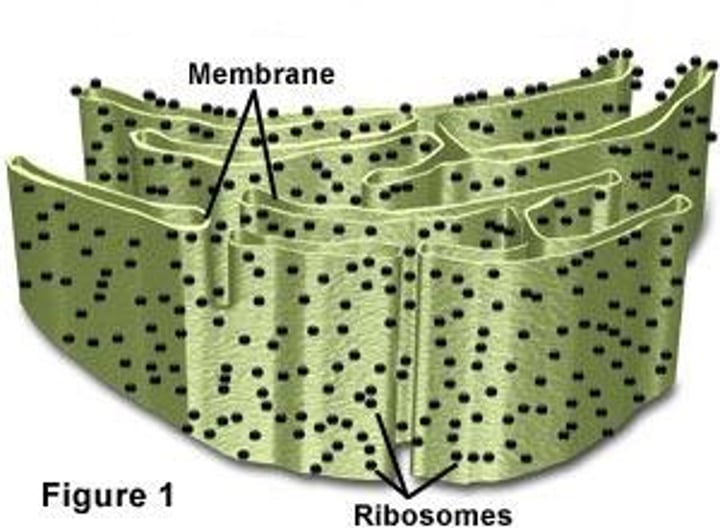
Smooth ER
Part of Endoplasmic Reticulum without Ribosomes attached, making its use for lipid synthesis and storage; transports "domestically" within the cell.
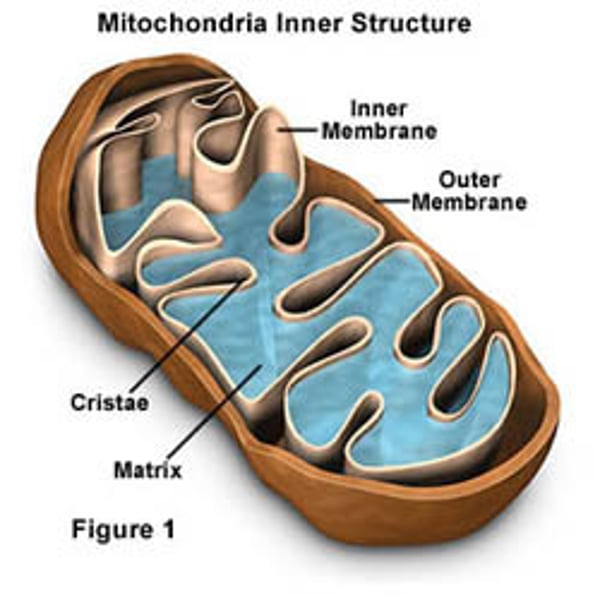
Mithochondria
Powerhouse of the cell as it produces ATP; double membrane with a folded inner one called cristae; has own DNA and ribosomes.
membrane=
phospholipids
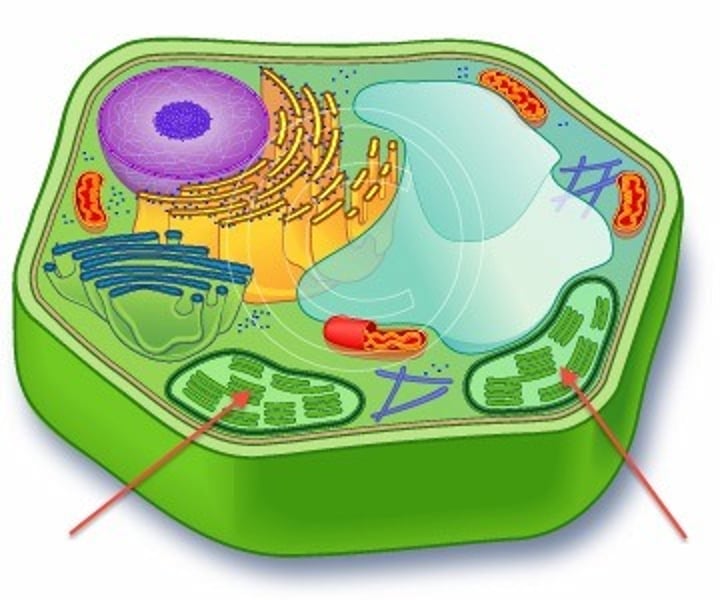
Chloroplast
Only found in plant cells; membrane bound with own DNA and ribosomes; contains inner membranous sacs called thylakoids; when stacked stoma; responsible for generating sugars through photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll.
vacuole
membranous sacs for storage of nutrients, water, and sometimes waste; tend to be larger in plants.
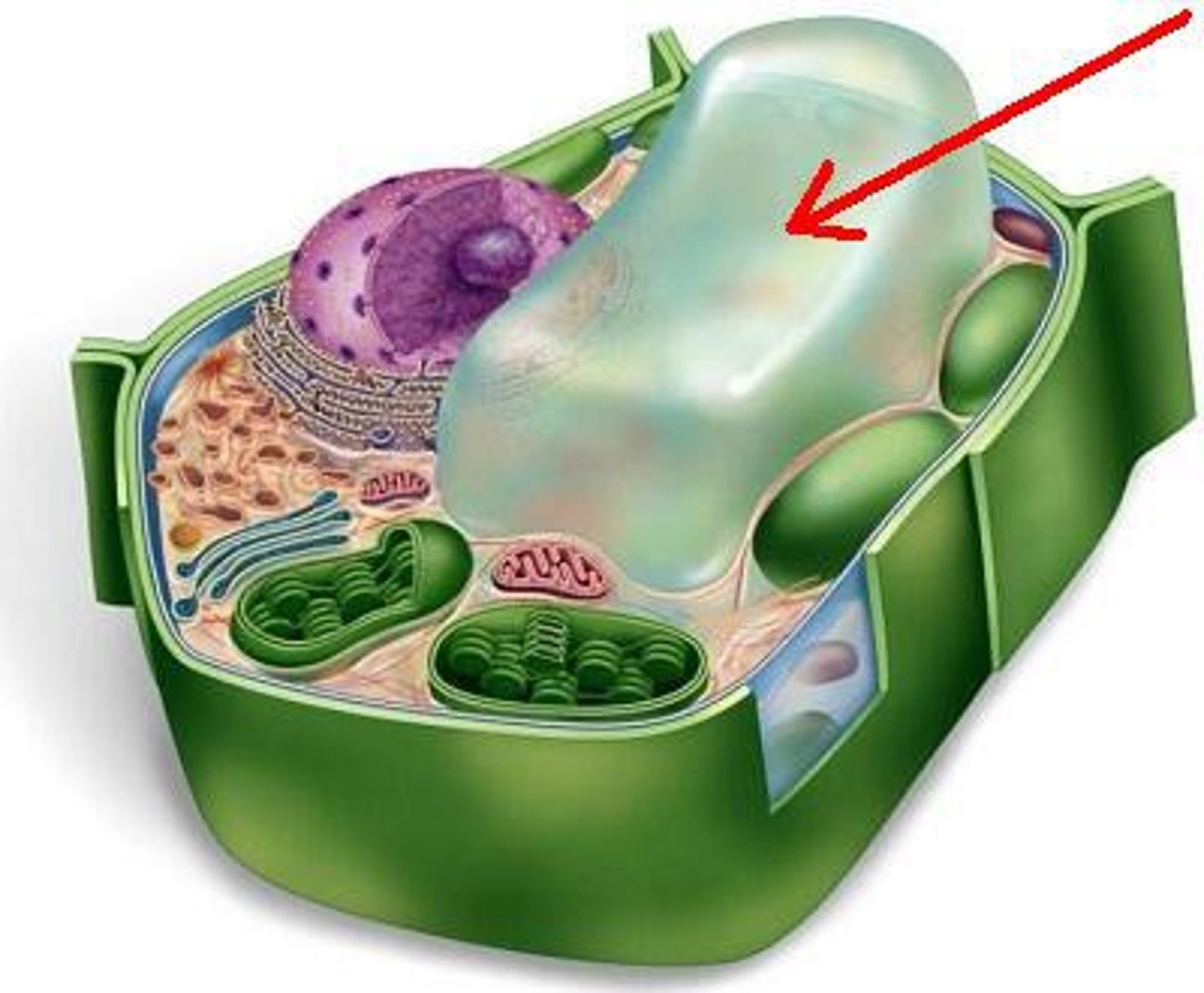
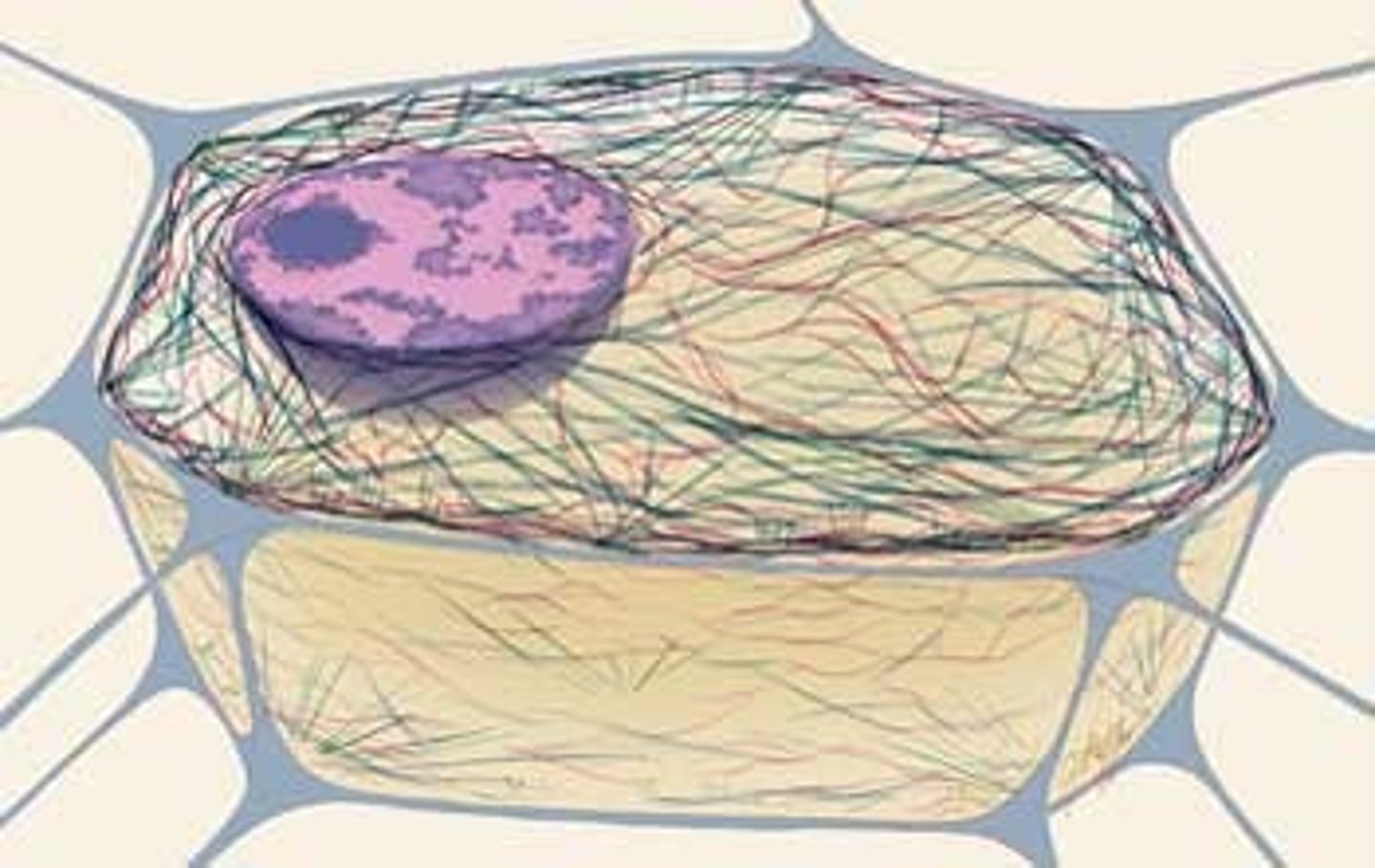
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement and transport; made of 3 parts: microtubules, intermediate filaments; and microfilaments.
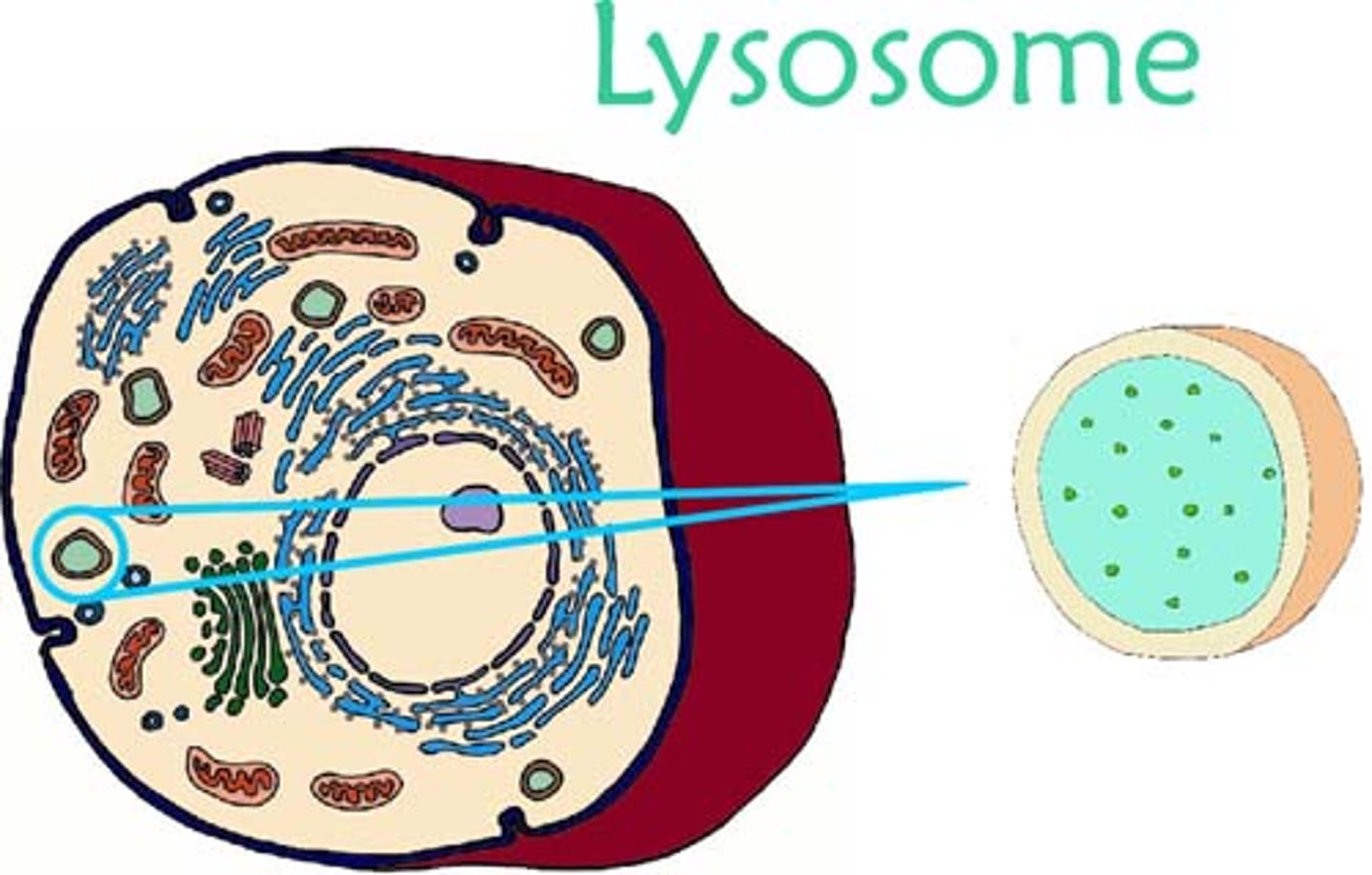
lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell; contains digestive enzymes.
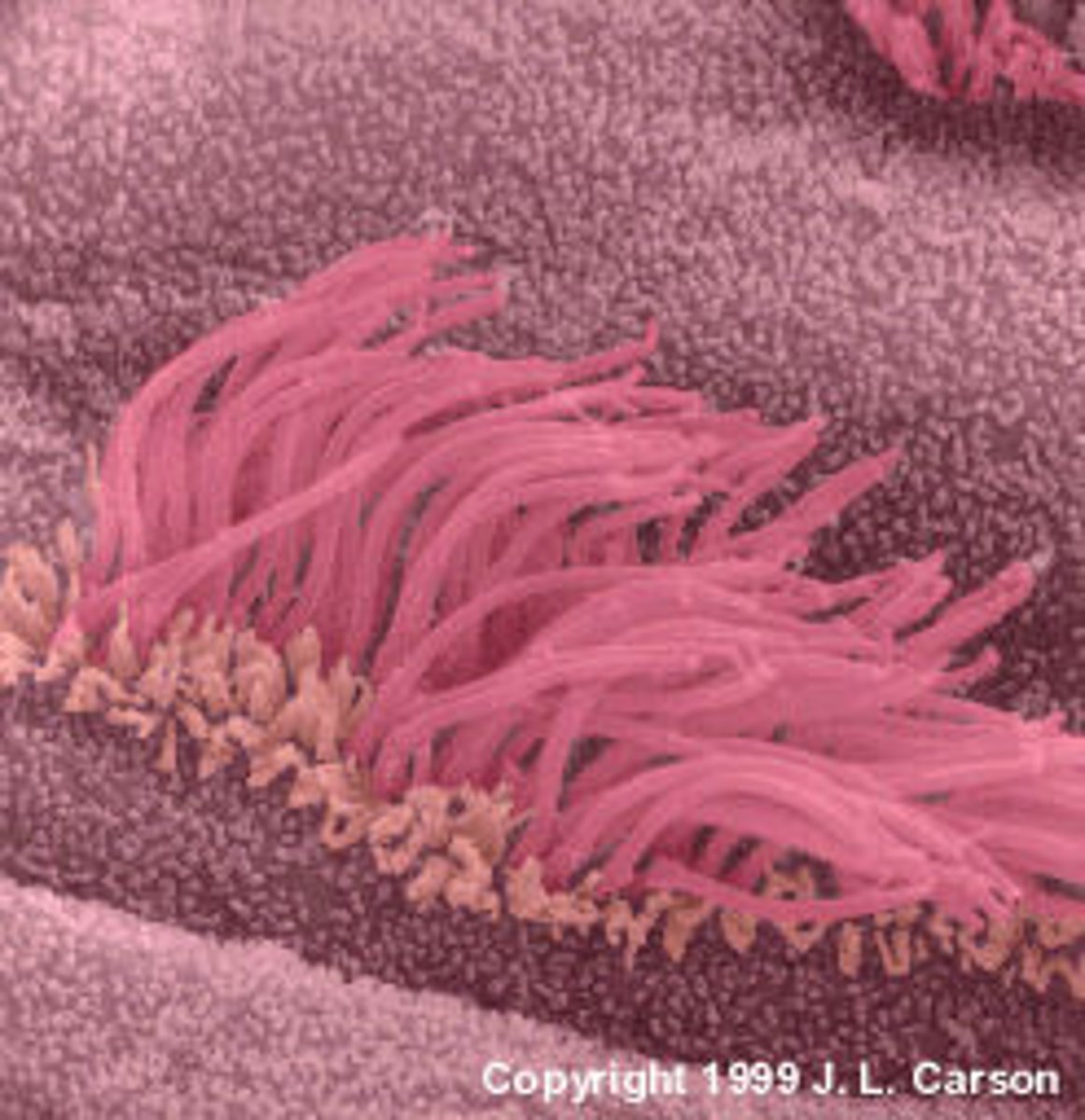
Cilium
short, numerous projections that look like hairs made of microtubules; move back and forth to move the cell or "sweep" substances out of the cell.
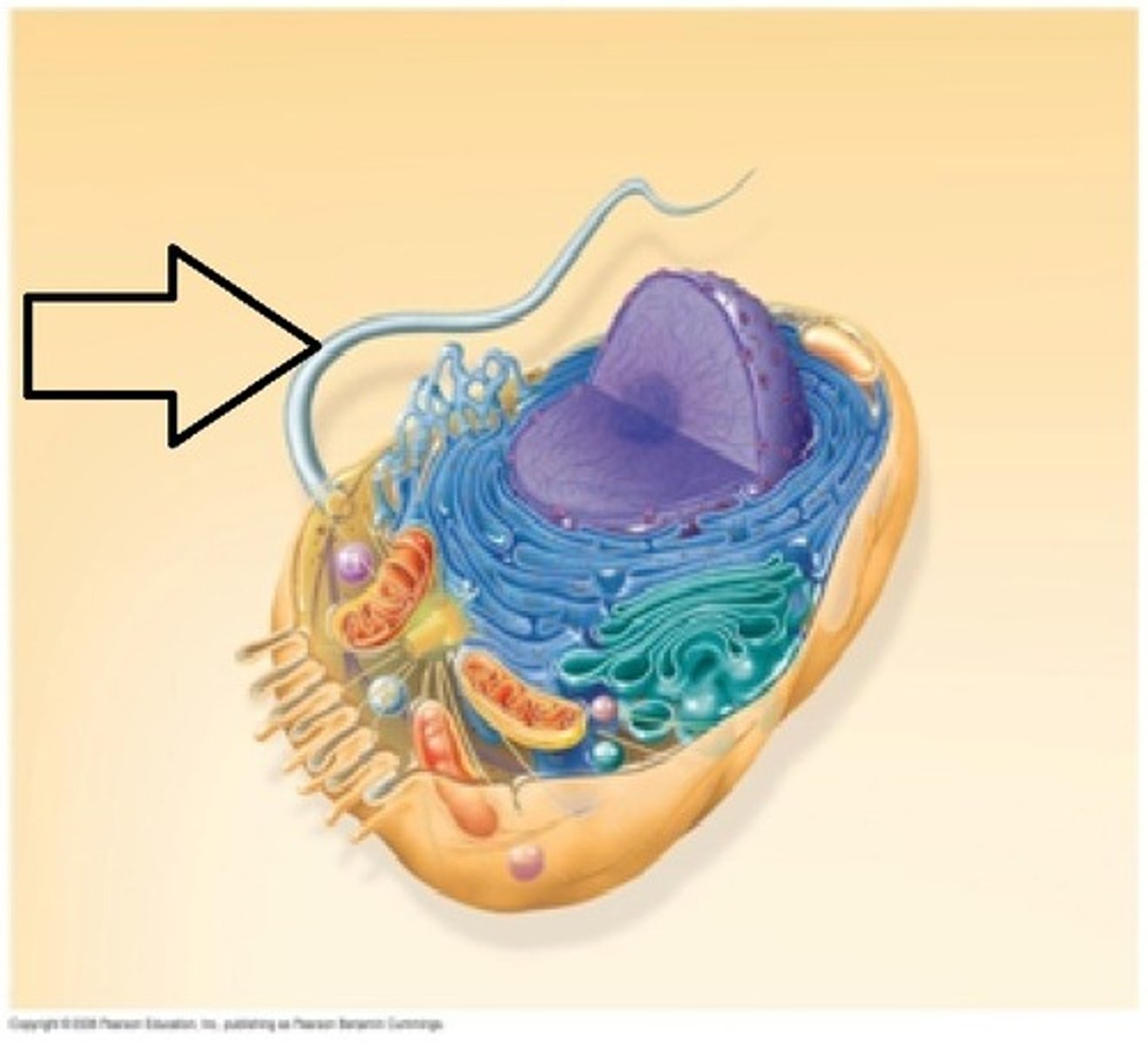
flagellum
A long, whiplike structure(s) that helps a cell to move
4 major differences between plant over animal cells
contains a cell wall, does not have centrioles; has chloroplasts, larger central vacuoles.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration; type of passive transportation.
facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins
simple diffusion
Diffusion that doesn't involve a assistance by carrier proteins; passing through the bilayer.
Osmosis
diffusion of water; movement of water to where there is less water by concentration
Hypertonic
lower concentration of water outside of cell, water moves out, cell shrinks.
Isotonic
Having the same solute (water) concentration as another solution.
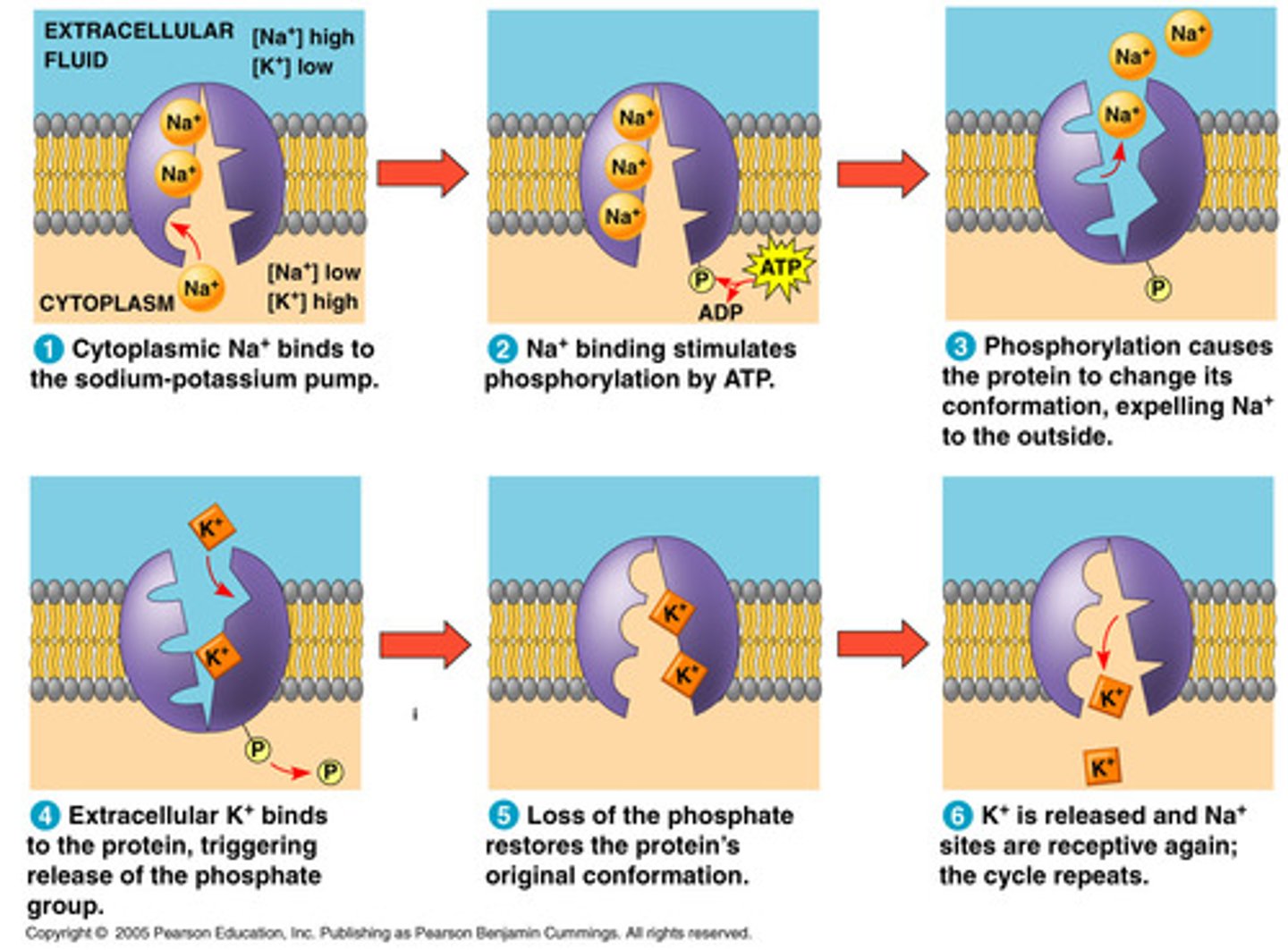
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
NaK+ Pump
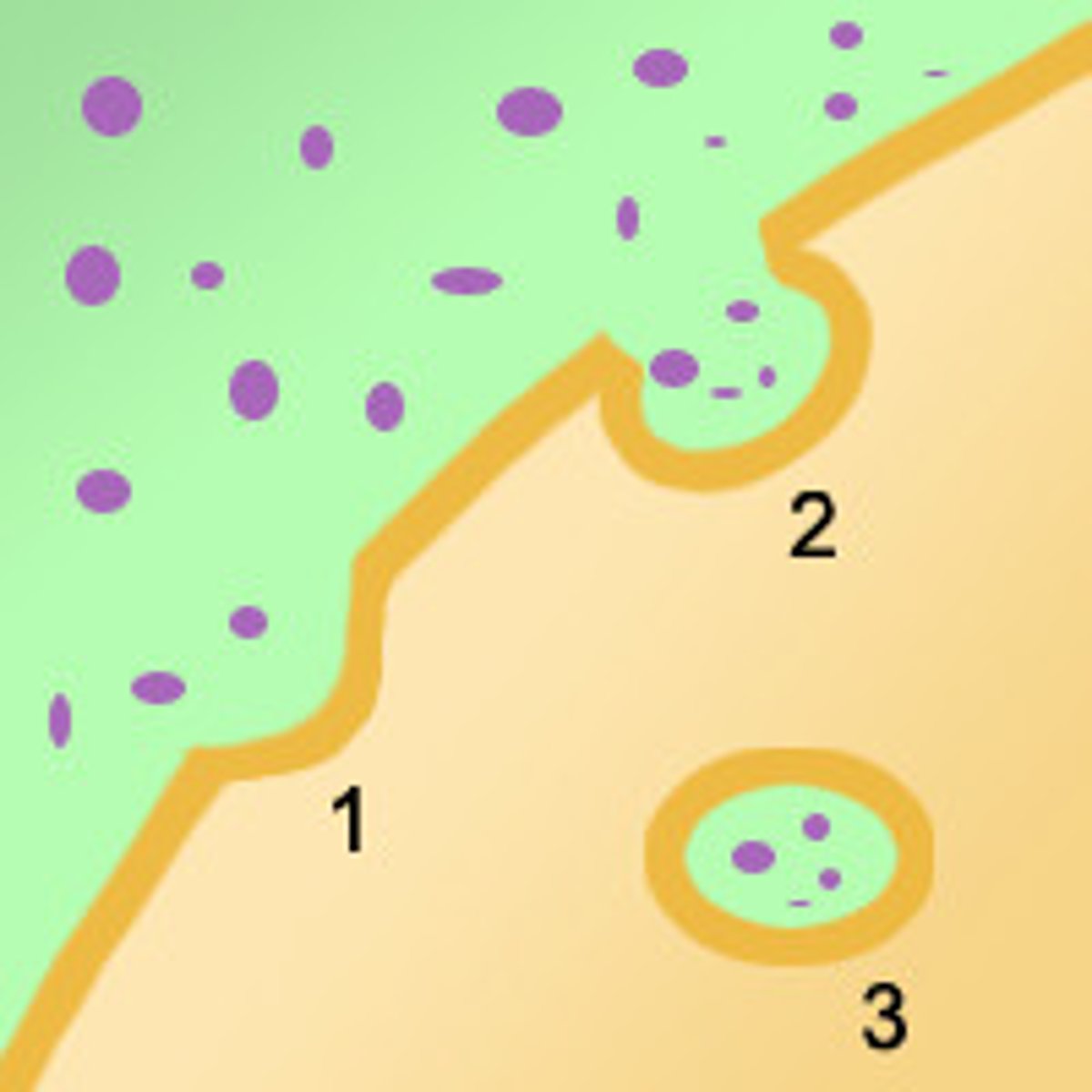
Endocytosis
when a particle is taken into the cell by the plasma membrane by making it a membrane around it in the form of a vesicle.
parts of cytoskeleton
microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments.