Ch.11 Aggregate Supply and Demand in Macro Economy
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Macro Economy
The overall economic activity in a country.
Internal Market Forces
Factors like population growth affecting the economy.
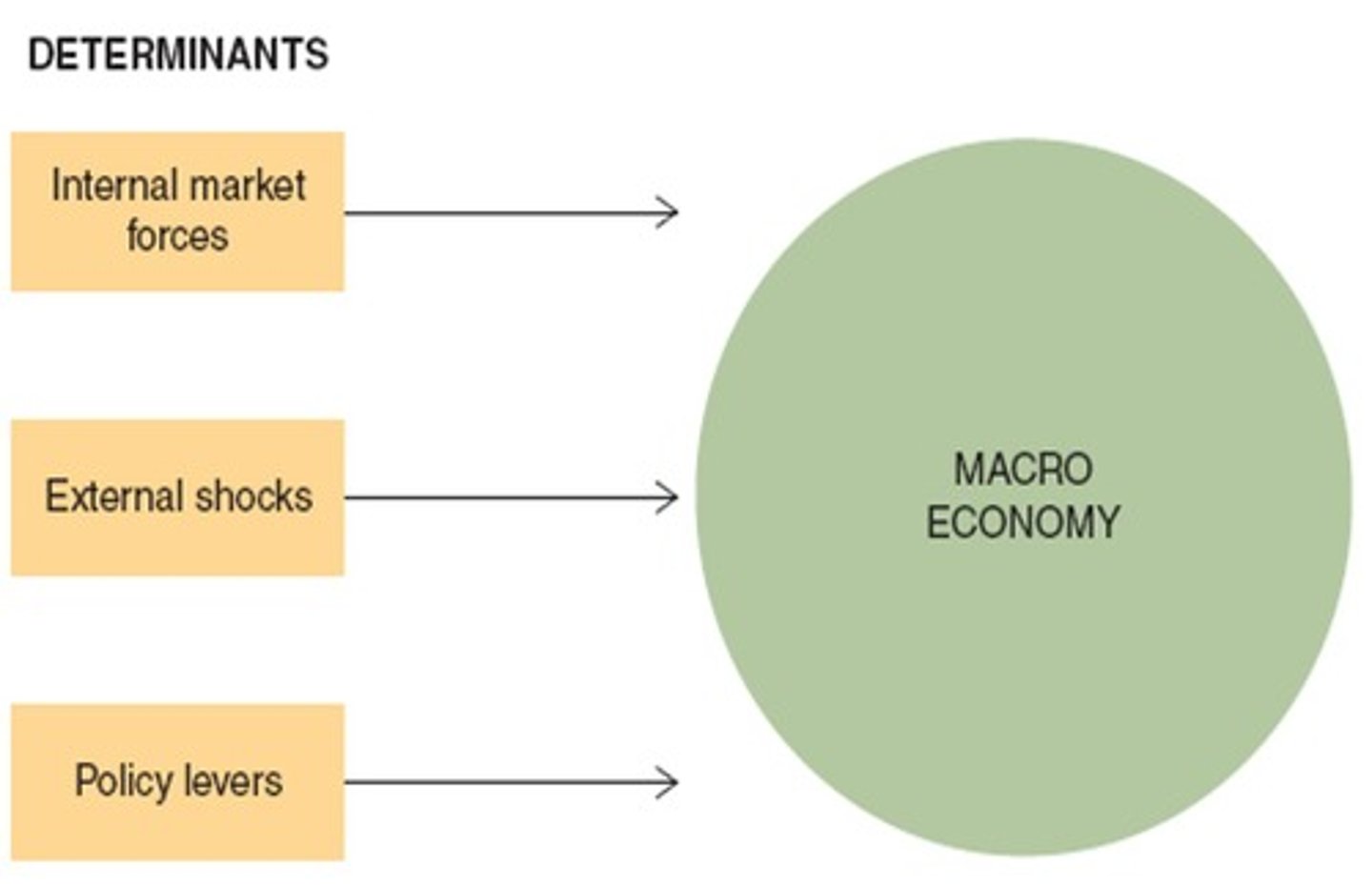
External Shocks
Unexpected events impacting economic performance.
Policy Levers
Government actions influencing economic conditions.
Output
Total volume of goods and services produced.
Jobs
Levels of employment and unemployment in the economy.
Prices
Average prices of goods and services in the market.
Growth
Year-to-year expansion in production capacity.
International Balances
Value of the dollar and trade balances internationally.
Aggregate Demand (AD)
Total quantity of output demanded at various price levels.
AD Curve
Graph showing the relationship between price levels and output demanded.
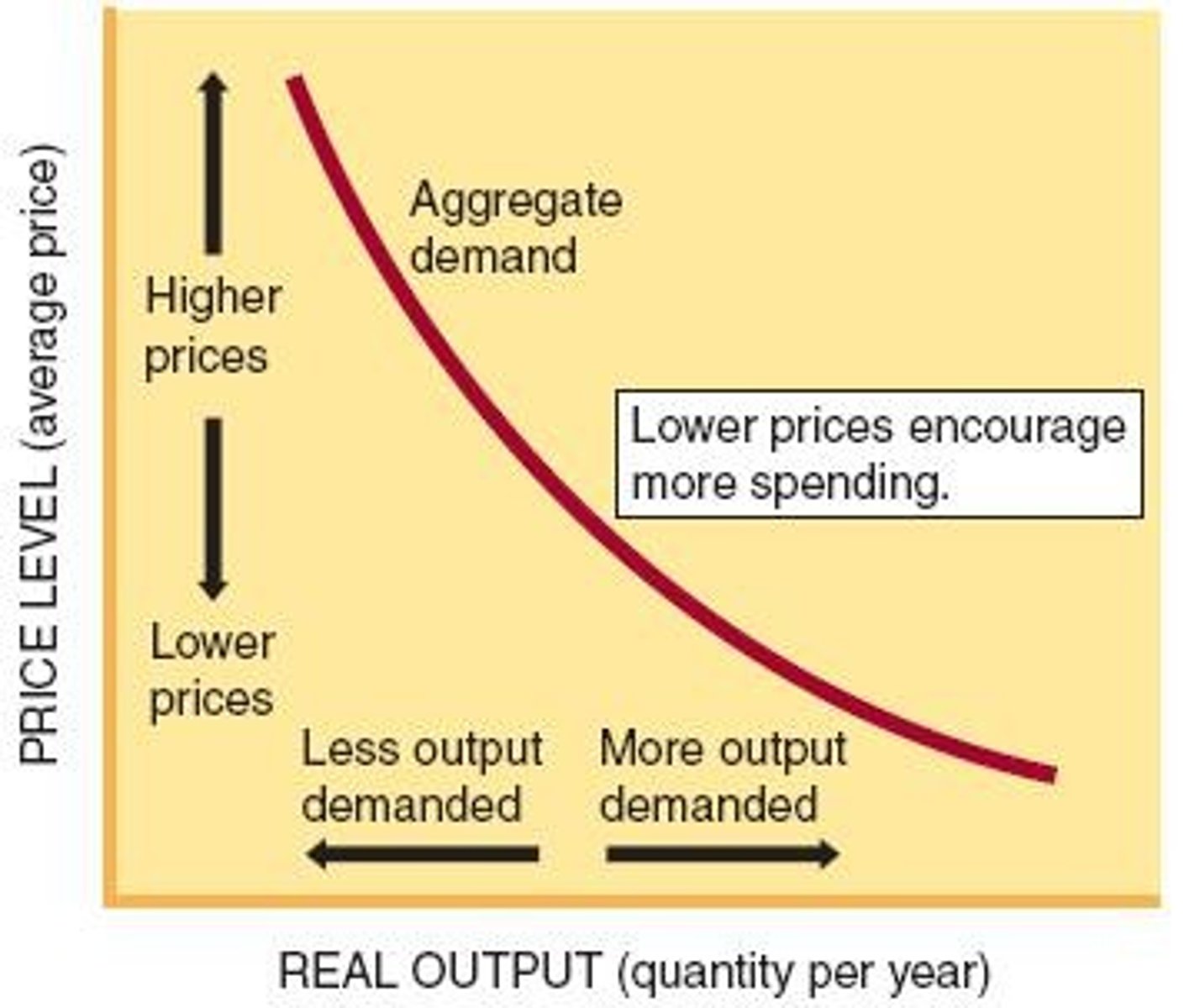
Real Balances Effect
Purchasing power increases as prices fall.
Foreign Trade Effect
Domestic price changes affect import and export demand.
Interest-Rate Effect
Lower prices lead to reduced interest rates and borrowing.
Aggregate Supply (AS)
Total quantity of output producers are willing to supply.
AS Curve
Graph showing the relationship between price levels and output supplied.
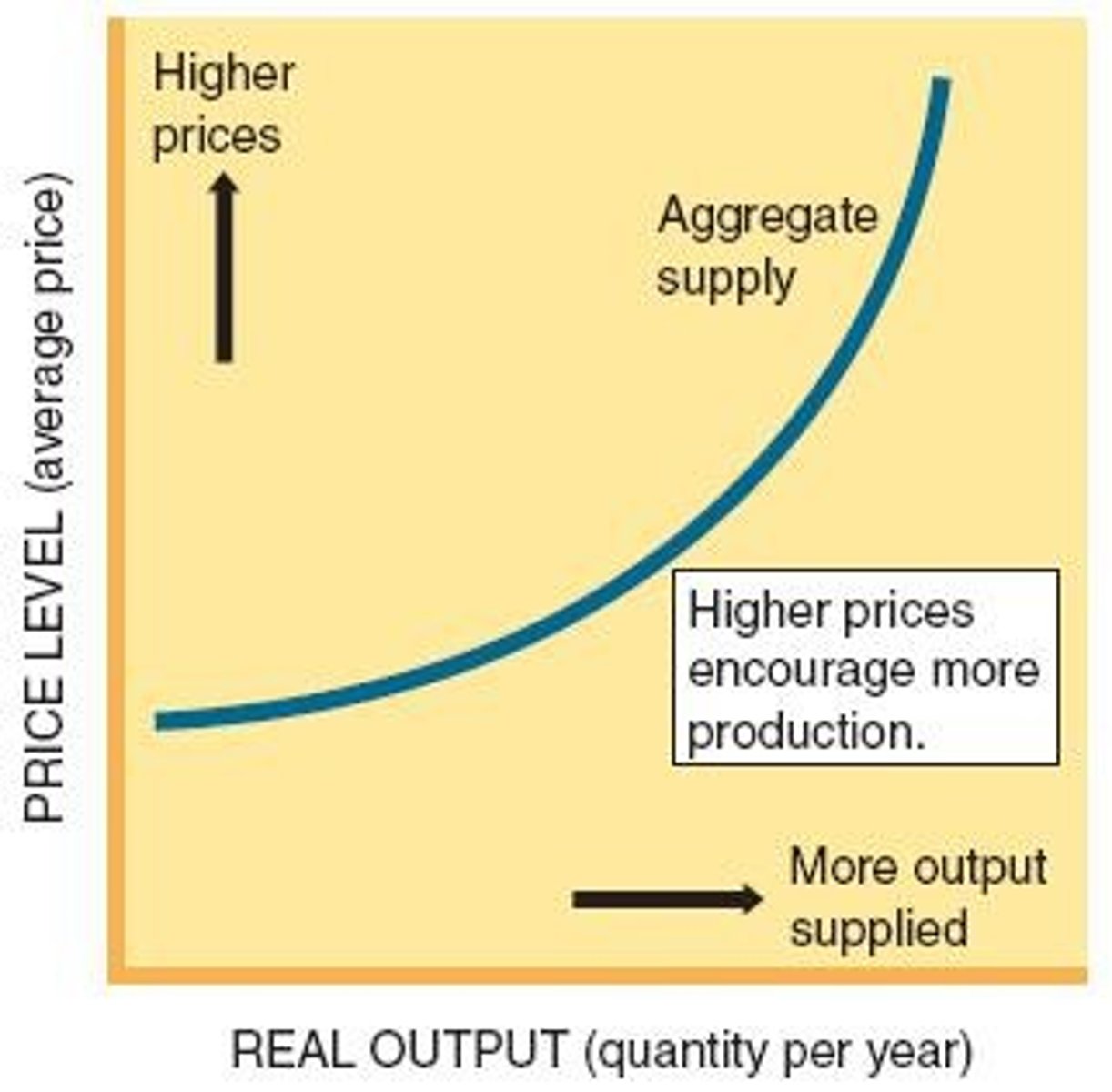
Profit Margins
Higher prices increase producers' willingness to supply more.
Costs
Production costs rise as output increases.
Macro Equilibrium
State where aggregate supply equals aggregate demand.
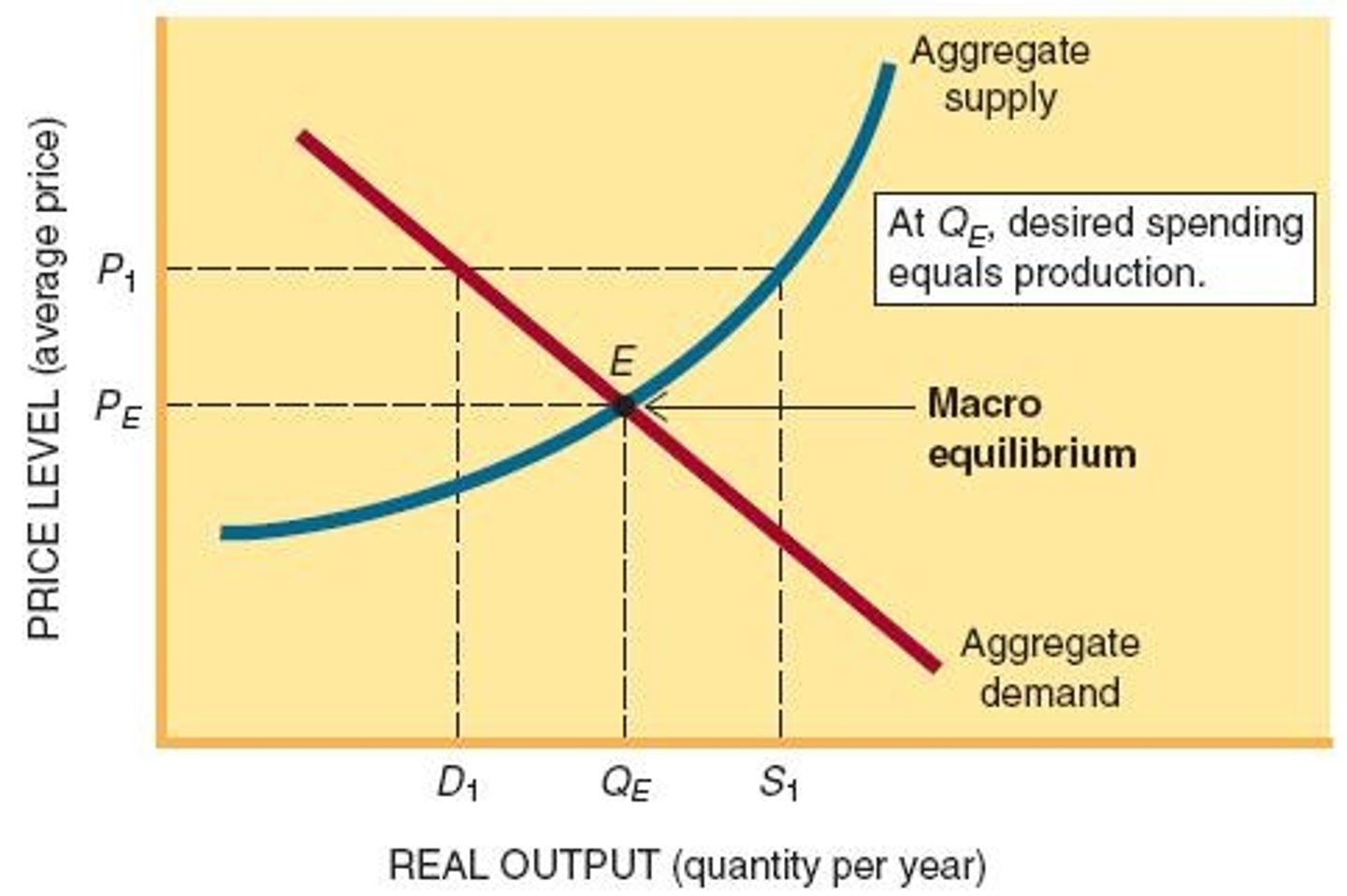
Macro Failure
Inefficiencies in achieving desired economic outcomes.
Undesirability
Equilibrium may not meet macroeconomic goals.
Full-employment GDP
Real GDP produced at full employment levels.
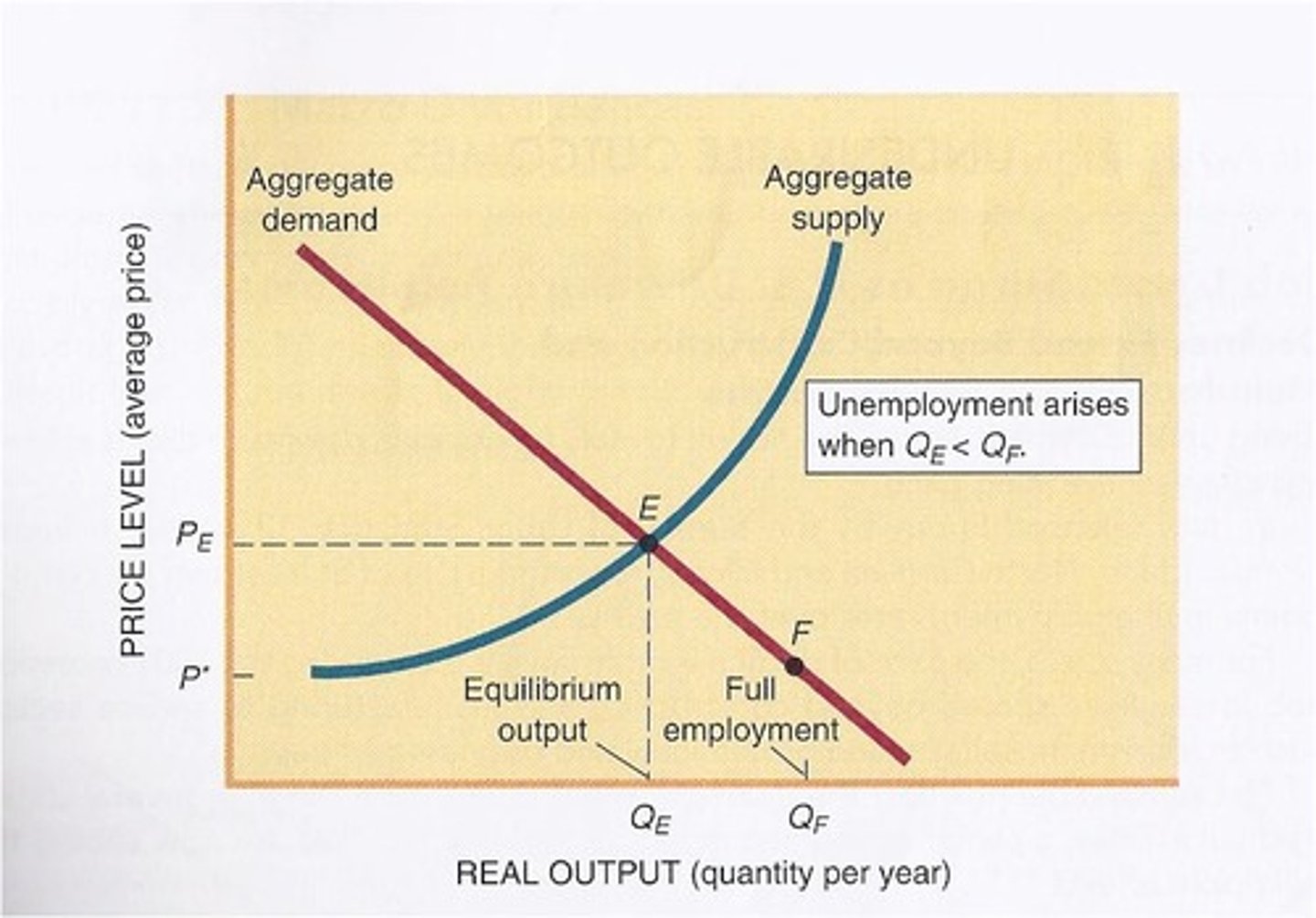
Unemployment
Labor force participants unable to find jobs.
Inflation
Increase in average price levels of goods.
Instability
Equilibrium may be disrupted by economic disturbances.
Leftward Shift of AD
Decreases price levels and output in the economy.
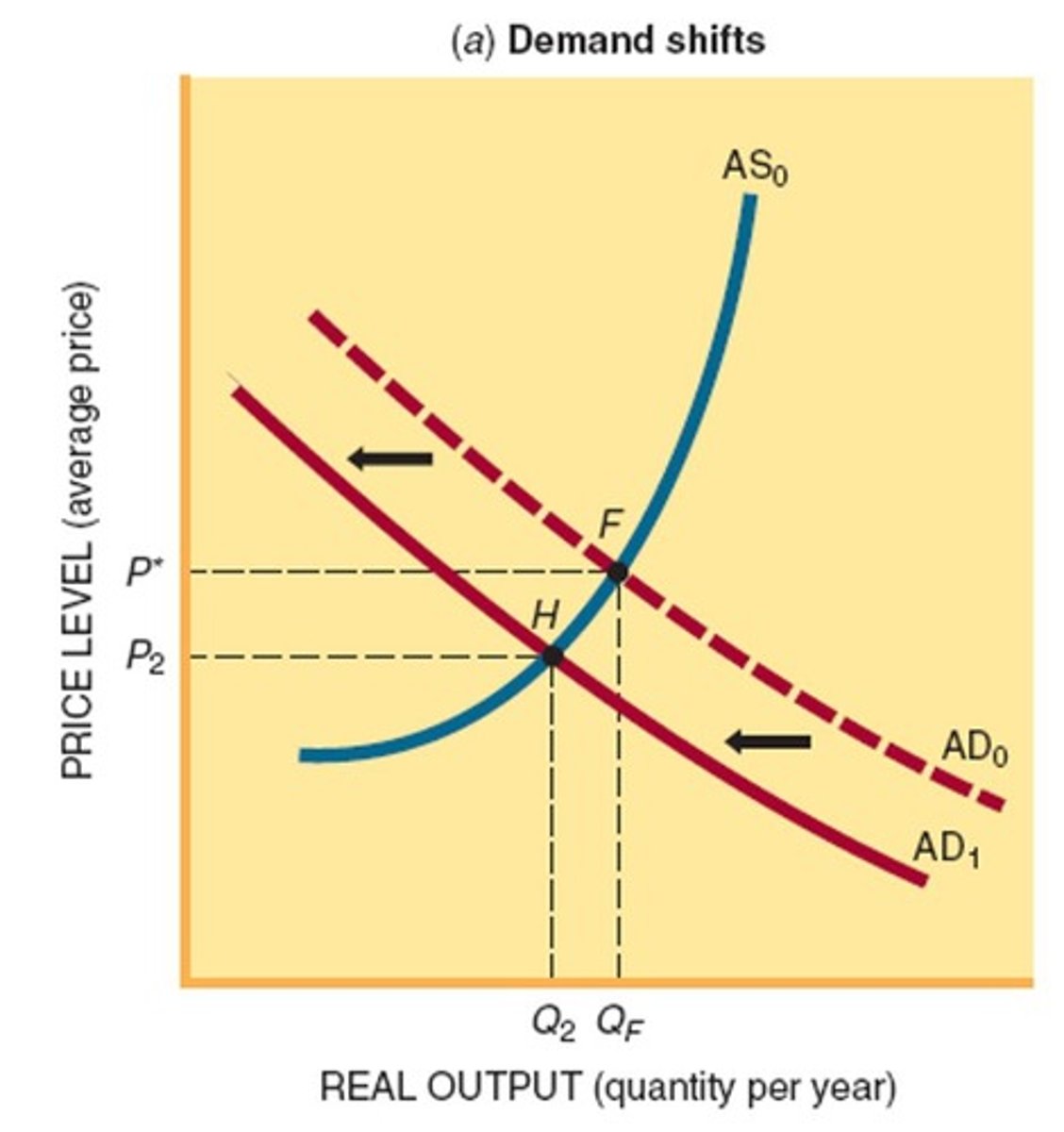
Leftward Shift of AS
Increases price levels and decreases output.