IB ESS Topic 1.1 Perspectives
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1.1 environmental value systems
Perspective
A perspective is how a particular situation is viewed and understood by an individual. It is based on a mix of personal and collective assumptions, values and beliefs.
Values
Values are qualities or principles that people feel have worth and importance in life.
Worldviews
Worldviews are the lenses shared by groups of people through which they perceive, make sense of and act within their environment. They shape people's values and perspectives through culture, philosophy, ideology, religion and politics.
Environmental perspectives
Environmental perspectives (worldviews) can be classified into the broad categories of technocentric, anthropocentric and ecocentric.
Environmental Value Systems (EVSs)
An environmental value system is a model that shows the inputs affecting our perspectives and the outputs resulting from our perspectives.
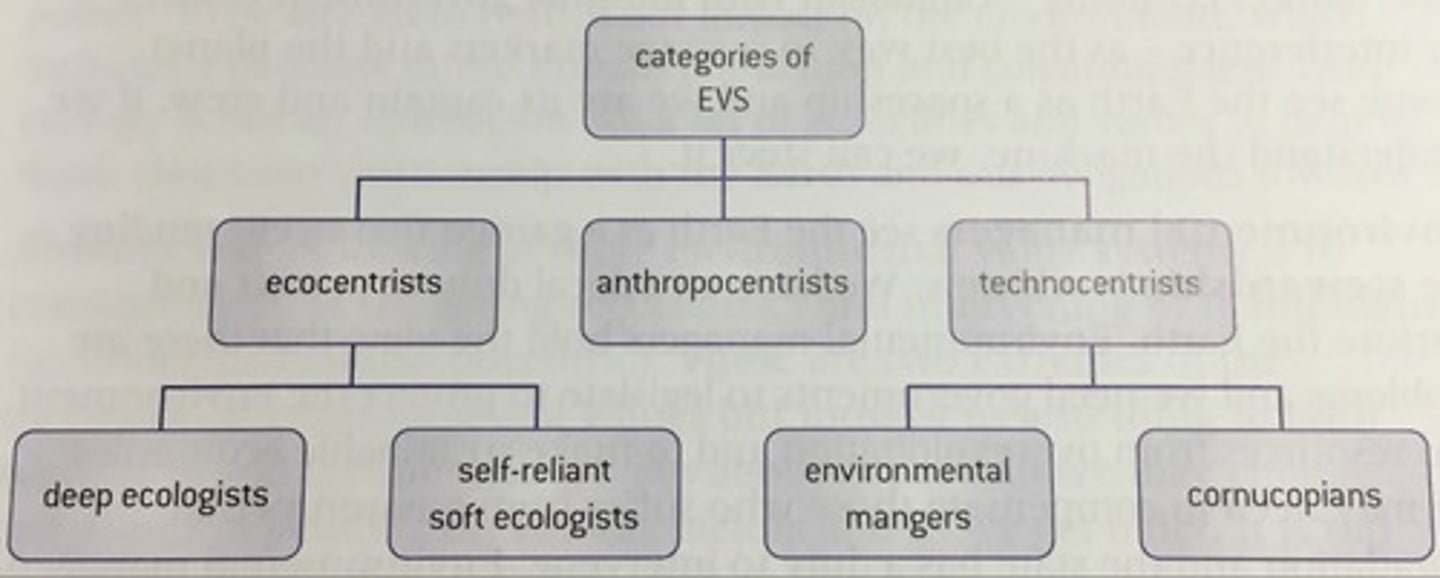
Classification of environmental philosophies
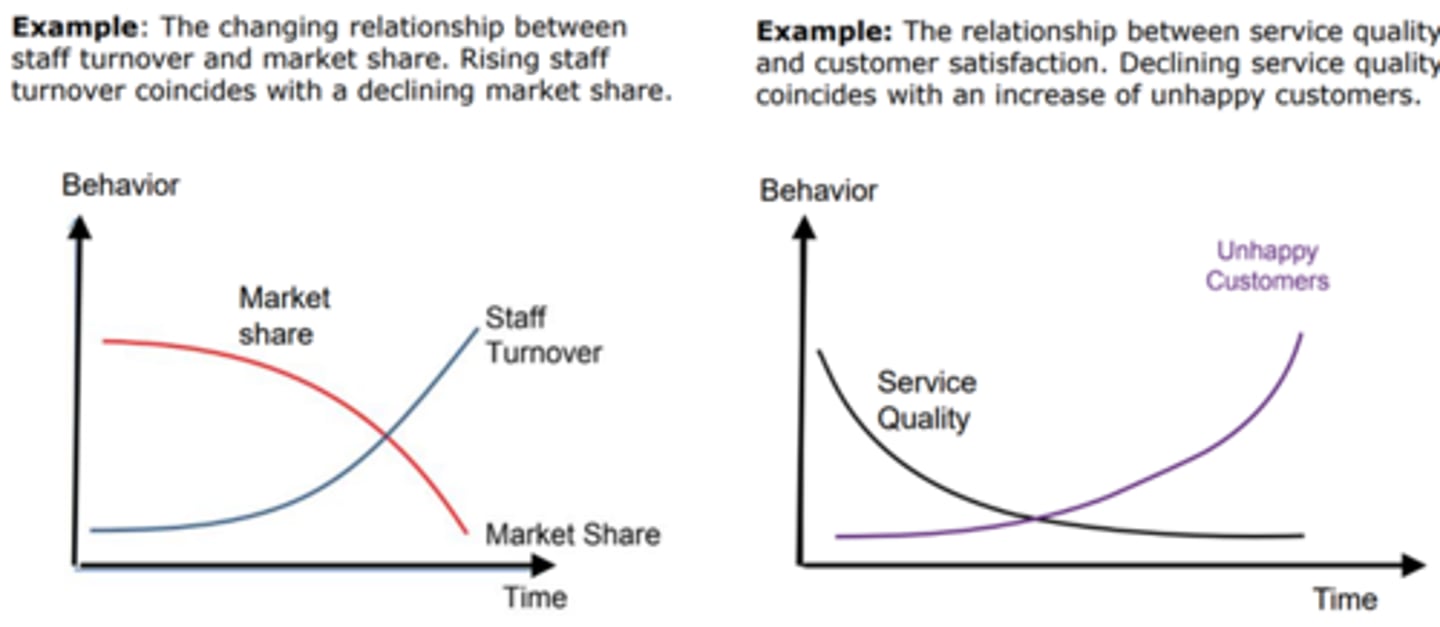
How perspectives change over time
- Perspectives and the beliefs that underpin them change over time in all societies.
- They can be influenced by government or non-governmental organization (NGO) campaigns or through social and demographic change.
- These can be shown with behavior-time graphs
Ecocentric
a nature-centred value system that views people as being under nature's control rather than in control of it.
Anthropocentric
a human-centred value system that places human as the central species and assesses the environment from an exclusively human perspective.
Technocentric
a technologically-based value system that believes the brain power of humans will enable us to control the environment.
Cornucopians
-extreme technocentrists
-think the world has infinite resources
-technology can solve any environmental issue
Environmental managers
-Earth is a garden that needs tending
-stewardship, ethical duty to look after the earth
-the government need to make legislations to protect the world
Biocentric
-all life has an inherent value, not just for humans
-we shouldn't cause extinction of other species
-praise small communities
Deep ecologists
-nature has more value than humanity
-humans have no right to interfere with nature
-wants a decrease in human population/ humans to consume less
Environmental movement
-influential individuals: media publications
-independent pressure groups: awareness campaigns
-corporate businesses: using resources such as coal
-governments: policy decisions
-intergovernmental bodies: influencing governments
Case study: historical influences
-Rachel Carson's book silent spring warned of the effect of pesticides
-pesticides move up the food chain to harm people
-her concerns were shared
-DDT was banned