PP2 1: Freudian psychoanalysis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Freudian Psychoanalysis
A psychological theory and therapeutic method developed by Sigmund Freud that emphasizes the role of the unconscious mind and early childhood experiences in shaping behavior and personality.
Breuer hypnosis
Breuer found that the womanʼs symptoms disappeared if she talked about them while in a hypnotic trance. She would relieve the terrifying experiences that gave rise to her symptoms and express the accompanying emotions fully (abreaction). This physical expression he labeled catharsis.
Catharsis
The physical expression and release of emotional tension, often through talking about traumatic experiences.
Abreaction
An abreaction is an emotional, unconscious reaction that you have in response to something that brings back a painful situation you’ve experienced.
Free Association
A therapeutic technique where patients express every thought that comes to mind, used to uncover repressed memories and emotions.
Repression
The unconscious act of keeping thoughts, memories, and desires out of conscious awareness, often related to painful or traumatic experiences.
Dream Analysis
A technique in psychoanalysis that involves interpreting dreams to unlock unconscious conflicts and desires.
Wish-fulfillment devices
Dreams
Psychic Determinism
The belief that all mental processes and behaviors have causes that can be identified, often rooted in the unconscious mind.
Instincts
rooted in unconscious, govern behavior
Eros
The life instincts in Freudian theory, which promote survival, reproduction, and other life-sustaining activities.
Thanatos
The death instincts in Freudian theory, which encompass aggression, self-destructive behavior, and the desire to return to a state of rest.
Topographic Model of Freud
A model that divides the mind into three regions: the conscious, the preconscious, and the unconscious, illustrating how thoughts and feelings are organized and processed.
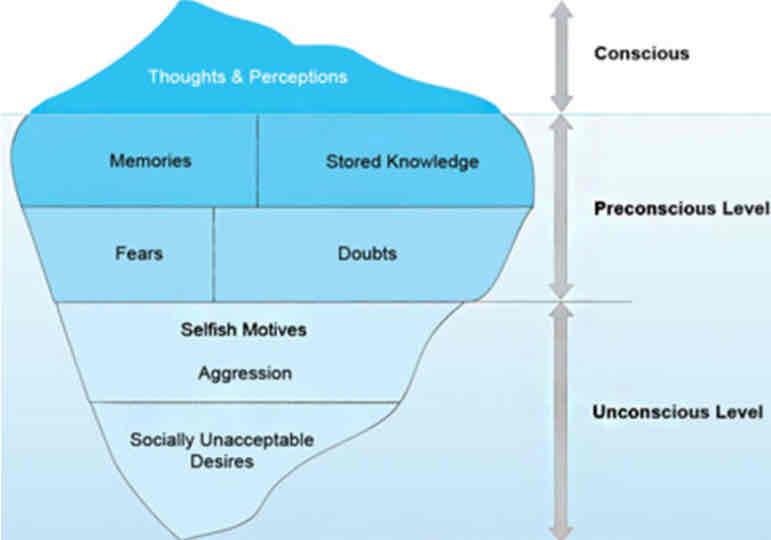
Components of consciousness (Freud)
immediate awareness: thoughts and perceptions
Components of preconscious level (Freud)
Accessible memories, stored knowledge, fears, doubts
Components of unconscious (Freud)
Socially unacceptable desires, drives, instincts, repressed memories, painful emotions
A theory that divides personality into three parts: the Id (unconscious desires), the Ego (the realistic part that mediates), and the Superego (moral standards).
Id
The part of the personality in Freudian theory that operates on the pleasure principle, seeking immediate gratification of desires and impulses.
Ego
The conscious part of personality that mediates between the unrealistic id and the external world, operating on the reality principle, used in decision making
Superego
The part of the personality representing incorporated societal values and morals, which is learned from parents and others, and develops during the phallic stage, uses morality principle
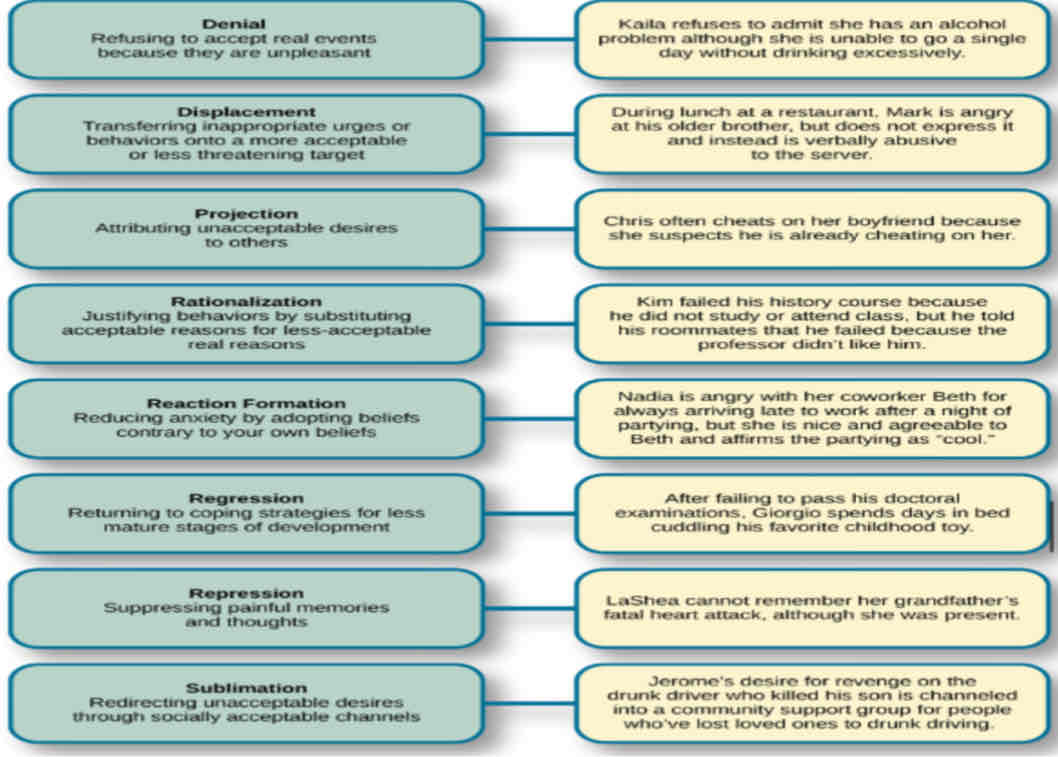
Defense Mechanism
Automatic, involuntary, unconscious psychological processes that protect an individual from anxiety or distress caused by unacceptable thoughts or feelings by excluding these from conscious awareness
Kernberg‘s classification of defense mechanisms
Primitive (splitting-based) and complex (repression-based) defenses
Coping vs defense
Coping: dealing with external threats/ challenges, conscious Defense: internal processes, leading to neurosis
Denial
refusing to accept real events because they’re unacceptable
Displacement
transferring inappropriate urges or behaviors onto a more acceptable or less threat target
Projection
attributing unacceptable desires to others
Rationalization
justifying behaviors by substituting acceptable reasons for less acceptable real reasons
Reaction Formation
A defense mechanism where an individual behaves in a way that is opposite to their true feelings or desires, often to reduce anxiety or distress caused by those feelings.
Oral Stage
The first stage of psychosexual development (0-1 years), where pleasure centers on the infant's mouth.
Regression
returning to coping strategies for less mature stages of development
Repression
suppressing painful memories and thoughts
Sublimation
redirecting unacceptable desires through socially acceptable channels
Theory of psychosexual development
personality development takes place during 5 stages, in each one sexual energy is expressed in different ways through different body parts (erogenous zones), each stage is associated with a particular conflict that must be resolved before the next stage
Anal Stage
The second stage of psychosexual development (1-3 years), where pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder control. Toilet training: first conflict with authority, metaphor of society, appropriate time and place for need satisfaction
Anal repulsive character
early or harsh tt; hate mess, obsessively tidy,
respect authority, stubborn
Anal expulsion character
liberal tt; sharing, messy, disorganized, rebellious
2 phases of the oral stage
Incorporation and oral sadistic (teething)
Incorporation phase
infant is helpless, dependent
experiencing benign world → optimism, trust
experiencing less supportive world → pessimism, mistrust too helpful world → dependent
Oral sadistic phase
pleasure comes from biting and chewing, determines verbal aggressiveness
Oral receptive character
overindulgence; used to receiving support and encouragement, dependent, too trusting, accepting, admire strength and leadership
Oral aggressive character
underindulgence; exploits others, sadistic, envying, manipulative
Phallic Stage
The third stage of psychosexual development (3-6 years), characterized by the focus on genitalia and the emergence of Oedipus and Electra complexes.
Phallic character
Males: reckless, resolute, self-assured, excessive vanity, exhibitionism
Females: penis envy, seductive with denial of own sexuality
Latency Stage
The fourth stage of psychosexual development (6+ years), where sexual impulses are repressed, and energy is channeled towards school and friendships.
Genital Stage
The final stage of psychosexual development (puberty onward), where sexual maturity occurs, and libido is directed toward heterosexual relationships.
Genital character
ideal type; sexually mature and capable of orgasm, able to love and be loved, capable of sublimating their idʼs impulses