Chapter 11
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
RAD 136
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What should all diagnotic imaging systems include?
-Protective tube housing
-correctly functioning control panel
-console
-exam table
What is required to safeguard the patient and imaging personnel from off-focus, or leakage, radiation by restricting the emission of x-rays to the area of the useful, or primary, beam?
Diagnostic-type protective tube housing
The housing enclosing the x-ray tube must be constructed with _ to reduce radiation leakage through any portion of the housing away from the useful beam.
Lead lining
Leakage radiation is measured at a distance of ____ meter from the x-ray source, and must not exceed an air kerma rate of ____ mGy/hr when the tube is operartd at it;s highest voltage at the highest current that allows continuous operation.
1; 0.88 mGy/hr
The place where technical exposure factors, such as milliamperes (mA), peak kilovoltage (kVp), and exposure duration (ms), are selected and visually displayed.
Control panel/console
For the radiation safety of the radiographer, where must the console be located that also has radiation-absorbent window?
Behind a shield barrier
For some state-of-the-art operating consoles, digital controls for kVp and mAs are availble on a what?
Touch screen
When happens when an x-ray exposure begins?
A tone is emitted and a radiation sign iliminates
What must be strong enough to adequately support patients whose weight can be up to 400 pounds?
Radiographic table
The _ of the tabletop must be uniform and for under-table x-ray tubes as used in fluoroscopy
Thickness
What is commonly used in a tabletop to reduce excessive x-ray tube emission?
Carbon fiber material
Is it OK for the collimator to be bigger than the IR?
NOOOOOOO
An x-ray beam limitation device that permits the equipment operator to adjust the size and shape of the x-ray beam either automatically or manually
Light-localizing, variable-aperture rectangular collimator
Any device that limits the dimensions of the useful beam to a designated size and shape before it enters the area of clinical interest
X-ray beam limitation device
All the non-useful image-forming radiation that arises from the interaction of an x-ray beam with the atoms of a patient or any other object in the path of the beam
Scatter radiation
X-rays emitted from parts of the x-ray tube other than the focal spot. Also called stem radiation
Off-focus radiation
Luminance is a technical term referring to the _ of a surface
Brightness
A feature of radiographic collimators that automatically adjusts them so that the radiation field size matches the size of the IR.
Positive Beal Limitation (PBL)
Elements that are part of or added to the x-ray tube to reduce exposure to the patient's skin and superficial tissue by absorbing most of the lower energy photons from the produced beam.
Filtration
The thickness of a designated absorber required to decrease the intensity of the primary beam by 50% of its initial value
Half-value layer (HVL)
The consistency in radiation output intensity for identical generator settings from one single exposure to subsequent exposures
Exposure Reproducibility
Refers to a consistency in output radiation intensity at any selected kVp when generator settings are changed from 1 milliamperage and time combination to another
Exposure linearity
Also known as "phototiming", that is an x-ray termination device that ends the radiation when an arrangement of sensors receives a predetermined amount of radiation.
Automated Exposure Control (AEC)
A device made of parallel radiopaque strips alternately separated with low-attenuation strips of a material such as aluminum or plastic
Radiographic grid
The use of a flat panel detector to record a radiographic image and render it in digital form without a film developing process or the scanning of the image receptor
Digital Radiography (DR)
The distance from the anode focal spot of an x-ray tube to the skin of the patient
Source-to-skin distance (SSD)
The array of pixels that comprises a digital image
Image Matrix
The term that x-ray systems that generate images using the process of photostimulable luminescence
Computer Radiography (CR)
Converts the pattern of x-rays transmitted through the patient into a corresponding and amplified visible light pattern
Image intensifier
A technique in which the fluoroscopic image is produced in digital form in the image acquisition process
Digital fluoroscopy
A device that measures the collective x-ray beam-on time and sounds an audible alarm, or, in some cases, temporarily interrupts the radiation until it is reset after the fluoroscope has been activated for 5 minutes
Cumulative timer
Limited by federal standards of general-purpose intensified fluoroscopic units to a maximum of 88 mGy, per minute.
Entrance skin irradiation rate
A barrier designed to prevent primary, or direct, radiation from reaching personnel or members of the general public on the other side of the barrier
Primary protective beam
When the x-ray beam is deactivated while the image is being scanned, thereby decreasing patient dose, and then pulsed back on for the next image
Pulsed progressive systems
A fluoroscopic technique used in interventional radiology for visualizing blood vessels
Digital subtraction angiography
A method of digital image subtraction in which the frame that contains the greatest amount of contrast material in vessels is indentified and is then subtracted from all subsequent images
Road mapping
An operating mode for state-of-the-art fluoroscopic equipment in which entrance radiation levels are substantially higher than those normally employed in routine procedures
High-level control fluoroscopy (HLCF)
Added filtration plus inherent filtration
Total filtration
What is a compensating filter used for?
To even out the radiation dose when imaging body parts of different thicknesses
What are some examples of a compensating filter?
Wedge filters (for feet), trough filters (for spine)
What is used to reduce scatter radiation from reaching the IR?
Radiographic grid
What are mobile units (portables) usually used for?
For patient's who cannot move
What is the minimum distance from source to patient on a mobile study?
12 inches
SSD much be at least ___ inches for fixed images and ___ inches for mobile studies
15; 12
The tube housing must not leak more than when tested
100 mR/hr
It is required that the _ be mechanically affixed to the console such that it cannot be activated while the operator is in an unshielded location
Exposure hand control
The thickness of the tabletop must be uniform, and for under-table x-ray tubes as used in fluroscopy, the patient support surface should be as _ as possible
Radiolucent
Distance and centering indicators must be accurate to within what percentages of the SID?
2% and 1%
The light-localizing variable-aperature is used in multipurpose x-ray units. IT is box-shaped and contains the radiographic beam-defining system. This system consists of:
Two sets of adjustable lead shutters mounted within the device at different levels
A light source to illuminate the x-ray field and permit it to be centered over the area of clinical interest
A mirror to deflect the light beam toward the patient to be imaged
To minimize skin exposure to electrons produced by photon interaction with the collimator, the patient's skin surface should be at least _ cm below the collimator for fixed radiographic equipment
15
Portable radiographic units are required to maintain a source-to-skin distance of at least how many cm?
30
Luminance is determined by measuring the concentration of light over a particular field of view. The primary unit is the _, known simply as ____.
Candela per square meter; nix
The SI-derived unit of luminous flux, also known as ____.
Lumen
What is equal to the amount of light emitted per second passing into a solid angle of the steradian from a uniform souce of one candela
Lumen
One lumen corresponds to about the same brilliance as a normal birthday candle has at a distance of _ foot.
1
Luminance must be high enough so that a calibrated light meter reading taken at a distance of ____ cm will, in the English system of units, be equal to at least _____ foot candle
100; 15
Besides a tape measure attached to the collimator, what else can be manually measured?
Laser
What is the predominant x-ray beam limitation device?
The collimator
What is the purpose of the collimator?
To reduce radiation scatter
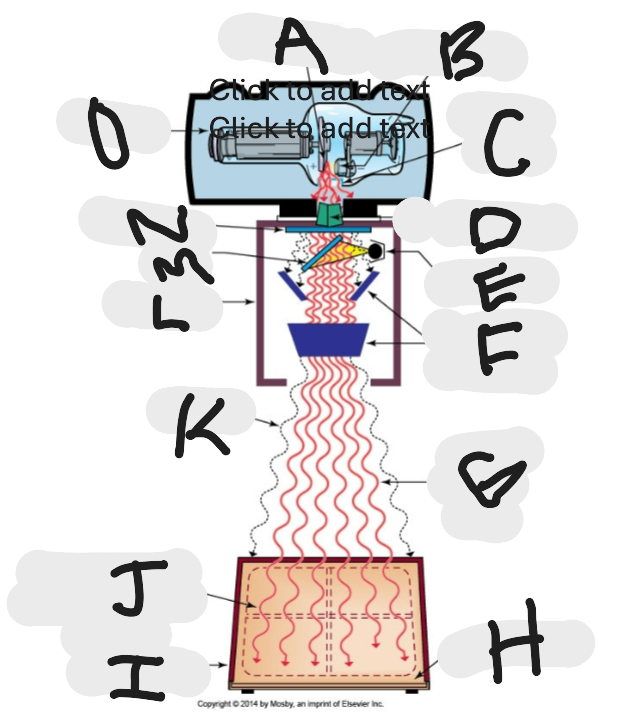
What is this?
X-ray beam limitation device
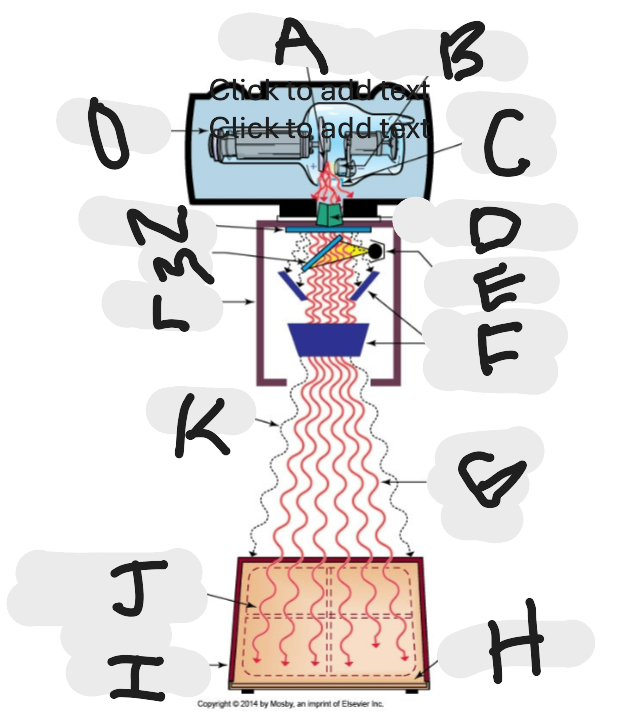
What is “A”?
Anode (+) focal spot in an X-ray tube that serves as the positive electrode and is responsible for the emission of X-rays when electrons collide with it.
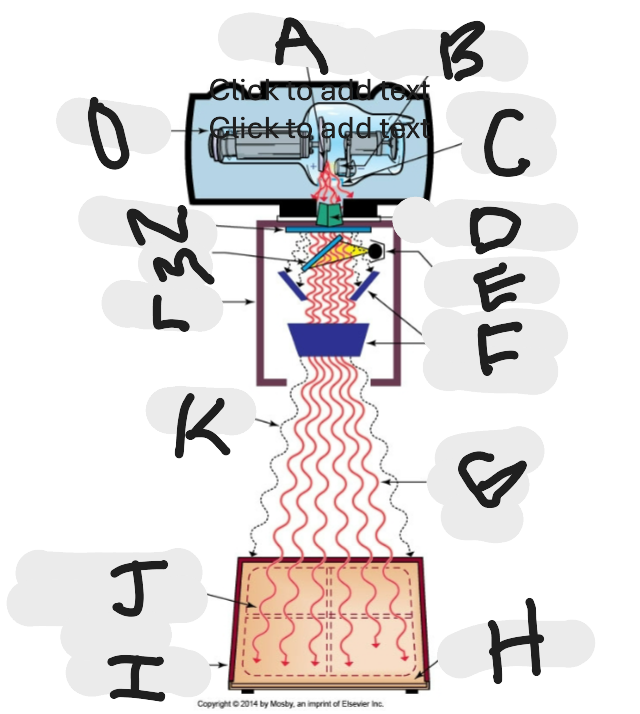
What is “B”?
Cathode (-)
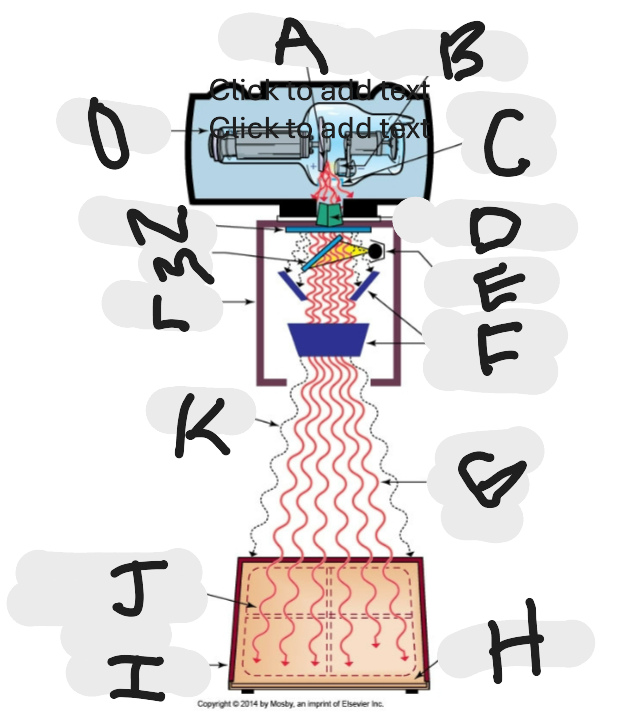
What is “C”?
X-ray tube window (port)
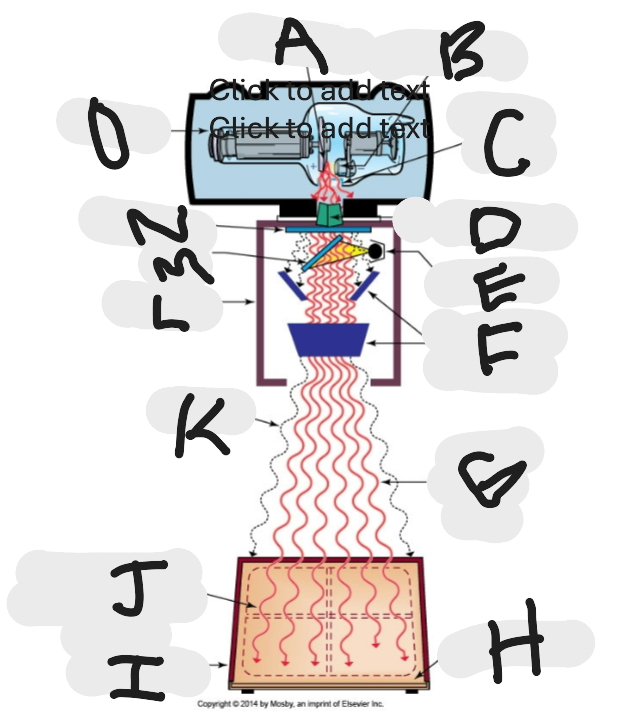
What is “D”?
First set or upper shutters
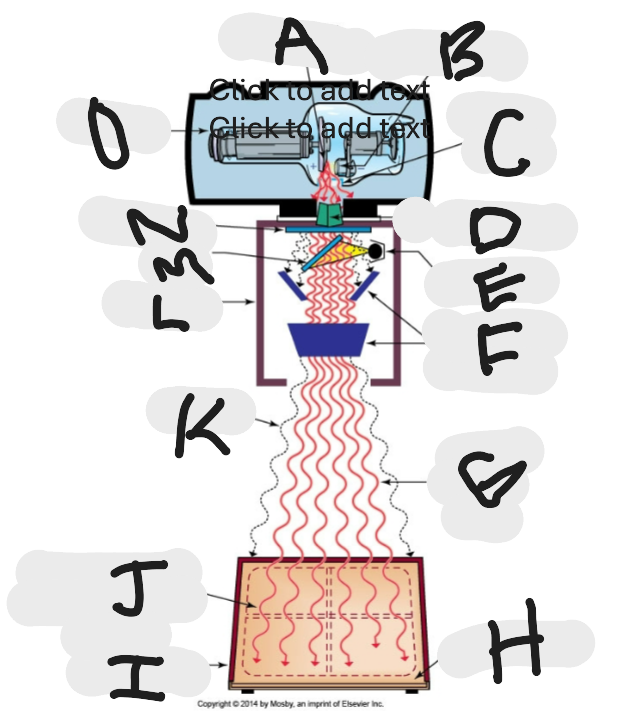
What is “E”?
Light source
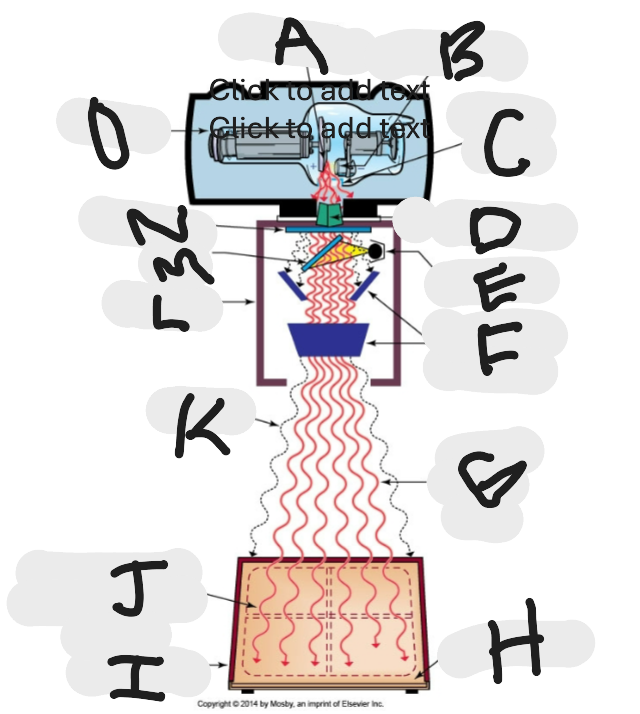
What is “F”?
Second set or lower shutters
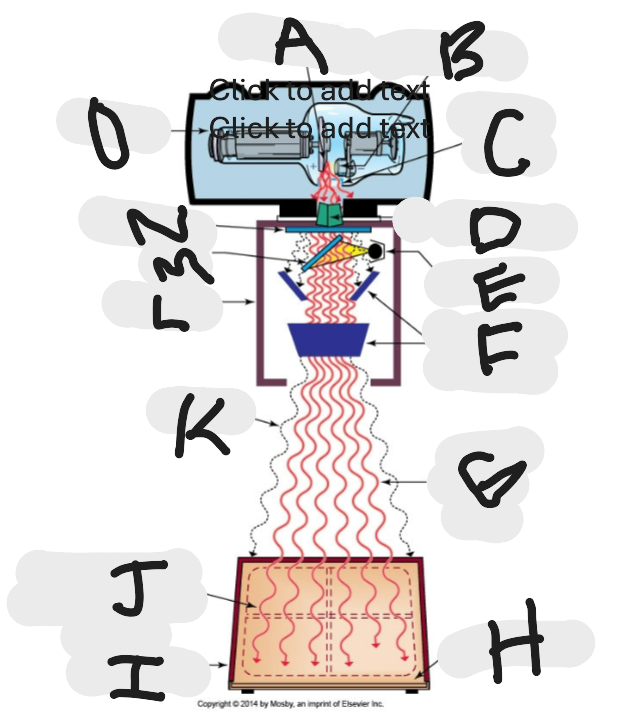
What is “G”?
Useful (primary) beam
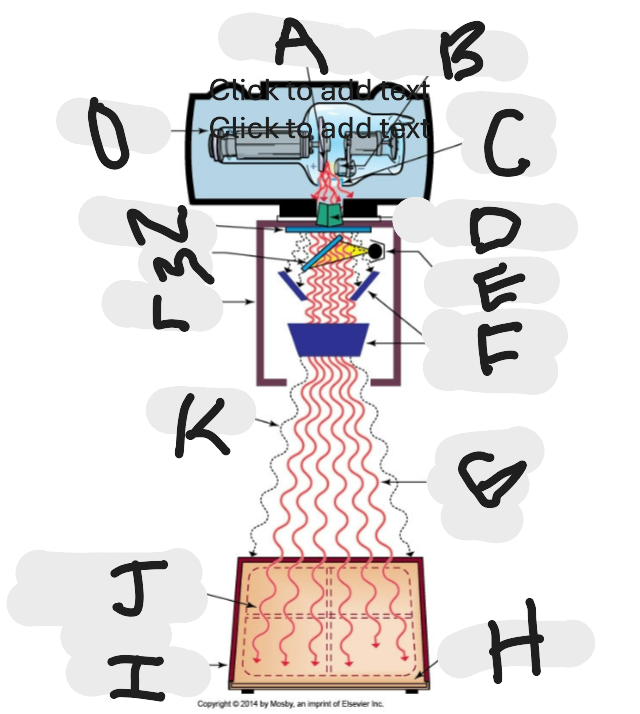
Whatis “H”?
Image receptor
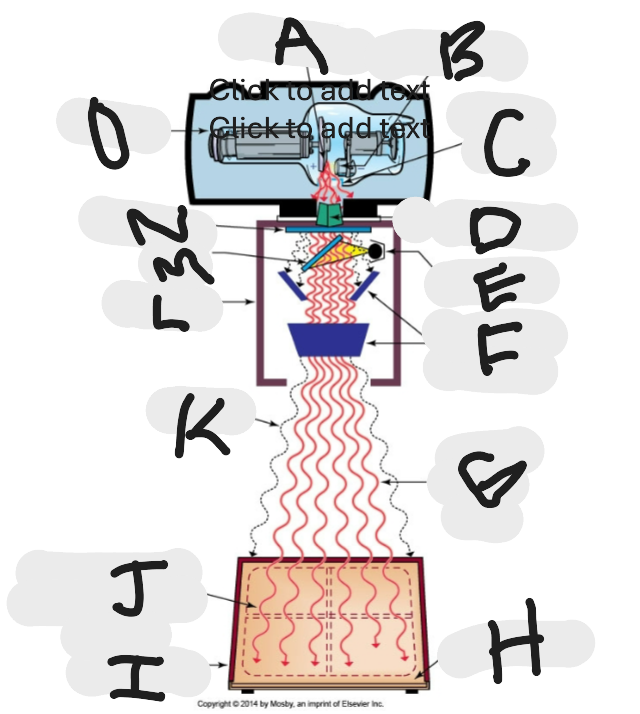
What is “I”?
Imaging plate
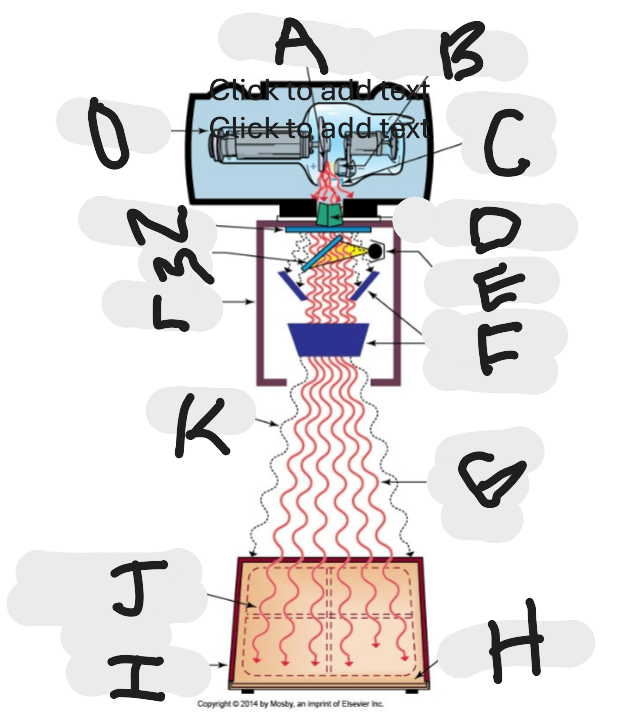
What is “J”?
Light source projection on image plate area of radiographic beam
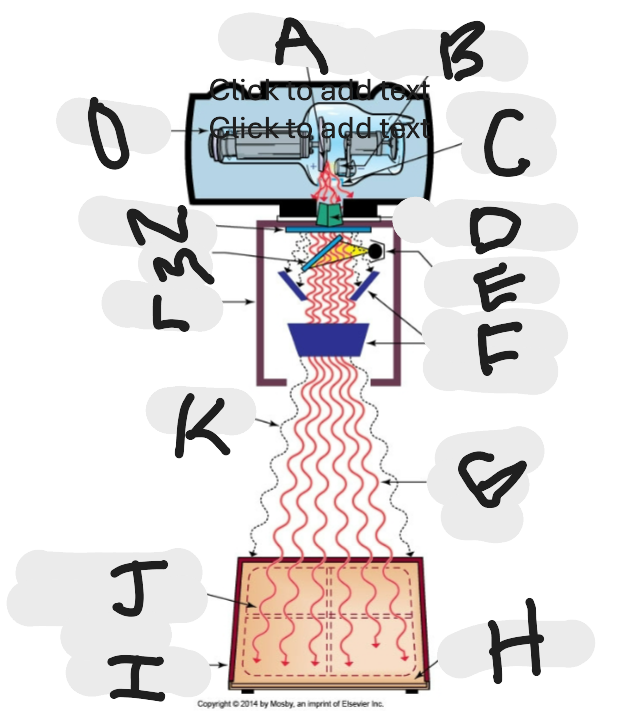
What is “K”?
Off-focus radiation
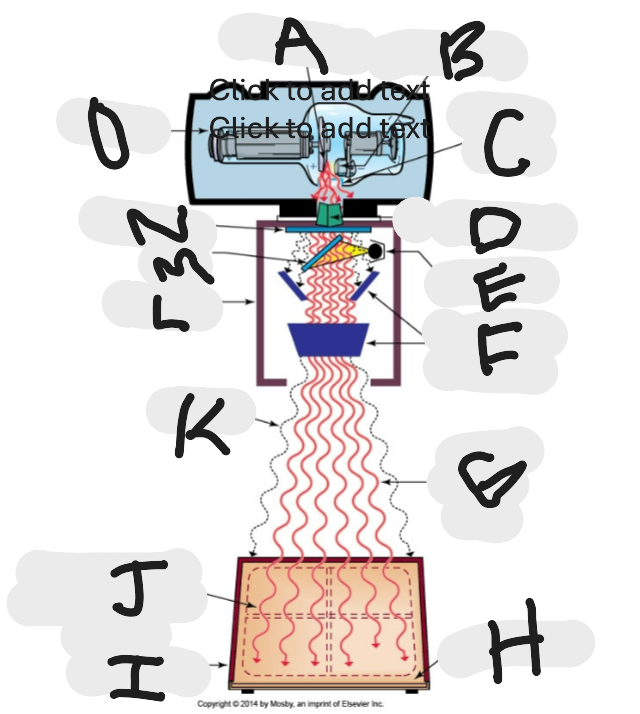
What is “L”?
Collimator
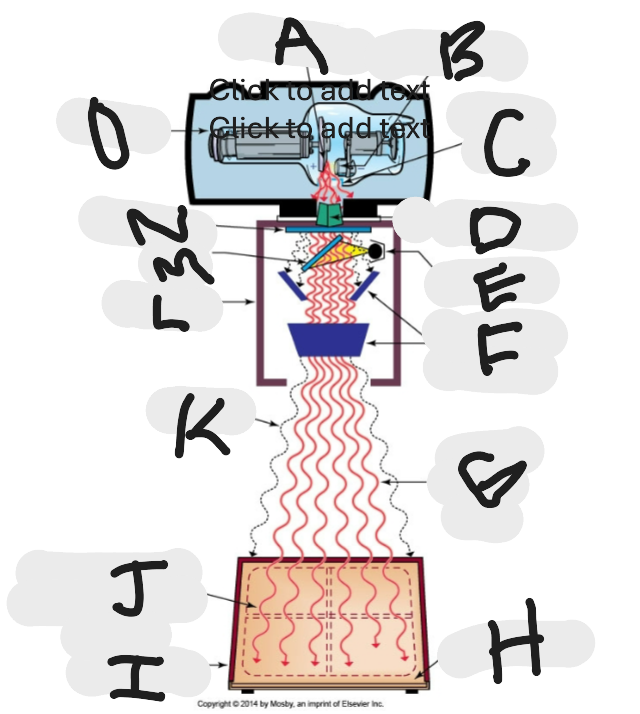
What is “M”?
Mirror
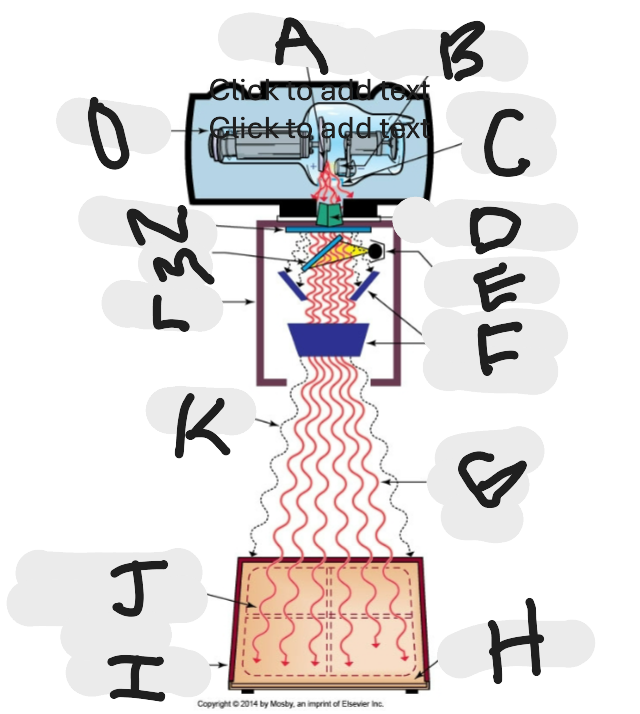
What is “N”?
Aluminum filter
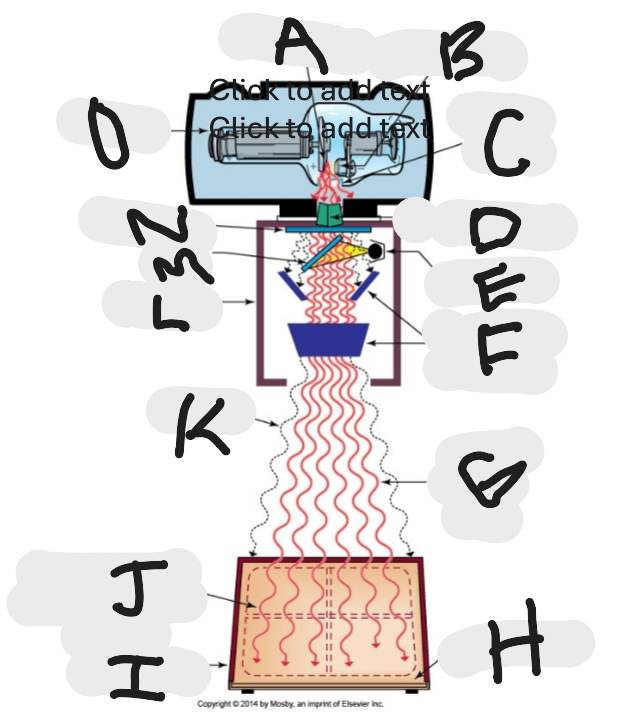
What is “O”?
X-ray tube
What are the two types of filters?
Added and Inherent
Inherent filtration always includes:
Glass envelope encasing the tube
Insulating oil surrounding the tube
Glass window in the tube housing
Added filtration + inherent filtration equals what?
Total filtration
A minimum of how much ____ mma aluminum equivalent total filtration is required for fixed radiographic units operating at above 70 kVp
2.5 mm
What metal is the most widely selected as a filter material?
Aluminum
Why is aluminum the most widely used metal as a selected filter material?
It effectively removes low-energy x-rays from a polyenergetic (heterogenous) x-ray beam without severely decreasing the x-ray beam intensity
What is HVL expressed in?
Millimeters of aluminum
What is HVL a measure of?
A measurement of beam quality, or effective energy of the xray beam
What are compensating filters made of?
Aluminum
Lead-acrylic
Or other suitable materials
Why are compensating filters used?
Used to accomplish dose reduction and uniform imaging of body parts
In exposure reproducibility, a variance of how much percent or less is acceptable?
5%
The ratio of the difference in mSv/mAs or mR/mAs values between two successive generator stations to the sum of these mSv/mAs or mR/mAs values. Must be less than 0.1
Linerarity
When settings are changed from one mA to a neighboring mA station, the most the linearity can vary is what by what percent?
10%
What are AECs designed to do?
To produce an acceptable diagnostic image while limiting the total amount of radiation exposure to the patient
Old terminiology for referring to photomultiplier tubes
Phototiming
Today’s AEC systems utilizie what?
Ionization chambers
T or F: Radiographic grids reduce patient dose
FALSE
When the SSD is small, because of the relatively greater rate of spreading out of the x-ray beam at a close distances fro the x-ray source than at larger distances, the patient’s entrance does is significally _____ than the exit exposure
Larger
Distance generally for mobile radiography is _____ cm to ______ cm
100;120
What are the 5 digital processed radiography imaging modes of xrays?
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed radiography (CR)
Digital radiography (DR)
Digital fluoroscopy (DF)
Digital mammography (DM)
For under-table tubes as used in fluoroscopy, the patient support surface also be what?
Radiolucent
What must be used to confine the useful beam before it enters the anatomic area of clinical interest?
X-ray beam limitation device
With digital radiography, the image receptor is divided into small detector elements that make up a 2-dimensional picture elements, or ______ of the image
Pixels
What kind of diagnostic imaging procedure results in the most radiation rates in radiology?
Fluoroscopy imaging
During what kind of fluroscopic procedures does the patient-image intensifier distance should be as short as possible?
C-arm fluoroscopic procedures