HEALTH CARE: Unit 1 test
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 1 of health care. FEB 12 MADE slides 1-70 80-83 everything to know for unit 1 test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
cervical has- many bones(of the neck)
7
theoretic has — many bones (of the chest)
12
lumbar has - many bones (lower back)
5
coccyx
4 or 5 fused vertebrae of the tailbone
atlas
on top of axis
axis
under atlas
how many bones in the lungs
24 (12 pairs)
Appendicular skeleton made up of
pectoral gridle
pelvic gridle
the upper limbs
the lower limbs
the pectoral gridle has….
scapula and clavicle
allows for great mobility
the upper limb has…
humeras, radius, ulna
lower limb has…
femur and patella
medial
inner
lateral
outer
5 functions of bones
provides support and structure
protect brain and organs
helps muscle attach to bones
reserves minerals and calcium
produce and store blood cells
five types of bones
long
short
flat
irregular
sesamoid
long bones are
Any bones that succeed the diameter
humerus, femur, phalanges, ulna, radius, fibula, tibia, metacarpals, metatarsals
short bones are
good shock absorbers
carpals, tarsals,
flat bones are
scapula, clavicle, cranium, ribs, ilium, sternum
irregular bones are
all vertebrae (coccyx, sacrum), face (zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal)
sesamoid bones are
patella
what are bones made up of
marrow
red marrow
in all bones, produce most red blood cells
yellow marrow
found in cavities along bones, made of mostly fat
outer membrane of bone
periosteum
inner membrane of bone (thinner)
endosteum
what part of body is the axial
head and trunk
what part of body is the appendicular
arms and legs
Periosteum
fibrous layer, dense, has blood vessels, nerves, connects tendons
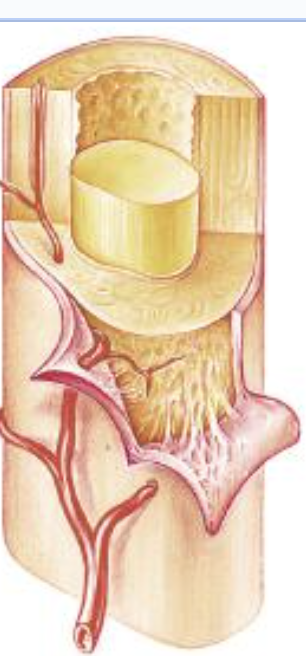
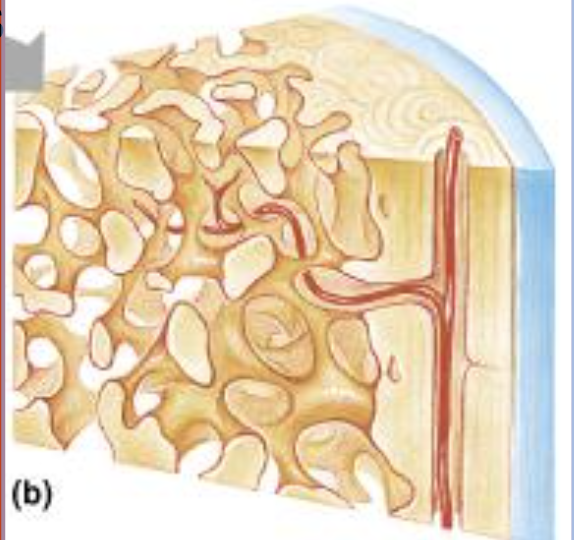
Endosteum
inner surface of compact bone, Covers trabeculae, Osteoblasts & osteoclasts
what is the anterior skeleton
the front
what is the posterior skeleton
the back
how many bones does the human skull have?
22- 8 cranial and 14 facial
what are the 8 cranial bones?
frontal (1), sphenoid (1), ethmoid (1), parietal (2), temporal (2), occipital (1)
what is the frontal bone
forhead area
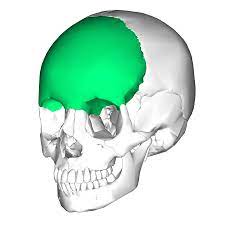
what is the highlighted area called?
frontal bone (1)
what is the sphenoid?
sideburns area
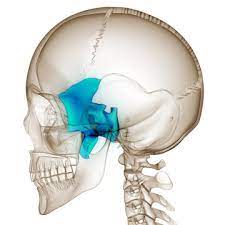
what bone is this?
sphenoid (1)
what is the ethmoid / lacrimal bone?
inner eye socket area
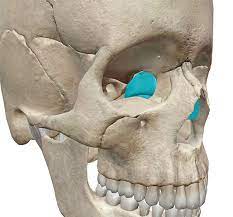
what bone is this?
ethmoid/ lacrimal
what is the parietal bone?
back of head
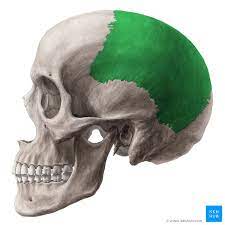
what bone is this?
parietal bone-there is 2
what is the temporal bone?
temples area
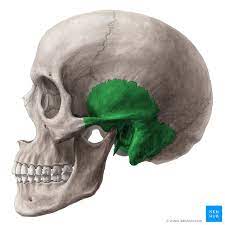
what bone is this?
temporal there is 2
what is the occipital bone?
lower back of head
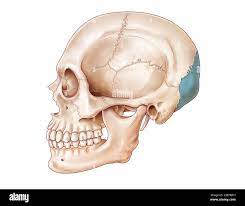
what bone is this?
occipital bone
parts of the vertebral column
cervical (7) theoretic (12) lumbar (5)
what is the appendicular skeleton made of?
1. The pectoral girdle (chest)
2. Pelvic girdle (hip)
3. The upper limbs
4. The lower limbs
what is the Pectoral Girdle
scapula and clavicle, allows upper limb mobility
functions of bones
Provide support and structure
Protect brain and organs
provides sites for the attachment of muscles
Provide a reservoir for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and sodium minerals.
Produce and store blood cells
what is the Diaphysis
the shaft of long bones
what is the Epiphysis
the end of long bones
4 types of fractures
comminuted
compound
simple
greenstick
what is a greenstick fracture?
hairline, bone only breaks on one side
what is a compound fracture?
broken part of bone breaks through skin
what is a simple fracture?
severe break underneath skin
what is a comminuted fracture?
bone is crushed into several pieces
what is a dislocation?
when bones of a joint are pulled out of alignment
what is a sprain?
ligaments stretched or torn
what is a ruptured vertebrae disk?
the disc bulging out and pushing on nerves or the spinal cord.
what is Osteoporosis?
Spaces between the bone tissue becomes enlarged, weakening the bone. This is due to a lack of calcium, aging
what is Osteoarthritis?
condition involving loss of cartilage at joints.
what does RICE stand for ?
rest
ice
compression
elevate
what does SHARP stand for and what is it used for?
To identify a bone injury.
Swelling
Heat
Altered
Red
Painful
what is a joint?
2 bones come together
what are the 5 types of joints?
ball and socket
hinge
gliding
pivot
immovable
whats a ligament?
tough, cord-like tissues that connect bone to bone.
what does superior mean?
above
what does inferior mean?
below
what does anterior mean?
infront
what does posterior mean?
behind
what does Proximal mean?
close to a specified region
what does distal mean?
further from a specified region

what position is this?
supine (laying on back)
what position is this?
prone (laying on chest)
what is the difference between deep and superficial?
deep is further from the outside of your body
superficial a on skin cut
what are the 3 types of muscles?
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
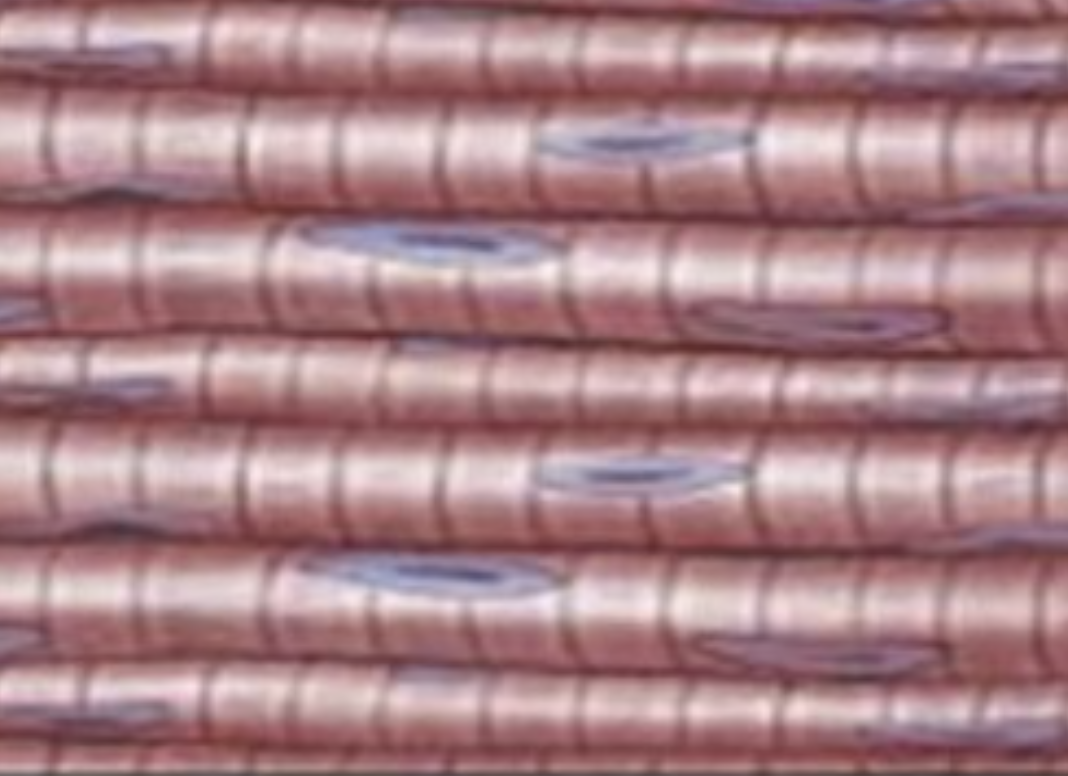

what type of muscle tissue is this?
skeletal muscle tissue
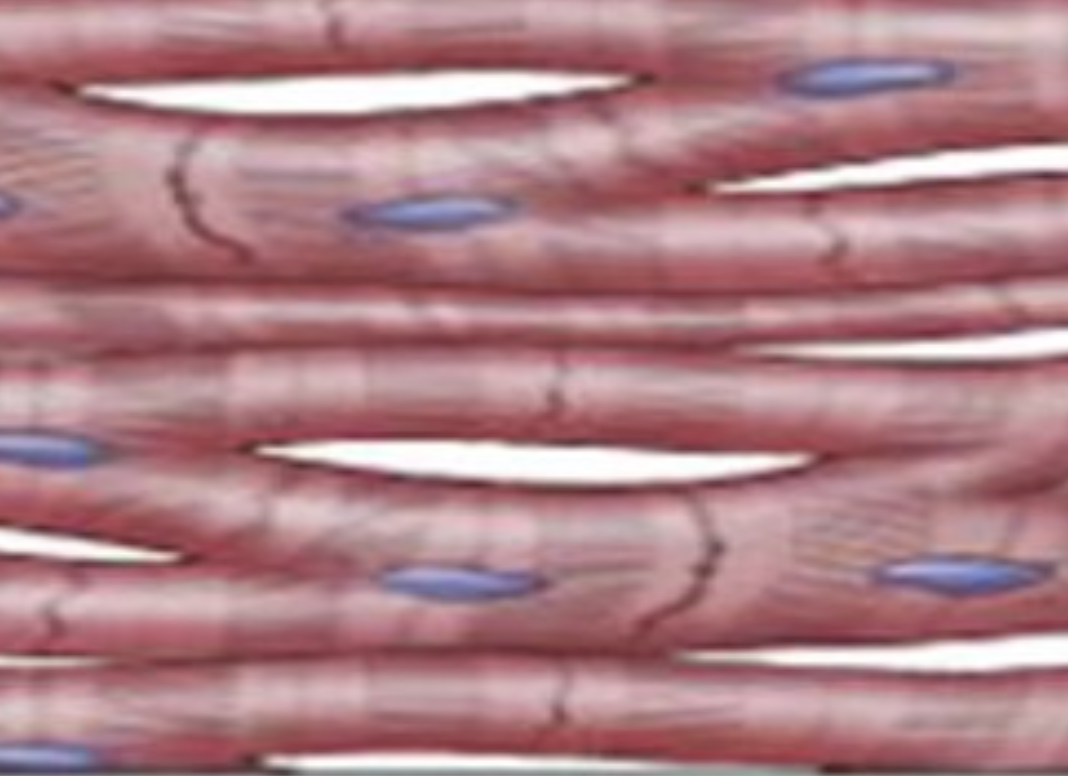
what type of muscle tissue is this?
cardiac muscle tissue
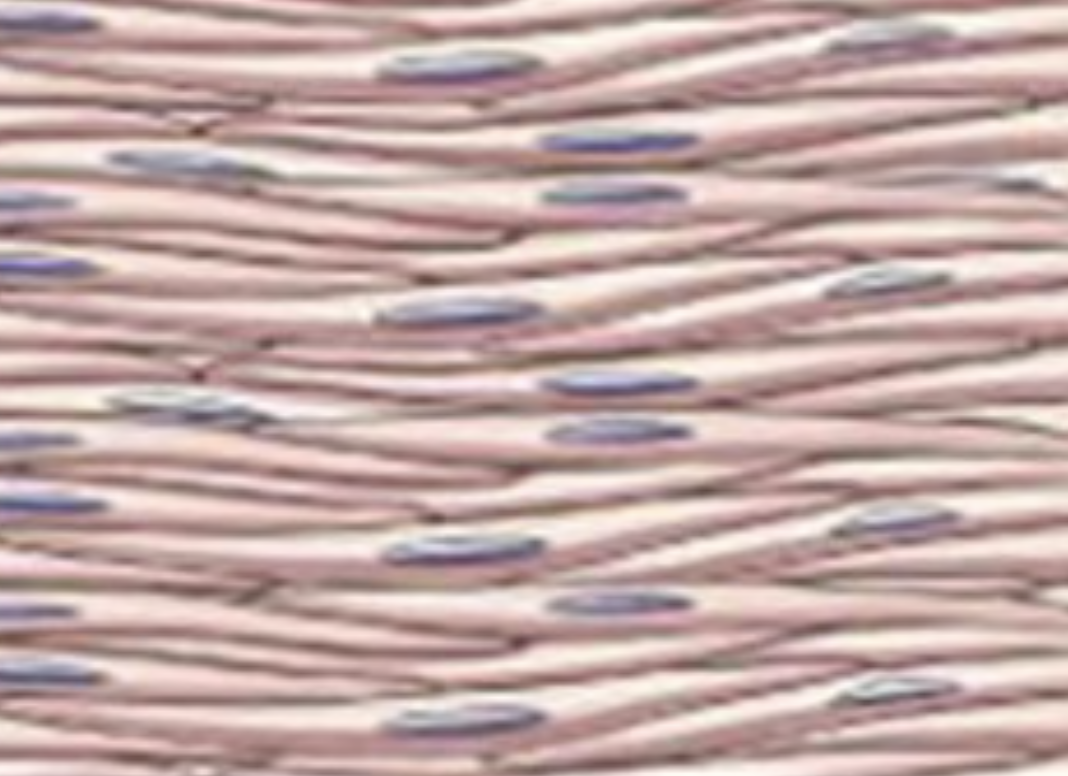
what type of muscle tissue is this?
smooth muscle tissue
what is the largest muscle of the body?
gluteus maximus
what is the smallest muscle of the body?
stapedius in the ear
what are some ways you can name muscles?
shape
size
location
actions
why do we need muscles?
locomotion
posture
heat protection
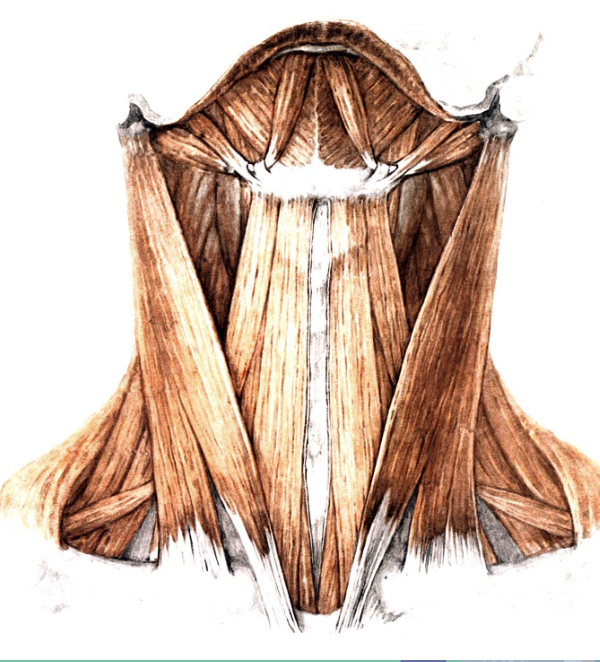
what muscle is this? what part of the body?
Sternocleidomastoids, neck muscle, anterior
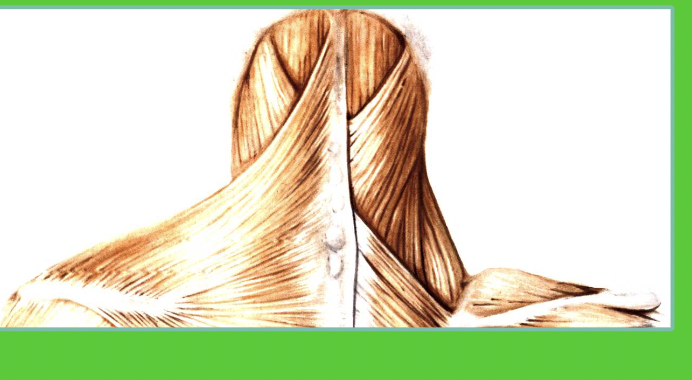
what muscle is this? what part of the body?which side?
Trapezius, neck muscle, lateral posterior
what is the Erector spinae muscles
posterior spine muscles
what is apart of the pectoral girdle ANTERIOR?
Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor
what is apart of the pectoral gridle POSTERIOR?
Trapezius, Latissimus Dorsi,
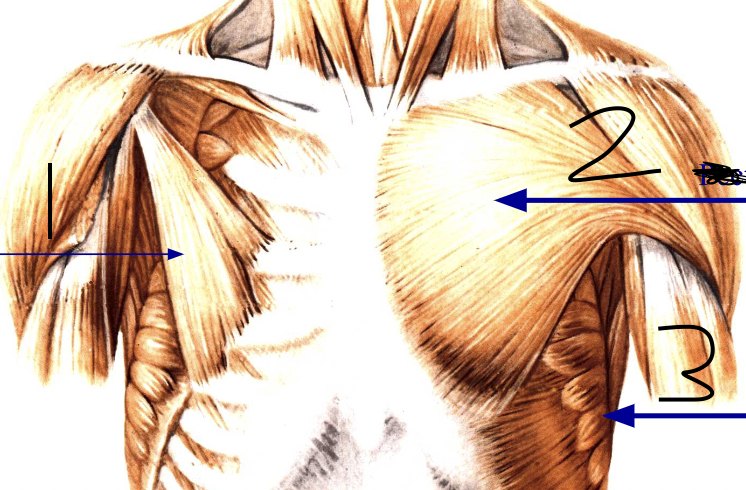
What is this and name 1 2 3
Pectorial gridle anterior. 1. pectoralis minor. 2. pectoralis major. 3. Serratus
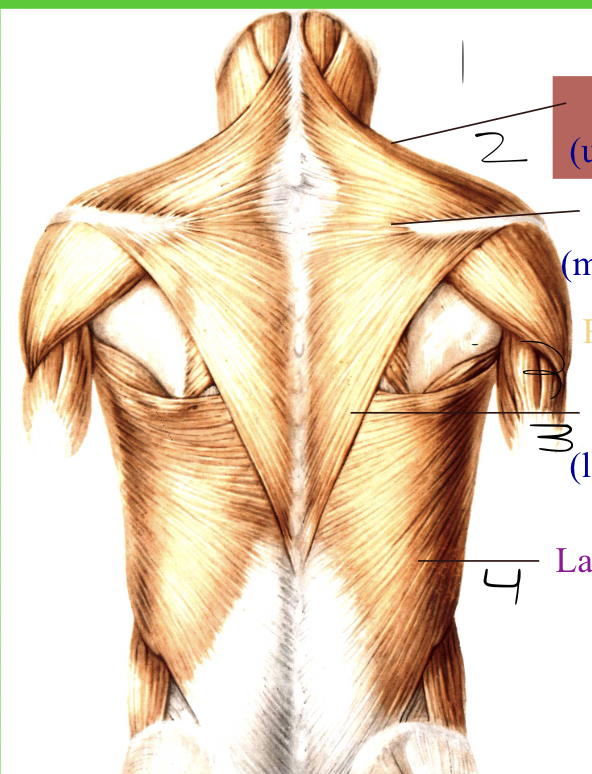
what is this? name the numbers
pectorial gridle posterior. 1. Trapezius upper 2. Trapezius middle. 3. trapezius lower 4. Latissimus Dorsi
where is the Biceps Brachii
upper bicep anterior side
where is the Triceps Brachii
Proximally to humerus (medial and lateral head)
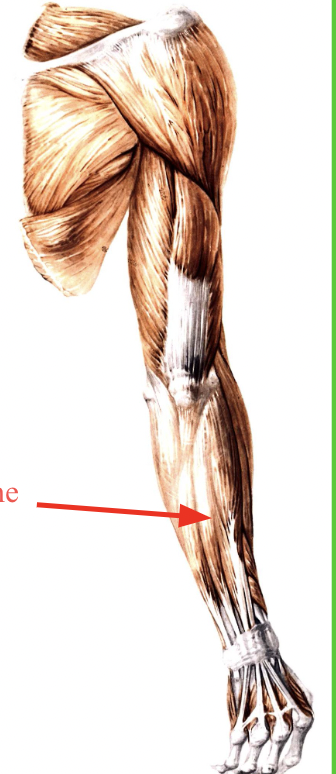
what is this an posterior view of
extensions of the forearm
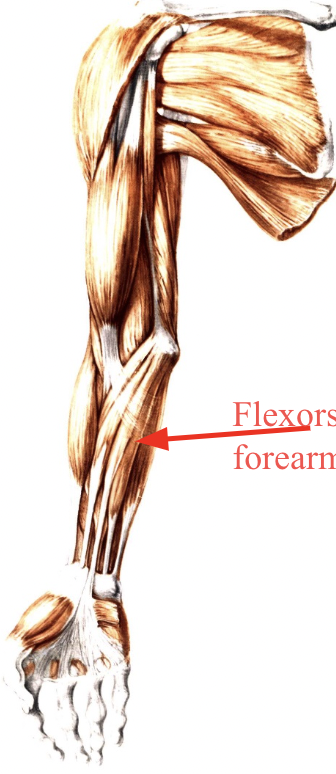
what is this a anterior view of
forearm of the flexors
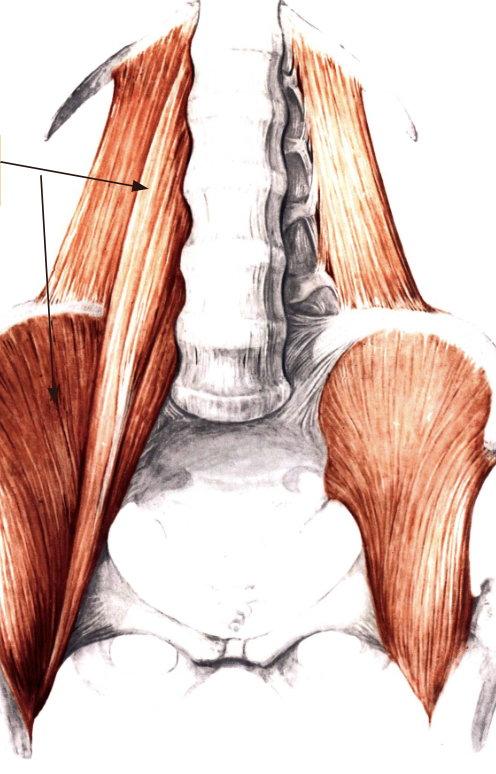
what muscle is this apart of and what is the muscle
Pelvic Girdle, lliopsoas
what is the gluteus maximus
glutes/ butt/ extender of the hip
what is the Sartorius?
longest muscle, wraps around your whole leg starts in thigh ends in calf
whats in your quadriceps
rectus femoris
vastus lateralis
vastus intermedius
vastus medialis.
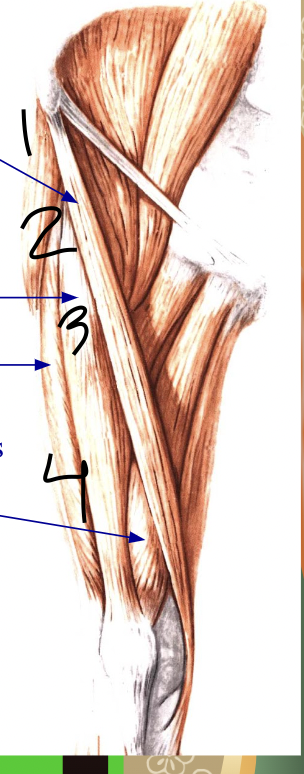
what is 2
rectus fermoris, anterior thigh
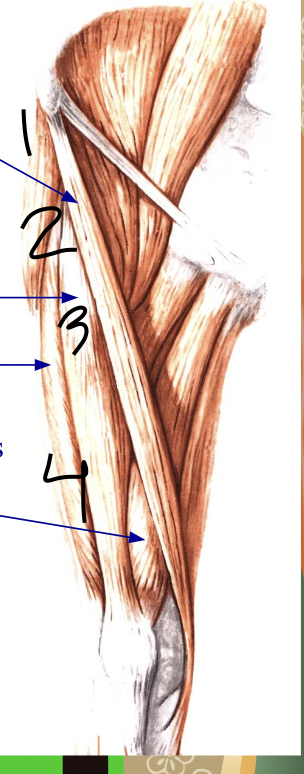
what is 3
vastus lateralis, lateral thigh