Chap 6D - Kinetics
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Catalysts and energy profile diagram
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Define and describe catalysts (characteristics)
(Def.): Is a substance that increases rate of reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change
In the presence of a catalyst, a reaction has a different reaction mechanism with a lower Ea -> higher rate constant -> higher rate of reaction.
Characteristics:
Catalyst does NOT affect enthalpy change of a reaction
Catalyst speeds up the rates of forward and backward reactions -> speeds up rate at which equilibrium is attained (equilibrium position remains the SAME) -> equilibrium constants Kc or Kp remain the same
Catalyst is chemically involved in a reaction -> consumed in one step and regenerated in a subsequent step
Define and describe heterogeneous catalysts
(Def.): substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change and it is in different physical states as the reactants
Catalyst in solid state, reactants in aqueous or gaseous state
All heterogeneous processes occur at the phase boundary
Describe the adsorption theory of heterogeneous
Diffusion
Reactant molecules diffuse towards the catalyst surface
Adsorption
Reactant molecules become chemically adsorbed through formation of weak temporary bonds with neighbouring active sites
This increases the surface concentration of reactants and weakens the covalent bonds in the molecules -> lower Ea
Chemical Reaction
Eventually, the molecules dissociate, forming highly reactive intermediates which then combine to form the product
Desorption
After reaction, the product molecules break free from the surface and diffuse away from the surface
The vacant active sites are now available for adsorbing other reactant molecules
Describe Haber process and its ideal conditions
Used to manufacture ammonia
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) , Hr = −92 kJ mol−1
The reaction is slow and does not go to completion
Optimal conditions :
Temperature : 450 C
Pressure : 250 atm
Catalyst : finely divided iron catalyst
A low temperature would favour the forward exothermic reaction and increase the yield of NH3 but the reaction would be too slow to be economical
Finely divided iron is used as a heterogeneous catalyst to further increase the rate of reaction by weakening the triple bond in N2
A high pressure favours the forward reaction as it reduces the number of moles of gases but the cost and maintenance of the equipment would be too high
The yield of NH3 is further increased by removing it as it forms as this continuously shifts the position of equilibrium to the right
Describe catalytic converters in cars
Used in some exhaust systems to convert gases that are environmentally harmful into harmless gases
A honeycomb of small beads coated with platinum and palladium catalysts convert:
Unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide into harmless water and carbon dioxide gas
Nitrogen oxide into nitrogen gas
Write all equations in catalytic converters and their catalysts

Describe and define homogeneous catalysts
(Def.): Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change and it is in the same physical states as the reactants
Reactants and catalyst should be in the same physical state
Describe SO2 and O2 reaction
Uncatalysed reaction: SO2(g) + 1/2O2(g) → SO3(g)
Reaction is slow due to high Ea because energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds in the reactants
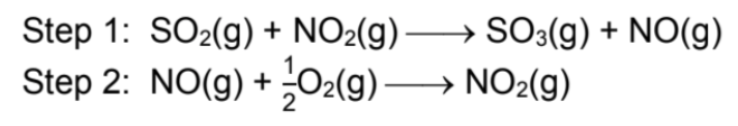
Describe Fe2+ catalyst for S2O82- and I- reaction
Uncatalysed reaction: S2O82– (aq) + 2I– (aq) → 2SO42– (aq) + I2 (aq)
Reaction between two anions is slow due to the high activation energy caused by the repulsion between the two negatively charged ions
Each step involves a reaction between oppositely charged ions which have a natural tendency to attract each other -> lowers the activation energy and increases the reaction rate
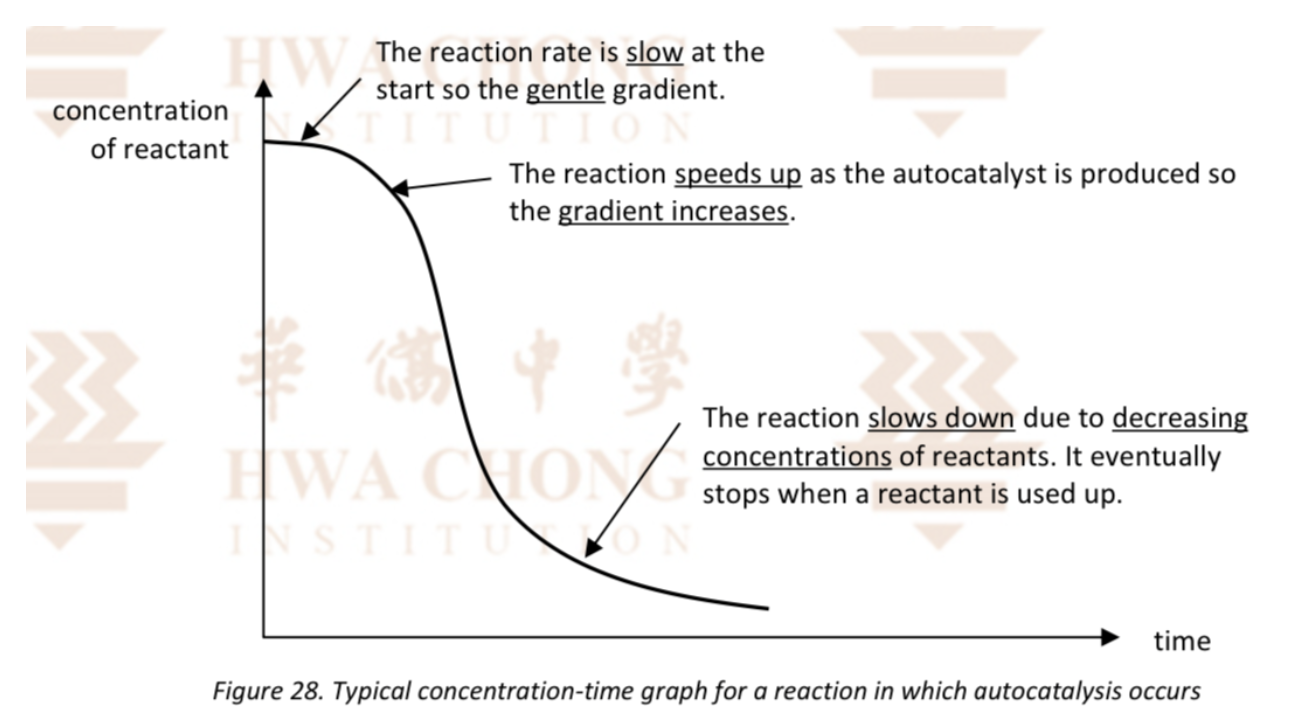
Define autocatalysis
(Def.): This is the catalysis of a reaction by one of the products of the reaction. The reaction is initially slow but as the products are formed, the reaction is speeded up
Describe Mn2+ as a autocatalyst and its graph
As the Mn2+ ions are produced, they increase the rate of the reaction by acting as an autocatalyst
Towards the end of the reaction, the concentration of the reactants has fallen to a low level and so the rate of the reaction decreases, even though there is an adequate supply of catalyst
Describe enzymes
Enzymes are neither homogeneous nor heterogeneous catalysts as they are colloidal in nature
Enzymes are highly specific and would only catalyse a specific reaction or specific type of reaction
Enzymes operate most efficiently at around body temperature
Describe the relationship between substrate and enzyme conc
At low substrate , the enzyme concentration is greater than substrate concentration. The rate of reaction increases proportionally with increasing substrate concentration as shown by the straight line graph. The reaction is first order with respect to the substrate
At high substrate, all the active sites are filled (saturated) with substrate molecules. Further increase in substrate does not affect the rate as shown by the horizontal line. The reaction is now zero order with respect to the substrate
To further increase the maximum rate of reaction, the concentration of the enzyme has to be increased
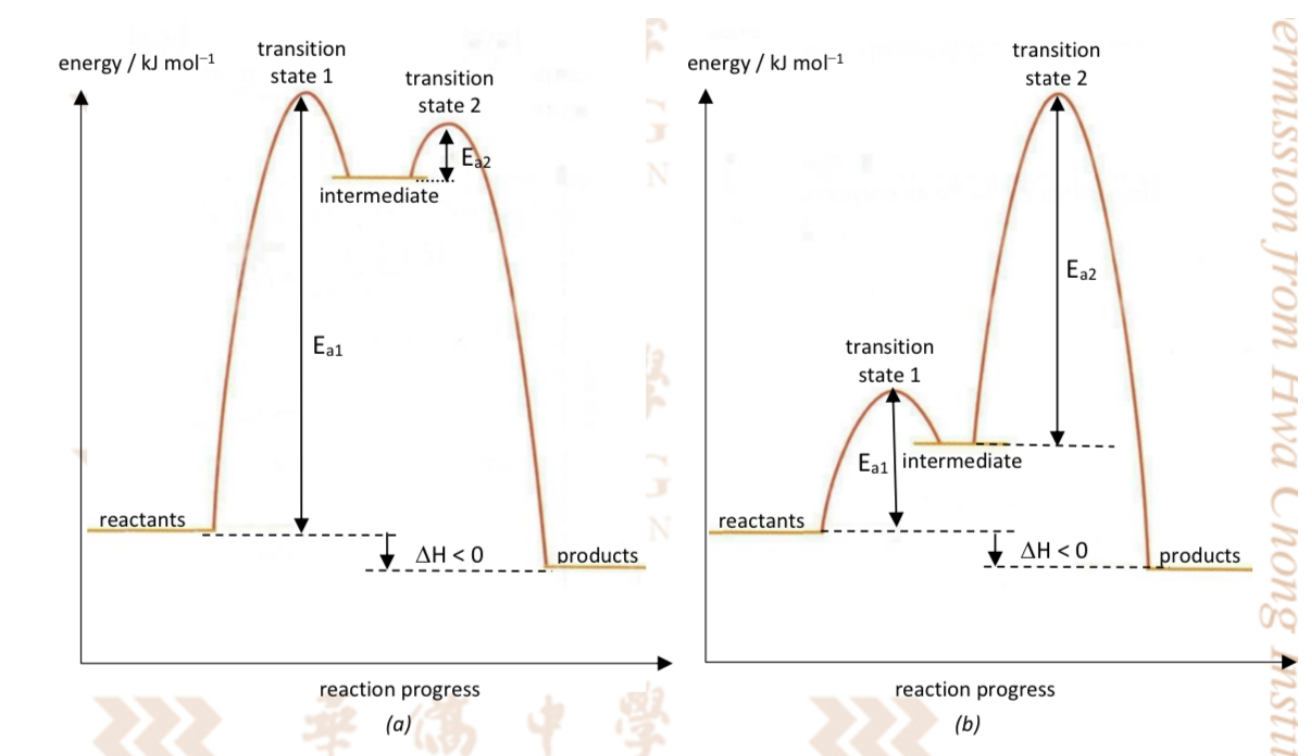
Describe energy profile diagram with 2 steps
Has 2 transition states and an intermediate
Intermediate : is a definite species which is formed during the reaction but are not part of the final products
Intermediates are relatively reactive with energy higher than the reactants and products, but may be stable enough to be detected or isolated
An intermediate occurs at an energy minimum
Draw 2 possible energy profile diagrams for 2-step exo reaction