Price elasticity of demand
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
price elasticity
defined as the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in the price of the good or service. is always negative because there’s a negative relationship between demand and price, so don’t worry if the answer comes out negative.
inelastic goods
Ed is less than one. percentage change in quantity is less than the percentage change in price
Usually determined by the substitution effect. necessity goods with few substitutes are inelastic e.g. coffee, alcohol, petrol, basic food products so change in price causes a weak response in quantity.
elasticity of demand is very useful for sellers to decide how they should change their prices according to how elastic the demand is. goods that are inelastic are beneficial for sellers because they can increase prices knowing they’ll make more profit because the demand will not be responsive.
e.g. apple can raise their prices because of brand loyalty which makes their demand inelastic but this can’t keep going on forever - at some point it will become elastic
elastic goods
For products that have relatively more close substitutes we would expect that quantity demanded would be more sensitive to a change in price.
When the value of Ed is greater than 1, it means that the law of demand is relatively strong - quantity demanded is responsive to a price change. In this case demand is said to be relatively elastic.
The larger the elasticity coefficient, the more responsive demand is to price which indicates that there is likely to be many close substitutes.
elastic goods will decrease revenue as you increase price.
inelastic goods
elasticity coefficient
answer for the point method
point method
this is the point method. it just shows the elasticity at one price point.
elasticity increases as price goes up (because it takes up more of our salary, so we react more)
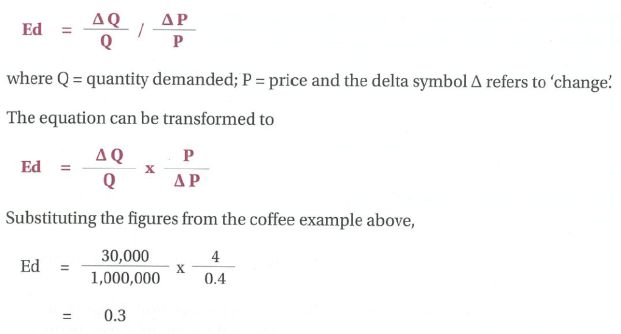
midpoint method
Using the point method gives two different answers depending on whether we are increasing or decreasing price.
To avoid this confusion, we use an averaging technique, called the midpoint method.
