Marketing 200 - Chapter 11, 12, 13, 14 and 3
1/474
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
475 Terms
What does B2B stand for?
Business-to-Business
What does VMS stand for?
Vertical Marketing System
True Value Hardware vs Ace Hardware
What does ERP stand for?
Enterprise Resource Planning
What does RFID stand for?
Radio Frequency Identification:
-Product tags with tiny chips containing information about the item’s contents, origin, and destination
What does JIT stand for?
Just in Time
Define Transportation and Storage.
Retailers and other channel members move the goods from the production point to other locations where they are held until consumers need them.
Peeps
Define Facilitating Function.
Channel intermediaries that make the purchase process easier for customers and manufacturers.
BNPL
Define Communication and Transaction Functions.
When channel members develop and execute both promotional and other types of communication among members of the channel.
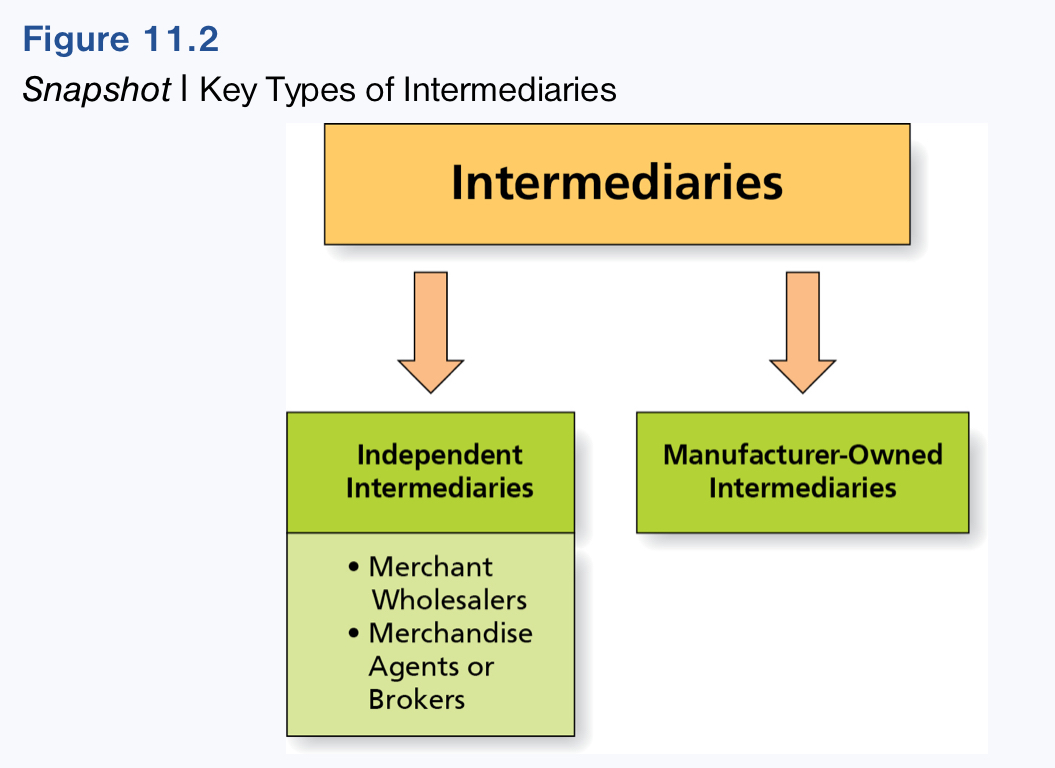
What are Independent Intermediaries?
Are not controlled by any manufacturer but instead do business with many different manufacturers and many different consumers.
Merchant wholesalers DO or Don’t take title to the goods?
-Do
-Assume Risks, can suffer lost
Merchandise agents/brokers DO or DO NOT take title to the goods?
-Don’t
-Provides services in exchange for commissions
What do Manufacturer-owned Intermediaries do?
Performs all functions of independent intermediaries while still maintaining complete control over the channel.
There is no single best channel for all products. True or False
True
Types of Consumer Distribution Channels?
Direct
Producer → Consumer
Indirect
Producer → Retailer → Consumer
What are B2B Distribution Channels?
Flow of goods from the Producer to the organization or Business customer.
Can be direct & indirect
What are Dual (multiple) channels?
Where producers, dealers, wholesalers, retailers, and customers participate in more than one type of channel.
What are Hybrid distribution channels?
Uses a number of different channels and communication methods to serve a target market
Ex. A company combining channels like direct sales, distributions, retail sales, and direct mail
Ex. Xerox
Example of Dual Channel Distribution
Pharmaceutical Companies
Sell to hospitals → Indirect consumer channels (Walgreens) → Companies sell to 3rd party buyers
Example of Hybrid Channel Distribution.
Xerox Copiers
Sells only through authorized dealers and usually to large business customers, offers competitive advantages; increased market coverage, lower market costs, greater potential for customization of service for local markets
Price and Place are related. True or False.
True
Ultradent teeth whitening only sold from dentist. Makes it more high end since sold by professionals
Mid price products are sold through mass merchandisers. True or False.
True
Prestige products are sold through upscale department stores and specialty stores. True or False.
True
Define Slotting Allowance.
Marketers paying more for access to shelf space
When Developing Objectives, what are the overall objectives?
Utility
How does distribution work with the other marketing mix elements
Make depend on nature of product
Develop Objective:
If the product is Bulky, then _ _ _ _ _?
minimize cost
Develop Objective:
If the product is Fragile, then _ _ _ _ _?
Minimize handling
Since Covid, Shipping costs are _ _ _ _ _ _!
Since Covid, Commodities costs are _ _ _ _ _ _!
Since Covid, Labor costs are _ _ _ _ _ _!
RISING for all
What are Internal/External Environmental Influences?
Geography
Degree of technical complexity of product
Internal/External Environmental Influences:
If the product is Perishable, the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ distribution.
Selective
Internal/External Environmental Influences:
If the product is Inexpensive, the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ distribution.
Intensive
What is Distribution Strategy Decision 2?
Intensive
Exclusive
Selective
When is an Intensive Distribution Strategy Used?
With Convenience Products
Selling products through all suitable wholesalers or retailers that are willing.
When is an Exclusive Distribution Strategy Used?
Used with Specialty Products
Limit distribution to a single outlet in a particular region
When is a Selective Distribution Strategy Used?
Used with Shopping Products
Distribution using fewer outlets than intensive distribution but more than exclusive
An example of Developing Distribution Tactics.
Small businesses such as Instant Pot outsource distribution via partnerships with Amazon. Amazon warehouses and ships products for companies; very helpful as small businesses scale up.
What is the Develop Distribution Tactics Decision 1.
Select Channel Partners
Ex. Should I seek distribution through Walmart?
Pro: Double Business
Con: Loss of marketing decision-making
Corporate Social Responsibility
Ex. Starbucks
Work with those who share values
What is the Develop Distribution Tactics Decision 2.
Manage the Channel
Channel power: Ability of one channel member to influence, control, and lead the entire channel based on sources of power. (Channel Captain)
Economic Power:If it has ability to control resources
Legitimate Power: Has legal authority to call the shots
Reward and Coercive Power: If engages in exclusive distribution and has ability to give profitable products and take them away from the channel intermediaries.
Photo showing reduced transactions via intermediaries.
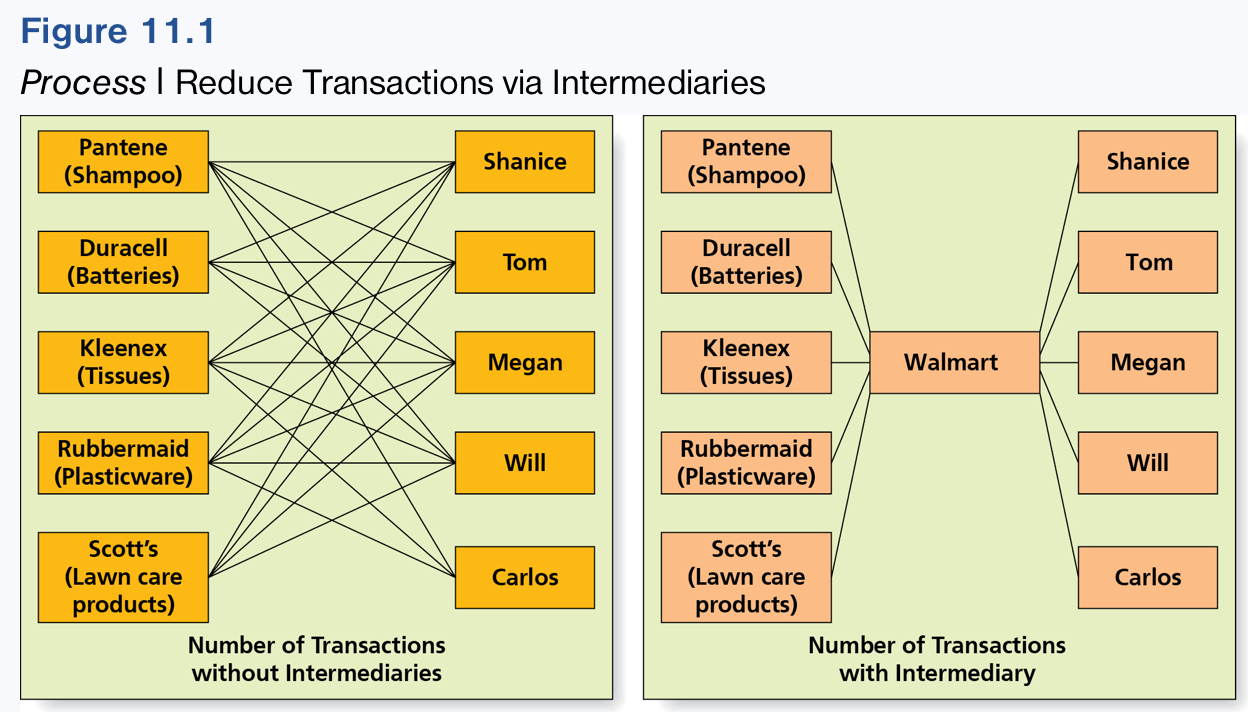
Photo of Key types of Intermediaries.
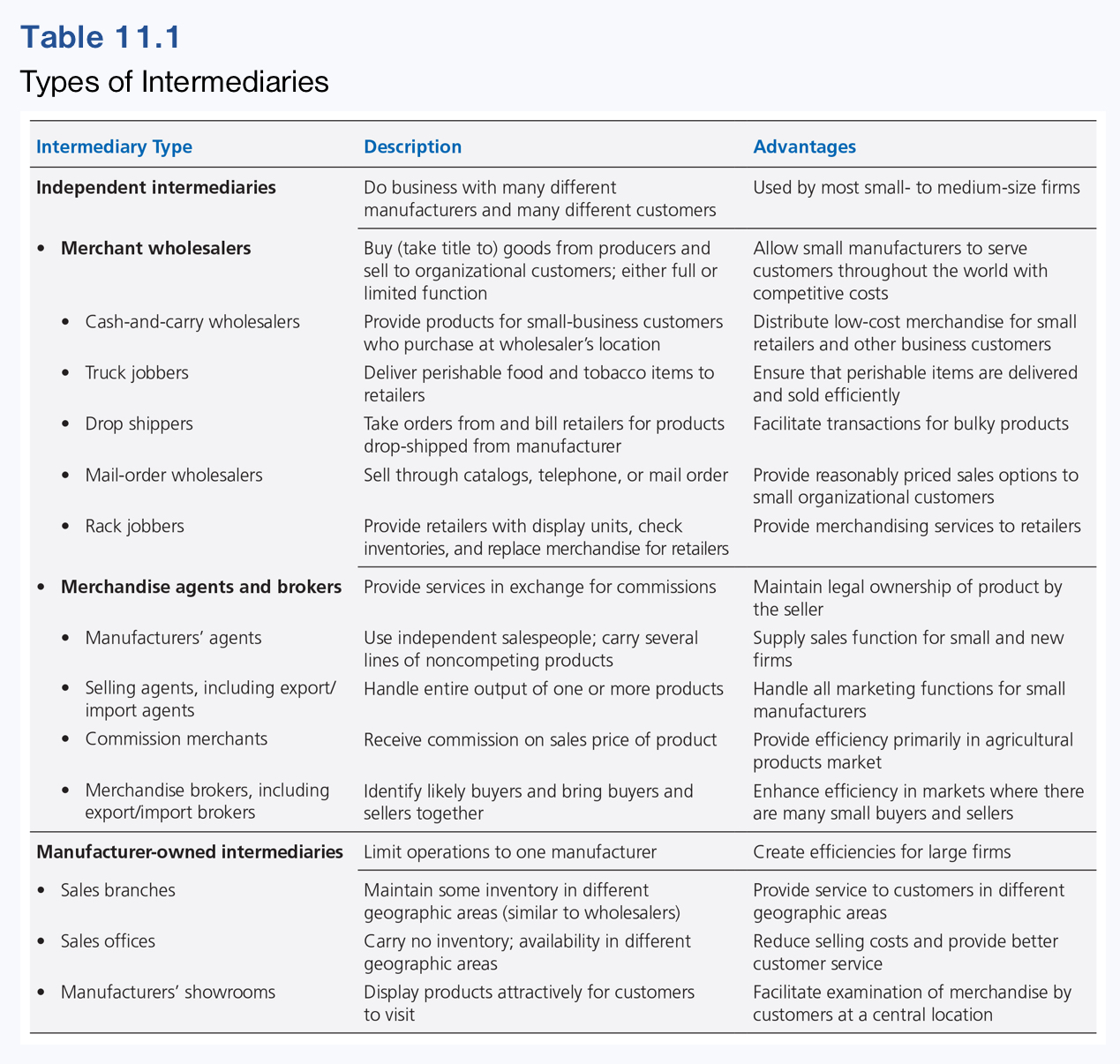
Learn about Types of Intermediaries from this photo.
What are the Five Functions of Logistics?
Order Processing
Warehousing
Materials Handling
Transportation
Inventory Control
Define Order Processing.
Series of activities that occurs between the time on order comes into the org and the time a product goes out the door.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Define Enterprise Resource Planning.
Software solution that integrates information from across the entire company, including finance, order fulfillment, manufacturing, and transportation.
Define Warehousing.
Storing goods in anticipation of sale or transfer to another member of the channel of distribution.
Time Utility
Define Materials Handling.
Moving products into, within; and out of warehouses.
Different Types of Channel Distribution
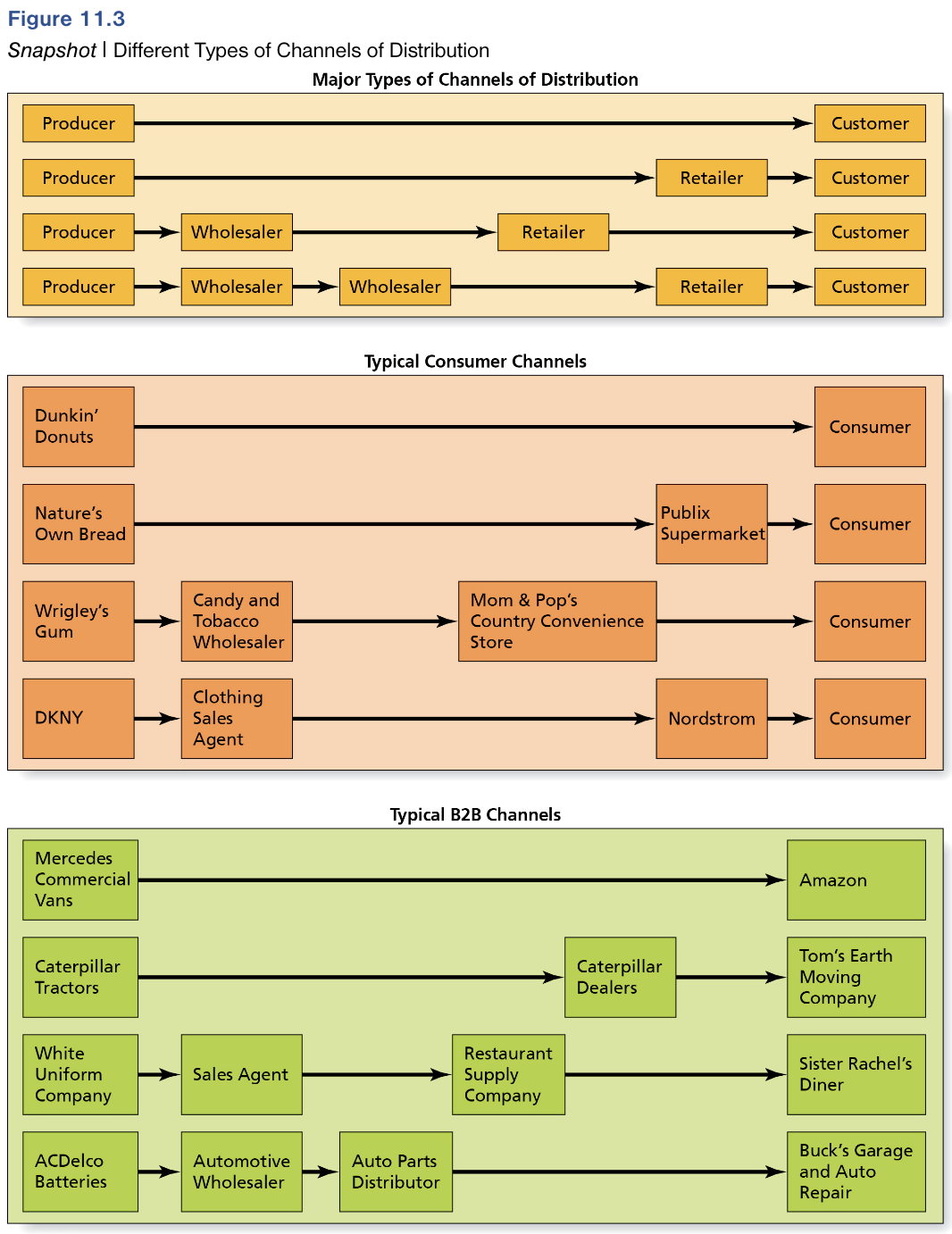
Define Transportation.
Mode by which product moves between channel members.
Six types of Transportation and Descriptions.
Dependability
Ability of carrier to deliver goods safely & on time
Cost
Total transportation cost to move goods one place to another. Includes charges for loading, etc.
Speed
Total time delivery takes. Including loading and unloading.
Accessibility
Number of locations carrier services
Capability
Ability of carrier to handle different products, large, bulky, small, fragile.
Traceability
Ability of carrier to locate goods in shipment
Define Inventory Control.
Activities to ensure goods are always available to meet customer demand.
RFID and JIT: Avoid stock-outs
What is Supply Chain.
All activities to turn raw materials into goods or services and put in hands of consumers or business customer.
Is place the “final frontier” for achieving long-term competitive advantage.
Ex. Walmart/Sam’s Club
Cross Docking
High-impact supply chain trend: insourcing - bring specialist company like UPS
What does CSA stand for?
Community Supported Agriculture
IKEA has control over all channel operations. True or False.
True
Case Study: BDP International Notes
Client: PepsiCo
Quaker Oats
World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davios, Switzerland
Quaker Opportunity with Breakfast Bars
Weren’t approved in the EU
Label for ingredients wasn’t approved
Define Physical Distribution.
Activities that move finished goods from manufacturers to final customers.
Define Channel of Distribution.
Series of firms or individuals that facilitates the movement of a product from producer to final consumer.
Define a producer.
The individual of firm that manufacturers or produces a good or service and a customer
Define Direct Channel.
Firm sells its own product first to customer.
Define Indirect Channel.
Firm sells their products through third parties.
Often include channel intermediaries: Middle Man
What are Functions of Distribution Channels?
Provide time, place, possession/ownership utility
Provide logistics and/or physical distribution
Create efficiencies by reducing the number of transactions
Define Breaking Bulk.
Purchase large quantities of goods from producers but sell only one or few at a time to many different customers.
Ex. Mulch
Creating Assortment
Provide a variety of products in one location to meet needs of buyers.
Ex. Walmart(Sells a little bit of everything)
What are Risk-Taking Functions?
Chance retailers take when they buy a product from a manufacturer, as product may sit on shelf.
What are communications and transaction functions?
Channel members develop and execute both promotional and other types of communication among members of the channel.
Define Disintermediation.
The elimination of some layers of the channel of distribution to cut costs and improve the efficiency of the channel.
New tech can render channel members obsolete
Ex. Self checkout, Family video
What are Channel Levels?
Number of distinct categories of intermediaries that make up a channel of distribution.
Define Hybrid Marketing Systems.
Uses a number of different channels and communication methods to serve a target market.
Ex. A company combining channels like direct sales, distributions, retail sales, and direct mail.
Define Subscription Boxes.
Sends boxes filled with items people didn’t know they wanted.
Define Product Diversion.
The distribution of a product through one or more channels not authorized for use by the manufacturer of the product.
What is a Diverter.
An entity that facilitates the distribution of a product through one or more channels not authorized for use by the manufacturer of the product.
Define Distribution Planning.
Process of developing distribution objectives, evaluating internal and external environmental influences on distribution, and choosing a distribution strategy.
Distribution Strategy Decision 1.
Conventional
Vertical
Horizontal
Define Conventional Distribution Strategy.
A multilevel distribution channel in which member work independently of one another.
Same Goals
Relationships are limited to simply buying and selling from each other
While members work independently, each recognizes self-interest is best served by fair dealing
Define Vertical Distribution Strategy. (VMS)
Channel in which there is formal cooperation among channel members at two or more different level; manufacturing, wholesaling, retailing
Retailer Cooperative
What are Retailer Cooperative?
Group of retailers that establishes a wholesaling operation to help them compete more effectively with the large chains.
Ex. Associated Grocers and True Value Hardware
Define Horizontal Distribution Strategy.
2 or more firms at the same channel level agree to work together to get their product to the consumer.
Most airlines do this today to get passengers where they need
Define Gray Market.
Legal but frowned upon by manufacturer. Usually high end item sold through exclusive distribution. (Rolex sold through Walmart.)
Define Channel Cooperation.
Occurs when produces, wholesalers, and retailers depnd on one another for success.
What is a channel conflict.
Incompatible goals, poor communication, disagreement, etc. Cause conflict.
What are logistics? Also the two kinds?
Process of designing, managing, and improving the movement of products through the supply chain.
Inbound and Outbound
What are some Inbound Logistics.
Raw materials, parts, components, and supplies.W
What are outbound logistics.
Work in progress and finished.
Define Reverse Logistic.
Includes product returns, recycling and material re use, and waste disposal.
What is a Distribution Center?
A warehouse that stores goods for short periods of time, usually for “breaking bulk”
What is inventory turnover?
Number of times a firm’s inventory completely cycles through during a time frame.
Define Level Loading.
Manufacturing approach intended to balance the inventory holding capabilities, and production capacity constraints of a manufacturer for a particular product through implementation of a schedule, employed during and beyond periods of peak demand.
What are Stock-Outs?
Zero-Inventory result, resulting in loss of sales and upset customers.
What are Just in Time Inventory Techniques?
Sets up delivery of goods just as they are needed on the production floor.
Reduce inventory to ensure deliveries arrive when needed
What is Cross Docking?
Efficient technique where products are transferred off a supplier truck directly onto buyer truck bound for next point, such as retail store.
What is Insourcing?
Company contacts with a specialist firm to handle all or part of its supply chain operations.
Chapter Ending Case: Rent the Runaway Notes.
Sharing Economy
Rents designer dress, giving consumer experiences
Reverse Logistics
Had an 11 day shut down, CEO issued apologies
Survived and not does athleisure and ski apparel
Quality and time delivery is crucial
Define Knowledge Management.
Comprehensive approach to collecting, organizing, storing, and retrieving a firm’s information assets.
Online Challenge:
What is the Online Distribution Piracy?
The theft and unauthorized repurposing of intellectual property via the internet.
What is Copyright Infringement?
The use of works protected by copyright law w/o the permission of the copyright holder.
What are Wholesaling Intermediaries?
Firms that handle the flow of products from the manufacturer to the retailer.
What are the two Merchant Wholesalers?
Full-service Merchant Wholesalers
Limited-service Merchant Wholesalers
Define Full-Service Merchant Wholesalers.
Provide a wide range of services for their customers.
Define Limited-Service Merchant Wholesalers.
Provide fewer services for their customers.
Cash and Carry wholesalers
Truck Jobbers
Mail-order wholesalers
Rack Jobbers
Define Cash and Carry wholesalers.
Provide low cost merchandise for retailers and industrial customers that are too small for other wholesalers sales reps to call on.
Define Truck Jobbers.
Carry their products to small business customer locations for their inspection and selection.
Define Mail-Order Wholesalers.
Sell products to small retailers and other industrial customers, often located in remote areas, through catalogs rather than sales force.