Chapter 6 lower limbs
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
phalanges
the most distal bones of the foot
common trauma site
tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal
sesamoid bones
most commonly found on the palmar surface near the metacarpophalangeal joints or interphalangeal joint of the thumb
patella
the largest sesamoid bone in the body
talus
astragalus
calcaneus
os calcis
the largest and strongest bone of the foot
calcaneal sulus
the deep depression between the posterior and middle articular facets
talus
the second largest tarsal bone
navicular
a flattened, oval bone located on the medial side of the foot between the talus and the three cuneiforms
cuboid
calcaneus articulates anteriorly with the
talus
calcaneus articulates superiorly with the
tibia and fibula
talus articulates superiorly with the
calcaneus
talus articulates inferiorly with the
nacivular
talus articulates anteriorly with the
talus
the navicular articulates posteriorly with the
cuboid
the navicular articulates laterally with the
three cuneiforms
the navicular articulates anteriorly with the
navicular
the medial cuneiform articulates proximally with the
first and second metatarsal
the medial cuneiform articulates distally with the
intermediate cuneiform
the medial cuneiform articulates laterally with the
navicular
the intermediate cuneiform articulates proximally with the
second metatarsal
the intermediate cuneiforms articulates distally with the
medial and lateral cuneiforms
the intermediate cuneiforms articulate on their side with the
navicular
the lateral cuneiforms articulate proximally with the
second, third and fourth
the lateral cuneiforms articulate distally with the
cuboid
the lateral cuneiforms articulate laterally with the
calcaneus
the cuboid articulates proximally with the
lateral cuneiform and navicular
the cuboid articulates medially with the
fourth and fifth metatarsals
the cuboid articulates distally with the
longitudinal and transverse arch
provide a strong, shock-absorbing support for the weight of the body
best demonstrated on weight bearing positions
longitudinal arch
the springy arch comprises of a medial and lateral component, with most of the arch located on the medial and mid aspects of the foot
transverse arch
located primarily along the plantar surface of the distal tarsals and the tarsometatarsal joints
primarily made up of the wedge- shaped cuneiforms
ankle joint
formed by the tibia and fibula and the talus
lateral malleolus
distal end of the fibula, extends down alongside the talus
mortise
the inferior portion of the tibia and fibula form this deep socket of a three sided opening
where the superior talus fits into
anterior tubercle
articulates with the superolateral talus
tibial plafond
forms the roof of the ankle mortise joint
articular facets
tibial plateau
articulates with the femur
tibial tuberosity
on the proximal extremity of the tibia is a rough-textured prominence located on the midanterior surface of the tibia just distal to the condyles
true lateral ankle
distal fibula over posterior half of tibia
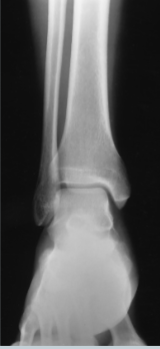
AP ankle
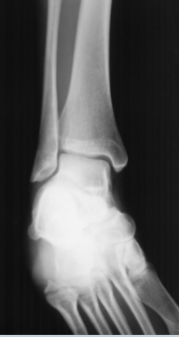
AP mortise ankle
femur
the longest and strongest bone
saddle joint
the patellofemoral joint is this type of joint
synovial
ALL joints in the lower limb are _______
diarthrodial
All joints mobility type in the lower limb are
fibrous
the distal tibiofibular is the only one classified as a
amphiarthrodial
the distal tibiofibular is the only one with this mobility type
15 degrees
AP axial toes the CR angulation of
AP toes
perpendicular to the central ray
sesamoid bones
the tangential lewis and holly method are used to view the ______ ____
prone
lewis method the the patient is in a ___ position
seated
for the holly method the patient is _____ for the exam
5-15 degrees
for the AP foot the tube is angled
15
for a high arched foot the tube is angled _______ degrees
5-10
for a flat footed person the tube is angled_____ degrees
30- 40
for and AP oblique foot the patient’s foot is medially rotated _____ -____ degrees
lisfranc fracture
for the lateral/AP foot weight- bearing method this fracture is can be seen
osteoarthritis and gouty arthritis
AP/ Oblique toe projection of the toes _____ _____ can be seen
medial lateral displacement
clinical indication for the axial calcaneous
ligament tear or rupture
AP stress projection of the ankle clinical indication
knee joint/ cartilage pathologies
clinical indication of the AP weight bearing bilateral knee projection
support may be needed
_____ ____ ______ for the axial (plantodorsal ) calcaneus
sustentaculum tali is in profile
1st to 5th metatarsals are not visible
evaluation criteria for the axial (plantidorsal) calcaneus
medial malleolus
the CR is 1 inch distal to the _________ _______ at subtalar joint for the lateral calcaneus
evaluation criteria for the lateral calcaneus
-tuberosity in profile
-sinus tarsi open
-calcaneocuboid and talonavicular joints open
AP Ankle evaluation criteria
-normal overlapping of tibiofibular articulation
-anterior tubercle slightly superimposed over the fibula
-talus slightly overlapping distal fibula
-no overlapping of the medial talomallolar articulation
oblique ankle evaluation criteria
distal tibofibular joint is open
lateral ankle evaluation criteria
-tibiotalar joint well visualized
-fibula over the posterior half of the tibia
rosenberg method
the PA weight bearing method for the knees
camp coventry method clinical indications
evidence of bony or cartilaginous pathology, osteochondral defects, or narrowing of joint space